RIP or The Routing Information Protocol
RIP or The Routing Information Protocol
Uploaded by
Arivazhagan ChinnamadhuCopyright:
Available Formats
RIP or The Routing Information Protocol
RIP or The Routing Information Protocol
Uploaded by
Arivazhagan ChinnamadhuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
RIP or The Routing Information Protocol
RIP or The Routing Information Protocol
Uploaded by
Arivazhagan ChinnamadhuCopyright:
Available Formats
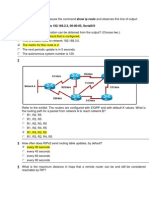
RIP or the Routing Information Protocol
RIP or the Routing Information Protocol is a dynamic routing protocol. RIP stands for Routing
Information Protocol which is an Interior Gateway Protocol. RIP is mainly used in local and
wide area networks .Rip based on distance vector algorithm called the Bellman-Ford algorithm.
RIP calculates the best route based on hop count .Here the maximum number of hops allowed
are 15. if the hop count is exceeding 15 it will be unreachable. The main purpose of RIP is to
prevent routing loops by implementing a limit on number of hops between a source and its
destination. RIP is available in three versions, RIPv1, RIPv2, RIPng(RIP next generation). RIPv1
uses only class full routing whereas RIPv2 uses classless routing.
RIP protocol select the shortest path to go from Source to Destination. All routers using RIP
protocol broadcast their Network address to each other after every 30 Seconds.
RIP implements mechanisms such as split horizon, hold-down timers, hop-count limits, and
poison reverse to prevent routing loops and maintain network stability, as explained in the list
that follows:
Split horizon: If a route is learned on an interface, the information about that route is not
sent back out the interface where it was learned. In this way, split horizon prevents routing
loops within the network.
Hold-down timers: These timers ignore routing update information for a specified period of
time. Hold-down timers can be reset when the timer expires, a routing update is received that
has a better metric, or a routing update is received indicating that the original route to the
network is valid. Hold-down timers are useful in preventing routing information from
flooding the network when network links are unstable.
Hop-count limit: This limits the number of hops allowed in a path from source to
destination. The maximum is 15, and 16 is deemed unreachable. The hop-count limit
prevents routing loops from continuing indefinitely.
Poison reverse: A route is "poisoned" when a router marks a route as unreachable by setting
the hop count to 16 and then passes this route out to a neighboring router, causing the
neighboring router to remove the route from its routing table. This speeds network
convergence by preventing invalid routes from being propagated throughout the network.
These features allow RIP to adjust to network-topology changes and prevent routing loops from
being propagated and continuing indefinitely.
Advantages of Rip Protocol: Easy Configuration and Minimum overload over the Processor.
Disadvantages of RIP: Broadcasting, Slow Coverage, Routing Loop and Hop Count Limit.
RIPV.2 -Supports Authentication.
You might also like
- 1 VoLTE Overview MasterclassDocument59 pages1 VoLTE Overview MasterclassNicu Prisacaru100% (2)
- Unit III Routing PDFDocument17 pagesUnit III Routing PDFNagaraj VaratharajNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 EeeDocument17 pagesUnit 3 EeeNavin DasNo ratings yet
- Routing: Unicast and Multicast RoutingDocument32 pagesRouting: Unicast and Multicast RoutingSuranga SampathNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 (Networking With TCP-IP Notes)Document9 pagesUNIT-4 (Networking With TCP-IP Notes)0901CS211114 SOURAV DINKARNo ratings yet
- Routing ProtocolDocument12 pagesRouting ProtocolKetan GargNo ratings yet
- Performance of Best Route Selection Using RIP and OSPF Routing ProtocolsDocument4 pagesPerformance of Best Route Selection Using RIP and OSPF Routing ProtocolsEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Sr. No. Topic No.: Types of Routing ProtocolsDocument27 pagesSr. No. Topic No.: Types of Routing ProtocolsPKTC Diploma DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Dynamic RoutingDocument27 pagesUnit 3 - Dynamic RoutingprafrenNo ratings yet
- Routing RIP OSPFDocument5 pagesRouting RIP OSPFnyashamagutsa93No ratings yet
- Basic of RoutingDocument56 pagesBasic of RoutingnjgregNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 4 NotesTim WaterburyNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Routing Routing (RIP, OSPF, and Metrics)Document17 pagesUnit Iii Routing Routing (RIP, OSPF, and Metrics)akashNo ratings yet
- 7 Types of Routing Protocols - zenarmor.comDocument18 pages7 Types of Routing Protocols - zenarmor.comzarifnoori2001No ratings yet
- CCN LAB 7 RIP (Dynamic Routing)Document5 pagesCCN LAB 7 RIP (Dynamic Routing)ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Interior Gateway Routing Protocol and Enhanced IGRP: BackgroundDocument8 pagesInterior Gateway Routing Protocol and Enhanced IGRP: Backgrounddhdeore81No ratings yet
- What Is Routing ?Document48 pagesWhat Is Routing ?murugeshanpmNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Routing Protocols (OSPF/RIP/BGP)Document41 pagesDynamic Routing Protocols (OSPF/RIP/BGP)ramillosssNo ratings yet
- Routing Information Protocol (Ripv1 & Ripv2)Document42 pagesRouting Information Protocol (Ripv1 & Ripv2)Sayyeda UmbereenNo ratings yet
- Ccna 3 Chapter 5 (Version 4.0)Document8 pagesCcna 3 Chapter 5 (Version 4.0)_mika_No ratings yet
- Remember: Use The Pop Quiz Feature To Test Your Understanding Throughout This CourseDocument17 pagesRemember: Use The Pop Quiz Feature To Test Your Understanding Throughout This CourseSathis Kumar ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- RIP - Distance VectorDocument5 pagesRIP - Distance VectorFrancis KamwatiNo ratings yet
- IGRPDocument9 pagesIGRPDion Odessy PaduaNo ratings yet
- 9Document25 pages9Zain Ul AbedinNo ratings yet
- Uni CastDocument31 pagesUni Castdiwansingh29081999No ratings yet
- RIP ProtocolDocument4 pagesRIP ProtocolDion Odessy PaduaNo ratings yet
- What Is Global Configuration Mode Used For?Document10 pagesWhat Is Global Configuration Mode Used For?Abhishek KulkarniNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 4 Distance Vector Routing ProtocolsDocument5 pagesCHAPTER - 4 Distance Vector Routing ProtocolsAlexandrosAristeridisNo ratings yet
- Free Cisco Lab Packet Tracer Activity Basic RipDocument1 pageFree Cisco Lab Packet Tracer Activity Basic RipmistabatuNo ratings yet
- Routing Information Protocol RIPDocument27 pagesRouting Information Protocol RIPomarkhanfar2No ratings yet
- Introd Uction To IP RoutingDocument14 pagesIntrod Uction To IP Routingapi-292985604No ratings yet
- G PDFDocument20 pagesG PDFokienaNo ratings yet
- 20BCS3966-CN-Exp - 2.1Document5 pages20BCS3966-CN-Exp - 2.1ayan.mishraNo ratings yet
- Module - RoutingDocument15 pagesModule - RoutingSurinderpal singhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 LabDocument6 pagesLecture 6 LabSerin AskecNo ratings yet
- Paper AComparativeDocument6 pagesPaper AComparativeAvotriniainaNo ratings yet
- North South University: CSE 338 L: Data Communication & Network LabDocument2 pagesNorth South University: CSE 338 L: Data Communication & Network LabTaqsim RajonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 3 Introduction To Dynamic Routing ProtocolDocument5 pagesCHAPTER - 3 Introduction To Dynamic Routing ProtocolAlexandrosAristeridisNo ratings yet
- Routing Rip PDFDocument19 pagesRouting Rip PDFAxel LwiantoroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CCNA 2Document5 pagesChapter 3 CCNA 2Bianca PetreNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Routing ProtocolsDocument11 pagesIntroduction of Routing ProtocolsSolomon JayasenaNo ratings yet
- Common Metric: The OneDocument27 pagesCommon Metric: The OneABHISHEK KUMAR SAHNo ratings yet
- 223A1131_UMAIR_MOMIN_EXP7Document14 pages223A1131_UMAIR_MOMIN_EXP7Umair MominNo ratings yet
- Comparison of RIP, OSPF and EIGRP Routing Protocols Based On OPNETDocument25 pagesComparison of RIP, OSPF and EIGRP Routing Protocols Based On OPNETprincessNo ratings yet
- CNM Chapter5Document18 pagesCNM Chapter5saadmulla1717No ratings yet
- Two Basic Methods: Lab Manual Section 1: Static vs. Dynamic RoutingDocument20 pagesTwo Basic Methods: Lab Manual Section 1: Static vs. Dynamic RoutingNurlign YitbarekNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Dynamic Routing Protocols: RIP and OSPFDocument4 pagesComparison of Dynamic Routing Protocols: RIP and OSPFseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- Data and Computer CommunicationsDocument31 pagesData and Computer CommunicationsMogahed SemyNo ratings yet
- Features of RIP v2:: RIP Stands For Routing Information ProtocolDocument2 pagesFeatures of RIP v2:: RIP Stands For Routing Information ProtocolSenan AlkaabyNo ratings yet
- Sample Oral Questions With Answers For CNSL Oral PreparationDocument63 pagesSample Oral Questions With Answers For CNSL Oral Preparationchaudharylalit025No ratings yet
- CN Assignment03Document4 pagesCN Assignment03alikhan125466akNo ratings yet
- 3.1 IP Routing Part 2Document15 pages3.1 IP Routing Part 2trustyNo ratings yet
- OSPF Design GuideDocument70 pagesOSPF Design Guidespecific4xNo ratings yet
- Semester II. - Chapter 3Document6 pagesSemester II. - Chapter 3KlokanNo ratings yet
- 04-RG-S7805C Switch RGOS Configuration Reference, Release 11.0 (4) B19 - IP Routing ConfigurationDocument586 pages04-RG-S7805C Switch RGOS Configuration Reference, Release 11.0 (4) B19 - IP Routing Configurationcindy yudi hermawanNo ratings yet
- 2 Dynamic Routing RIPDocument17 pages2 Dynamic Routing RIProhullah bakhtaryNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exploration2: Routing Protocols - Chapter 3 Exam: Distance of EIGRP Is Lower Than RIPDocument5 pagesCCNA Exploration2: Routing Protocols - Chapter 3 Exam: Distance of EIGRP Is Lower Than RIPsayedahmedNo ratings yet
- Lab Supervisor: Ahsan Riaz (140967)Document9 pagesLab Supervisor: Ahsan Riaz (140967)joy leeNo ratings yet
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONFrom EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONNo ratings yet
- History of ComputersDocument36 pagesHistory of ComputersArivazhagan ChinnamadhuNo ratings yet
- Arp ProtocolDocument38 pagesArp ProtocolArivazhagan ChinnamadhuNo ratings yet
- Training Set: LearningDocument2 pagesTraining Set: LearningArivazhagan ChinnamadhuNo ratings yet
- Bagging ND BoostingDocument12 pagesBagging ND BoostingArivazhagan ChinnamadhuNo ratings yet
- ESE680: Wireless Sensor Networks: Prof. Rahul MangharamDocument73 pagesESE680: Wireless Sensor Networks: Prof. Rahul MangharamArivazhagan ChinnamadhuNo ratings yet
- Ccna1full PDFDocument572 pagesCcna1full PDFaji kusumoNo ratings yet
- Socket Programming in JavaDocument22 pagesSocket Programming in Javanalluri_08No ratings yet
- CN Module 4Document116 pagesCN Module 4Subhash ParitalaNo ratings yet
- Moden DSL-362T Manual 1.00Document69 pagesModen DSL-362T Manual 1.00mochazo2No ratings yet
- UM BasicConfig L2P Rel90 enDocument288 pagesUM BasicConfig L2P Rel90 enEric Castillo PonceNo ratings yet
- SIM800 Series - AT Command Manual - V1.10 PDFDocument384 pagesSIM800 Series - AT Command Manual - V1.10 PDFmanuelestrella2011No ratings yet
- DCN Manual 2019Document73 pagesDCN Manual 2019Suhani SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 1 - SPROUTE 1.0 - Student Guide Vol1 PDFDocument310 pages1 - SPROUTE 1.0 - Student Guide Vol1 PDFddungui100% (1)
- Netflow Con FlowDocument11 pagesNetflow Con FlowAngel Mendoza LoredoNo ratings yet
- Canh Bao Core CS Ericsson Tuan 47 (28!11!2014)Document10 pagesCanh Bao Core CS Ericsson Tuan 47 (28!11!2014)NPHNPHNo ratings yet
- HW 4Document6 pagesHW 4Nemo CanıNo ratings yet
- Unit-V: Dns-Domain Name SpaceDocument33 pagesUnit-V: Dns-Domain Name SpaceMr.T.Vijayakumar Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Building A Simple Web ServerDocument6 pagesBuilding A Simple Web ServerAnh WeasleyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Socket Programming: (Recommended Reading: Comer, Vol 3, Chapter 5) - Review of C ProgrammingDocument38 pagesFundamentals of Socket Programming: (Recommended Reading: Comer, Vol 3, Chapter 5) - Review of C ProgrammingVũ Văn ThiênNo ratings yet
- EAP AKA AuthenticationDocument27 pagesEAP AKA AuthenticationvenkateshpappuNo ratings yet
- Network Access TechnologiesDocument9 pagesNetwork Access TechnologiesAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- CX600 Product DescriptionDocument200 pagesCX600 Product DescriptionMuhammad SyarifuddinNo ratings yet
- CO1Document8 pagesCO1YunanNo ratings yet
- OSPF Part2 - Study Notes CheatSheet - (Waqas Karim) WK v2Document1 pageOSPF Part2 - Study Notes CheatSheet - (Waqas Karim) WK v2Sivaraman AlagappanNo ratings yet
- Bettercap :: WiFiDocument7 pagesBettercap :: WiFiwaraceoNo ratings yet
- Yeastar TA100&TA200 User Manual en PDFDocument52 pagesYeastar TA100&TA200 User Manual en PDFKurtNo ratings yet
- Westermo Ds Lynx-5512 2305 en RevlDocument4 pagesWestermo Ds Lynx-5512 2305 en Revlvinay moogiNo ratings yet
- Internet ProtocolDocument4 pagesInternet ProtocolMark Lester PicazoNo ratings yet
- Imp CodesDocument8 pagesImp CodesmhzNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Chapter 5 NotesDocument2 pagesCCNA 2 Chapter 5 NotesTim Waterbury100% (1)
- Chapter 8: DHCP: Instructor MaterialsDocument45 pagesChapter 8: DHCP: Instructor MaterialsAmjad hassanNo ratings yet
- Deif Hybrid Controller Compatibility 4189341288 UkDocument11 pagesDeif Hybrid Controller Compatibility 4189341288 UkWaseem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Nov. 7 G10Document56 pagesNov. 7 G10Honey Diana MejiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Module 2Document147 pagesChapter 2 Module 2Dr Sreekanth RNo ratings yet