04 Forces Vectors and Moments 04..
04 Forces Vectors and Moments 04..
Uploaded by
Ashani0001Copyright:
Available Formats
04 Forces Vectors and Moments 04..
04 Forces Vectors and Moments 04..
Uploaded by
Ashani0001Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
04 Forces Vectors and Moments 04..
04 Forces Vectors and Moments 04..
Uploaded by
Ashani0001Copyright:
Available Formats
4 Worksheet (AS)
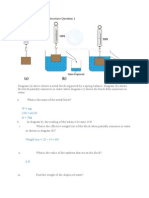
Data needed to answer questions can be found in the Data, formulae and relationships sheet. 1 Two forces, each of magnitude 8 N, act on an object. The angle between the two forces is 60. What is the magnitude of the resultant force acting on the object? A B C D 2 4N 7N 8N 14 N [1]
F
[1]
20 N
The object in the diagram is in equilibrium. Which equation is correct about the forces? A B C D 15 = 20 cos 20 = F cos F = 15 sin F = 15 tan
15 N
A force of 10 N is resolved into two components at right angles to each other. One of the components is 8 N. What is the other component? A B C D 2N 4N 6N 12 N
[1]
A man of weight 600 N stands at the end of a uniform wooden plank, which is pivoted as shown in the diagram. What is the weight of the wooden plank? [1] A B C D 100 N 200 N 300 N 400 N
0.5 m 3.0 m
A uniform square block is pushed along a rough surface at constant speed by a force of 100 N. A horizontal force of friction acts between the surface and the block. What is the moment of the force of friction about the centre of gravity? [1] A B C D 80 N m clockwise 80 N m anticlockwise 160 N m clockwise 160 N m anticlockwise
direction of movement
centre of gravity
1.6 m
AS and A Level Physics
Original material Cambridge University Press 2010
4 Worksheet (AS)
6 Calculate the magnitude of the resultant force in each case below. a b
[2]
[3]
7 In each case below, resolve the vector into two perpendicular components in the x and y directions. a b
[2] 8 a Define the moment of a force. b State two conditions that must be met for the equilibrium of an extended object. 9 The diagram shows a uniform beam of length 1.5 m and weight 60 N resting horizontally on two supports.
[2] [1] [2]
a By taking moments about the support A, determine the force RB at the support B. b Use your answer to a to calculate the force RA at support A. 10 A child of mass 35 kg on a swing is pulled to one side. The diagram shows the forces acting on the seat of the swing when it is in equilibrium. a What is the net force on the seat? [1] [4] [2] b Draw a triangle of forces. Hence determine: i the tension T in the rope ii the angle made by the rope with the vertical.
[3] [1]
AS and A Level Physics
Original material Cambridge University Press 2010
4 Worksheet (AS)
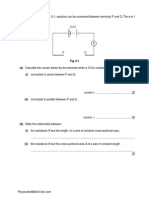
11 A gardener pulls a 50 kg roller along level ground, as shown in the diagram. The roller moves at a steady speed along the level ground when the handle makes an angle of 30 to the horizontal ground and the gardener pulls with a force of 300 N along the handle.
a Calculate the horizontal component of the force 300 N. b What is the net force in the horizontal direction? Hence determine the magnitude of the resistive force acting on the roller. c Determine the vertical contact force acting on the roller due to the ground. 12 A ladder of mass 32 kg rests at an angle against a smooth wall as shown in the diagram. The centre of gravity of the ladder is at its mid-point. a Determine the force R exerted by the wall on the ladder by taking moments about the base of the ladder. [3] b Explain why the force at the base of the ladder was not included when doing the calculation in a. [1]
[2] [2] [3]
13 A 62 kg person lies flat on a uniform plank of mass 15 kg. The plank, with the person lying on it, is placed on a brick and some bathroom scales, as shown in the diagram below.
The persons toe-to-head distance is 1.56 m. The length of the plank is also 1.56 m. a Sketch the diagram above. On your sketch, show all the forces acting on the plank. b The reading on the bathroom scales is 30 kg. Use this information to determine how far the centre of gravity of the person is from the toes. Total: Score: [2] [4] %
45
AS and A Level Physics
Original material Cambridge University Press 2010
You might also like
- Annett Book 2-1Document201 pagesAnnett Book 2-1Benedetta Flebus100% (1)
- Moments WorksheetDocument2 pagesMoments Worksheetarieljuwo75% (8)
- IGCSE-Hooke's Law Worksheet 1.1Document8 pagesIGCSE-Hooke's Law Worksheet 1.1Sharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 20 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 20 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 12 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 12 PDFVijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- Mid-Term IGCSE PhysicsDocument4 pagesMid-Term IGCSE Physicsgdsuta90% (10)
- Current-Electricity (Edexcel Igcse) WorksheetDocument27 pagesCurrent-Electricity (Edexcel Igcse) Worksheetertugoz100% (2)
- As Student WorksheetsDocument54 pagesAs Student WorksheetsHiyahiyahiya HuhahuhahuhaNo ratings yet
- Notes 5.turning Effects of ForcesDocument10 pagesNotes 5.turning Effects of ForcesNg Yong Hui Melvin69% (13)
- WS1 1Document3 pagesWS1 1Yoshua Yanottama0% (1)
- Worksheet 13 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet 13 PDFVijay Bhaskar50% (2)
- M Schemes 04Document3 pagesM Schemes 04Pathmanathan Nadeson0% (2)
- Modal Verbs - TEXTDocument3 pagesModal Verbs - TEXTBerlinghiero1100% (2)
- Scarred Lands - Edge of Infinity - The Scarred Planes PDFDocument146 pagesScarred Lands - Edge of Infinity - The Scarred Planes PDFcameronhyndman100% (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Moments QuestionsDocument12 pagesMoments Questionsmuxadey100% (1)
- Turning Effect of Forces - Worksheet 3Document5 pagesTurning Effect of Forces - Worksheet 3Azhar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Pressure 8th Grade WorksheetDocument4 pagesPressure 8th Grade WorksheetEnkhbayasgalan SodbayarNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - Physics - Worksheet 5 - The Turning Effect of ForcesDocument2 pagesIGCSE - Physics - Worksheet 5 - The Turning Effect of Forceseminnayal.enNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - Physics - MCQ 3 - Forces and MovementDocument7 pagesIGCSE - Physics - MCQ 3 - Forces and MovementKyi Nue Khin0% (1)
- P G7 Turning Effect of ForceDocument2 pagesP G7 Turning Effect of ForceD'ferti Anggraeni100% (2)
- IGCSE - Physics - Worksheet 3 - Forces and MovementDocument3 pagesIGCSE - Physics - Worksheet 3 - Forces and Movementeminnayal.en100% (1)
- Force and Turning EffectDocument3 pagesForce and Turning EffectDhanBahadur100% (1)
- Turning Forces - MomentsDocument4 pagesTurning Forces - Momentsphydotsi100% (5)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 12.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 12.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic EffectsDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic EffectsTran Phuong LinhNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Mass WeightDocument17 pagesIGCSE Physics Mass WeightVijay Bhaskar100% (2)
- O Level Wave MCDocument6 pagesO Level Wave MCDora Aye50% (2)
- Worksheet 10 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 10 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Resultant Forces - Practice QsDocument9 pagesResultant Forces - Practice Qsphydotsi50% (2)
- Mass, Weight and Density IGCSEDocument2 pagesMass, Weight and Density IGCSEsapini100% (1)
- Unit Physics WorksheetsDocument10 pagesUnit Physics WorksheetsVarshLok100% (2)
- Year 9 Science Chapter 15 - Turning On A PivotDocument18 pagesYear 9 Science Chapter 15 - Turning On A PivotVentus TanNo ratings yet
- Sound, Waves & EchoDocument2 pagesSound, Waves & Echonewtonfogg123No ratings yet
- Measurement (Answers)Document16 pagesMeasurement (Answers)keyur.galaNo ratings yet
- Energy Stores and Transfers WorksheetDocument3 pagesEnergy Stores and Transfers WorksheetAndreas LambriasNo ratings yet
- 3 Moment of A Force1Document5 pages3 Moment of A Force1Philip MooreNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Worksheet IGCSEDocument2 pagesRadioactive Worksheet IGCSESyakti PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet PDFDocument10 pagesPhysics Worksheet PDFanas ahmed100% (1)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 15.1Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 15.1Alex Datsyuk0% (1)
- Moment of Forces WorksheetDocument4 pagesMoment of Forces Worksheetjessica100% (1)
- Series and Parallel Circuits WorksheetDocument3 pagesSeries and Parallel Circuits WorksheetanishNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - Physics - MCQ 2 - Forces and ShapeDocument7 pagesIGCSE - Physics - MCQ 2 - Forces and ShapeKyi Nue KhinNo ratings yet
- IGCSE PHYSICS Revision 2 - MomentsDocument9 pagesIGCSE PHYSICS Revision 2 - MomentsPhysicsNo ratings yet
- General Wave Properties 3 QPDocument8 pagesGeneral Wave Properties 3 QPshadybitxhespamNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics MCQDocument11 pagesIGCSE Physics MCQSriram ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet PressureDocument2 pagesPhysics Worksheet PressuretuvvacNo ratings yet
- Pressure: Question Paper 3Document17 pagesPressure: Question Paper 3Suhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law Practice Questions PDFDocument3 pagesHooke's Law Practice Questions PDFmelissa80% (5)
- Archimedes Principle Q & ADocument4 pagesArchimedes Principle Q & Asimonckt100% (2)
- MomentsDocument5 pagesMomentsPichakorn100% (1)
- Physics Ib 10 Waves Worksheet AnswerkeyDocument2 pagesPhysics Ib 10 Waves Worksheet Answerkeyapi-301605346No ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 2.2Document3 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 2.2Alex Datsyuk100% (1)
- Year 9 Physics Pressure WorksheetDocument5 pagesYear 9 Physics Pressure Worksheetaswata Narayan100% (3)
- The Earth Igcse Physics 0625Document38 pagesThe Earth Igcse Physics 0625Aminah Shahzad100% (1)
- Electric Circuits 2 QPDocument12 pagesElectric Circuits 2 QPAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics DensityDocument12 pagesIGCSE Physics DensityNethra Sasikumar100% (1)
- 08 Deforming Solids 08Document4 pages08 Deforming Solids 08Ashani0001No ratings yet
- 28lattiDocument4 pages28lattifaizana_8No ratings yet
- 15 Superposition of Waves 15Document5 pages15 Superposition of Waves 15Ashani0001100% (1)
- T/S I/Microa LN (I) 0 100 4.60517 10 68 4.219508 20 47 3.850148 30 32 3.465736 40 22 3.091042 50 15 2.70805 60 10 2.302585Document2 pagesT/S I/Microa LN (I) 0 100 4.60517 10 68 4.219508 20 47 3.850148 30 32 3.465736 40 22 3.091042 50 15 2.70805 60 10 2.302585Ashani0001No ratings yet
- 9701 Chemistry Applications BookletDocument161 pages9701 Chemistry Applications BookletZain RehanNo ratings yet
- Predator PreyDocument14 pagesPredator PreyAshani0001No ratings yet
- A1 Bonding WS5Document13 pagesA1 Bonding WS5Ashani0001No ratings yet
- A1 Equilibria WS5Document6 pagesA1 Equilibria WS5Ashani0001No ratings yet
- Practicals Recap Type IIDocument2 pagesPracticals Recap Type IIAshani0001No ratings yet
- Stationary WavesDocument10 pagesStationary WavesAshani0001No ratings yet
- Refraction Diagrams: Select The Correct Ray in Each of The Diagrams Below. A 1Document1 pageRefraction Diagrams: Select The Correct Ray in Each of The Diagrams Below. A 1Ashani0001No ratings yet
- Capacitors in DDocument2 pagesCapacitors in DAshani0001No ratings yet
- Current Flow Notes&QuestionsDocument1 pageCurrent Flow Notes&QuestionsAshani0001No ratings yet
- Physics Revision Notes - Electricity: Acetate Rod With A Cloth, It Becomes Positively ChargedDocument1 pagePhysics Revision Notes - Electricity: Acetate Rod With A Cloth, It Becomes Positively ChargedAshani0001No ratings yet
- Chemistry QuestionsDocument40 pagesChemistry Questionskaotao1No ratings yet
- Rasi Chart (Nirayan) : TransitDocument1 pageRasi Chart (Nirayan) : TransitsedanseNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literatures and StudiesDocument11 pagesReview of Related Literatures and Studiesمہنور مہتابNo ratings yet
- Land in The Enlightened Imagination: From Astrobiology To Commodification. Agricultural Debates in Eighteenth Century ItalyDocument245 pagesLand in The Enlightened Imagination: From Astrobiology To Commodification. Agricultural Debates in Eighteenth Century Italysmcgehee100% (1)
- CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics - Lecture 5: Ch.12, Sec.9Document20 pagesCEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics - Lecture 5: Ch.12, Sec.9abdsu75No ratings yet
- Effect of Saturn TransitDocument3 pagesEffect of Saturn TransitjginuNo ratings yet
- History of MathDocument3 pagesHistory of MathChelsweetNo ratings yet
- Dark Earth PDFDocument106 pagesDark Earth PDFbanapte59100% (1)
- Vimshottari - Vedic AstrologyDocument2 pagesVimshottari - Vedic AstrologyBhaskar ThakurnagarNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Force - Slide/Image Introduction and ObjectivesDocument10 pagesHydrostatic Force - Slide/Image Introduction and ObjectivesUditha WedageNo ratings yet
- Copernican RevolutionDocument9 pagesCopernican RevolutionSherwin D. SungcalangNo ratings yet
- Jaimini AspectsDocument5 pagesJaimini AspectsDivakar SaripalliNo ratings yet
- Mandook Dasha PDFDocument102 pagesMandook Dasha PDFChchatrapati100% (2)
- The Natal Guardian Angel(s) & Other Astrologically-Derived AngelsDocument26 pagesThe Natal Guardian Angel(s) & Other Astrologically-Derived Angelsfarzana25100% (1)
- Cipher Manuscripts of The Golden Dawn by Benpadiah (Ciphers - PDF) (116 Pages)Document43 pagesCipher Manuscripts of The Golden Dawn by Benpadiah (Ciphers - PDF) (116 Pages)dove0% (1)
- Sartre, - Patterns of Bad FaithDocument11 pagesSartre, - Patterns of Bad FaithHP40No ratings yet
- Sun 1Document2 pagesSun 1ysabelle rocoNo ratings yet
- LEP 5.1.06 Fine Structure and One-Electron Spectrum: Related TopicsDocument3 pagesLEP 5.1.06 Fine Structure and One-Electron Spectrum: Related TopicsRaúlChamorroTobarNo ratings yet
- Dimba Chakra Saptarishis Astrology BWDocument16 pagesDimba Chakra Saptarishis Astrology BWGarga80% (5)
- JedhaDocument1 pageJedhap_haganNo ratings yet
- 2019 - AstroTwins Marie ForleoDocument211 pages2019 - AstroTwins Marie ForleoAgua Con AzucarNo ratings yet
- Phonetics in Phonology: John J. OhalaDocument6 pagesPhonetics in Phonology: John J. OhalaNoorul JannahNo ratings yet
- Hollow-Earth Theories: A List of ReferencesDocument5 pagesHollow-Earth Theories: A List of ReferencesVen GeanciaNo ratings yet
- Planet: Planets in Astrology and in Your Kundli: SUN ConsiderationDocument4 pagesPlanet: Planets in Astrology and in Your Kundli: SUN ConsiderationVishal DhekaleNo ratings yet
- Student's Booklet - The Earth in The UniverseDocument9 pagesStudent's Booklet - The Earth in The UniverseRafa Rguez PerezNo ratings yet
- Zelinskywibbelt C Ed The Semantics of Prepositions From MentDocument537 pagesZelinskywibbelt C Ed The Semantics of Prepositions From Menthalllrexxxalll100% (2)
- Ch17習題解答Document24 pagesCh17習題解答RavKiranNo ratings yet
- Abhijit Strategy For PhyDocument13 pagesAbhijit Strategy For PhyJAIVEERU37No ratings yet