English Notes For Year 6 Pupils
English Notes For Year 6 Pupils
Uploaded by
Anonymous cJE0PiZ2Copyright:
Available Formats
English Notes For Year 6 Pupils
English Notes For Year 6 Pupils
Uploaded by
Anonymous cJE0PiZ2Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
English Notes For Year 6 Pupils
English Notes For Year 6 Pupils
Uploaded by
Anonymous cJE0PiZ2Copyright:
Available Formats
1
Articles
1. There are 3 types of articles a, an and the.
2. A and an indefinite articles and only used with singular countable nouns.
2.1 a is used before words that begin with consonants sounds or words which
begin with the vowel u but has a consonant sound (you).
a) a boy
b) a flower
c) a pineapple
d) a zebra
e) a university
f) a unit
g) a unique school
h) a one-way street
2.2 an is used before words which begin with vowels (a, e, i, o, u) or words
which begin with the silent h.
a) an ant
b) an apple
c) an earring
d) an elephant
e) an insect
f) an onion
g) an umbrella
h) an hour
i) an honour
j) an honest girl
2.3 a and an are not use before uncountable nouns. E.g: rice, sand, oil, etc.
3 The definite article and is used with plural countable nouns and also
3.1 To show something that is special and one of its kinds in the world.
a) The sun is setting in the west.
b) The air is fresher in the countryside.
3.2 To refer to a particular person, animal, thing or place.
a) The white cat is under the chair.
b) That is the car which honked at me yesterday.
3.3 For the superlative form of an adjective.
a) She is the tallest girl in her class.
b) I bought the cheapest book.
3.4 With things which are already mentioned before.
a) A pupil is in a library. The pupil is reading quietly.
2
Nouns
Countable and Uncountable Nouns
1. A noun is used to refer to a person, place, animal or thing.
a) teacher (person)
b) market (place)
c) rabbit (animal)
d) car (thing)
2. Nouns can be countable or uncountable.
Countable Nouns
(can be counted)
Uncountable Nouns
(cannot be counted)
pen
boy
house
cat
car
bag
key
plate
oil
sand
dust
ink
water
curry
rice
paper
3. Can be used in the following ways.
Countable Nouns Uncountable Nouns
a lot of
many
a few
plenty of
a few
several
some
a large number of
a small number of
books
pencils
houses
cars
bags
keys
books
cows
durians
a little
a lot of
plenty of
some
much
less
more
a large amount of
a small amount of
oil
water
sand
rice
ink
butter
money
curry
petrol
a lot of positive statements, negative statements, questions.
some positive statements, questions.
any negative statements, questions
plenty of
3
Collective Nouns
Used to refer to people, animals or things as a unit.
People
1. a band of musicians 9. a patrol of policemen
2. a choir of singers 10. an army of soldiers
3. a class of pupils 11. a staff of servants
4. a caravan of gypsies 12. a team of players
5. a batch of students 13. a tribe of natives
6. a gang of prisoners 14. a troupe of artistes
7. a crew of sailors 15. a panel of judges
8. a crowd of people 16. a party of friends
Animal
1. an army of ants 11. a plague of locusts
2. a brood of chickens 12. parliament of owls
3. a cloud of flies 13. a shoal of fish
4. a nest of mice 14. a smack of jellyfish
5. a gaggle of geese 15. a team of oxen
6. a flight of swallows 16. a swarm of bees
7. a flock of birds 17. a pack of wolves
8. a troop of monkeys 18. a pride of lions
9. a litter of kittens
a litter of puppies
19. a flock of birds
a flock of sheep
10. a school of dolphins
a school of whales
20. a herd of buffaloes
a herd of elephants
Things / Plants
1. a string of pearls 11. a garland of flowers
2. a bale of cotton 12. a layer of dirt
3. a bowl of rice 13. a queue of vehicles
4. a bunch of keys 14. a pack of cards
5. a cluster of coconuts 15. a bouquet of flowers
6. a column of smoke 16. a tuft of grass
7. a bundle of sticks 17. a wad of currency
8. a suit of clothes 18. a cloud of dust
9. a clutch of eggs 19. a comb of bananas
10. a crate of fruits 20. a set of tools
4
Singular and Plural Nouns
A singular noun 1 person, animal, place or thing.
A plural noun more than 1 person, animal, place or thing.
2) The letter s is usually added to form a plural noun.
a) fruit fruits
b) girl girls
c) lamp lamps
d) song songs
3) For nouns which end with s, x, sh and ch, the plural is formed by adding es.
a) class classes
b) box boxes
c) dish dishes
d) match matches
4) For a noun which ends with y preceded by a consonant, the letter y is changed
into ies to form the plural.
a) activity activities
b) berry berries
c) lorry lorries
d) puppy - puppies
5) For a noun which ends with y preceded by a vowel (ay, ey, oy, uy), the letter s
is added to form the plural.
a) boy boys
b) day days
c) key keys
d) guy - guys
6) For a noun which ends with the letter o preceded by a vowel, the letter s is
added to form the plural.
a) radio radios
b) studio studios
c) bamboo bamboos
d) piano pianos
e) zoo zoos
5
7) For a noun which ends with the letter o preceded by a consonant, s or es is
added to form the plural.
a) photo photos
b) potato potatoes
c) hero heroes
8) For a noun which ends with the letter f or fe, the plural form is made by either
adding the letter s or by changing f/ fe to ves.
a) leaf leaves
b) knife knives
c) half halves
d) thief - thieves
e) roof - roofs
f) safe safes
g) chef - chefs
9) Some nouns are called irregular as their plural form is spelt very differently from
the singular form.
a) ox oxen
b) child children
c) foot feet
d) tooth teeth
e) goose geese
f) mouse mice
g) man men
h) woman women
10) A few irregular nouns maintain the same spelling and pronunciation for both
singular and plural forms.
a) deer deer
b) sheep sheep
c) salmon salmon
d) furniture furniture
11) Some nouns occur only in the plural form:
binoculars, glasses, scissors, spectacles, pants, pyjamas, shorts, tights, trousers,
clothes, stairs, goods
12) Some nouns have no plural:
news, work, homework, rubbish
6
Pronouns
Singular Plural
First
Second
Third
I
You
He / She / It
We
You
They
Subject of the verb Object of the verb
Singular I like to play badminton.
You are late.
He is an engineer.
She is an only child.
It is a Persian cat.
My parents took me out.
I called you last night.
The teacher scolded him.
They found her in the room.
The car knocked it down.
Plural We visited the museum.
They won the singing competition.
They are waiting for us.
The teacher praised them.
Personal
Pronouns
Possessive
Adjectives
Possessive
Pronouns
Reflexive Pronouns
I
You
He
She
It
We
They
my
your
his
her
its
our
their
mine
yours
his
hers
its
ours
theirs
myself
yourself
himself
herself
itself
ourselves
themselves
This is my bag.
This is your book.
This is his pen.
This is her pencil.
This is its kennel.
That is our house.
These are their chairs.
The bag is mine.
The book is yours.
The pen is his.
The pencil is hers.
The kennel is its.
The house is ours.
The chairs are theirs.
I paint the picture myself.
You have to do it yourself.
He writes the poem himself.
She cut the fruit herself.
The dog scratched itself.
We saw it ourselves.
They helped themselves.
7
Adjectives
Comparison of Adjectives (Regular)
Positive Comparative Superlative
1 big bigger than the biggest
2 brave braver than the bravest
3 bright brighter than the brightest
4 busy busier than the busiest
5 cheap cheaper than the cheapest
6 clean cleaner than the cleanest
7 clear clearer than the clearest
8 clever cleverer than the cleverest
9 cold colder than the coldest
10 cool cooler than the coolest
11 cruel crueler than the cruelest
12 dark darker than the darkest
13 deep deeper than the deepest
14 dirty dirtier than the dirtiest
15 fat fatter than the fattest
16 friend friendlier than the friendliest
17 great greater than the greatest
18 happy happier than the happiest
19 hard harder than the hardest
20 healthy healthier than the healthiest
21 heavy heavier than the heaviest
22 high higher than the highest
23 hot hotter than the hottest
24 large larger than the largest
25 lazy lazier than the laziest
26 light lighter than the lightest
27 long longer than the longest
28 low lower than the lowest
29 near nearer than the nearest
30 neat neater than the neatest
31 nice nicer than the nicest
32 noisy noisier than the noisiest
33 pretty prettier than the prettiest
34 poor poorer than the poorest
35 quiet quieter than the quietest
36 rich richer than the richest
37 strong stronger than the strongest
38 tall taller than the tallest
39 thick thicker than the thickest
8
40 thin / thinner than the thinnest
41 weak weaker than the weakest
42 warm warmer than the warmest
43 wise wiser than the wisest
44 young younger than the youngest
Comparison of Adjectives (By adding more and most)
Positive Comparative Superlative
1 beautiful more beautiful most beautiful
2 careful more careful most careful
3 comfortable more comfortable most comfortable
4 dangerous more dangerous most dangerous
5 difficult more difficult most difficult
6 exciting more exciting most exciting
7 expensive more expensive most expensive
8 famous more famous most famous
9 helpful more helpful most helpful
10 intelligent more intelligent most intelligent
11 joyful more joyful most joyful
12 obedient more obedient most obedient
13 peaceful more peaceful most peaceful
Comparison of Adjective (Irregular)
Positive Comparative Superlative
bad worse worst
good better best
little less least
many more most
much / more most
far further/farther furthest/farthest
There is no comparison for positive
The comparative is used to compare two things
The superlative is used to compare three or more things
The suffixes -er and -est are added to the positive adjectives to form most
comparatives and superlatives. However, -ier and -iest are needed when a two-
syllable adjective ends in y.
When an adjective of one syllable ends in a single consonant, double the consonant
for the comparative and superlatives forms. However, letters -w and -x are not
doubled.
9
Conjunctions
Conjunction Usage Example
and To join two sentences with
the same or similar ideas
- Sandy likes singing.
- Sandy likes dancing.
Sandy likes singing and dancing.
but To join two sentences with
different ideas
- I want to go Singapore by bus.
- He insists on taking the plane.
I want to go Singapore by bus but he
insists on taking the plane.
because To give reason - Danny was punished.
- He did not do his homework.
Danny was punished because he did not
do his homework.
so To show cause and effect - The children are tired.
- They go to bed early.
The children are tired so they go to bed
early.
or To show a choice or
possibility can be made
- Would you prefer tea?
- Would you prefer coffee?
Would you prefer tea or coffee?
if To show a condition - You work harder.
- You will pass your examination.
If you work harder, you will pass your
examination.
although To show contrast
(beginning / middle)
- It is raining heavily.
- They continue with the climb.
Although it is raining heavily, they
continue with the climb.
- Nobody wants to live in that mansion.
- It is beautiful.
Nobody wants to live in that mansion
although it is beautiful.
10
Wh-question Words
Wh-question Word Usage Example
Who To ask about people Who are you?
Who is the man?
Who is your mother?
Who is your best friend?
What To ask about things
or something
general.
What is this?
What is in your bag?
What are they doing?
What does he want?
What did you do yesterday?
Which Choices between a
few possibilities
(people, things /
places)
Which is your pen?
Which is the capital?
Which book is better?
Which shirt should I wear?
Why To ask the reason for
something
Why are you here?
Why is the bag wet?
Why is he going out?
Why do you want to be a singer?
Whose To ask about who the
owner of something
is / belong to
(possessives)
Whose pencil is this?
Whose ruler is this?
Whose car is that?
Whose books are these?
Where To ask about places Where are you?
Where is the ruler?
Where do you live?
Where is the car key?
When To ask about the time
something happens
When is your brothers birthday?
When are we going home?
When did you come?
When will you leave?
How To ask about the way
how something is
done / quality,
quantity
How are you?
How was your trip?
How do you cook the fish?
How do you get to London?
* 7 W, 1 H used to ask questions.
11
Verbs to be, to have and to do
Verb Present Tense Past Tense Example
to be
is
am
was
He is the head prefect.
I am a boy.
She was in Langkawi yesterday.
are were
These boys are my nephews.
We were there last month.
to have
has
have
had
She has a yellow raincoat.
You have a dictionary.
He had a football practice yesterday.
to do
does
do
did
She does the housework every day.
We do our work quietly.
They did their homework just now.
Subject-Verb Agreement
The verb must agree with its subject. If the subject is singular, the verb must be
singular. If the subject is plural, the verb must be plural as well.
Singular Plural
The pupil sings during the music class. The pupils sing during the music class.
He / She prepares some food for
supper.
They prepare some food for supper.
The child runs around in the field. The children run around in the field.
The dog does not like its new owner. The dogs do not like their new owner.
The backpacker has no place to sleep
tonight.
The backpackers have no place to
sleep tonight.
He is a friend of mine They are friends of mine.
Singular Plural
is
has
does
are
have
do
12
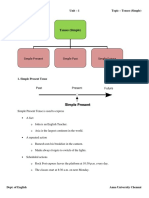
Simple Present Tense
1) Facts, things that are always or generally true.
The sky is blue.
The moon is round.
A hen lays eggs.
A dog has four legs.
The sun rises in the east.
Tropical fish are beautiful.
Water boils at 100 degrees.
Plants die without water.
My birthday is in September.
2) For situations that are (more / less) permanent.
I live in Malaysia.
She likes drawing.
They love coffee.
My father works in a bank.
She has three children.
The boy studies in SJK(C) Kundang.
3) Things that we do regularly / often routines, habits.
(every day, once a week, twice a month, every Sunday, four times a year)
(always, often, usually, sometimes, rarely, never)
I go to school by car.
He always wakes up at 6 a.m.
Mei Ling often listens to music.
Carol brushes her teeth twice a day.
I drink a cup of coffee every morning.
4) Short actions.
He looks at his watch.
She opens the door.
I switch on the computer.
13
5) Imperatives statements / order
Do not litter!
Keep off the grass!
Do not feed the animals.
Go to your bedroom now.
6) We also use it to talk about the future after words like when, until, after,
before, as soon as in a future sentence.
I will call you when I have time.
I won't go out until it stops raining.
She'll come as soon as her babysitter arrives.
I'm going to make dinner after I watch the news.
I'll give you the book before you go.
***Spelling: In general, for single subject we add s in the verb. However...
a) For verbs that end in -o, -ch, -sh, -ss, -x, or -z we add -es.
o go goes
o catch catches
o wash washes
o kiss kisses
o fix fixes
o buzz buzzes
b) For verbs that end in a consonant + y, we remove the y and add -ies.
o marry marries
o study studies
o carry carries
o worry worries
c) For verbs that end in a vowel + y, we just add -s.
o play plays
o enjoy enjoys
o say says
14
Present Continuous Tense
1) Used to show something which is happening now.
a. I am cutting the grass now.
b. The waiter is serving the customers now.
c. We are waiting for him at the bus stop.
2) Used to express the future.
a. I am going camping next week.
b. She is going for a holiday soon.
c. We are going to China tomorrow.
3) Used to express developing and changing situations.
a. The wind is getting stronger and the temperature is dropping faster.
b. More people are buying organic products nowadays.
***Spelling: Verbs when adding -ing.
a) Consonant after a short, stressed vowel at the end of the word.
Double the consonant:
sit he is sitting
put he is putting
travel they are travelling
If the consonant is not stressed, we do not double it:
benefit - benefiting (we stress the first 'e', not the 'i'.)
b) One -e at the end of the word
Leave out the e:
write he is writing
take he is taking
BUT double e add ing:
see he is seeing
c) Verbs ending in ie
Change 'ie' to 'y':
lie - he is lying
d) Verbs ending in c
Change 'c' to 'ck':
picnic - he is picnicking
15
Simple Past Tense
1) Something has happened in the past (specific time) and has finished.
I took her home just now.
They were at his birthday party last night.
The cleaned the house last weekend.
He knew the answer yesterday.
2) Telling stories or past events.
Once upon a time, a lord lived in the castle.
There was an ugly witch living in the middle of the forest.
In the past, the knights travelled on strong horses.
3) Indicate a time in the past.
I lived in Johor in 1994.
4) Express habit in the pass.
I collected stamps when I was a child.
*** Spelling: Verbs in the Past Simple Tense
Regular Verb
-d, -ed, -ied
Irregular Verb Verb
remaining same
live lived
want wanted
carry carried
stop stopped
plan planned
panic panicked
sell sold
drink drank
buy bought
cut cut
put put
let let
16
Positive and Negative Statements
Positive statement in the Present Tense
I
You
We
They
go
to the towns library on
weekends.
He
She
It
goes
Negative statement in the Present Tense
I
You
We
They
do not go
to the towns library on
weekends.
He
She
It
does not go
Positive statement in the Past Tense
I
You
We
They
He
She
It
went to the zoo last Saturday.
Negative statement in the Past Tense
I
You
We
They
He
She
It
did not go to the zoo last Saturday.
17
Prepositions of Time
Prepositions Use
in
month
year
season
part of the day (morning, afternoon, evening)
duration
at
specific time of day (noon, midnight)
part of the day (night)
celebrations
on
days of the week
dates
special days
after something will happen later
by a deadline in the future
during through the whole of a period of time
Prepositions Examples
in
- My birthday is in December.
- Jenny was born in 1990.
- Tom wakes up early in the morning.
- Mr Siew will be here in three minutes.
- The van will be here in ten minutes.
at
- Lunch is at noon.
- Dinner is at 6 oclock.
- Tuition is at 2.30 p.m.
on
- Ali is going to Ipoh on Friday.
- I am going to visit my grandmother on Saturday.
- My birthday is on the 25th of June.
- We are going to the party on my birthday.
after
- I will see you after school.
- After the holidays, I will start studying French.
by
- I expect rain by noon.
- I want to have those papers by Friday.
during - during the holidays
You might also like
- Integrated Korean Beginning 2 Third Edition Klear Annas Archive Zlib 21295735Document395 pagesIntegrated Korean Beginning 2 Third Edition Klear Annas Archive Zlib 21295735Lily Yu100% (7)
- Year 3 English Practice Questions Answer BookletDocument40 pagesYear 3 English Practice Questions Answer BookletÃlî Bôqórkà Çâbdî Wàrsãmë50% (2)
- Year 4 English Practice Questions Answer BookletDocument40 pagesYear 4 English Practice Questions Answer BookletMd Amirul80% (5)
- Year 3 English Paper 1 SJKCDocument7 pagesYear 3 English Paper 1 SJKCAudrey Yee100% (3)
- English Worksheet Year 1Document38 pagesEnglish Worksheet Year 1alya jamal100% (1)
- English Year 6 ExercisesDocument10 pagesEnglish Year 6 ExercisesCarmelya Pippie100% (2)
- Exam Form 1 English PT3 FormatDocument6 pagesExam Form 1 English PT3 FormatGary Charles Tay100% (2)
- English Year 4Document16 pagesEnglish Year 4Nur Faradilla Kamal100% (1)
- Year 6 English Paper 1Document13 pagesYear 6 English Paper 1Ati Mamora67% (3)
- English Year 4 Paper2Document6 pagesEnglish Year 4 Paper2Zuhaira Zainordin100% (3)
- English Year 2 Final SJKCDocument3 pagesEnglish Year 2 Final SJKCBhutan Chay100% (2)
- Mid Year Mathematics Form 2Document7 pagesMid Year Mathematics Form 2wahee88100% (1)
- English Paper 2 Year 4 KSSR SJKCDocument5 pagesEnglish Paper 2 Year 4 KSSR SJKCLeslie Michael Chang100% (2)
- Difference Between English and FrenchDocument2 pagesDifference Between English and FrenchSubbu RamaniNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Notes For UPSRDocument16 pagesEnglish Grammar Notes For UPSRAnonymous cJE0PiZ2No ratings yet
- SJK (C) Pei Hwa Year 6 English Language Assessment (4) Comprehension Paper 1 Hour 15 MinutesDocument10 pagesSJK (C) Pei Hwa Year 6 English Language Assessment (4) Comprehension Paper 1 Hour 15 MinutesGunalatcumy KarunanitheNo ratings yet
- English Year 5 (Paper 2)Document9 pagesEnglish Year 5 (Paper 2)Marie Jane Salleh71% (7)
- Topical Test Chapter 1 Math Form 1 Paper 2Document1 pageTopical Test Chapter 1 Math Form 1 Paper 2syukrie3100% (2)
- English SJKC VocabularyDocument6 pagesEnglish SJKC Vocabularynaima moraNo ratings yet
- UEC Junior High English 7Document24 pagesUEC Junior High English 7寒月No ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggeris Darjah 4 March ExerciseDocument6 pagesBahasa Inggeris Darjah 4 March ExerciseNur Adilah DilaNo ratings yet
- English Year 3 KSSRDocument8 pagesEnglish Year 3 KSSRmages87No ratings yet
- Form 1 pt3 ExerciseDocument8 pagesForm 1 pt3 ExerciseSiti Fathiyah Ramli100% (2)
- Foon Yew High School Entrance Exam 2021 Preparation QuestionsDocument4 pagesFoon Yew High School Entrance Exam 2021 Preparation QuestionsLao Shi Qiu100% (2)
- Quiz Science Year 6 2008Document7 pagesQuiz Science Year 6 2008wongsc70100% (15)
- PMR English Language ModulesDocument86 pagesPMR English Language Moduleshoneym694576100% (4)
- UPSR English - Grammar - Worksheets For Weaker PupilsDocument29 pagesUPSR English - Grammar - Worksheets For Weaker Pupilsshare4u100% (2)
- MATHEMATICS Form 1 Chapter 1Document21 pagesMATHEMATICS Form 1 Chapter 1Teoh MilayNo ratings yet
- English Year 5 Paper 1 (Limbang)Document12 pagesEnglish Year 5 Paper 1 (Limbang)Muhammad Amirul86% (21)
- You Saw An Advertisement For Awesome Instant NoodleDocument2 pagesYou Saw An Advertisement For Awesome Instant Noodlezawani_azmiNo ratings yet
- Ujian Bulanan English T1Document8 pagesUjian Bulanan English T1teachernizzNo ratings yet
- English Paper 2 Year 5Document9 pagesEnglish Paper 2 Year 5Uganes WariNo ratings yet
- Year 6 Unit 1: Textbook-Based English WorksheetsDocument25 pagesYear 6 Unit 1: Textbook-Based English WorksheetsAhmad Ridhwan Bin Zawawi100% (1)
- English Form 2 2018Document3 pagesEnglish Form 2 2018Ramesh Ramsamy100% (1)
- SJK (C) Pu Sze Year 3 English Language Assessment (4) : Paper 1Document8 pagesSJK (C) Pu Sze Year 3 English Language Assessment (4) : Paper 1Anonymous 7dHDP4jNo ratings yet
- English Form 2 Units 1Document6 pagesEnglish Form 2 Units 1ClaireNo ratings yet
- SJKT Batu Arang English Mac Test Paper 2 NAME: - YEAR:4 - (10 Marks)Document9 pagesSJKT Batu Arang English Mac Test Paper 2 NAME: - YEAR:4 - (10 Marks)gunaNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - SJKC Pu Sze Year 1 English Language School 1 English Language School BasedDocument8 pagesDokumen - Tips - SJKC Pu Sze Year 1 English Language School 1 English Language School BasedJaganes SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2015 PPT3 Kedah BI W AnsDocument27 pages2015 PPT3 Kedah BI W Ansjee2kk69% (13)
- Form 1 English Week 12 Essay SPCADocument2 pagesForm 1 English Week 12 Essay SPCAnatashasyraf50% (2)
- Latihan Math Th6-Upsr Kertas 2Document63 pagesLatihan Math Th6-Upsr Kertas 2cgazmi88% (24)
- SJK (C) Chung Hua BT 29 Year 4 English Language Assessment 1 Comprehension Paper 1 Hour 15 MinutesDocument10 pagesSJK (C) Chung Hua BT 29 Year 4 English Language Assessment 1 Comprehension Paper 1 Hour 15 MinutesADELINE WONG SY HIE MoeNo ratings yet
- SJK (C) Pei Hwa Ear 2 English Language Assessment 3: A.M.Chong/Bahasa Inggeris/Tahun 2/Ogos/Muka Surat 1Document6 pagesSJK (C) Pei Hwa Ear 2 English Language Assessment 3: A.M.Chong/Bahasa Inggeris/Tahun 2/Ogos/Muka Surat 1kctNo ratings yet
- UASA Year 6 2023Document7 pagesUASA Year 6 2023izatttahaNo ratings yet
- Unit 12 Positive StatementsDocument2 pagesUnit 12 Positive StatementsTing KimNo ratings yet
- English - 50 - Essays (STD 6)Document22 pagesEnglish - 50 - Essays (STD 6)Rachel LeeNo ratings yet
- English NotesDocument17 pagesEnglish NotesWong Yew Moy0% (1)
- English UPSRDocument17 pagesEnglish UPSRAnonymous ItbpGmNo ratings yet
- Nouns 名词: Countable and Uncountable Nouns 可数名词和不可数名词Document4 pagesNouns 名词: Countable and Uncountable Nouns 可数名词和不可数名词Chua Wei PingNo ratings yet
- NounsDocument30 pagesNounsPaulina FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Individual Work (4 Course)Document3 pagesIndividual Work (4 Course)Владислав ЛитвінNo ratings yet
- Class 4 Eng Grammar Lesson 6 The Noun NumberDocument5 pagesClass 4 Eng Grammar Lesson 6 The Noun NumberKaruna VermaNo ratings yet
- Grammar For Life WorkbookDocument58 pagesGrammar For Life Workbookleonobita0306No ratings yet
- Singular Nouns: Exercise 2Document12 pagesSingular Nouns: Exercise 2psycho_psychoNo ratings yet
- Sing PluralDocument8 pagesSing Pluralperseus_1No ratings yet
- 0207241857333961717Document18 pages0207241857333961717gamesisgameandalsofunNo ratings yet
- Noun - Noun PhraseDocument66 pagesNoun - Noun Phraseestu kaniraNo ratings yet
- Pronoun NounDocument21 pagesPronoun NounSabil SabilNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Proper Nouns: No Category Proper NounDocument12 pagesUnit 3: Proper Nouns: No Category Proper NounrazzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzeenNo ratings yet
- Plural of NounsDocument6 pagesPlural of NounsMiguel ElgersmaNo ratings yet
- Grammar BookDocument58 pagesGrammar BookDisha Shahani100% (2)
- A1509790902 - 25661 - 2 - 2021 - Tutorial Book - PEL121 - CompressedDocument136 pagesA1509790902 - 25661 - 2 - 2021 - Tutorial Book - PEL121 - CompressedRohan RajNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document23 pagesBook 1Anonymous cJE0PiZ2No ratings yet
- Marcus Lily Amy: Look at The Picture. Answer The Questions and Choose The Correct AnswerDocument1 pageMarcus Lily Amy: Look at The Picture. Answer The Questions and Choose The Correct AnswerAnonymous cJE0PiZ2No ratings yet
- Essay - Fill in The BlanksDocument1 pageEssay - Fill in The BlanksAnonymous cJE0PiZ2No ratings yet
- Fill in The Blanks - Sec CDocument2 pagesFill in The Blanks - Sec CAnonymous cJE0PiZ2No ratings yet
- Prepositions At, In, OnDocument2 pagesPrepositions At, In, OnAnonymous cJE0PiZ2No ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument2 pagesDengue FeverAnonymous cJE0PiZ2No ratings yet
- Similes Are Used To Compare One Thing To AnotherDocument3 pagesSimiles Are Used To Compare One Thing To AnotherAnonymous cJE0PiZ2No ratings yet
- 7th-8thth Grade Regular Verbs QuizDocument2 pages7th-8thth Grade Regular Verbs QuizDANIELA BEATRIZ SILVA CANALESNo ratings yet
- Diagramming Sentences: de Vera, Dina Garcia, Trixie Melendez, Jenzyl KayeDocument22 pagesDiagramming Sentences: de Vera, Dina Garcia, Trixie Melendez, Jenzyl KayeBilly De Guzman UsonNo ratings yet
- Translation Studies Chapter 4, 5 and 6Document30 pagesTranslation Studies Chapter 4, 5 and 6Anonymous R99uDjY100% (1)
- The Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesThe Passive Voicen4ftaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument23 pagesConditionalsToytoy FamilyNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: and But For Nor or So YetDocument2 pagesConjunctions: and But For Nor or So YetLawrence IcasianoNo ratings yet
- Narrative Tenses - StoryDocument2 pagesNarrative Tenses - StoryajsanchezfloresNo ratings yet
- 9 Рівень ПовністюDocument106 pages9 Рівень ПовністюЯна СамсонюкNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Compound NounsDocument6 pagesUnit 6 Compound NounsFrancisco Chaire Gonzalez0% (1)
- Reduced Adverbial ClauseDocument5 pagesReduced Adverbial Clausemichael timothyNo ratings yet
- Tom's Job: Answer The Following QuestionsDocument2 pagesTom's Job: Answer The Following QuestionsPatricia GomezNo ratings yet
- Modalization in Translation The Picture of Dorian Gray: Facultatea de Litere Specializare: Engleză - FrancezăDocument21 pagesModalization in Translation The Picture of Dorian Gray: Facultatea de Litere Specializare: Engleză - Francezămadutza_auroraNo ratings yet
- Friday, April 9, 2010: Translation ShiftsDocument3 pagesFriday, April 9, 2010: Translation Shiftshamzan wadiNo ratings yet
- Grammar and Beyond 2e, Level 3 Scope and Sequence: Unit Theme Grammar Topics Avoid Common Mistakes Academic WritingDocument10 pagesGrammar and Beyond 2e, Level 3 Scope and Sequence: Unit Theme Grammar Topics Avoid Common Mistakes Academic WritingHani oveissyNo ratings yet
- Vokabular - Describing PeopleDocument3 pagesVokabular - Describing PeopleJelena KukulićNo ratings yet
- EL CT1T4 Adverb, Adjectives, VerbDocument4 pagesEL CT1T4 Adverb, Adjectives, VerbCeline ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Focus4 2E Cumulative Test 2 Units1-4 ANSWERSDocument3 pagesFocus4 2E Cumulative Test 2 Units1-4 ANSWERSKasia BiałasNo ratings yet
- Textbook A University Grammar of English QuirkDocument247 pagesTextbook A University Grammar of English QuirkNgọc ThảoNo ratings yet
- Edible Ottawa Style GuideDocument6 pagesEdible Ottawa Style GuideBrandon PhamNo ratings yet
- امتحان الوحدة (Unit 12) مع الإجابات لمادة اللغة الانجليزية Action Pack الصف الرابع الفصل الثاني 2021Document4 pagesامتحان الوحدة (Unit 12) مع الإجابات لمادة اللغة الانجليزية Action Pack الصف الرابع الفصل الثاني 2021Noura AdhamNo ratings yet
- Syntactical Changes Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesSyntactical Changes Cheat SheetLaura Cánovas HernándezNo ratings yet
- 2 Learning and Teaching Different Types of GrammarDocument8 pages2 Learning and Teaching Different Types of GrammarscintillamxNo ratings yet
- OUT AND ABOUT 1 Unit 4 Grammar Practice-StandardDocument1 pageOUT AND ABOUT 1 Unit 4 Grammar Practice-StandardMARTA SAMPEDRONo ratings yet
- Empower A 2 UNIT 11 " ": EntertainmentDocument43 pagesEmpower A 2 UNIT 11 " ": EntertainmentWillian MachaiNo ratings yet
- Anguage: Name - ClassDocument4 pagesAnguage: Name - ClassВалерия Грушина100% (1)
- English-Thai Code-Mixing in Thai TV ProgramsDocument18 pagesEnglish-Thai Code-Mixing in Thai TV ProgramsJittima ChalothontaksinNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Simple Past Simple FutureDocument6 pagesSimple Present Simple Past Simple FutureNarendran KumaravelNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Maeri Speaking Gen CommunicationDocument12 pagesKumpulan Maeri Speaking Gen Communicationlukman arifNo ratings yet