NCP'S
NCP'S
Uploaded by
Ejie Boy IsagaCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP'S
NCP'S
Uploaded by
Ejie Boy IsagaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
NCP'S
NCP'S
Uploaded by
Ejie Boy IsagaCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSESSMENT
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
SCIENTIFIC BASIS Pleural Effusion is collection of fluid in the pleural space of the lungs. Fluid normally resides in the pleural space and acts as a lubricant for the pleural membranes to slide across one another when we breathe. Fluid is constantly being added and reabsorbed by capillaries and lymph vessels in the pleura. When this recycling process is interrupted, a pleural effusion can result.
PLANNING
INTERVENTION
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
Subjective: Ga sige rako ug ubo-ubo sir as verbalized by the patient. Objective: - cough - restlessness - yellowish sputum - tachycardia (PR=107 bpm) - pale - RR=26 cpm
Ineffective airway clearance related to retained secretions.
After 8 hours of care, patient will be able to: a. maintain airway patency b. expectorate/ clear secretions readily.
Independent: - Elevate head of the bed/change position every 2 hours. - Encouraged deep-breathing and coughing exercises. - Auscultate breath sounds and assess air movement. - Evaluate changes in sleep pattern.
-To take advantage of gravity decreasing pressure on the diaphragm. -To mobilize secretions.
-To ascertain status and note progress. -To assess changes.
After 8 hours of care Goals partially met. Patient was able to: a. Maintain airway patency. b. Expectorate clear secretions readily as evidenced by less secretions retained.
ASSESSMENT
NURSING DIAGNOSIS Impaired gas exchange related to alveolarcapillary membrane changes.
SCIENTIFIC BASIS Pleural Effusion is collection of fluid in the pleural space of the lungs. Fluid normally resides in the pleural space and acts as a lubricant for the pleural membranes to slide across one another when we breathe. Fluid is constantly being added and reabsorbed by capillaries and lymph vessels in the pleura. When this recycling process is interrupted, a pleural effusion can result.
PLANNING
INTERVENTION
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
Subjective: Galisud ko ug ginhawa kung mahago ko ug ubo as verbalized by the patient. Objective: - RR=26 - Dyspnea - Restlessness - Tachycardia (PR=107 bpm) - Pale
After 8 hours of care patient will be able to: a. Participate in treatment regimen b. Demonstrate improve ventilation.
Independent: - To evaluate - Monitor vital signs degree of compromise. - Elevate head of bed/position client - To maintain appropriately. airway.
After 8 hours of duty goals not met.
Patient was not able to: a. Participate in - Maintain adequate - For mobilization of treatment regimen. I/O. secretions. b. Demonstrate Encourage frequent - To improve ventilation. position correct/improve changes and deep- existing condition breathing coughing exercises. deficiencies. Dependent: - Administer medications as indicated. -02 prn 24litres/min
-To treat underlying conditions.
ASSESSMENT
NURSING DIAGNOSIS Ineffective tissue perfusion (cardiopulmonary) related to impaired transportation of the oxygen across the alveolar and/or capillary membrane.
SCIENTIFIC BASIS Pleural Effusion is collection of fluid in the pleural space of the lungs. Fluid normally resides in the pleural space and acts as a lubricant for the pleural membranes to slide across one another when we breathe. Fluid is constantly being added and reabsorbed by capillaries and lymph vessels in the pleura. When this recycling process is interrupted, a pleural effusion can result.
PLANNING
INTERVENTION
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
Subjective: Galisod ko ug ginhawa as verbalized by the patient. Objective: - RR=26 cpm - Irritability - Restlessness
After 8 hours of care patient will be able to: a. Demonstrate behaviors/lifestyle changes to improve circulation. b. Demonstrate increased perfusion as individually appropriate.
Independent: -Identify changes related to systemic or peripheral alterations in circulation. -Determine duration of problem. -Monitor vital signs -Investigate report of chest pain Dependent: -Administer medication as ordered
-To assess contributing factors
After 8 hours of care Goals met. Patient was able to: a. Demonstrate behaviors/lifestyle - To note degree of changes to improve impairment circulation - To maximize b. Demonstrate tissue perfusion increased perfusion - To note degree of as impairment individually appropriate. -To maximize tissue perfusion
ASSESSMENT
NURSING DIAGNOSIS Imbalanced nutrition, less than body requirement related to illness.
SCIENTIFIC BASIS Pleural Effusion is collection of fluid in the pleural space of the lungs. Fluid normally resides in the pleural space and acts as a lubricant for the pleural membranes to slide across one another when we breathe. Fluid is constantly being added and reabsorbed by capillaries and lymph vessels in the pleura. When this recycling process is interrupted, a pleural effusion can result.
PLANNING
INTERVENTION
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
Subjective: Wala koy gana mo kaon maam as verbalized by the patient. Objective: - Poor muscle tone - Pale -weight loss - Weakness
After 8 hours of care patient will be able to demonstrate progressive good appetite.
Independent: -Identify underlying condition involved. -Identify clients at risk for malnutrition. - Discuss eating habits, including food preferences, intolerance. -Assess weight, age, body build, and strength of the client. Dependent: -Administer pharmaceutical agents as indicated.
-To assess causative factors.
After 8 hours of care Goals met. Patient was able to - to assess demonstrate contributing factors. progressive good appetite. -To appeal to clients like and dislike. - To evaluate degree of deficit.
-To evaluate degree deficit.
Name of drug Generic name: Levofloxacin Brand name: levaquin
Classification & mechanism of action -Antibiotic, Fluoroquinolone
Indication & dosage
contraindication Contraindicated with allergy to fluoroquinolones, lactation. Use cautiously with renal dysfunction, seizures, pregnancy.
Side effects/ adverse reaction CNS: Headache, dizziness, insomnia, fatigue, somnolence, blurred vision GI: Nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, diarrhea, abdominal pain (occur less with this drug than with oflaxacin), constipation, flatulence Hematologic: Elevated BUN, AST, ALT, serum creatinine, and alkaline phosphatase; neutropenia, anemia Other: Fever, rash, photosensitivity, muscle and joint tenderness
Nursing responsibilities Assessment: History: Allergy to fluoroquinolones, renal dysfunction, seizures, lactation, pregnancy Physical: Skin color, lesions; orientation, reflexes, affect; mucous membranes, bowel sounds; renal and liver function tests
-Treatment of adults with community-Bactericidal: acquired interferes with DNA pneumonia, acute by inhibiting DNA exacerbation of synapse replication chronic bronchitis, in susceptible complicated and gram- negative and uncomplicated skin gram- positive and skin structure bacteria, preventing infections, UTIs and cell production. acute pyelonephritis & acute maxillary sinusitis caused by susceptible bacteria
-Pneumonia: 500
Sinusitis: 500 mg
mg daily PO or IV
daily PO or IV daily PO or IV
Chronic bronchitis: 500 mg
Name of drug Generic name: Ascorbic Acid(Vitamin C) Brand name: cecon
Classification & mechanism of action - vitamin - Water-soluble vitamin essential for synthesis and maintenance of collagen and intercellular ground substance of body tissue cells, blood vessels, cartilage, bones, teeth, skin, and tendons. Unlike most mammals, humans are unable to synthesize ascorbic acid in the body; therefore it must be consumed daily.
Indication & dosage -Prophylaxis and treatment of scurvy and as a dietary supplement. -adult: PO/IV/IM/SC 150500 mg/d in 12 doses
contraindication Use of sodium ascorbate in patients on sodium restriction; use of calcium ascorbate in patients receiving digitalis.
Side effects/ adverse reaction GI: Nausea, vomiting, heartburn, diarrhea, or abdominal cramps (high doses). Hematologic: Acute hemolytic anemia (patients with deficiency of G6PD); sickle cell crisis. CNS: Headache or insomnia (high doses). Urogenital: Urethritis, dysuria, crystalluria, hyperoxaluria, or hyperuricemia (high doses). Other: Mild soreness at injection site; dizziness and temporary faintness with rapid IV administration.
Nursing responsibilities Assessment : -Lab tests: Periodic Hct & Hgb, serum electrolytes. -Monitor for S&S of acute hemolytic anemia, sickle cell crisis.
Name of drug Generic name: Acetylcysteine Brand name: Fluimucil granules
Classification & mechanism of action -Mucolytic -N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), active ingredient of Fluimucil, exerts an intensive mucolyticfluidifying action on mucous and mucopurulent secretions, by depolymerizing the mucoproteic complexes and the nucleic acids which confer viscosity to the vitreous and purulent component of the sputum and of the secretions.
Indication & dosage -Treatment of respiratory affections characterized by thick and viscous hypersecretions: acute bronchitis, chronic bronchitis and its exacerbations; pulmonary emphysema, mucoviscidosis and bronchieactasis. -1 Acetylcysteine (Fluimucil) 600 mg effervescent tablet daily (preferably in the evening)
contraindication Known hypersensitivity to acetylcesteine. As Acetylcysteine (Fluimucil) granules and tablets contain aspartame, it is contraindicated in patients suffering from phenylketonuria.
Side effects/ adverse reaction bronchospasm, angioedema, rashes, pruritus, nausea and vomiting, fever, syncope, sweating, arthralgia, blurred vision, disturbances of liver function.
Nursing responsibilities Monitor effectiveness of therapy and advent of adverse/allergic effects. Instruct patient inappropriate use and adverse effects to report.
Name of drug Generic name: Piperacillin / Tazobactam Brand name: zosyn
Classification & mechanism of action -Antiinfective; Betalactam antibiotic -it is similar to that of other penicillins. Interfere with bacterial cell wall synthesis promotes loss of membrane integrity and leads to death of the organism
Indication & dosage -Treatment of moderate to severe appendicitis, uncomplicated and complicated skin and skin structure infections, nosocomial or community-acquired pneumonia caused piperacillin-resistant, piperacillin/tazobactam susceptible, betalactamase-producing bacteria. -280 mg IVTT every 12hr
contraindication Hypersensitivity to penicilli ns, cephalosphorins, or other drugs. Safety in children< 12 years old, pregnancy, lactation.
Side effects/ adverse reaction CNS: headache, insomnia, fever GI: diarrhea, nausea, constipation, vomiting, pseudo membranous colitis SKIN: Hypersensitivity reactions, rash, pruritus
Nursing responsibilities Obtain history of hypersensitiv ity to penicillins, cephalosphorins, or other drugs prior to administration - Obtain specimen for culture and sensitivity prior to first dose of the drug; start drug pending results. Periodic CBC with differential, platelet count, Hgb & Hgt, and serum electrolytes. - Monitor for hypersensitivity response; discontinue drug and notify physician if allergic response noted. -Monitor vital signs because of cardiac arrhythmias, hypertension and fever as adverse reactions.
SAPUGAYS FAMILY GENOGRAM
Female HTN
Female FEVER
W&A
W&A
W&A (MAID)
EDUARDO 56, M Massive Plueral Effusion
Male Paralized (HTN)
W&A
Legend: Male Female Deceased Patient
You might also like
- Little EKit of Household RitualsDocument20 pagesLittle EKit of Household RitualsCoral Tyack100% (2)
- Toned in 90 Days: Meal PlanDocument10 pagesToned in 90 Days: Meal PlanTamara A. Lewis100% (1)
- Copd NCPDocument16 pagesCopd NCPSuperMaye100% (1)
- Assessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationApol Pen67% (3)
- PSY 3206 Health Psychology Final Exam Study GuideDocument14 pagesPSY 3206 Health Psychology Final Exam Study GuideShiv PatelNo ratings yet
- NCP Pleural EffusionDocument7 pagesNCP Pleural EffusionEjie Boy Isaga100% (2)
- Diabetes Mellitus NCPDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus NCPjfgnzls182892% (12)
- 3 Nursing Care Plan Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pages3 Nursing Care Plan Diabetes MellitusAnnisa Silvera II50% (2)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- NCPs For Diabetes MellitusDocument6 pagesNCPs For Diabetes MellitusEjie Boy Isaga100% (1)
- NCP Pleural EffusionDocument7 pagesNCP Pleural EffusionEjie Boy Isaga100% (2)
- 8NCP's For ColostomyDocument23 pages8NCP's For ColostomyCzarina Porciuncula79% (14)
- Glen Johnson - Sciatica SOS EbookDocument84 pagesGlen Johnson - Sciatica SOS EbookRodrigo Lima33% (3)
- BIOLOGY FORM 4 Chapter 4 - Chemical Composition of The CellDocument11 pagesBIOLOGY FORM 4 Chapter 4 - Chemical Composition of The Cellalpha centauri86% (7)
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study and NCP!Document8 pagesDrug Study and NCP!Abegail Abaygar100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan - Lateral Neck Mass Probably MalignantDocument5 pagesHealth Teaching Plan - Lateral Neck Mass Probably MalignantRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Revised NCP (Baiae)Document9 pagesRevised NCP (Baiae)Jennifer BactatNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion R/T Impaired RAS Mechanism As Manifested by A High Blood Pressure LevelDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion R/T Impaired RAS Mechanism As Manifested by A High Blood Pressure LevelRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationJharene BasbañoNo ratings yet
- NCPsDocument13 pagesNCPsRocel DevillesNo ratings yet
- Date Ordered: Generic NameDocument5 pagesDate Ordered: Generic NameMhariel MacalindongNo ratings yet
- NCP 106Document8 pagesNCP 106yer tagalajNo ratings yet
- Name of The Drug Date Ordered Classification Dose Frequency Route Mechanism of Action Specific Indication Side Effects Nursing ImplicationDocument9 pagesName of The Drug Date Ordered Classification Dose Frequency Route Mechanism of Action Specific Indication Side Effects Nursing ImplicationFrances Oscar GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document7 pagesDrug Study 2Jediale CarcelerNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of COPDDocument6 pagesNursing Management of COPDZulyca JamalulNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ComplicationDocument12 pagesCardiac ComplicationResa ShotsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingIvan Louise Fajardo ManiquizNo ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyAllan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlansTwobee Kriz LeghidNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPDidith AbanNo ratings yet
- DM Care PlanDocument9 pagesDM Care PlanHarish Kumar KumawatNo ratings yet
- NCP SampleDocument3 pagesNCP SampleReuben LouisNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention/S Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention/S Rationale EvaluationRachel Anne Ascaño-DavidNo ratings yet
- NCPGDMDocument8 pagesNCPGDMChristopher LontocNo ratings yet
- Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesSubjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objectivechaoz09No ratings yet
- Comprehensive ExaminationDocument8 pagesComprehensive ExaminationAnonymous dquW2YmO7No ratings yet
- Case Study Multiple Organ Dysfunction and ShockDocument3 pagesCase Study Multiple Organ Dysfunction and ShockJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Using NandaDocument16 pagesNursing Care Plan - Using NandaWardinatul ImanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument14 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Blood ChemDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Blood ChemMary Gold EleveraNo ratings yet
- NCP For PneumoniaDocument3 pagesNCP For PneumoniaKahMallari100% (12)
- Acute Gastroentiritis (NCP)Document3 pagesAcute Gastroentiritis (NCP)April ParanganNo ratings yet
- LUNGcancer NCPregieDocument1 pageLUNGcancer NCPregieShermay MortelNo ratings yet
- Medical Management: Can Help Control Weight, Blood Pressure and CholesterolDocument2 pagesMedical Management: Can Help Control Weight, Blood Pressure and CholesterolKen BaxNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAbegail Abaygar100% (1)
- Diarrhea Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDiarrhea Drug StudyCeelin Robles0% (1)
- Parenteral Nutrition Basic IVT Nov 2008Document53 pagesParenteral Nutrition Basic IVT Nov 2008Crystal Mae Castrodes DaquipilNo ratings yet
- Care of Unconscious PatientDocument5 pagesCare of Unconscious PatientRuchika Kaushal67% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanmariasomorayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ProjectDocument7 pagesDrug Study ProjectMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis Impaired Gas ExchangeZycon Rodney Ae'zecquel Gachallan50% (2)
- Iii. Nursing Care PlansDocument13 pagesIii. Nursing Care PlansLharra Cagulada-Postrano100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyHennah ReblandoNo ratings yet
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha Suazo100% (1)
- NCP FinalDocument18 pagesNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- Almaarefa College Adult Nursing Care Practice II Weekly Report Name of Student: Najwa Thawab - Day/DateDocument2 pagesAlmaarefa College Adult Nursing Care Practice II Weekly Report Name of Student: Najwa Thawab - Day/DateNajwa1991No ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGY GROUP 4Document62 pagesPHARMACOLOGY GROUP 4cutty.santillanNo ratings yet
- NCP CaseDocument34 pagesNCP CaseIsobel Mae JacelaNo ratings yet
- NCP Laryngeal CancerDocument10 pagesNCP Laryngeal CancerAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (2)
- NCP Nephrotic SyndromeDocument3 pagesNCP Nephrotic SyndromeThesa Federico100% (1)
- Cues/Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goals of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesCues/Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goals of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationEjie Boy Isaga100% (1)
- Philippine Nurses Licensure Examination Failure: A Lived ExperienceDocument16 pagesPhilippine Nurses Licensure Examination Failure: A Lived ExperienceEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Perpetual Succour Hospital 3A-Floor PlanDocument1 pagePerpetual Succour Hospital 3A-Floor PlanEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- NCP SviDocument4 pagesNCP SviEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- TPR Monitoring Sheet: University of San Jose-Recoletos College of NursingDocument1 pageTPR Monitoring Sheet: University of San Jose-Recoletos College of NursingEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Trait TheoryDocument6 pagesTrait TheoryEjie Boy Isaga100% (1)
- Patient - S Load FormDocument2 pagesPatient - S Load FormEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- I. Physical Exam: Poor Skin TurgorDocument8 pagesI. Physical Exam: Poor Skin TurgorEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Trait TheoryDocument6 pagesTrait TheoryEjie Boy Isaga100% (1)
- Physical AssessmentDocument3 pagesPhysical AssessmentEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- CHN ActivitiesDocument11 pagesCHN ActivitiesEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Treatment Guidelines For Tuberculosis (RIPE) : Preventive TherapyDocument4 pagesTreatment Guidelines For Tuberculosis (RIPE) : Preventive TherapyEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan FormDocument2 pagesDischarge Plan FormEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Informed ConsentDocument1 pageInformed ConsentEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Inhaled SteriodsDocument7 pagesInhaled SteriodsEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
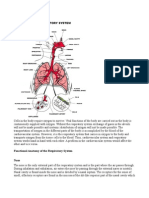
- Functional Anatomy of The Respiratory System NoseDocument5 pagesFunctional Anatomy of The Respiratory System NoseEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument4 pagesRRLRan Marie LaritaNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Feeding For InfantsDocument50 pagesSupplementary Feeding For Infantspppamm0% (1)
- Designer Simone Pallotto - PortfolioDocument90 pagesDesigner Simone Pallotto - PortfoliopallotsNo ratings yet
- Abyip 2023Document7 pagesAbyip 2023Allan AlbanoNo ratings yet
- CFC 7days of Fun Clean RecipesDocument23 pagesCFC 7days of Fun Clean Recipeslilredark100% (3)
- 4life CatalogueDocument44 pages4life CatalogueDenis McCarthy0% (1)
- Variable 1Document6 pagesVariable 1derlynpoleNo ratings yet
- Plant Based Protein GuideDocument16 pagesPlant Based Protein GuideInma A.S.100% (1)
- Bangladesh Tetra Pak Case StudyDocument8 pagesBangladesh Tetra Pak Case StudymunemNo ratings yet
- Basic Weight Lifting Exercises PDFDocument6 pagesBasic Weight Lifting Exercises PDFGerald KwinjoNo ratings yet
- Apovian 2016Document10 pagesApovian 2016Sandy PranadaNo ratings yet
- (SLE) and PregnancyDocument39 pages(SLE) and PregnancyRake SardevaNo ratings yet
- COT Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesCOT Lesson PlanAngelo Jude CobachaNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument33 pagesNutritionBeverly Grace TamondongNo ratings yet
- Synthia Correct ProjectDocument35 pagesSynthia Correct ProjectSunday MichaelNo ratings yet
- Odisha Malnutrition VF PDFDocument16 pagesOdisha Malnutrition VF PDFMukundNo ratings yet
- GTPS20 Stage 22Document37 pagesGTPS20 Stage 22Jan DušekNo ratings yet
- 1.endocrine and Metabolic Response To TraumaDocument35 pages1.endocrine and Metabolic Response To TraumaDenise JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Ladies and Gentlemen..Document2 pagesLadies and Gentlemen..Laelatul FitriyahNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Lactose From Milk: CHEM 334L Organic Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.0Document9 pagesIsolation of Lactose From Milk: CHEM 334L Organic Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.0Hasene Keskin100% (1)
- Sr. No. Title Page No.: 1. Historical Background On Mushroom CultivationDocument93 pagesSr. No. Title Page No.: 1. Historical Background On Mushroom CultivationTushar JadhavNo ratings yet
- Ivana Samani Ipp Girls Rugby 7s 2019 - IppDocument5 pagesIvana Samani Ipp Girls Rugby 7s 2019 - Ippapi-374593974No ratings yet
- Shave Your Balls and 100 Other Things Your Mother Should Have Told YouDocument112 pagesShave Your Balls and 100 Other Things Your Mother Should Have Told Youdelski14No ratings yet
- Blue Book 2012: Behavior, Learning & Health: The Dietary ConnectionDocument60 pagesBlue Book 2012: Behavior, Learning & Health: The Dietary ConnectionShula EdelkindNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Proporsi Tepung Talas Dan Tepung Tempe Terhadap KadarDocument11 pagesPengaruh Proporsi Tepung Talas Dan Tepung Tempe Terhadap KadarAlzhenaaPutriNo ratings yet