0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
259 viewsCardiovascular System Worksheet
Cardiovascular System Worksheet
Uploaded by
api-255473579Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Cardiovascular System Worksheet
Cardiovascular System Worksheet
Uploaded by
api-2554735790 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
259 views5 pagesOriginal Title
cardiovascular system worksheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
259 views5 pagesCardiovascular System Worksheet
Cardiovascular System Worksheet
Uploaded by
api-255473579Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
Cardiovascular System Worksheet
By: Sean McManus, David Orlando, and Kraig Puccia
Cardiovascular System Overview:
1. What are the two main functions of the cardiovascular system?
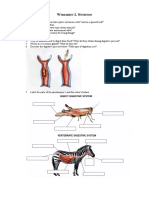
2. Which organism has the most efficient heart?
a. Fish
b. Human
c. Butterfly
d. Worm
3. What is the function of the atria?
4. What is the function of the ventricle?
5. Do all organisms have to have a heart consisting of an atrium and a ventricle?
6. Identify which orgasm does NOT have a heart consisting of at least one
atrium and at least one ventricle.
a. Bird
b. Human
c. Frog
d. Sand dollar
7. Does the heart replenish or deplete oxygen in the bloodstream?
8. Which organism has a three-chambered heart?
a. Lizard
b. Bird
c. Octopus
d. Fish
9. Which gas present in blood is essential to life?
10. Give an example of an organism that does NOT have an actual heart.
Seans Phylums:
11. What is the name of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart in
humans?
12. What is the name of the blood vessels that carry blood to the heart in
humans?
13. What is the name of the smallest blood vessels in the human body?
14. How much can a blue whale weigh?
15. How many chambers does a bear heart have?
16. How many rings are in the circulatory system of the starfish?
17. Do sand dollars have a cardiovascular system?
18. The sea cucumber possesses a water vascular system. What is the other
system named?
19. What is the color of the sea cucumber in the upper photo on the page?
20. What process do almost all porifera go through?
21. What is the exception to question #10?
22. Is the sea cucumber like a cucumber consumed by humans?
23. Echinoderms are animals found where: On land or in water?
Kraigs Phylums:
24. A Gastrovascular system consists of all the following except:
a. Cardiovascular System
b. Endocrine System
c. Digestive System
d. Respiratory System
25. The gastrovascular system functions by:
a. Absorbing nutrients into the gastrovascular cavity, where they are
collected, and have the internal structures bathe in the nutrients
b. Digesting food along a central digestive system, and having nutrients
dispersed throughout the blood stream
c. Absorbs nutrients necessary to survive and diffuses them into the
blood stream
d. None of the above
26. Because Cnidarians only have the gastrovascular cavity for the intake and
excretion of materials:
a. Food cannot be continuously processed because it has to be excreted
through the mouth
b. It is grinded up and kept within the body until fully depleted
c. All materials are absorbed and there is no need for excretion
d. It makes it easier for the constant digestion of food
27. Platyhelminthes and Nematodes have a similar system to the Cnidarians, but
they:
a. Have a respiratory system
b. Have a digestive system
c. Receive nutrients through simple diffusion
d. None of the above
28. Nematodes can receive an abundance of nutrients through other methods,
because a large majority of nematodes are:
a. Parasitic
b. Self-sufficient
c. Large predators
d. Micro-organisms
29. The phylum Platyhelminthes is solely comprised of:
a. Roundworms
b. Flatworms
c. Medusa
d. Polyps
30. Platyhelminthes are restricted to their flat shape because:
a. The environment they live in
b. The lack of a cardiovascular or respiratory systems
c. Evolutionary changes
d. They are unable to sustain higher pressures
31. Jellyfish and sea anemones are very similar because:
a. The environment in which they live
b. The structural similarities in their anatomy
c. The same life cycle they share that develops from a polyp into a
medusa
d. All of the above
32. The Loa Loa worm is very different in behavior to other parasitic worms
because:
a. It tends to burrow across the eyeball
b. This worm can be very lethal
c. The worm is very common throughout the world
d. The Loa Loa does not lay eggs in its host
33. Because of the phylum Nematodes shape and parasitic nature, they absorb
their hosts nutrients by:
a. Sucking them out of the intestinal wall of the host
b. Bathing in the intestinal liquids and lets nutrients diffuse into them
c. Eating the innards of its host
d. Attaches itself to the vital organs
34. When heartworm is found within the heart, and they continue to reproduce
and create more, the real threat is:
a. They eat your heart
a. They absorb too much blood so there is not enough left for its host
b. It can clog up the pulmonary arteries of the heart
c. Cause backflow of blood within the body
35. Jellyfish and polyps maintain structure through a gel in between the inner
and outer layers called:
a. Gastrodermis
b. Epidermus
c. Mesoglea
d. Exoderm
36. In corals they use an exoskeleton to protect themselves, as well as maintain
shape, which is called:
a. Calcium carbonate
b. Fossilization
c. Epidermus
d. Mesoglea
Davids Phylums:
37. What organism has three hearts?
38. Why do octopuses need to maintain such high blood pressure?
39. How does the earthworm contribute to human livelihood?
a. It works on Wall Street
b. It fertilizes the soil that we farm
c. It gives off oxygen
d. It destroys parasites in the ground
40. What is the name of the pair of muscles that is attached to the walls of the
chamber of the heart in grasshoppers?
41. What is the largest phylum in the Animal Kingdom?
42. How many document species of annelids exist?
43. What special structure does an apple snail have that helps it to regulate
blood pressure?
44. How many pairs of aortic arches does an earthworm have?
45. What two things do the aortic arches in an earthworm connect?
46. What is the usual heart rate of an adult lobster?
a. 50-100 bpm
b. 30-75 bpm
c. 50-136 bpm
d. 100-250 bpm
47. Which phylum contains species that have exoskeletons?
a. Phylum Anthropoda
b. Phylum Cnidaria
c. Phylum Annelida
d. Phylum Mollusca
48. What are the exoskeletons of species in Phylum Anthropoda made of?
49. What is the name of an octopus main heart?
50. Which organism has remained unchanged for millions of years?
a. Crocodile
b. Human
c. Lobster
d. Horseshoe crab
You might also like
- Hosa Practice Questions 1Document12 pagesHosa Practice Questions 1rohitmital0% (1)
- Management of Chick, Grower, Layer and BroilerDocument15 pagesManagement of Chick, Grower, Layer and BroilerSambasiva Rao100% (3)
- Neonatal and Paediatric Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesNeonatal and Paediatric Anatomy and PhysiologyIonela ConstantinNo ratings yet
- 2ND Quarter Periodical Exam in Science 6 2022 2023Document5 pages2ND Quarter Periodical Exam in Science 6 2022 2023Haidee Rabino71% (7)
- A.P. Chapter 33 TestDocument10 pagesA.P. Chapter 33 TestErica MizzIndependent Bubuchu100% (1)
- Bio Psychology 16 Points by Drj. SinghDocument75 pagesBio Psychology 16 Points by Drj. Singhthegreatman100% (2)
- Necropsy - Killer Whale NootkaDocument5 pagesNecropsy - Killer Whale NootkaThe Orca Project Corp100% (2)
- Farmer, Philip Jose - Riverworld 1 - To Your Scattered Bodies GoDocument103 pagesFarmer, Philip Jose - Riverworld 1 - To Your Scattered Bodies GoatimonoNo ratings yet
- Cee MBBS Questions of Nepal.Document10 pagesCee MBBS Questions of Nepal.Ram Narayan SinghNo ratings yet
- Periodical Exam - Science 4Document12 pagesPeriodical Exam - Science 4mikeereyes81No ratings yet
- First Periodical Test in Science and Health VDocument4 pagesFirst Periodical Test in Science and Health Vrubieann_danzalanNo ratings yet
- 2nd Periodical Test in Science VI Jerrianne Tique QuestionsDocument8 pages2nd Periodical Test in Science VI Jerrianne Tique QuestionstiquejerrianneaubreyNo ratings yet
- Biological ScienceDocument13 pagesBiological Sciencenhoj eca yabujNo ratings yet
- 2nd-QuarterDocument6 pages2nd-Quartersalijabacay0926No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Pre TestDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Pre TestPADILLA ELISA B.No ratings yet
- Biology - 10 Minuits TestDocument7 pagesBiology - 10 Minuits TestFathimaNo ratings yet
- Biologyfinalcoaching 200208094137Document7 pagesBiologyfinalcoaching 200208094137Raeh YooNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Quarter 2 Periodical Test in ScienceDocument37 pagesReviewer - Quarter 2 Periodical Test in ScienceCalay StagramNo ratings yet
- Bio 6204 Quiz3,4&MidtermsDocument11 pagesBio 6204 Quiz3,4&MidtermsReynante RamosNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument3 pagesEarth Sciencechulnayeon0No ratings yet
- 14 SET QuestionDocument16 pages14 SET Questionsonukewat9807549427No ratings yet
- Test Chap Animalia MdcatDocument11 pagesTest Chap Animalia MdcatGhulam zahraNo ratings yet
- PT - Science 6 - Q2 2023-2024Document5 pagesPT - Science 6 - Q2 2023-2024Norlyn PascualNo ratings yet
- Q Bank LPDocument6 pagesQ Bank LPSaumyaNo ratings yet
- 'DLO Maputi National High School Science 9Document3 pages'DLO Maputi National High School Science 9Jocelyn Acog Bisas MestizoNo ratings yet
- Gen - Ed ScienceDocument10 pagesGen - Ed ScienceRonnel ManilingNo ratings yet
- Genbio 2 ExamDocument9 pagesGenbio 2 ExamRaisa Louise Gamiao TattaoNo ratings yet
- 9 Bio BankDocument15 pages9 Bio BankMrMidoo2020No ratings yet
- Pre IGDocument25 pagesPre IGlemonsnowlayNo ratings yet
- Rose - Comprehensive Exam in Science6... 2015Document17 pagesRose - Comprehensive Exam in Science6... 2015Miriam VillegasNo ratings yet
- A Vertebrate Is Any Chordate That Has ADocument7 pagesA Vertebrate Is Any Chordate That Has Aomariae100% (1)
- Worksheet - Life ProcessesDocument4 pagesWorksheet - Life ProcessesPadma pulivarthiNo ratings yet
- TEAS Science Practice ExamDocument10 pagesTEAS Science Practice Examalicia100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Kingdom Animalia MCQs PDF Class 11Document11 pagesChapter 10 Kingdom Animalia MCQs PDF Class 11Rahi Habib100% (1)
- Biology McqsDocument58 pagesBiology McqskmmNo ratings yet
- Science 4 2nd PTDocument4 pagesScience 4 2nd PTJaymar Kevin PadayaoNo ratings yet
- Divine Word College of Laoag School of Arts, Sciences and Education Laoag CityDocument5 pagesDivine Word College of Laoag School of Arts, Sciences and Education Laoag Cityelfe deramaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer ADocument41 pagesScience Reviewer AbriolalyanNo ratings yet
- Utme Preparatory TestDocument4 pagesUtme Preparatory TestIfeoluwa Deborah OlopadeNo ratings yet
- Biology MCQS: Mcqs Biology 1St Year & 2Nd Year and For Medical Entry TestDocument58 pagesBiology MCQS: Mcqs Biology 1St Year & 2Nd Year and For Medical Entry TestR.S.H67% (3)
- Cells Study Guide Answer KeyDocument13 pagesCells Study Guide Answer KeyLouise SagalesNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument4 pagesSciencemskristinenabioflores13No ratings yet
- SOI Biology Model Exam 1Document9 pagesSOI Biology Model Exam 1Kerod MohamedNo ratings yet
- SS1 Biology First Term ExaminationDocument14 pagesSS1 Biology First Term ExaminationGodswill100% (4)
- TQ - Q2 - Earth and Life ScienceDocument7 pagesTQ - Q2 - Earth and Life SciencePrudevenoNo ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter Examination in Science 8Document3 pages4TH Quarter Examination in Science 8Zooey LucenarioNo ratings yet
- Reviewer AdditionalDocument5 pagesReviewer Additionaldemigod9712No ratings yet
- Major in Biological Science1Document13 pagesMajor in Biological Science1Sir JoshNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2. NutritionDocument6 pagesWorksheet 2. NutritionrosaronceroNo ratings yet
- Science RevDocument4 pagesScience RevJANILLE QUINTOSNo ratings yet
- Majorship Biology 1Document9 pagesMajorship Biology 1rjayfranNo ratings yet
- Biology - Life ProcessesDocument17 pagesBiology - Life ProcessesAnuradha ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Wbjee 2012 Biology Question PaperDocument8 pagesWbjee 2012 Biology Question Papersaurav guptaNo ratings yet
- Refresher GenEd SciDocument48 pagesRefresher GenEd SciMaria Lourdes OndayNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Examination: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Examination: Republic of The PhilippinesKay LagunaNo ratings yet
- Xhweet Kashu . : Biology Complete Important Mcqs For Medical Entry Test PreparationDocument47 pagesXhweet Kashu . : Biology Complete Important Mcqs For Medical Entry Test PreparationawaisjinnahNo ratings yet
- Biology Pedagogy McqsDocument47 pagesBiology Pedagogy McqsImran SibghaNo ratings yet
- Fisheries Biology and EcologyDocument18 pagesFisheries Biology and EcologyvendiolacheNo ratings yet
- Q2 SCI 6Document4 pagesQ2 SCI 6roselyn.cloresNo ratings yet
- Biology Complete Important Mcqs For Medical Entry Test PreparationDocument24 pagesBiology Complete Important Mcqs For Medical Entry Test Preparationaamir100% (3)
- Eals 2ND Quarter ReviewerDocument12 pagesEals 2ND Quarter RevieweraltrishatrishNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Quiz TheoryDocument76 pagesBiodiversity Quiz TheoryFelix SimsungNo ratings yet
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- SOP Blood AgarDocument4 pagesSOP Blood AgarLuis Ferdinand Dacera-Gabronino Gamponia-NonanNo ratings yet
- The Eye HistologyDocument16 pagesThe Eye HistologyFarah AkhwanisNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Concept MapDocument4 pagesUpper Respiratory Concept MapLynzel Faith GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Dr. Moroni Final It ReportDocument42 pagesDr. Moroni Final It Reportogwal morrisNo ratings yet
- General Topic: Fun Facts About HorsesDocument5 pagesGeneral Topic: Fun Facts About HorsesLittle SleepybirdNo ratings yet
- Northwest Kennels USDA Inspection Reports: 2014-2020Document22 pagesNorthwest Kennels USDA Inspection Reports: 2014-2020Katie CoppleNo ratings yet
- Journal of Surgery April2014Document62 pagesJournal of Surgery April2014petrarizkyNo ratings yet
- Supratech MicropathDocument33 pagesSupratech MicropathKiran MandapatiNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Masticatory Muscle Function in Dentofacial GrowthDocument10 pagesThe Importance of Masticatory Muscle Function in Dentofacial GrowthAbhay TandonNo ratings yet
- Hashem Al GhailiDocument5 pagesHashem Al GhailiAmirul AsyrafNo ratings yet
- AbdomenDocument2 pagesAbdomenCloie Danielle AvilaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument14 pagesThe Respiratory SystemkristineNo ratings yet
- CATS & DOGS Nutrition PDFDocument71 pagesCATS & DOGS Nutrition PDFErald Renz LaurenteNo ratings yet
- SHCDocument58 pagesSHCElizabethmike100% (4)
- DIACOM EnglishmanualDocument27 pagesDIACOM EnglishmanualDavid Luca100% (1)
- 2 Review Diphtheria Results April2017 Final Clean PDFDocument20 pages2 Review Diphtheria Results April2017 Final Clean PDFchameleonNo ratings yet
- 5090 s17 Ms 22Document11 pages5090 s17 Ms 22Aalif IbràhimNo ratings yet
- SinulDocument38 pagesSinulCucos NataliaNo ratings yet
- CCBF, HessarghattaDocument6 pagesCCBF, HessarghattaPulkit PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Complete Vaccine ListingDocument5 pagesComplete Vaccine ListingSyed Esa MushranNo ratings yet
- 5 Types of Brain Waves FrequenciesDocument7 pages5 Types of Brain Waves FrequenciesMiguelitomnitrixNo ratings yet
- Science Form 4 Exam QuestionDocument7 pagesScience Form 4 Exam QuestionWindy WayneNo ratings yet
- Tinea Pedis Et ManusDocument14 pagesTinea Pedis Et ManusagisagitaNo ratings yet
- Cloning EssayDocument2 pagesCloning EssaynotevaleNo ratings yet