Math102 Equation Sheet
Uploaded by
Maureen LaiMath102 Equation Sheet
Uploaded by
Maureen LaiPrep101
Lotsmorefreestudyaidsathttp://www.prep101.com/freestuff
Math 102 Equation Sheet
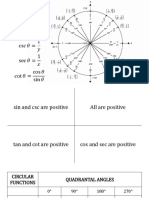
Logarithm Laws & Exponent Rules
y x xy
a a a
log log log + =
n m n m
a a a
+
=
y x
y
x
a a a
log log log =
n m
n
m
a
a
a
=
x n x
a
n
a
log log =
mn n m
a a = ) (
x
x
a a
log
1
log =
n
n
a
a
1
=
0 1 log =
a
1
0
= a
1 log = a
a
a a =
1
x a
x
a
= log x a
x
a
=
log
Trigonometric Identities
1 cos sin
2 2
= + u u u u
2 2
sec tan 1 = + u u
2 2
csc cot 1 = +
u
u
cos
1
sec =
u
u
sin
1
csc =
u
u
tan
1
cot =
u
u
u
cos
sin
tan =
u
u
u
sin
cos
cot =
u u cos ) sin(
2
=
u u sin ) cos(
2
=
u u cot ) tan(
2
=
u u sec ) csc(
2
=
u u csc ) sec(
2
=
u u tan ) cot(
2
=
u u sin ) sin( = u u cos ) cos( = u u tan ) tan( =
u u csc ) csc( = u u sec ) sec( = u u cot ) cot( =
v u v u v u sin cos cos sin ) sin( = v u v u v u sin sin cos cos ) cos( m =
v u
v u
v u
tan tan 1
tan tan
) tan(
m
=
u u u cos sin 2 2 sin = u u u u u
2 2 2 2
sin 2 1 1 cos 2 sin cos 2 cos = = =
u
u
u
2
tan 1
tan 2
2 tan
=
2
2 cos 1
sin
2
u
u
=
2
2 cos 1
cos
2
u
u
+
=
u
u
u
2 cos 1
2 cos 1
tan
2
+
=
Prep101
Lotsmorefreestudyaidsathttp://www.prep101.com/freestuff
Special Angles
0 0 sin =
2
1
6
sin =
2
2
4
sin =
2
3
3
sin =
1 0 cos =
2
3
6
cos =
2
2
4
cos =
2
1
3
cos =
0 0 tan =
3
1
6
tan =
1 tan
4
=
3 tan
3
=
Analytic Geometry
If ) , (
1 1 1
y x P and ) , (
2 2 2
y x P are two points, then
Distance between
1
P and
2
P is
2
1 2
2
1 2
) ( ) ( y y x x d + = .
Midpoint of line segment
2 1
P P is
+ +
2
,
2
2 1 2 1
y y x x
.
Slope of line segment
2 1
P P is
1 2
1 2
x x
y y
x
y
m
= .
Point-slope equation of straight line : ) (
0 0
x x m y y = .
Slope-intercept equation of straight line : b mx y + = .
Two lines are parallel if
2 1
m m = .
Two lines are perpendicular if
2
1
1
m
m = .
Equation of circle :
2 2 2
) ( ) ( r k y h x = + . Centre = ) , ( k h ; radius r = .
Geometric Formulas
Area of triangle : bh A
2
1
= . Area of trapezoid : h b a A ) (
2
1
+ = .
Area of circle :
2
r A = . Circumference of circle : r C 2 = .
Area of sphere :
2
4 r A = . Volume of sphere:
3
3
4
r V = .
Area of cylinder :
2
2 2 r rh A + = . Volume of cylinder: h r V
2
= .
Area of cone : rs r A + =
2
. Volume of cone: h r V
2
3
1
= .
Volume of prism : Ah V = . Volume of pyramid: Ah V
3
1
= .
Derivatives
If ) (x f y = , then
h
x f h x f
x f
dx
dy
h
) ( ) (
lim ) (
0
+
= =
or
a x
a f x f
a f
a x
=
) ( ) (
lim ) ( .
Prep101
Lotsmorefreestudyaidsathttp://www.prep101.com/freestuff
The derivative ) (x f is a function that represents either
(i) the slope of the tangent line; or
(ii) the rate of change of y with respect to x.
Derivative Formulas
0 ) ( = c
dx
d
1
) (
=
n n
nx x
dx
d
) ( )) ( ( x f c x cf
dx
d
=
) ( ) ( )) ( ) ( ( x g x f x g x f
dx
d
+ = +
) ( ) ( )) ( ) ( ( x g x f x g x f
dx
d
=
) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )) ( ) ( ( x g x f x g x f x g x f
dx
d
+ =
[ ]
2
) (
) ( ) ( ) ( ) (
) (
) (
x g
x g x f x g x f
x g
x f
dx
d
=
) ( )) ( ( ))) ( ( ( x g x g f x g f
dx
d
=
x x
dx
d
cos ) (sin =
x x
dx
d
sin ) (cos =
x x
dx
d
2
sec ) (tan =
x x
dx
d
2
csc ) (cot =
x x x
dx
d
tan sec ) (sec =
x x x
dx
d
cot csc ) (csc =
x
x
dx
d 1
) (ln =
a x
x
dx
d
a
ln
1
) (log =
x x
e e
dx
d
= ) (
Prep101
Lotsmorefreestudyaidsathttp://www.prep101.com/freestuff
a a a
dx
d
x x
ln ) ( =
2
1
1
1
) (sin
x
x
dx
d
2
1
1
1
) (cos
x
x
dx
d
2
1
1
1
) (tan
x
x
dx
d
+
=
Linear Approximation
) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( a x a f a f x f +
The error [ ] ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( a x a f a f x f E + = in this approximation is less than
2
2
1
) ( a x M
where M is the maximum value of | ) ( | x f between x and a.
Graphing
1
st
Derivative
If 0 ) ( > x f , then the graph of f is increasing.
If 0 ) ( < x f , then the graph of f is decreasing.
If 0 ) ( = x f , then x is critical point of f , (a possible extremum of f ).
2
nd
Derivative
If 0 ) ( > x f , then the graph of f is concave up.
If 0 ) ( < x f , then the graph of f is concave down.
If 0 ) ( = x f , then x is a possible inflection point of f.
1
st
Derivative Test
If c is a critical point of f ( 0 ) ( = x f ) and
(i) 0 ) ( > x f when c x < and 0 ) ( < x f when c x > , then c is a local maximum;
(ii) 0 ) ( < x f when c x < and 0 ) ( > x f when c x > , then c is a local minimum.
2
nd
Derivative Test
If c is a critical point of f ( 0 ) ( = x f ) and
(i) 0 ) ( > c f , then c is a local maximum;
Prep101
Lotsmorefreestudyaidsathttp://www.prep101.com/freestuff
(ii) 0 ) ( < c f , then c is a local minimum;
(iii) 0 ) ( = c f , then the test fails. (ii) 0 ) ( < c f , then c is a local minimum.
Asymptotes
Horizontal Asymptotes : b y = is a horizontal asymptote of ) (x f y = if b x f
x
=
) ( lim .
Vertical Asymptotes : a x = is a vertical asymptote of ) (x f y = if =
) ( lim x f
a x
.
Newtons Method
) (
) (
1
n
n
n n
x f
x f
x x
=
+
Differential Equations
kt
Ce y ky
dt
dy
= = .
Doubling time :
k
t
2 ln
2
= .
Steady States : C y C f = = 0 ) ( is a steady state solution of ) (y f
dt
dy
= .
Eulers Method : If ) (y f
dt
dy
= ,
0
) 0 ( y y = , then h y f y y
k k k
) (
1
+ =
+
.
You might also like
- Development of Crash Wall Design Loads From Theoretical Train Impact100% (1)Development of Crash Wall Design Loads From Theoretical Train Impact22 pages
- Chapter 5 Parametric Equations: Example 1: Sketching A Curve100% (1)Chapter 5 Parametric Equations: Example 1: Sketching A Curve2 pages
- Combined Rotation & Translation / Rolling Motion: By: Mr. L. M. PatelNo ratings yetCombined Rotation & Translation / Rolling Motion: By: Mr. L. M. Patel7 pages
- Calculus I Summary: Tabulated by Lambert Peng at Brown in Summer 2008No ratings yetCalculus I Summary: Tabulated by Lambert Peng at Brown in Summer 20083 pages
- W7 Second Order Linear Differential Equation Part 1 - ModuleNo ratings yetW7 Second Order Linear Differential Equation Part 1 - Module5 pages
- Thomas Calculus Early Transcendentals 12th TXTBK Solution ManualNo ratings yetThomas Calculus Early Transcendentals 12th TXTBK Solution Manual7 pages
- A3 Trigonometry Topic Booklet 1 Hard CIE A Level Maths P3 - 1No ratings yetA3 Trigonometry Topic Booklet 1 Hard CIE A Level Maths P3 - 16 pages
- Function and Graph: Chapter 1.2 Properties of Function100% (1)Function and Graph: Chapter 1.2 Properties of Function22 pages
- The Fractional Fourier Transform and Time-Frequency RepresentationsNo ratings yetThe Fractional Fourier Transform and Time-Frequency Representations8 pages
- Solution Manual For Trigonometry 3rd Edition by YoungNo ratings yetSolution Manual For Trigonometry 3rd Edition by Young90 pages
- 2022 Euclid Contest: The Centre For Education in Mathematics and Computing Cemc - Uwaterloo.caNo ratings yet2022 Euclid Contest: The Centre For Education in Mathematics and Computing Cemc - Uwaterloo.ca422 pages
- The First Order Quasi-Linear Pdes: 2.1 Characteristic Curves and Integral SurfacesNo ratings yetThe First Order Quasi-Linear Pdes: 2.1 Characteristic Curves and Integral Surfaces12 pages
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizNo ratings yetWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz37 pages
- Multivariable Calculus: Section 4 Maxima and Minima Using Lagrange MultipliersNo ratings yetMultivariable Calculus: Section 4 Maxima and Minima Using Lagrange Multipliers18 pages
- Thomas' Calculus - Early Transcendentals, 15 - EdNo ratings yetThomas' Calculus - Early Transcendentals, 15 - Ed5 pages
- Unit 3 - Polynomial and Rational Functions100% (1)Unit 3 - Polynomial and Rational Functions40 pages
- Algebra 2 (Honors) First Semester Final: X X X XNo ratings yetAlgebra 2 (Honors) First Semester Final: X X X X12 pages
- 1.2:rates of Change & Limits Learning GoalsNo ratings yet1.2:rates of Change & Limits Learning Goals58 pages
- Working With Vectors: Magnitude and DirectionNo ratings yetWorking With Vectors: Magnitude and Direction16 pages
- Calculus 7th Edition James Stewart - The full ebook set is available with all chapters for download100% (3)Calculus 7th Edition James Stewart - The full ebook set is available with all chapters for download49 pages
- Numerical Methods - Fixed Point IterationNo ratings yetNumerical Methods - Fixed Point Iteration4 pages
- Kinematics of Machines Chapter 8 Cam Design: Dr. Jaafar HallalNo ratings yetKinematics of Machines Chapter 8 Cam Design: Dr. Jaafar Hallal75 pages
- Foundation Year Program Entrance Tests Mathematics Specification For Nufyp Set 2020No ratings yetFoundation Year Program Entrance Tests Mathematics Specification For Nufyp Set 20209 pages
- Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 14 PreCalculus ConceptsNo ratings yetAnswer Key - CK-12 Chapter 14 PreCalculus Concepts10 pages
- Iygb Gce: Mathematics MP2 Advanced LevelNo ratings yetIygb Gce: Mathematics MP2 Advanced Level7 pages
- Instant download (Ebook) Math for Business and Economics: Compendium of Essential Formulas 3rd Edition by Franz W. Peren ISBN 9783662688601, 3662688603 pdf all chapter100% (3)Instant download (Ebook) Math for Business and Economics: Compendium of Essential Formulas 3rd Edition by Franz W. Peren ISBN 9783662688601, 3662688603 pdf all chapter71 pages