Test 11
Test 11
Uploaded by
Babbi SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Test 11
Test 11
Uploaded by
Babbi SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Test 11
Test 11
Uploaded by
Babbi SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
7. Two vectors A and B are such that I A + B I = I A B I.
. The angle between the vectors, A and B will be (a) 180o (b) 60o (c) 90o (d) 0o 8. Two vectors A and B are perpendicular if A x B equals: (a) I A. B I (b) I A I I B I (c) One (d) Zero 9. If A.B = I A x B I the angle between the two vectors A and B is : (a) 00 (b) 30o (c) 45o (d) 90o 10. Which of the following is a scalar quantity? (a) Torque (b) Work (c) Force
(d) Displacement
Answer Keys: 7. (c) 8. (d) 9. (c) 10. (b)
2. The angle between the directions two vectors (AxB) and (BxA) is (in radians) (a) (b) /2 (c) /4 (d) 0.0 7. In a Cartesian coordinate system, if i, j, k are unit vectors along the axes x, y and z respectively, then (a) i x j = k; j x k = I x k = j (b) i x j = k ; k x j = i; k x i = j (c) i x j = k; j x k = i; k x i = j (d) j x i = k ; k x j = i; k x i = j 8. If A = i + 4 j + 3 k and B = 4 i + 2 j 4 k then the angle between the two vectors A and B is :(a) 0 Degree (b) 30o (c) 45o
(d) 90o 9. A force F = 2 i + 2j + 2k passes through a point P. If OP = 3i + j + 4k the moment of the force about O will be:(a) 4i + 2j + 6k (b) 6i + 2j + 4k (c) 5i + 3j + 6k (d) i + 6j + 8k 10. If OP = 4i 2j + 3k and OQ = 2i + 3j + 4k then the value of PQ will be: (a) 6i + 5j + 7k (b) 8i 6j + 12k (c) 2i 5j k (d) 2i + 5j + k Answer Keys: 1. (a) 2. (a) 3. (a) 4. (d) 5. (c) 6. (b) 7. (c) 8. (d) 9. (b) 10. (d) 1.A ball is thrown at an angle with the horizontal. It was observed that the maximum vertical height attained was equal to the horizontal range. The the angle . (a) equal to 45o (b) less than 60o (c) greater than 60o (d) equal to 90o
2. A ball is thrown in air with a velocity u at an angle of 60o from the horizontal. During its entire path the quantity which remains constant is . (a) the kinetic energy (b) the vertical component of velocity (c) the horizontal component of velocity (d) the potential energy 8. The acceleration of a body is defined to be the rate of change of its . (a) Displacement (b) Momentum (c) Speed (d) Velocity 9. A body of mass 0.5 kg is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 2m/s. On the return journey its speed at the starting point will be: (a) 9.8 m/s (b) 2 m/s (c) 1 m/s (d) 0.5 m/s 10. The path traveled by a bomb released from an aeroplane moving horizontally with a constant speed is: (a) A circle (b) A parabola
(c) A straight line (d) None of the above Answer Keys: 1. (c) 2. (c) 3. (c) 4. (d) 5. (b) 6. (a) 7. (b) 8. (d) 9. (b) 10. (b)
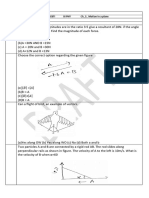
6. The distance traveled by a body falling from rest in the first, second and third seconds are in the ratio: (a) 1:2:3 (b) 1:3:5 (c) 1:4:9 (d) None of the above 10. Two identical guns having same nozzle speed are short at angles 60o and 30o with the horizontal direction. The rations of their ranges and maximum heights are (a) 2 : 1 and 2 : 1 (b) 2 : 1 and 1 : 1 (c) 3 : 1 and 1 : 1 (d) 1 : 3 and 1 : 1 Answer Keys: 1. (b) 2.(d) 3.( c) 4. (b) 5. (b) 6. (b) 7.(c) 8.(d) 9.(c) 10. (c) 6. A stone is released from a balloon which is rising steadily at 4m/sec. After 3 sec. the velocity of the stone is:
(a) 33.4 m sec1 (b) 25.4 m sec-1 (c) 21.8 m sec-1 (d) 17.8 m sec1 Answer Keys: 1. (d) 2. (a) 3. (c) 4. (b) 5. (c) 6. (b) 7. (d) 8. (c) 9. (d) 10. (c) 1. Two different bodies of masses m1and m2 are dropped from two different height h1and h2 respectively. The time taken by the bodies to fall freely, t1 and t2, are in the ratio: (a) h1 : h2 (b) h1 : h2 (c) m1 h1 : m2 h2 (d) m1 h12 : m2 h22 4. A cricket ball of mass 0.1 kg, moving horizontally with a speed of 30 m/sec is struck by a bat such that after being hit the ball leaves the bat at a speed 40 m/s in and exactly opposite direction. If the ball an the bat are in contact for 0.1 second the average force of the bat on the ball is (a) 30 N (b) 70 N (c) 7 N (d) 700 N
5. A little girl walks on a straight road for the first half time of her journey with speed v1 and the second half time of her journey with speed v2. the average speed of the girls is -
(a)
(b)
(c)
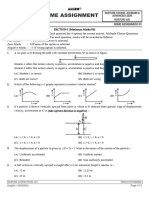
(d) Answer Keys: 1. (a) 2. (c) 3. (d) 4.(b) 5.(a) 6. (c) 7. (d) 8. (a) 9. (b) 10.(a) 3. A man wants to hit a target. He should point his rifle. (a) In the vertical direction. (b) In the direction of the target (c) Higher than the target (d) Lower than the target 4. A body of mass 2 kg. has an initial velocity of 3 m/s along OE and it is subjected of a force of 4 newtons in OF direction perpendicular to OE. The distance of the body from O after 4 second will be: (a) 48 metre (b) 12 metre
(c) 28 metre (d) 20 metre 7. The maximum height attained by a body when it is throws vertically up ward is (a) u/g (b) 2 u/g (c) u2/2g (d) u2/g 9. Two balls are projected with the same velocity at angles of projection 30o and 60o. If they have horizontal ranges R1 and R2 respectively then(a) R1 = R2 (b) R1 = 2 R2 (c) 2 R1 = R2 (d) R1 = 4 R2 10. The horizontal range of a projectile is maximum when the angle of projection is (a) 30o (b) 45o (c) 60o (d) 90o Answer Keys: 1. (b) 2. (c) 3. (c) 4. (d) 5. (b) 6. (a) 7. (c) 8. (d) 9. (a) 10. (b)
An object is projected at an angle to the horizontal in a gravitational field and it follows a parabolic path, PQRST. These points are the positions of the object after successive equal time intervals. T being the highest point reached. Assuming negligible air resistance, the displacements PQ, QR, RS and ST. A are equal. B decrease at a constant rate. C have equal horizontal components. D increase at a constant rate. E have equal vertical components. Answer: C
A United Airlines jet is flying at 300 km/hr, while an Air France Concord is speeding along at 1200 km/hr Both airplanes are flying at the same altitude If each aircraft experiences problems with an unruly passenger, and they both decide simultaneously to push the passenger out the door, which of the unruly passengers will hit the earth first? (Ignore air resistance) (A) The Air France passenger (B) The United Airlines passenger (C) Neither They will both hit the ground at the same time (D) Impossible to determine The answer depends on which passenger is heavier Assuming the airplanes in the previous problem continue to travel at the same velocity after ejecting their respective passengers, where will the passengers land with respect to their aircraft's path? (A) When they hit the ground, they will be directly beneath the airplane they fell from (B) When they hit the ground, they will be directly beneath the spot at which the airplane threw them out (C) They will be in front of the aircraft they fell from (D) It depends on which plane the passenger fell from
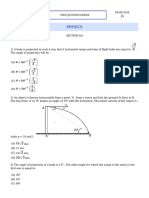
A car traveling at constant velocity v suddenly brakes in an effort to keep from hitting a rabbit which is 8 ft away If the braking action causes a constant deceleration a , how long does it take for the car to come to a complete stop? (A) t = va (B) t = 8a/v (C) t = 8a (D) t = v/a In the previous question, how far did the car travel as it was braking? (A) (B) (C) 8av (D) a 2 If the car from the last two questions had initially been traveling at a speed of 10 ft/s, and experienced (from the braking) a deceleration of 5 ft/s 2 , would it have hit the rabbit which was 8 ft away? (Assume the rabbit was dazed and didn't move at all) (A) yes (B) no (C) Impossible to determine without knowing the weight of the car (D) Impossible to determine because the car can never reach a complete stop Test complete
1.) At time t = 0 s, a body has starts from rest and moves with constant acceleration. Which graph best represents how s, the displacement of the body, varies with time t?
Answer: E The parachutist experience free-fall initially, implying the only force acting on him or her is gravitational force. The acceleration will therefore be constant at 9.81 m s-2. The opening of the parachute causes a significant air resistance and hence, causes a resultant force upwards instead of down. Hence, acceleration is now in the opposite direction. The object slows down and hence, air resistance reduces gradually to arrive at terminal velocity when acceleration is zero.
An object is projected at an angle to the horizontal in a gravitational field and it follows a parabolic path, PQRST. These points are the positions of the object after successive equal time intervals. T being the highest point reached. Assuming negligible air resistance, the displacements PQ, QR, RS and ST. A are equal. B decrease at a constant rate. C have equal horizontal components. D increase at a constant rate. E have equal vertical components. Answer: C The horizontal speed remains constant and hence, the horizontal components are equal. 10 When a rifle is fired horizontally at a target P on a screen at a range of 25 m, the bullet strikes the screen at a point 5.0 mm below P. The screen is now moved to a distance of 75 m and the rifle again fired horizontally at P in its new position.
Answer: C Initial velocity is zero since object starts from rest. Displacement-time graph should have zero gradient at time t = 0 s. 2 A particle starts from rest and moves in a straight line. Its motion is represented by the accelerationtime graph shown below. At which point is its velocity maximum?
Answer: B Area under acceleration-time graph represents change in velocity. The particle experiences an increase in velocity in the negative direction continuously to point B. From point B onwards, the velocity decreases until acceleration is zero again, as acceleration and velocity is now in opposite direction (i.e. acceleration positive, velocity negative). Hence, the velocity decreases. The velocity increases again to point C but, the increase is less than the decrease before that, hence overall, the velocity is still lesser than at B. 3.) An aeroplane, flying in a straight line at a constant height of 400 m with a speed of 300 m s-1, drops an object. The object takes a time t to reach the ground and travels a horizontal distance d in doing so. Taking g as 10 m s-2 and ignoring air resistance, which one of the following gives the values of t and d? td A 1.3 s 0.40 km B 8.9 s 2.7 km C 8.9 s 4.0 km D 40 s 3.0 km E 40 s 120 km Answer: B
4.) A body dropped from a tower is timed to take (3.00.3) s to fall to the ground. If the acceleration of free fall is taken as 10 m s-2, the calculated height of the tower should be quoted as A (15.00.2) m B (150.1) m C (45.00.2) m D (455) m E (459) m
5.) A lunar landing module is descending to the Moons surface at a steady velocity of 25.0 m s-1. At a height of 40 m, a small object falls from its landing gear. Taking the Moons gravitational acceleration as 1.60 m s-2, at what speed does the object strikes the Moon? A 22.3 m s-1 B 27.4 m s-1 C 497 m s-1 D 753 m s-1 Answer: B
Take note as u,s and a are all in the same direction, they should have the same sign. 6.) A parachutist steps from an aircraft, falls freely for 2 s and then opens his parachute. Which graph best represents how his vertical acceleration a, varies with time t during the first 5 s?
Answer: E The parachutist experience free-fall initially, implying the only force acting on him or her is gravitational force. The acceleration will therefore be constant at 9.81 m s-2. The opening of the parachute causes a significant air resistance and hence, causes a resultant force upwards instead of down. Hence, acceleration is now in the opposite direction. The object slows down and hence, air resistance reduces gradually to arrive at terminal velocity when acceleration is zero. 7.) When a rifle is fired horizontally at a target P on a screen at a range of 25 m, the bullet strikes the screen at a point 5.0 mm below P. The screen is now moved to a distance of 75 m and the rifle again fired horizontally at P in its new position.
Assuming that air resistance may be neglected, what is the new distance below P at which the screen would now be struck? A B 15.0 mm C 20.0 mm D 25.0 mm E 45.0 mm Answer: E For horizontal direction, Speed remains constant. Hence, if time needed to travel 25 m is t, time needed to travel 75 m will be 3t.
Two birds are flying directly towards each other at the same speed If the first bird is flying at a velocity v , what is the the velocity of the second bird? (A) v (B) - v (C) 2v (D) Impossible to determine A United Airlines jet is flying at 300 km/hr, while an Air France Concord is speeding along at 1200 km/hr Both airplanes are flying at the same altitude If each aircraft experiences problems with an unruly passenger, and they both decide simultaneously to push the passenger out the door, which of the unruly passengers will hit the earth first? (Ignore air resistance) (A) The Air France passenger (B) The United Airlines passenger (C) Neither They will both hit the ground at the same time
(D) Impossible to determine The answer depends on which passenger is heavier Assuming the airplanes in the previous problem continue to travel at the same velocity after ejecting their respective passengers, where will the passengers land with respect to their aircraft's path? (A) When they hit the ground, they will be directly beneath the airplane they fell from (B) When they hit the ground, they will be directly beneath the spot at which the airplane threw them out (C) They will be in front of the aircraft they fell from (D) It depends on which plane the passenger fell from The velocity function is all of the following EXCEPT (A) A function of time (B) The derivative of the position function (C) A function which gives the velocity of an object at any point in time (D) None of the above A police officer living on a planet with no air resistance drops a pair of handcuffs and a handkerchief from the same height at the same time Which one will reach the ground first? (A) The handkerchief (B) The handcuffs (C) They will both hit the ground at the same time (D) The answer depends on how far above the ground they were when he dropped them What kind of function is an acceleration function describing one-dimensional motion? (A) A scalar-valued function (B) A vector-valued function (C) There is no such thing as acceleration in one dimension (D) A constant function In general, the acceleration of objects due to the earth's gravitational pull is (A) constant (B) 98 m/s 2 (C) smaller if the object is further away
(D) greater if the object is further away Kinematics is concerned with (A) understanding why objects move the way they do (B) describing the movement of objects (C) action at a distance (D) None of the above A raindrop on a drizzly day takes one minute from the time it leaves the cloud until it hits your umbrella, 3 miles below The average velocity of the raindrop on its journey is (A) 3 miles/hr (B) 60 miles/hr (C) 180 miles/hr (D) Impossible to determine because the raindrop accelerates due to gravity The average velocity and the instantaneous velocity of an object will be the same if (A) the object's speed is constant (B) the object's acceleration is zero (C) the object's velocity is always positive (D) They are never the same A car traveling at constant velocity v suddenly brakes in an effort to keep from hitting a rabbit which is 8 ft away If the braking action causes a constant deceleration a , how long does it take for the car to come to a complete stop? (A) t = va (B) t = 8a/v (C) t = 8a (D) t = v/a In the previous question, how far did the car travel as it was braking? (A) (B) (C) 8av (D) a 2
If the car from the last two questions had initially been traveling at a speed of 10 ft/s, and experienced (from the braking) a deceleration of 5 ft/s 2 , would it have hit the rabbit which was 8 ft away? (Assume the rabbit was dazed and didn't move at all) (A) yes (B) no (C) Impossible to determine without knowing the weight of the car (D) Impossible to determine because the car can never reach a complete stop Find the derivative of 2x 5 + x 3 + + 5 (A) 10x 5 + x 2 + 5 (B) 10x 4 + x 2 (C) 10x 4 + x 2 + +5
(D) None of the above Evaluate the derivative of x 3 + x 2 + 5x at x = - 2 (A) -3 (B) -14 (C) -2 (D) None of the above Find the velocity of an object described by the position functionx(t) = 3x 2 + (A) -2 (B) 5 (C) 2 (D) -5 Find the acceleration of an object described by the position function x(t) = 3x 2 + (A) -8 (B) 5 (C) 18 (D) None of the above For the following 5 questions, consider an object with position function x(t) = (0, 0, - g)t 2 + (2, 3, 4)t + (5, 0, 1) What is the magnitude of the initial (ie at t = 0 ) velocity vector? at time t = - 1 at time t = - 1
(A) 5 (B) (C) (D) - g/2 What is the position of the object at time t = - 2 ? (A) (1, - 6, - 2g - 7) (B) -12 (C) (1, - 6, - 7) (D) (0, 0, 0) The object is moving (A) in one dimension (B) in two dimensions (C) in three dimensions (D) None of the above What is the acceleration of this object at time t = 25 ? (A) - g (B) 25(0, 0, - g) (C) g
(D) - (0, 0, g) This equation might describe an object (A) in free fall (B) moving as a projectile (C) bouncing straight up and down (D) with changing acceleration In creature-land, the measure of one's hardcoreness is directly correlated to how high one can jump Unfortunately, creatures cannot jump straight up, but must take a running start If creature A jumps with initial velocity vector (2, 2, 5) , and creature B jumps with initial velocity vector (5, 4, 2) (where the z -direction points upwards), which creature is more hardcore? (A) creature A
(B) creature B (C) Both creatures are equally hardcore (D) Impossible to determine without knowing the gravitational acceleration in creature-land According to the previous question, which creature travels furthest during its jump? (A) creature A (B) creature B (C) Both creatures land an equal distance away from their starting point (D) Impossible to determine without knowing the gravitational acceleration in creature-land Which function could describe the velocity of a ball being thrown horizontally off a fire escape? (A) v(t) = - (0, 0, g)t 2 + (0, v, 0)t + (0, 0, h) (B) v(t) = - (0, 0, g)t + (v, 0, 0)t (C) v(t) = - gt + vt (D) v(t) = - (0, 0, g)t + (0, 0, v)t Phin and Wittgenstein are hanging out on the moon when they decide to have a contest to see who can shoot a bullet farther Both use identical guns Phin decides to shoot at a 60 degree angle, while Wittgenstein holds his gun at 45 degrees when shooting Whose bullet lands the furthest away? (A) Phin's (B) Wittgenstein's (C) Both bullets land the same distance away (D) Impossible to determine without knowing the acceleration due to gravity on the moon The office of the Harvard Review of Philosophy is located approximately 10 ft below the earth's surface The acceleration due to gravity experienced by members working in this office is (A) significantly greater than that of people on the earth's surface (B) significantly smaller than that of people on the earth's surface (C) approximately equal to that of people on the earth's surface (D) exactly equal to that of people on the earth's surface A couple of students at Putney decide to go bicycle riding one day Simon rides at a speed of 10 miles per hour, while Liz's average speed is 20 miles per hour After bicycling for several hours,
both Simon and Liz come home and park their bicycles exactly where they started Simons's average velocity for the entire ride is (A) lower than Liz's average velocity (B) higher than Liz's average velocity (C) zero (D) impossible to determine without knowing the actual directions in which he biked If, during their bike ride, Simon and Liz were always biking at a constant speed, (A) their acceleration was always zero (B) their velocity was constant (C) their average velocity after one hour of biking was the same as their average velocity after two hours of biking (D) None of the above While sitting at his office desk, Stephen Greenblatt enjoys throwing crumpled pieces of paper into a wastebasket across the room Over the years, he has carefully kept track of all the different combinations of initial speeds and angles at which he can throw the crumpled pieces of paper while still making the same basket He hopes to some day have a complete list of all the possibilities Professor Greenblatt's efforts are useless because (A) although such a list can theoretically be made, he will never have enough time to exhaust all possibilities (B) there is really only one way to make the basket, and Greenblatt is confused about this because a janitor keeps moving the wastebasket at night (C) there are infinitely many ways to make this basket from the same position (D) None of the above
You might also like
- GravityDocument9 pagesGravitySebastian Cristobal Adolfo Salinas GamboaNo ratings yet
- PhET Kepler's Laws & Orbits QuDocument7 pagesPhET Kepler's Laws & Orbits Queulla shaneNo ratings yet
- Motion in One Dimension QuestionDocument6 pagesMotion in One Dimension Questionabh_omega33% (3)
- Mid-Term IGCSE PhysicsDocument4 pagesMid-Term IGCSE Physicsgdsuta90% (10)
- Mcqs With One Correct Answer Type: Exercise-1Document24 pagesMcqs With One Correct Answer Type: Exercise-1KsNo ratings yet
- 112學年A卷題庫Document10 pages112學年A卷題庫larry940106No ratings yet
- Solution 241111 185145Document24 pagesSolution 241111 185145paavaividyashram22No ratings yet
- PT 1Document8 pagesPT 1LOVELESH KHATTERNo ratings yet
- Physics Irfan MCATDocument6 pagesPhysics Irfan MCATjaipal singhNo ratings yet
- Crash Chapter 4 TestDocument4 pagesCrash Chapter 4 TestKamran Ali100% (1)
- DJDTHRTDJHRGFFD DhirdDocument25 pagesDJDTHRTDJHRGFFD DhirdkratikamathurNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions KinematicsDocument7 pagesChapter Questions KinematicsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- ProjectileMotion PDFDocument14 pagesProjectileMotion PDFShameem AkhterNo ratings yet
- ABC XI TEST SERIES TEST-02 CHAPTER 2 and 3 2023-24Document2 pagesABC XI TEST SERIES TEST-02 CHAPTER 2 and 3 2023-24Ashish GargNo ratings yet
- Objective Question Bank: KinematicsDocument11 pagesObjective Question Bank: KinematicsAtulNo ratings yet
- 1 - 7 Kinematics_Conquer_student ElpDocument15 pages1 - 7 Kinematics_Conquer_student Elpromitdutta2004No ratings yet
- Jee 2014 Booklet2 HWT Motion in 2dDocument16 pagesJee 2014 Booklet2 HWT Motion in 2dvarunkohliinNo ratings yet
- TWT - Kinematics - Nerul MedicalDocument8 pagesTWT - Kinematics - Nerul MedicalAbhishek BahukhandiNo ratings yet
- unit-2-kinematicsDocument8 pagesunit-2-kinematicsManish MishraNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment: Full Marks Zero Marks Negative MarksDocument14 pagesHome Assignment: Full Marks Zero Marks Negative Markssahil.lulani24No ratings yet
- Motion in Plane-SubjectiveDocument4 pagesMotion in Plane-Subjective21- VARNIKA DALALNo ratings yet
- XI MCQ UP To ROTATION-converted-compressedDocument22 pagesXI MCQ UP To ROTATION-converted-compressedEkamjot SINGHNo ratings yet
- Worksheet IX PhysicsDocument16 pagesWorksheet IX PhysicsGuru PrasannaNo ratings yet
- NLM and Projectile Test PaperDocument7 pagesNLM and Projectile Test Papershriyansh singhaniaNo ratings yet
- Physics-I 11THDocument5 pagesPhysics-I 11THbabasain308No ratings yet
- P - 3Y - Test Paper - Motion in 2 Dimension.Document5 pagesP - 3Y - Test Paper - Motion in 2 Dimension.sudhir_kumar_33No ratings yet
- Center of Mass and The Motion of A SystemDocument13 pagesCenter of Mass and The Motion of A SystemNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics 23Document20 pagesPhysics 23Kazuto ShibaNo ratings yet
- Ss 2 First Term Physics Examination-1Document6 pagesSs 2 First Term Physics Examination-1Uzoma ObasiNo ratings yet
- Kinematics MC PracticeDocument17 pagesKinematics MC Practicescientific1576No ratings yet
- KINEMATICS Sheet PDFDocument21 pagesKINEMATICS Sheet PDFAmazing ThingsNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument9 pagesKinematicsChunu Physics loverNo ratings yet
- Test 4 AVJC Final Paper - PCBDocument6 pagesTest 4 AVJC Final Paper - PCBzoologyNo ratings yet
- Xi Physics Hy QP (2023-24)Document6 pagesXi Physics Hy QP (2023-24)dahiyalakshay600No ratings yet
- Twins PhysicsDocument6 pagesTwins PhysicsWale AdeneyeNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Projectile and Kinematics Projectile Motion: Short QuestionsDocument12 pagesAssignment - Projectile and Kinematics Projectile Motion: Short QuestionsManish GoyalNo ratings yet
- 04 - Motion in Two DimensionDocument3 pages04 - Motion in Two DimensionMathan KalyanasundaramNo ratings yet
- 1st QTR Cumulative MC PracticeDocument5 pages1st QTR Cumulative MC PracticeForsbergPhysicsNo ratings yet
- Equation of Motion HWDocument4 pagesEquation of Motion HWdivyanshNo ratings yet
- NCERT-Ch 3-MCQDocument19 pagesNCERT-Ch 3-MCQyash.sharmamsiNo ratings yet
- 01 Kinematics Questions 1Document5 pages01 Kinematics Questions 1Anamika SinghNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument61 pagesIlovepdf Mergedakshitwalia209No ratings yet
- Common TestDocument3 pagesCommon Testaggarwalk9911No ratings yet
- Module Exercise 2 - Kinematics-2DDocument8 pagesModule Exercise 2 - Kinematics-2DzmatbolNo ratings yet
- Physics 4Document20 pagesPhysics 4Kazuto ShibaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Part Test-01 Class 11Document34 pagesPhysics: Part Test-01 Class 11itz malikNo ratings yet
- Casu93a01, A02 - Phase - 1 Jee Advamce On 21-07-2019Document9 pagesCasu93a01, A02 - Phase - 1 Jee Advamce On 21-07-2019VPNNo ratings yet
- 10 - Revision - Phy - PCMDocument3 pages10 - Revision - Phy - PCMC.M.M GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Objective Booklet - 2/physics: Motion in Two Dimension Chapter - 3Document8 pagesObjective Booklet - 2/physics: Motion in Two Dimension Chapter - 3abhishekagarwala21No ratings yet
- SS2 PhysicsDocument3 pagesSS2 PhysicsSUNDAY JAMESNo ratings yet
- 11 Army School Half YearlyDocument8 pages11 Army School Half Yearlyvarundiwakar518No ratings yet
- Home Assignment: Full Marks Zero Marks Negative MarksDocument18 pagesHome Assignment: Full Marks Zero Marks Negative Marks6623abhishekNo ratings yet
- Exam Review 3Document24 pagesExam Review 3api-223793512No ratings yet
- Kinematics 2D - HW - 1Document3 pagesKinematics 2D - HW - 1studyhimansh09No ratings yet
- Iit (M+a) & Jee Mains Only - Asat Preparation Assignment - XiDocument66 pagesIit (M+a) & Jee Mains Only - Asat Preparation Assignment - XimeethcalNo ratings yet
- Phys101 1stexam 1Document2 pagesPhys101 1stexam 1abdulrhmanshanteerNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument23 pagesSolutionrohanbhuyan562No ratings yet
- Paper 1Document5 pagesPaper 1Yash BhalekarNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two Dimension - LDA - 18Document2 pagesMotion in Two Dimension - LDA - 18SaήjaγKsNo ratings yet
- 21-06-2023_JEE(M+A) NUR (WD-MRNG BATCH)_IT-2_P 1 & 2 (1)Document12 pages21-06-2023_JEE(M+A) NUR (WD-MRNG BATCH)_IT-2_P 1 & 2 (1)RetroNo ratings yet
- XI Physics KEY Irfan Sanjrani 4TH FNTDocument3 pagesXI Physics KEY Irfan Sanjrani 4TH FNTjaipal singhNo ratings yet
- 12th House Signs - MahadashaDocument3 pages12th House Signs - MahadashathavaNo ratings yet
- Functional English PDFDocument64 pagesFunctional English PDFlubnaNo ratings yet
- History of NavigationDocument3 pagesHistory of NavigationDanang PrayogiNo ratings yet
- THE Assignment ON Jantar Mantar: Arya College of Engineering and I.T. JaipurDocument15 pagesTHE Assignment ON Jantar Mantar: Arya College of Engineering and I.T. Jaipurharshabid0% (1)
- Bài tập câu so sánhDocument3 pagesBài tập câu so sánhNguyễn Quỳnh NgânNo ratings yet
- 06-Nokia's New Era - Challenges and ChancesDocument12 pages06-Nokia's New Era - Challenges and ChancesSaptarishisAstrologyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document2 pagesChapter 3Adriel Denzel C. Lim100% (1)
- Ryden SolutionsDocument59 pagesRyden Solutionsiantyler329No ratings yet
- Semelas MagicDocument19 pagesSemelas MagickrataiosNo ratings yet
- Michael Ibison - Massless Classical ElectrodynamicsDocument24 pagesMichael Ibison - Massless Classical ElectrodynamicsUtnyuNo ratings yet
- Chemically Enriched UniverseDocument41 pagesChemically Enriched UniverseMark JamesNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument3 pagesNotesDeepankumar AthiyannanNo ratings yet
- Mastering Astronomy Homework AnswersDocument181 pagesMastering Astronomy Homework AnswerskasnanwlfNo ratings yet
- A High Resolution Total Solar Eclipse PDFDocument11 pagesA High Resolution Total Solar Eclipse PDFabhishek reddyNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Exam Session - 2018-19: Class - V Subject: ENGLISHDocument9 pagesHalf Yearly Exam Session - 2018-19: Class - V Subject: ENGLISHPrabhuNo ratings yet
- Astro-Databank Michael ErlewineDocument2 pagesAstro-Databank Michael ErlewinedvtherionNo ratings yet
- Sacred GeometryDocument11 pagesSacred Geometrymcknightm100% (2)
- Hung SocietyDocument338 pagesHung SocietyibodruciNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Solar Angles Simulation and Calculation Using MatlabDocument11 pagesA Comprehensive Solar Angles Simulation and Calculation Using Matlabaoauaz2000No ratings yet
- Nakshatra TableDocument8 pagesNakshatra Tablevenkat_nz0% (1)
- Galileo GalileiDocument7 pagesGalileo Galileinato.kharshiladze.1No ratings yet
- StarsDocument2 pagesStarsОленка КушнірNo ratings yet
- Airy FunctionDocument6 pagesAiry Functionmenonita89No ratings yet
- The Pattern by Mohammad Obaid QamarDocument145 pagesThe Pattern by Mohammad Obaid QamarObaid Qamar100% (1)
- PitrudoshDocument19 pagesPitrudoshUpendra BhadoriyaNo ratings yet
- Andean Evolution and The Terrane Concept: Ian W. D - DalzielDocument1 pageAndean Evolution and The Terrane Concept: Ian W. D - DalzielVictor ValdiviaNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy: Christian A. GueymardDocument8 pagesSolar Energy: Christian A. GueymardMonica CanafNo ratings yet