0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
221 viewsME2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy QB
ME2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy QB
Uploaded by
Vasantha KumarThis document outlines the topics and questions covered in 5 units for the subject Engineering Materials and Metallurgy. Unit I covers material science fundamentals like material classification, properties of metals, solidification and crystal structures. Unit II focuses on heat treatment processes like annealing, normalizing, quenching and tempering. Unit III discusses mechanical testing methods for strength, hardness and fatigue. Unit IV presents various alloy systems and engineering alloys of steel, aluminum and copper. Finally, Unit V examines polymeric materials, composites, ceramics and other specialty materials. The document provides short answer and long answer questions to test comprehension of these key materials science concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
ME2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy QB
ME2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy QB
Uploaded by
Vasantha Kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
221 views3 pagesThis document outlines the topics and questions covered in 5 units for the subject Engineering Materials and Metallurgy. Unit I covers material science fundamentals like material classification, properties of metals, solidification and crystal structures. Unit II focuses on heat treatment processes like annealing, normalizing, quenching and tempering. Unit III discusses mechanical testing methods for strength, hardness and fatigue. Unit IV presents various alloy systems and engineering alloys of steel, aluminum and copper. Finally, Unit V examines polymeric materials, composites, ceramics and other specialty materials. The document provides short answer and long answer questions to test comprehension of these key materials science concepts.
Original Description:
question paper of engineering material; and metralogy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document outlines the topics and questions covered in 5 units for the subject Engineering Materials and Metallurgy. Unit I covers material science fundamentals like material classification, properties of metals, solidification and crystal structures. Unit II focuses on heat treatment processes like annealing, normalizing, quenching and tempering. Unit III discusses mechanical testing methods for strength, hardness and fatigue. Unit IV presents various alloy systems and engineering alloys of steel, aluminum and copper. Finally, Unit V examines polymeric materials, composites, ceramics and other specialty materials. The document provides short answer and long answer questions to test comprehension of these key materials science concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
221 views3 pagesME2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy QB
ME2253 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy QB
Uploaded by
Vasantha KumarThis document outlines the topics and questions covered in 5 units for the subject Engineering Materials and Metallurgy. Unit I covers material science fundamentals like material classification, properties of metals, solidification and crystal structures. Unit II focuses on heat treatment processes like annealing, normalizing, quenching and tempering. Unit III discusses mechanical testing methods for strength, hardness and fatigue. Unit IV presents various alloy systems and engineering alloys of steel, aluminum and copper. Finally, Unit V examines polymeric materials, composites, ceramics and other specialty materials. The document provides short answer and long answer questions to test comprehension of these key materials science concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Subject Name : Engineering Materials and Metallurgy
Subject Code: ME2253
UNIT-I
2MARKS
1. What is the meaning of material science?
2. How are materials classified?
3. In what respect 'Conductors' differ from Semiconductors?
4. Give the classification of magnetic materials. Explain
briefly the following mechanical properties of metals
5. Explain Elasticity, Plasticity, Ductility, Malleability and Hardness.
6. Write a short note on 'Superconductivity'
7. Explain briefly the process of crystallization of pure metal.
8. What do you mean by 'Dendritic solidification? Show with the help of a
diagram various step involved in the formation of crystal.
9. Explain briefly the following:
(i) Unit cell (ii) Space lattice(iii) Space lattice groups.
10. What do you mean by 'Allotropy of metals' '? Explain.
16MARKS
1.Draw Fe-C diagram and mark all the phasesand explain the reactions? Solid phases in Fe-
Fe
3
C phase diagram?
2.What are the different types of cast iron? Draw the microstructure of any four types of cast
iron?
3.Isomorphous phase diagram for Cu-Ni system ?Ideal phase diagram(soluble and insoluble)
4.Explain Hume Rothery rule ?
5.Explain the different types of carbon steel?
UNI T-I I
2MARKS
1. State the objects of "annealing".
2.Explain full annealing processes.
3. What is accomplished by normalising ?
4. Describe the "critical rate" of quenching.
5.Name and explain the various quenching media used for heat treatment of steel.
6. Explain hardening methods :
7. Describe with a neat sketch Jominy hardenability test.
8.Write a
s
hort note on 'Sub-zero treatment of steel'.
9. What is the purpose of tempering?
10. What do you mean by "Age hardening"?
16MARKS
1.Types of annealing Process and explain it?
2.Explain Isothermal Transformation diagram(TTT)or(c-curve)or(s-curve)
3.Explain Tempering process ? and explain CCT diagram?
4.Explain :Martempering and Austempering
5.Explain case hardening process:
i.Carburising ii)carbonitriding iii)induction hardening iv)Nitriding v)Flame hardening
UNI T-I I I
2MARKS
1.Describe briefly any two of the following non-destructive tests
2.Name the important mechanical test which give valuable information
about metals and alloys.
3.What does impact test signify ? Explain with necessary formulations,
the procedures to be adopted in the impact test. conducted on a pendulum
type impact testing machine.
4.What are different hardness tests of interest to the testing engineer under
various situations ?
5.Explain the Brinell hardness testing of mild steel specimen.
6.What is a 'rebound test' ? How is it carried out ?
7.What is a fatigue failure ? How is a fatigue test carried out?
8.Explain briefly the procedure of conducting a torsion test.
9.What is creep ?
10. Draw a typical creep curve and explain the different stages of creep.
UNI T-I V
2MARKS
1. State the effects of adding following alloying elements to steel:
Nickel, Chromium,.
2. Give the composition, properties and uses of the following alloy steels :
High speed steel, Silicon steel.
3. Enumerate the physical and mechanical properties of aluminium.
4. State the importance of commercially pure aluminium as a general engineering material.
5. How is copper manufactured '?
6. What are the commercial alloys of aluminium? Briefly describe their
composition and
uses.
7. What are the typical alloys of copper used in engineering'? Describe
briefly their composition and uses.
8. What are the pronounced effects of beryllium on the physical properties
of copper'?
9. What are the compositions, structure
and
characteristics of copper tin
bronzes ? Why are these alloys used for springs ?
10. What are the requirements of an alloy to be used as a bearing metal
16MARKS
1.Types of austenitic stainless steel and explain?
2.Effect of alloying addition in steel.(types of alloy steel)
3.Explain HSS and HSLA steel.
4.Types of Copper alloy and explain?
5.Types of Al alloy and explain?
6.Precipitation strengthening.and explain bearing alloy
UNI T-V
2MARKS
1.Short notes on following materials:
i)PVC ii)PMMA
2.What is FRB?
3.What is Elastomers?
4.What is babbit ?
5. What is temper embrittlenient ? How is it avoided ?
6.Explain engineering ceramics.
7.Describe glass manufacturing method?
8.What is Fiber reinforced plastics.
16MARKS
1.Short notes on following materials:
i)PVC ii)PMMA iii)PE iv)PP v)PEEK vi)PET
2.Types of Engineering ceramic materials.
3.short notes on Elastomers and Composites
4.Explain FRP and FRC
5.(i)Plastic and polymer Properties and application
(ii)Thermo and thermosetting plastics
(iii)addition and co polymerization
6.special properties in polymer(i.Mechanical.ii,Thermal,iii,Electrical)
You might also like
- ChemECar Project ProposalDocument4 pagesChemECar Project ProposalArdago Lengga100% (1)
- Materials Science - Examination QuestionsDocument2 pagesMaterials Science - Examination QuestionsNoura Nour ElshamsNo ratings yet
- Emm Question BankDocument6 pagesEmm Question BankMurugesan JeevaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials & Metallurgy Question BankDocument7 pagesEngineering Materials & Metallurgy Question BankJOHN PAUL V67% (3)
- Important Questions Material ScienceDocument3 pagesImportant Questions Material Sciencetheamg7272No ratings yet
- Unit 3 &4 Question BankDocument4 pagesUnit 3 &4 Question BankcprabhakaranNo ratings yet
- Me6403 Engineering Materials and Metallurgy: Unit 1.alloys and Phase Diagram Part ADocument6 pagesMe6403 Engineering Materials and Metallurgy: Unit 1.alloys and Phase Diagram Part Ajamunaa83No ratings yet
- Unit-I - Alloys and Phase Diagrams Part-A (2 Marks) : Question BankDocument10 pagesUnit-I - Alloys and Phase Diagrams Part-A (2 Marks) : Question BankDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- ME6403-Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument10 pagesME6403-Engineering Materials and Metallurgykannan100% (1)
- B3B032 Total Pages:2: (Answer Any Two Questions)Document11 pagesB3B032 Total Pages:2: (Answer Any Two Questions)Sourabh PradhanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials and Metallurgy QBDocument13 pagesEngineering Materials and Metallurgy QBParamasivam VeerappanNo ratings yet
- MOM OU Old Question PaperDocument2 pagesMOM OU Old Question PaperAmmineni Syam PrasadNo ratings yet
- 20ME403 Engineering Materials and Metallurgy Unit - IV Digital MaterialDocument55 pages20ME403 Engineering Materials and Metallurgy Unit - IV Digital MaterialDark ranger YtNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument14 pagesEngineering Materials and Metallurgyashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- 2770-ST7103-Theory of Elasticity and PlasticityDocument11 pages2770-ST7103-Theory of Elasticity and PlasticitySri D50% (2)
- 2 MarksDocument15 pages2 MarksVignesh Durai100% (3)
- Elasticity and PlasticityDocument26 pagesElasticity and PlasticityRAMA BAGAS ADITYA TM 2DNo ratings yet
- CM7202-Applied Materials EngineeringDocument6 pagesCM7202-Applied Materials EngineeringJayaraman TamilvendhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9d FractureDocument70 pagesChapter 9d FracturenaveenaNo ratings yet
- 4 Me MQ EMMDocument2 pages4 Me MQ EMMBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Theory of Elasticity and Plasticity Model QuestionsDocument2 pagesTheory of Elasticity and Plasticity Model Questionsrameshbabu_1979No ratings yet
- Engg Chemistry Important Questions For SemesterDocument1 pageEngg Chemistry Important Questions For SemesterguruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Stress - Transformation (Equations)Document41 pagesChapter 9 - Stress - Transformation (Equations)Nyan Htet WinNo ratings yet
- Power Point Slides Lecture12Document15 pagesPower Point Slides Lecture12Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- 131212-131904-Material Science and MetallurgyDocument1 page131212-131904-Material Science and Metallurgysameer_m_daniNo ratings yet
- Machine Tools LabDocument37 pagesMachine Tools LabAbdelhay Mohamed HassanNo ratings yet
- Model Question PaperDocument3 pagesModel Question PaperMohanraj KulandasamyNo ratings yet
- Mme 201 - Introduction To Physical MetallurgyDocument633 pagesMme 201 - Introduction To Physical Metallurgynarasimhareddy415100% (1)
- MSM R19 - Unit-1Document62 pagesMSM R19 - Unit-1Madheswaran DharmapuriNo ratings yet
- Materials Science CHAPTER 1Document5 pagesMaterials Science CHAPTER 1KTINE08No ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MetalsDocument258 pagesMechanical Properties of MetalsIsza Marie N. SocorinNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis Sample QuestionDocument1 pageStress Analysis Sample QuestionUmairZahidNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: Material Science: 1 Defective Int EnsityDocument18 pagesChapter-3: Material Science: 1 Defective Int Ensitybhushan wandreNo ratings yet
- Mos Lab ManualDocument71 pagesMos Lab ManualAtul GaurNo ratings yet
- 081 - ME8594, ME6505 Dynamics of Machines - 2 MarksDocument20 pages081 - ME8594, ME6505 Dynamics of Machines - 2 Markssara vanaNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy Question Bank Quize Metals 2Document31 pagesMetallurgy Question Bank Quize Metals 2abhishek_m_more67% (3)
- BMP QuestionsDocument8 pagesBMP Questionsashok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Question Papers Metallurgy and Material Science Jntu Previous YearsDocument9 pagesQuestion Papers Metallurgy and Material Science Jntu Previous YearsAtul GaurNo ratings yet
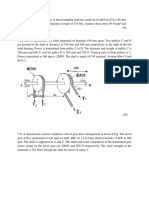
- International Institute of Management & Technical Studies: Subject Name: Mechanics of Solid (GPME3701)Document4 pagesInternational Institute of Management & Technical Studies: Subject Name: Mechanics of Solid (GPME3701)Shubham Pal0% (1)
- SM Model Exam QuestionDocument5 pagesSM Model Exam QuestionAravind PhoenixNo ratings yet
- ME8491 Engineering Metallurgy COURSE PLANDocument4 pagesME8491 Engineering Metallurgy COURSE PLANKarthick NNo ratings yet
- Determine The Diameter of A Shaft Which Carries 2 Pulleys Each Weight 2KNDocument2 pagesDetermine The Diameter of A Shaft Which Carries 2 Pulleys Each Weight 2KNSundara MoorthyNo ratings yet
- Me6302 - Manufacturing Technology - I: Iii Semester Mechanical EngineeringDocument69 pagesMe6302 - Manufacturing Technology - I: Iii Semester Mechanical EngineeringamdevaNo ratings yet
- ME6604 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion 2 MarksDocument14 pagesME6604 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion 2 MarksMALANo ratings yet
- Review Questions CMS PDFDocument2 pagesReview Questions CMS PDFAbdul NazèêrNo ratings yet
- Lec5-Yield Phenomenon, Strain Aging, & Bauchinger EffectDocument14 pagesLec5-Yield Phenomenon, Strain Aging, & Bauchinger Effectsamurai7_77No ratings yet
- 1-Mechanics of Material - I (Mid Term)Document134 pages1-Mechanics of Material - I (Mid Term)irum,100% (1)
- Lab Questions Set 1Document3 pagesLab Questions Set 1sriniNo ratings yet
- Creep in MaterialsDocument2 pagesCreep in MaterialsAnonymous pmPNWGpNo ratings yet
- MoM Summary PointsDocument39 pagesMoM Summary PointsAmmarNo ratings yet
- ME2121 - ME2121E Slides Chapter 1 (2014)Document13 pagesME2121 - ME2121E Slides Chapter 1 (2014)FlancNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis AE2351Document5 pagesFinite Element Analysis AE2351Aghil BuddyNo ratings yet
- Constitution of AlloysDocument23 pagesConstitution of AlloysRamanathan Durai100% (1)
- UNIT 1 PPT 2Document30 pagesUNIT 1 PPT 2neha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- A109210306-Metallurgyandmaterialsscience - November 2010Document6 pagesA109210306-Metallurgyandmaterialsscience - November 2010venkateshyadav2116No ratings yet
- Midterm VibrationsDocument18 pagesMidterm VibrationsAravind KumarNo ratings yet
- ME6403-Engineering Materials and Metallurgy Question BankDocument10 pagesME6403-Engineering Materials and Metallurgy Question BankmeganathanNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I (Constitution of Alloys and Phase Diagrams) Part-ADocument7 pagesUNIT-I (Constitution of Alloys and Phase Diagrams) Part-AkarthisanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Industrial Metallurgy Part A - 2 MarksDocument8 pagesQuestion Bank - Industrial Metallurgy Part A - 2 Marks17TUME212 ROHITH.MNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy Question Bank - Questions OnlyDocument6 pagesMetallurgy Question Bank - Questions OnlyMANYAM. HARI KRISHNA MECHANICAL ENGINEERINGNo ratings yet
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsFrom EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsNo ratings yet
- Coordinate SystemDocument6 pagesCoordinate SystemVasantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Ref FramesDocument6 pagesRef FramesVasantha KumarNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Compressible Flow: Gas DynamicsDocument32 pagesAn Introduction To Compressible Flow: Gas DynamicsVasantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Sri Aravindar Engineering College: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesSri Aravindar Engineering College: Department of Mechanical EngineeringVasantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Me64 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion L T P CDocument1 pageMe64 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion L T P CchellamvNo ratings yet
- Mae 331 Lecture 1Document13 pagesMae 331 Lecture 1Vasantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Aeronautical EngineerDocument8 pagesAeronautical EngineerVasantha KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.) Welcome To The American Cultures & Global Contexts CenterDocument6 pages1.) Welcome To The American Cultures & Global Contexts CenterVasantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Glucose DeterminationDocument3 pagesGlucose DeterminationMelody PardilloNo ratings yet
- Hysys Simulation of N 2 Extraction ProceDocument11 pagesHysys Simulation of N 2 Extraction Proceabdullah farhanNo ratings yet
- Borchi Gol MADocument2 pagesBorchi Gol MAAlexander ThomasNo ratings yet
- Study On Removal of Iron Rust From Paper Objects W PDFDocument9 pagesStudy On Removal of Iron Rust From Paper Objects W PDFLaira M. OnteNo ratings yet
- Water Properties and Chemistry Notes AccDocument52 pagesWater Properties and Chemistry Notes AccAngela CuiNo ratings yet
- Static and Dynamic BalancingDocument8 pagesStatic and Dynamic Balancingvijay2293No ratings yet
- Fired Equipment and DesignDocument35 pagesFired Equipment and DesignBensmatNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases - 0Document124 pagesAcids and Bases - 0Kizzy-Anne BoatswainNo ratings yet
- Principles of Numerical Weather Prediction and Modeling-7 by Prof.A.S.N.MurtyDocument14 pagesPrinciples of Numerical Weather Prediction and Modeling-7 by Prof.A.S.N.MurtyPantulu MurtyNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Shear Strength of Unsaturated Soil Over A WDocument13 pagesExperimental Study On Shear Strength of Unsaturated Soil Over A WAsma SamiNo ratings yet
- Paper 4Document10 pagesPaper 4UmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Health and Disease by Yuichi Hattori, Roland Seifert (Eds.)Document353 pagesHistamine and Histamine Receptors in Health and Disease by Yuichi Hattori, Roland Seifert (Eds.)Liliana AskMeNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study On The Electrochemical Production of H2O2 GrafitoDocument9 pagesA Comparative Study On The Electrochemical Production of H2O2 GrafitoMaycol Owen Echevarria MendozaNo ratings yet
- Energy Paper INB Template BundleDocument136 pagesEnergy Paper INB Template BundleAngela LatonaNo ratings yet
- Print-Interpretation of SEM ImagesDocument4 pagesPrint-Interpretation of SEM ImagesMagdalena BandaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Plates Data Sheet HEFDocument3 pagesBipolar Plates Data Sheet HEFmichaelNo ratings yet
- Applied Surface Science: Shanmugam Vignesh, Jeyaperumal Kalyana SundarDocument14 pagesApplied Surface Science: Shanmugam Vignesh, Jeyaperumal Kalyana SundarPrince Malik FaheemNo ratings yet
- PE and KE Practice KEYDocument2 pagesPE and KE Practice KEYLia FakhryNo ratings yet
- Subsidiary File-7 (Electric Potential - Updated) PDFDocument88 pagesSubsidiary File-7 (Electric Potential - Updated) PDFGlitchNo ratings yet
- Gmail - FWD - Term PaperDocument2 pagesGmail - FWD - Term PaperSarthak DasNo ratings yet
- Polaris A Polaris AB Polaris BDocument1 pagePolaris A Polaris AB Polaris BJanaki RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Introduction Quantum ComputingDocument3 pagesIntroduction Quantum ComputingDak DaekNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: Dr. Mohd Khir Mohd NorDocument54 pagesDynamics: Dr. Mohd Khir Mohd NorKong DuiDuiNo ratings yet
- English For Electrical EngineeringDocument37 pagesEnglish For Electrical Engineeringعطية الأوجليNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities, Units and DimensionsDocument15 pagesPhysical Quantities, Units and DimensionsAmelia OwensNo ratings yet
- Grade 10Document27 pagesGrade 10Julius SalasNo ratings yet
- QualityControl 1 ReviewerDocument15 pagesQualityControl 1 Reviewerprinz1mendezNo ratings yet
- WME01 01 Que 20180607Document28 pagesWME01 01 Que 20180607Newton JohnNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4. Potential of A Galvanic CellDocument2 pagesExperiment 4. Potential of A Galvanic CellChynna Kaye GregorioNo ratings yet