Experiment No. 1: AIM: To Study About CAD, CAM and CAE Software and Its Advantages
Experiment No. 1: AIM: To Study About CAD, CAM and CAE Software and Its Advantages
Uploaded by
suryavigneCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No. 1: AIM: To Study About CAD, CAM and CAE Software and Its Advantages
Experiment No. 1: AIM: To Study About CAD, CAM and CAE Software and Its Advantages
Uploaded by
suryavigneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No. 1: AIM: To Study About CAD, CAM and CAE Software and Its Advantages
Experiment No. 1: AIM: To Study About CAD, CAM and CAE Software and Its Advantages
Uploaded by
suryavigneCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No.
1
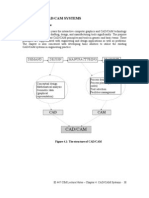
AIM: To study about CAD, CAM and CAE software and its advantages.
CAD
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computer systems to assist in the
creation, modification, analysis or optimization of a design. CAD software is
used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of
design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a
database for manufacturing. CAD output is often in the form of electronic
files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations.
Computer-aided design is used in many fields. Its use in electronic design is
known as Electronic Design Automation (EDA). In mechanical design, it is also
known as computer-aided drafting (CAD) or computer-aided design and
drafting (CADD), which describes the process of creating a technical with the
use of computer software.
CAD may be used to design curves and figures in two-dimensional (2D) space;
or curves, surfaces, and solids in three-dimensional (3D) space.
CAD is an important industrial art extensively used in many applications,
including automotive, shipbuilding, and aerospace industries, industrial and
architectural design, prosthetics, and many more. CAD is also widely used to
produce computer animation for special effects in movies, advertising and
technical manuals. The modern ubiquity and power of computers means that
even perfume bottles and shampoo dispensers are designed using techniques
unheard of by engineers of the 1960s. Because of its enormous economic
importance, CAD has been a major driving force for research in computational
geometry, computer graphics (both hardware and software), and discrete
differential geometry.
Advantages of CAD
One of the most obvious advantages of CAD software is the use of
digital models instead of paper blueprints. Here measurements are
automatic, and lines, shapes and objects can be created with simple
mouse clicks as opposed to slide rulers and calculators. Models can
also be viewed in three dimensions.
Another advantage of CAD software is data centralization. All digital
blueprints are saved on the same server, not in disparate file cabinets,
and can be accessed by anyone who uses the software. (Some CAD
software also gives users the chance to view files on mobile devices.)
This lets designers in different locations work on the same project,
sharing edits and modifications, which reduces communication
bottlenecks and improves efficiency, accountability and project
execution.
Finally, many CAD software tools integrate with cost estimating
software or, at the very least, let users export information such as lists
of building components (windows, doors, pieces of furniture, etc.)
This, too, saves time and reduces the likelihood of transcription
errors, since part lists need not be recreated.
CAM
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) is the use of computer software to
control machine tools and related machinery in the manufacturing of work
pieces. This is not the only definition for CAM, but it is the most common. CAM
may also refer to the use of a computer to assist in all operations of a
manufacturing plant, including planning, management, transportation and
storage. Its primary purpose is to create a faster production process and
components and tooling with more precise dimensions and material
consistency, which in some cases, uses only the required amount of raw
material (thus minimizing waste), while simultaneously reducing energy
consumption. CAM is now a system used in schools and lower educational
purposes CAM is a subsequent computer-aided process after computer-aided
design (CAD) and sometimes computer-aided engineering (CAE), as the model
generated in CAD and verified in CAE can be input into CAM software, which
then controls the machine tool.
CAD model (above) and CNC machined part (below)
Companies providing CAM software are
Dassault Systems
Siemens PLM Software
Delcam
Planit Holdings
PTC
Tebis
Cimatron
Open Mind Technologies
C&G System
Advantages of CAM
In large-scale production, the results are consistent (always the same).
Enables very high accuracy levels in large-scale production.
Usually speeds up production of low-volume products
CAE
CAE tools are being used, for example, to analyze the robustness and
performance of components and assemblies. The term encompasses
simulation, validation, and optimization of products and manufacturing tools.
In regard to information networks, CAE systems are individually considered a
single node on a total information network and each node may interact with
other nodes on the network.
CAE systems can provide support to businesses. This is achieved by the use of
reference architectures and their ability to place information views on the
business process. Reference architecture is the basis from which information
model, especially product and manufacturing models.
Fields and Phases in CAE
CAE areas covered include:
Stress analysis on components and assemblies using FEA (Finite Element
Analysis);
Thermal and fluid flow analysis Computational fluid dynamics (CFD);
Multi-body dynamics(MBD) & Kinematics;
Analysis tools for process simulation for operations such
as casting, molding, and die press forming.
Optimization of the product or process.
Safety analysis of postulate loss-of-coolant accident in nuclear
reactor using realistic thermal-hydraulics code.
In general, there are three phases in any computer-aided engineering task:
Pre-processing defining the model and environmental factors to be
applied to it. (typically a finite element model, but facet, voxel and thin
sheet methods are also used)
Analysis solver (usually performed on high powered computers)
Post-processing of results (using visualization tools).
Experiment No. 2
AIM: To study various commands in pro E used in 3-D modeling.
1. Extrude :this command is used to make 3-D model.
2. Rotate :this command is used to make models symmetrical about an
axis.
3. Hole :this command is used to cut different type of holes through
model.
Example:
: Uses predefined rectangle as the drill hole profile.
: Uses standard hole profile as the drill hole profile.
: Lets us add countersink to the hole that we create.
: Lets us add counter bore to the hole that we create.
4. Round :this command is used to round the sharp edges of desired
radius.
5. Edge Chamfer : this command is used to chamfer the sharp edge at
desired angle.
6. Shell : this command is used to shell give thickness to a solid model
instead of complete solid model.
7. Pattern : this command is used to make a part at many points
creating patterns such as dimension, direction, axis, table etc.
Experiment No. 3
AIM: Modeling of simple machine parts and its component.
Command used :- extrude, revolve, mirror, shell, round, chamfer,pattern,
datum plane, datum axis.
You might also like
- Hickman Pedagogy BookDocument521 pagesHickman Pedagogy BookMiguel Rodrigues75% (4)
- Stances & Motions For Cheerleading: Includes Step-By-Step Visuals!Document36 pagesStances & Motions For Cheerleading: Includes Step-By-Step Visuals!regine romeroNo ratings yet
- Armoured Trains Sneak PreviewDocument9 pagesArmoured Trains Sneak PreviewNaval Institute PressNo ratings yet
- CAD CAM PresentationDocument27 pagesCAD CAM Presentationanon_877650732100% (7)
- Introduction To CAD/CAMDocument81 pagesIntroduction To CAD/CAMTafesse100% (7)
- CAD/CAMDocument13 pagesCAD/CAMMuhammad Iqbal ZahidNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam CaeDocument10 pagesCad Cam CaeSanketDhandeNo ratings yet
- 804 Cad Cam Cim (Me-804) Exp. ManualDocument38 pages804 Cad Cam Cim (Me-804) Exp. ManualAnonymous z3RsdPToNo ratings yet
- Cad - Cam - Eto - MRP2Document13 pagesCad - Cam - Eto - MRP2dixittankNo ratings yet
- Unit - I - Introduction To Cad/CamDocument73 pagesUnit - I - Introduction To Cad/CamPrakhar JainNo ratings yet
- A ReportDocument8 pagesA ReportTyNo ratings yet
- Note 1493621926Document92 pagesNote 1493621926Surya BhupathirajuNo ratings yet
- Gangam Style 48Document14 pagesGangam Style 48Nanda KishoreNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CADDocument3 pagesIntroduction To CADMaaruf Khan PathanNo ratings yet
- Universiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Marine Engineering Technology (Unikl Mimet)Document14 pagesUniversiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Marine Engineering Technology (Unikl Mimet)Haiqal MarizanNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: 1 ME 1356 CAD/CAM Lab Manual RECDocument42 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: 1 ME 1356 CAD/CAM Lab Manual RECsimalaravi0% (1)
- Additive Manufacturing: Presented by Nazma AmrinDocument23 pagesAdditive Manufacturing: Presented by Nazma AmrinSai SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Report Cad CamDocument10 pagesReport Cad Camالمهندس زاهر بكريNo ratings yet
- Moi University School of Information Science Dit 010: Management Information System Section A Question OneDocument7 pagesMoi University School of Information Science Dit 010: Management Information System Section A Question OneKiprotich KibetNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam NotesDocument21 pagesCad Cam NotesarivaazhiNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: Question: Explain The Design Process With Computer and Without ComputerDocument17 pagesUnit - 1: Question: Explain The Design Process With Computer and Without Computerbrar352No ratings yet
- CAD / Computer-Aided DesignDocument3 pagesCAD / Computer-Aided Designsatya prakash mallNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 01: Objective: - Study The Basics of CAD/CAMDocument4 pagesPractical No. 01: Objective: - Study The Basics of CAD/CAMapi-26046805No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1Filiz ÖztürkNo ratings yet
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Is TheDocument3 pagesComputer-Aided Design (CAD) Is TheAhmed AdelNo ratings yet
- The Application of Pro Engineer in CADCAMDocument9 pagesThe Application of Pro Engineer in CADCAMHafiezul HassanNo ratings yet
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD), Also Known As Computer-Aided Design and Drafting (CADD)Document15 pagesComputer-Aided Design (CAD), Also Known As Computer-Aided Design and Drafting (CADD)mech118No ratings yet
- Cadsystems - PPT: Computer-Aided DesignDocument8 pagesCadsystems - PPT: Computer-Aided DesignMichael Dinesh100% (1)
- Computer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) Is TheDocument24 pagesComputer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) Is TheBhupinder Singh MakanNo ratings yet
- Cad CamDocument36 pagesCad Camqmggymypk8No ratings yet
- Gangam Style 50Document13 pagesGangam Style 50Nanda KishoreNo ratings yet
- C A D M: Omputer Ided Esign and AnufacturingDocument6 pagesC A D M: Omputer Ided Esign and AnufacturingMenna TantawiNo ratings yet
- Simulation Lab Manual-2Document48 pagesSimulation Lab Manual-2Satti NagendrareddyNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment 3: TopicDocument18 pagesDigital Assignment 3: Topicprajari ghoshNo ratings yet
- CADM Mod 2Document39 pagesCADM Mod 2Aswin MNo ratings yet
- Ed5161 - Cad - Record (1) - 2 PDFDocument35 pagesEd5161 - Cad - Record (1) - 2 PDFNaveenprakash100% (1)
- Cad Notes in Word1Document71 pagesCad Notes in Word1arunNo ratings yet
- Cad-Cam Manual PDFDocument34 pagesCad-Cam Manual PDFM.Saravana Kumar..M.E100% (3)
- Cad CamDocument6 pagesCad CamKuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Design For Manufacture: CAD CAM CAE Transportability CIM Need of CIMDocument50 pagesDesign For Manufacture: CAD CAM CAE Transportability CIM Need of CIMعبدالرحمن سليمانNo ratings yet
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) : Page 1 of 38Document38 pagesComputer-Aided Design (CAD) : Page 1 of 38Ahtisham KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit I: 3D Modeling & Viewing (08 HRS)Document26 pagesUnit I: 3D Modeling & Viewing (08 HRS)vishwajeet patilNo ratings yet
- Ship Building Computer AidsDocument4 pagesShip Building Computer AidsAnkit MauryaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Computer Aided DraftingDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Computer Aided DraftingLlyann espadaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Cad Unit 1 PDFDocument256 pagesEngineering Cad Unit 1 PDFShri Vignesh KNo ratings yet
- Sub-Module 1.1 - Introduction of Computer Graphics - E-BookDocument8 pagesSub-Module 1.1 - Introduction of Computer Graphics - E-BookNeeraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cam-Cad. Lab PDFDocument51 pagesCam-Cad. Lab PDFDrBollapu SudarshanNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Drafting Week 1Document7 pagesComputer Aided Drafting Week 1mosesbala078No ratings yet
- Unit 2 AIM NotesDocument33 pagesUnit 2 AIM NotesVikash PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided DesignDocument7 pagesComputer Aided DesignRicardo AqpNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Drawing and Design NotesrDocument16 pagesComputer Aided Drawing and Design NotesrMue ngineerNo ratings yet
- CadDocument8 pagesCadLuck VelascoNo ratings yet
- Prodcut CCDocument11 pagesProdcut CCKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Cad-Computer Aided DesignDocument11 pagesCad-Computer Aided DesignP.Punit Mishra100% (1)
- DO Seminar ReportDocument18 pagesDO Seminar ReportMithun N Gowda ME-MD-2019-21No ratings yet
- ME1355-CAD / CAM Laboratory: Lab ManualDocument42 pagesME1355-CAD / CAM Laboratory: Lab ManualVeeria Chandran S100% (1)
- 05 - AbundanceDocument8 pages05 - AbundanceNanda KishoreNo ratings yet
- Geometric Modeling: Exploring Geometric Modeling in Computer VisionFrom EverandGeometric Modeling: Exploring Geometric Modeling in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing: Unlocking Computer Vision Through Technical DrawingFrom EverandTechnical Drawing: Unlocking Computer Vision Through Technical DrawingNo ratings yet
- 301 Top Tips for Design Engineers: To Help You 'Measure Up' in the World of EngineeringFrom Everand301 Top Tips for Design Engineers: To Help You 'Measure Up' in the World of EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 3 Point StarterDocument6 pages3 Point StartersuryavigneNo ratings yet
- All You Need To Know About South-East'S Vaastu: InshareDocument1 pageAll You Need To Know About South-East'S Vaastu: InsharesuryavigneNo ratings yet
- Metacentric HeightDocument2 pagesMetacentric HeightsuryavigneNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Link and TypesDocument4 pagesKinematic Link and TypessuryavigneNo ratings yet
- Core and Core MakingDocument8 pagesCore and Core MakingsuryavigneNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManualDocument0 pagesLaboratory ManualsuryavigneNo ratings yet
- Single Start Worm WheelDocument2 pagesSingle Start Worm WheelsuryavigneNo ratings yet
- 3 Point StarterDocument6 pages3 Point StartersuryavigneNo ratings yet
- SWFR Rwy-05-23 Vac 20210128Document2 pagesSWFR Rwy-05-23 Vac 20210128Thatiane Marçal Dos ReisNo ratings yet
- Winter 16Document2 pagesWinter 16Bala DuttNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Sec04 Full Notes02 PDFDocument7 pagesMechanics Sec04 Full Notes02 PDFMDR PRAPHUNo ratings yet
- May 22 U4 QPDocument28 pagesMay 22 U4 QPrsmo lamoNo ratings yet
- 9701 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2009 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument8 pages9701 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2009 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersYue ShiNo ratings yet
- Pyro-Chem FM-200Document109 pagesPyro-Chem FM-200aliNo ratings yet
- Modern AND Traditional Families: Cristiana Galateanu Iulia Teodora Gheonea 11DDocument11 pagesModern AND Traditional Families: Cristiana Galateanu Iulia Teodora Gheonea 11DCristiana GalateanuNo ratings yet
- HaiderandLevenspiel DragCoefficient PDFDocument9 pagesHaiderandLevenspiel DragCoefficient PDFramanNo ratings yet
- BT2 Working Drawings Table of Contents 2Document1 pageBT2 Working Drawings Table of Contents 2JR CaberteNo ratings yet
- 2020 August, Preliminary Design of Post-Tensioned Transfer GirdersDocument7 pages2020 August, Preliminary Design of Post-Tensioned Transfer GirdersMonika jainNo ratings yet
- Estimation and Costing: Gcpia, Vnsgu Year-3 Group-2Document7 pagesEstimation and Costing: Gcpia, Vnsgu Year-3 Group-2Kush ParikhNo ratings yet
- Profbreaker: Parts ListDocument47 pagesProfbreaker: Parts Listmurat HATONo ratings yet
- With 105N4710 & 105N4760 ControllersDocument3 pagesWith 105N4710 & 105N4760 ControllersHarold ReyesNo ratings yet
- BMW 325i 1988Document12 pagesBMW 325i 1988Piotr JaworskiNo ratings yet
- Flow RigDocument8 pagesFlow Rigsg3569No ratings yet
- Care (Health Insurance Product) Prospectus Cum Sales Literature NewDocument52 pagesCare (Health Insurance Product) Prospectus Cum Sales Literature NewGoutam HotaNo ratings yet
- Exercise TherapyDocument22 pagesExercise Therapykkn0023No ratings yet
- Safe Access To VesselDocument27 pagesSafe Access To Vesselsukhjit78No ratings yet
- 01 Sinusoidal Excitation 2013Document10 pages01 Sinusoidal Excitation 2013Divyang PatelNo ratings yet
- Luganville Beautification Design BriefDocument26 pagesLuganville Beautification Design BriefJ Hunter SizemoreNo ratings yet
- Pickled AutomotiveDocument36 pagesPickled Automotivejade.chen.hx2023No ratings yet
- Target 2024 SSC CGL CHSL Mock Test Based On New Pattern15 03 202410PMDocument13 pagesTarget 2024 SSC CGL CHSL Mock Test Based On New Pattern15 03 202410PMmoharana1998No ratings yet
- Agile BA Interview QuestionsDocument24 pagesAgile BA Interview QuestionsThe CSMTNo ratings yet
- Lateral and Vertical Clearances Underpasses Vehicular TrafficDocument11 pagesLateral and Vertical Clearances Underpasses Vehicular TrafficharivennelaNo ratings yet
- Bitterblooms PDFDocument20 pagesBitterblooms PDFMikołaj Em100% (1)
- Ibong Tiririt (MDSP 7)Document51 pagesIbong Tiririt (MDSP 7)Gerald EspanillaNo ratings yet
- Pee Lab ManualDocument77 pagesPee Lab ManualRajendraTuraka100% (1)