Diffraction Grating: dsinθ
Uploaded by
TuhinVariaDiffraction Grating: dsinθ
Uploaded by
TuhinVariaDiffraction Grating
The condition for maxima is
d sin
bright
= m
m = 0, 1, 2,
The integer m is the order
number of the diffraction
pattern pattern
If the incident radiation
containsseveral wavelengths contains several wavelengths,
each wavelength deviates
through a specific angle g p g
Diffraction Grating, Intensity
All the wavelengths are seen at
m =0 m 0
This is called the zeroth-order
maximum
The first-order maximum
corresponds to m = 1
Note the sharpness of the
principle maxima and the broad
rangeof thedarkareas range of the dark areas
Diffraction Grating Spectrometer
The collimated beam is
incident onthegrating incident on the grating
The diffracted light leaves
the gratings and the telescope g g p
is used to view the image
The wavelength can be
d t i db i th determined by measuring the
precise angles at which the
images of the slit appear for g pp
the various orders
Resolving Power of a Diffraction Resolving Power of a Diffraction
Gratingg
For two nearly equal wavelengths,
1
and
2
, between
which a diffraction grating can just barely distinguish, g g j y g ,
the resolving power, R, of the grating is defined as
R
Therefore agratingwithahighresolutioncan
2 1
R
=
Therefore, a grating with a high resolution can
distinguish between small differences in wavelength
Resolving Power of a Diffraction Resolving Power of a Diffraction
Gratingg
The resolving power in the mth-order
diffractionisR N diffraction is R = Nm
N is the number of slits
m is the order number
Resolvingpower increaseswithincreasing Resolving power increases with increasing
order number and with increasing number of
ill i t d lit illuminated slits
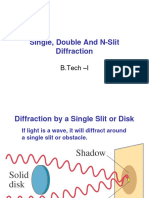
A single-slit diffraction experiment
Light of wavelength
comparable to or larger than the
width of a slit spreads out in all
forward directions upon passing
through the slit. through the slit.
This indicates that light g
spreads beyond the narrow path
defined by the slit into regions
that would be in shadow if light that would be in shadow if light
traveled in straight lines
Light from a small source passes by the edge of an
opaque object and continues on to a screen. A diffraction
pattern consisting of bright and dark fringes appears on
the screen in the region above the edge of the object.
Diffraction Pattern, Object Edge
This shows the upper
h lf f th diff ti half of the diffraction
pattern formed by
light fromasingle light from a single
source passing by the
edge of an opaque edgeo a opaque
object
The diffraction pattern ed c o p e
is vertical with the
central maximum at
the bottom
Diffraction vs. Diffraction Pattern
Diffraction refers to the general behavior of waves
spreadingout astheypassthroughaslit spreading out as they pass through a slit
A diffraction pattern is another interference pattern
Th i t f i b t t f th i id t li ht The interference is between parts of the incident light
illuminating different regions of the slit
Diffraction Pattern, Single Slit
The diffraction pattern
consistsof thecentral consists of the central
maximum and a series
of secondarymaxima of secondary maxima
and minima
Thepatternissimilar to The pattern is similar to
an interference pattern
Fraunhofer Diffraction Pattern
A Fraunhofer diffraction
pattern occurswhenthe pattern occurs when the
rays leave the diffracting
object inparallel directions object in parallel directions
Screen very far from the
slit slit
Could be accomplished
b i l by a converging lens
Huygens Principle and Diffraction Huygens Principle and Diffraction
Pattern
sin
=
a The condition for destractive
2
sin
2
1
=
interference:
Destructive interference:
m
= sin
a
m sin
3 2 1 = m ,.. 3 , 2 , 1 = m
The Width of a Single-Slit The Width of a Single Slit
Diffraction Patterns
m
= sin
Locations of dark fringes:
a
Small angle
,.. 3 , 2 , 1 = m
Small angle
approximation
sin=tg= sin=tg=
tg=y/L
L 2
L m
y
=
3 2 1 = m
Locations of dark fringes: The width of a bright fringe:
a
w =
a
y
m
=
,.. 3 , 2 , 1 = m
Intensity of Single-Slit Diffraction Patterns
Slit width a can be thought g
of as being divided into
zones
Thezoneshaveawidthof y The zones have a width of y
Each zone acts as a source
of coherent radiation
The incremental fields
between adjacent zones are
t f h ith out of phase with one
another by an amount
2 2
sin
=
Intensityof Single-Slit Diffraction Intensity of SingleSlit Diffraction
Patterns
2
) / sin sin(
a
I I
max
/ sin
) (
=
a
I I
Resolution of single-slit
Rayleighs criterion: the central maximum of one image
falls on the first minimumof the other image the images are falls on the first minimum of the other image the images are
said to be just resolved.
(a) The sources are far apart, and the patterns are well (a) e sou ces a e a apa t, a d t e patte s a e we
resolved. (b) The sources are closer together such that the
angular separation just satisfies Rayleighs criterion, and
the patterns are just resolved. (c) The sources are so close
together that the patterns are not resolved.
The limiting angle of resolution, The limiting angle of resolution,
min
=
i
a
min
= sin
a
= sin
The width of central maximum is The width of central maximum is
2x
min
22 . 1
min
=
a
You might also like
- Refractive Index of Liquids Using Laser Light: Experiment-231 S100% (1)Refractive Index of Liquids Using Laser Light: Experiment-231 S7 pages
- Diffraction: Bending of Light Around The Obstacles: Lecture 35: Diffraction: Single SlitNo ratings yetDiffraction: Bending of Light Around The Obstacles: Lecture 35: Diffraction: Single Slit5 pages
- 7-Diffraction at A Slit and Double Slit PDFNo ratings yet7-Diffraction at A Slit and Double Slit PDF9 pages
- Superposition Part 4 Diffraction GratingNo ratings yetSuperposition Part 4 Diffraction Grating18 pages
- Important Questions and Answers On Diffraction and Interference Part 1No ratings yetImportant Questions and Answers On Diffraction and Interference Part 19 pages
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsNo ratings yetB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering Physics72 pages
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsNo ratings yetB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering Physics72 pages
- UP3 4.1. Single-Slit Diffraction Pg146-150No ratings yetUP3 4.1. Single-Slit Diffraction Pg146-1505 pages
- P3507 - Diffraction - Double Slit and Slit - N Slit 2024No ratings yetP3507 - Diffraction - Double Slit and Slit - N Slit 20246 pages
- 11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single SlitNo ratings yet11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single Slit4 pages
- Optics, Set 2 Diffraction Gratings: D Detector ANo ratings yetOptics, Set 2 Diffraction Gratings: D Detector A20 pages
- Long and Short Question and Answers OpticsNo ratings yetLong and Short Question and Answers Optics9 pages
- Physics 223 Experiment 7: Diffraction From A Single Slit: March 24, 2009No ratings yetPhysics 223 Experiment 7: Diffraction From A Single Slit: March 24, 20092 pages
- Diffraction and Thin Film Interference - 1No ratings yetDiffraction and Thin Film Interference - 124 pages
- Railway Recruitment Board (RRB) Asm Solved Question PaperNo ratings yetRailway Recruitment Board (RRB) Asm Solved Question Paper5 pages
- Physics 102 Lab 9: Using The Spectrometer To Measure The Spectrum of HeNo ratings yetPhysics 102 Lab 9: Using The Spectrometer To Measure The Spectrum of He4 pages
- Composites:: L 8. Material Science by Vijay Suthar Date:31/1/2013 (6 To 7 P.M.)No ratings yetComposites:: L 8. Material Science by Vijay Suthar Date:31/1/2013 (6 To 7 P.M.)2 pages
- Experiment 112-8: Grating and Prism SpectrometerNo ratings yetExperiment 112-8: Grating and Prism Spectrometer6 pages
- Experiment IX Diffraction Grating: ObjectiveNo ratings yetExperiment IX Diffraction Grating: Objective7 pages
- How To Read The Metric Vernier Caliper: MAIN (Stationary) BAR SCALE MMNo ratings yetHow To Read The Metric Vernier Caliper: MAIN (Stationary) BAR SCALE MM1 page
- Physics 390, Lab 5: Diffraction and Optical SpectrosNo ratings yetPhysics 390, Lab 5: Diffraction and Optical Spectros11 pages
- M.S University: Faculty of Technology & Engineering Sheet - BARODA - 20 CLASSNo ratings yetM.S University: Faculty of Technology & Engineering Sheet - BARODA - 20 CLASS4 pages
- Effective Design For Absorption and StrippingNo ratings yetEffective Design For Absorption and Stripping9 pages
- 3.3.5 - 146 - A Device Controlled Using Eye Movement100% (1)3.3.5 - 146 - A Device Controlled Using Eye Movement4 pages
- Nikon School Basics of Exposure and Camera Controls NotesNo ratings yetNikon School Basics of Exposure and Camera Controls Notes12 pages
- Quality That Makes Every Occasion Special - Nikon Digital SLRNo ratings yetQuality That Makes Every Occasion Special - Nikon Digital SLR2 pages
- Atoms and Nuclei K-CET Crash: Homework QuestionsNo ratings yetAtoms and Nuclei K-CET Crash: Homework Questions3 pages
- Observation of Negative Photoconductivity in Lead-Free Cs3Bi2Br9 Perovskite Single CrystalNo ratings yetObservation of Negative Photoconductivity in Lead-Free Cs3Bi2Br9 Perovskite Single Crystal9 pages
- Analysis of Beam Propagation in Optical Fiber Structures With A High Step IndexNo ratings yetAnalysis of Beam Propagation in Optical Fiber Structures With A High Step Index3 pages
- A Journey Through Implementing Multiscattering BRDFs and Area LightsNo ratings yetA Journey Through Implementing Multiscattering BRDFs and Area Lights161 pages
- Refractive Index of Liquids Using Laser Light: Experiment-231 SRefractive Index of Liquids Using Laser Light: Experiment-231 S
- Diffraction: Bending of Light Around The Obstacles: Lecture 35: Diffraction: Single SlitDiffraction: Bending of Light Around The Obstacles: Lecture 35: Diffraction: Single Slit
- Important Questions and Answers On Diffraction and Interference Part 1Important Questions and Answers On Diffraction and Interference Part 1
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering Physics
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering Physics
- P3507 - Diffraction - Double Slit and Slit - N Slit 2024P3507 - Diffraction - Double Slit and Slit - N Slit 2024
- 11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single Slit11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single Slit
- Physics 223 Experiment 7: Diffraction From A Single Slit: March 24, 2009Physics 223 Experiment 7: Diffraction From A Single Slit: March 24, 2009
- Shading: Exploring Image Shading in Computer VisionFrom EverandShading: Exploring Image Shading in Computer Vision
- Railway Recruitment Board (RRB) Asm Solved Question PaperRailway Recruitment Board (RRB) Asm Solved Question Paper
- Physics 102 Lab 9: Using The Spectrometer To Measure The Spectrum of HePhysics 102 Lab 9: Using The Spectrometer To Measure The Spectrum of He
- Composites:: L 8. Material Science by Vijay Suthar Date:31/1/2013 (6 To 7 P.M.)Composites:: L 8. Material Science by Vijay Suthar Date:31/1/2013 (6 To 7 P.M.)
- How To Read The Metric Vernier Caliper: MAIN (Stationary) BAR SCALE MMHow To Read The Metric Vernier Caliper: MAIN (Stationary) BAR SCALE MM
- Physics 390, Lab 5: Diffraction and Optical SpectrosPhysics 390, Lab 5: Diffraction and Optical Spectros
- M.S University: Faculty of Technology & Engineering Sheet - BARODA - 20 CLASSM.S University: Faculty of Technology & Engineering Sheet - BARODA - 20 CLASS
- 3.3.5 - 146 - A Device Controlled Using Eye Movement3.3.5 - 146 - A Device Controlled Using Eye Movement
- Nikon School Basics of Exposure and Camera Controls NotesNikon School Basics of Exposure and Camera Controls Notes
- Quality That Makes Every Occasion Special - Nikon Digital SLRQuality That Makes Every Occasion Special - Nikon Digital SLR
- Observation of Negative Photoconductivity in Lead-Free Cs3Bi2Br9 Perovskite Single CrystalObservation of Negative Photoconductivity in Lead-Free Cs3Bi2Br9 Perovskite Single Crystal
- Analysis of Beam Propagation in Optical Fiber Structures With A High Step IndexAnalysis of Beam Propagation in Optical Fiber Structures With A High Step Index
- A Journey Through Implementing Multiscattering BRDFs and Area LightsA Journey Through Implementing Multiscattering BRDFs and Area Lights