Motherboard Major Parts and Function
Motherboard Major Parts and Function
Uploaded by
Vic PicarCopyright:
Available Formats
Motherboard Major Parts and Function
Motherboard Major Parts and Function
Uploaded by
Vic PicarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Motherboard Major Parts and Function
Motherboard Major Parts and Function
Uploaded by
Vic PicarCopyright:
Available Formats
Motherboard Major Parts and Function.
Motherboard is the central printed circuit board (PCB) in many modern computers and holds many
of the crucial components of the system, while providing connectors for other peripherals.
Every motherboard has connectors and slots to connect all the remaining parts of CPU. here the list of all the slot and connector of
motherboard.
CPU Socket
North Bridge
South Bridge
RAM Slots
AGP Slot
PCI Slots
PCIe slots
CNR Slot
Floppy slot
IDE Slot
SATA Port
BIOS
CMOS battery
Front Panel Port headers and connectors
1. CPU Socket - CPU Socket or Processor Socket. Which is used to install or insert the processor. we have two types of sockets.
LIF sockets and ZIF socket. LIF stands for Low Insertion Force, this is the old model sockets and ZIF stands for Zero Insertion
Force, this is the present model sockets.
2. North Bridge- typically handles communications among the CPU, RAM, BIOS ROM, and PCI Express (or AGP) video cards,
and the south bridge.
3. South Bridge - also known as an I/O controller hub (ICH) in Intel systems (AMD, VIA, SiS and others usually use
Southbridge). Is a chip that implement the slower capabilities of the motherboard in a Northbridge/Southbridge chipset
computer architecture
4. Memory slot, or RAM slot- is what allows computer memory (RAM) to be inserted into the computer. Depending on
the motherboard, there will usually be 2 to 4 memory slots (sometimes more on high-end motherboards) and are what
determine the type of RAM used with the computer. The most common types of RAM are SDRAM and DDR for desktop
computers and SODIMM for laptop computers, each having various types and speeds.
5. Accelerated Graphic Port (AGP) - is a high speed point to point channel for attaching a video card to a computers
motherboard, primarily to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics.
6. PCIe Slot (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) - is a major redesign that uses high speed serial signaling arranged
in lanes. This allows different sized cards to be used that may or may not require high speed transfers.
7. PCI Slot-"Peripheral Component Interconnect." It is a hardware bus designed by Intel and used in both PCs and Macs. Most
add-on cards such as SCSI, Firewire, and USB controllers, use a PCI connection. Some graphics cards use PCI, but most new
graphics cards connect to the AGP slot. PCI slots are found in the back of your computer and are about 3.5" long and about
0.5" high. So before you go buy that Firewire expansion card, make sure you have at least one PCI slot available.
8. Communications and Networking Riser (CNR) is a slot found on certain PC motherboards and used for specialized
networking, audio, and telephony equipment.
9. Audio Modem Riser Slot (AMR) - is a riser expansion slot found on the motherboards of some Pentium III, Pentium 4,
Duron, and Athlon personal computers. It was designed by Intel to interface with chipsets and provide analog functionality,
such as sound cards
10. FDD Slot (Floppy Disk Drive) a slot that supports the 33 pin FDD connector.
11. IDE (Integrated Drive Electronic refers not just to the connector and interface definition, but also to the fact that the
drive controller is integrated into the drive.
- An interface standard for the connection of storage devices such as hard disk, solid state drives, floppy drives, and cd rom
drives in computers.
12. SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is a computer bus interface for connecting host bus adapters to mass
storage devices such as hard disk drive and optical drives.
13. BIOS (Basic Input Output System) - The BIOS is the motherboard serves to connect between the existing software in
computers with hardware that is installed on the motherboard. The BIOS itself is an acronym for Basic Input / Output
System. In the BIOS there are programs that can be used to regulate how a component mounted on the motherboard can
work..
Bios runs when the PC is started.
To check the status of the motherboard circuitry.
To prepare the system ready for the DOS (Disk Operating System) normally Windows or Linux to boot and take over.
To allow access to the computers settings stored in CMOS memory.
14. Parallel Port is a type of interface found on computers (personal and otherwise) for connecting various peripherals. In
computing, a parallel port is a parallel communication physical interface. It is also known as a printer port or centronics
port.
15. Serial Port is a serial communication physical interface through which information transfers in or out one bit at a time
(contrast parallel port).
16. CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) the PC motherboard needed a non-volatile memory to store
system settings, designers used a CMOS SRAM powered by battery. This chip became known as the CMOS Memory.
17. ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) is a computer form factor specification developed by Intel in 1995 to improve on
previous de-facto standards like the AT form factor.
ATX Connects to the 24-pin ATX power cable of a power supply unit which supplies power to the motherboard.
18. USB Port (Universal Serial Bus) is intended to replace many varieties of serial and parallel ports. USB can connect
computer peripherals such as mice, keyboard, digital cameras, printers, personal media players, flash drive, and external
hard drives.
19. Ethernet Port a port use to connect a registered jack (RJ 45) enables our computer to connect our Local Area Network or
the Internet.
20. Personal System Port (PS/2) port is used for connecting some keyboards and mouse to a PC compatible computer
system.
Note: violet is for keyboard, while green is for mouse.
21. Audio Jack a socket for plugging in an audio source. Audio jacks are found on many types of audio equipment and musical
instruments that accept external sound sources.
Front Panel Port Header and Connectors
System Panel header and Connectors
*Alternatively referred to as the fpanel or front panel connector, the system panel connector is what controls
the computer's power button, reset button, and LED's found on the front bezel of a computer using
the system panel cables.
HDD LED (IDE LED) - The LED activity light for the hard drive. This is the LED that
flashes as information is being written and read from the hard drive.
Power LED (PLED) - The LED power light, which indicates when the computer is
on, off, or in Standby.
Power SW (PWRSW) - Controls the power button that allows you to turn on
and off the computer.
Reset SW - Handles the reset button to restart the computer.
Speaker - The internal speaker used to sound the beep noises you hear from
your computer when it is booting.
1. USB Header - The 1394 header and USB header is a pin
connection found on a computer motherboard that allow additional 1394 and USB
connections to be added to the computer.
2. Fan Headers - Supplies power to the CPU heat sink fan and
computer case fan.
3. Audio Header - The front panel audio header on an Intel
Desktop Board lets you connect to a front panel audio module built into a system
chassis.
3.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
You might also like
- Introducing Hardware (Laptop) PDFDocument5 pagesIntroducing Hardware (Laptop) PDFBong Manuel67% (3)
- Parts of The Motherboard & Their FunctionsDocument17 pagesParts of The Motherboard & Their FunctionsClaren Baltazar100% (2)
- Disassemble and Assemble A Computer LabDocument6 pagesDisassemble and Assemble A Computer LabInderjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Windows 10 Installation StepsDocument12 pagesWindows 10 Installation StepsMihemed Zedan50% (2)
- Parts of System Unit and Their FunctionsDocument14 pagesParts of System Unit and Their FunctionsClaren Baltazar75% (8)
- ComputerPorts, Cables and WiresDocument2 pagesComputerPorts, Cables and WiresMeAnnLarrosa100% (3)
- TLE ICT CSS 10 Q2 - ICCS Week 1 4 - ICCSDocument20 pagesTLE ICT CSS 10 Q2 - ICCS Week 1 4 - ICCSnhoj eiram Rodavlas100% (1)
- Module 4 - Parts of The Motherboard and Their FunctionsDocument13 pagesModule 4 - Parts of The Motherboard and Their Functionsjussan roaring100% (4)
- Types of Computer System ErrorDocument7 pagesTypes of Computer System ErrorKenneth Santos100% (7)
- 100 Hardware Questions and Answers:: AnswerDocument15 pages100 Hardware Questions and Answers:: AnswerSamala BhanuNo ratings yet
- Computer Motherboard PDFDocument10 pagesComputer Motherboard PDFKharidyKazumary100% (3)
- Computer Disassembly AssemblyDocument29 pagesComputer Disassembly AssemblyCecille Pagana100% (2)
- Computer System (Hardware, Software & Peopleware)Document19 pagesComputer System (Hardware, Software & Peopleware)drewNo ratings yet
- TVL - Computer Systems Servicing: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Computer Hardware Disassembly and AssemblyDocument38 pagesTVL - Computer Systems Servicing: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Computer Hardware Disassembly and AssemblyMa. Clarissa De RamosNo ratings yet
- Bootable USB PDFDocument5 pagesBootable USB PDFkatari haribabuNo ratings yet
- Assembly and Disassembly of A Personal ComputerDocument18 pagesAssembly and Disassembly of A Personal Computerkimidors14360% (10)
- Identification of Parts of The Computer SystemDocument49 pagesIdentification of Parts of The Computer SystemFretzie Cambiado100% (1)
- Computer DealersDocument43 pagesComputer DealersZafar Mirza100% (1)
- Computer Motherboard PDFDocument10 pagesComputer Motherboard PDFKharidyKazumary100% (3)
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionDocument14 pagesIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionBrenda Macanlalay Asuncion80% (5)
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionDocument31 pagesIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionNhil Cabillon Quieta100% (1)
- The Major Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesThe Major Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsCavs Nek100% (2)
- How To Assemble (15 Steps) and Disassemble (9 Steps) A ComputerDocument14 pagesHow To Assemble (15 Steps) and Disassemble (9 Steps) A ComputerYenewligne Ayenew100% (1)
- 27 Main Parts of Motherboard and Its FunctionDocument30 pages27 Main Parts of Motherboard and Its FunctionAngelica CarbonquilloNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Parts and FunctionsDocument4 pagesMotherboard Parts and Functionsliezle munezNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Multimedia Storage DevicesDocument10 pagesModule 5 - Multimedia Storage Devicesjussan roaring100% (1)
- Tle Css ReviewerDocument4 pagesTle Css ReviewerHannah Ataza100% (1)
- TLE CHS q3 Mod3 Diagnosing Computer Systems Part IDocument17 pagesTLE CHS q3 Mod3 Diagnosing Computer Systems Part IAlona Acot100% (2)
- CSS Ncii G 11 ReviewerDocument7 pagesCSS Ncii G 11 Reviewerjustin cabaneroNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware-Related AcronymsDocument3 pagesComputer Hardware-Related Acronymsghoul cipriano100% (1)
- CSS G11 Module 5 Q1Document25 pagesCSS G11 Module 5 Q1Pril Gueta100% (4)
- Tle Ict Css 10 q1 - Iccs Week 2Document26 pagesTle Ict Css 10 q1 - Iccs Week 2jayson santosNo ratings yet
- Flash Update BIOS/UEFIDocument11 pagesFlash Update BIOS/UEFIۦۦ ۦۦNo ratings yet
- Installer Preparation and Creating Bootable DevicesDocument17 pagesInstaller Preparation and Creating Bootable DevicesBenson Falco100% (5)
- Tvl-Ict: Quarter 3 - Module 4Document16 pagesTvl-Ict: Quarter 3 - Module 4THRISTAN Bungay100% (1)
- 3 Fundamental Elements of Computer and Their ExamplesDocument2 pages3 Fundamental Elements of Computer and Their ExamplesCelestine88% (8)
- 2.1-2network Tools and Testing Devices Power PointDocument22 pages2.1-2network Tools and Testing Devices Power Pointecardnyl25100% (1)
- Installation of Hardware Components and Other PeripheralsDocument3 pagesInstallation of Hardware Components and Other PeripheralsIan Clyde Torio100% (3)
- Assembling & Disassembling of System UnitDocument16 pagesAssembling & Disassembling of System UnitJericho PadillaNo ratings yet
- TLE Computer Systems Servicing 10 Installing and Configuring Computer Systems (ICCS) Quarter 2 - Week 1 ModuleDocument10 pagesTLE Computer Systems Servicing 10 Installing and Configuring Computer Systems (ICCS) Quarter 2 - Week 1 ModulePauljam OnamorNo ratings yet
- TVL CSS11 Q2 M2Document8 pagesTVL CSS11 Q2 M2charmaine jornadalNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A Multimedia SystemDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of A Multimedia SystemGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Acronyms For CSS NCIIDocument1 pageAcronyms For CSS NCIIjeffrey del mundoNo ratings yet
- Practical No 3 - Motherboard Components and TypesDocument10 pagesPractical No 3 - Motherboard Components and TypesAshish SethiNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1: Week 4: Bootable DevicesDocument30 pagesQuarter 1: Week 4: Bootable DevicesHanzel NietesNo ratings yet
- CSS G11 Module 3 Q1Document24 pagesCSS G11 Module 3 Q1greatcenter registrar100% (2)
- Tle10 Ict Css q2 Mod3 Week6-7Document28 pagesTle10 Ict Css q2 Mod3 Week6-7my musicNo ratings yet
- TLE10 ICT CSS Q1 M4 v3Document90 pagesTLE10 ICT CSS Q1 M4 v3lhuk banaag0% (1)
- done-TLE ICTCSS10 Q1 CLAS5 Performing-BIOS-ConfigurationDocument20 pagesdone-TLE ICTCSS10 Q1 CLAS5 Performing-BIOS-ConfigurationMARIES IMEE VENTURILLONo ratings yet
- Computer Peripheral DevicesDocument15 pagesComputer Peripheral DevicesEmmanuel SulitNo ratings yet
- Types of ProcessorsDocument7 pagesTypes of ProcessorsTayyab1467% (3)
- Computer Systems Servicing NC II: Quarter 1 - Module 6: Installers Preparation and OS Installation ProceduresDocument17 pagesComputer Systems Servicing NC II: Quarter 1 - Module 6: Installers Preparation and OS Installation ProceduresMark carlo RemedilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-4 - Materials, Tools, Equipment and Testing DevicesDocument21 pagesLesson 1-4 - Materials, Tools, Equipment and Testing Devicesanthony t. aviles100% (5)
- Computer Hardware Maintenance ToolsDocument3 pagesComputer Hardware Maintenance ToolsMelkamu Tadege75% (4)
- TLE CSS Q3 - Mod2 - Types of Computer System Errors EditedDocument13 pagesTLE CSS Q3 - Mod2 - Types of Computer System Errors EditedJames Darrel Castro Nicolas67% (3)
- 1.1-2 System SpecificationDocument35 pages1.1-2 System SpecificationRonnil QuietaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Identification of Faulty SystemDocument25 pagesDiagnosis and Identification of Faulty SystemJayr Maslog Nator33% (3)
- Unit-II: Accessory BoardDocument39 pagesUnit-II: Accessory BoardNavi KaurNo ratings yet
- Motherboard and Its Component (11813705)Document10 pagesMotherboard and Its Component (11813705)DeePäk YädävNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10Document4 pagesParts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10DeathNo ratings yet
- BIOS or Basic Input Output SystemDocument13 pagesBIOS or Basic Input Output SystemSaymon Casilang SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument86 pagesParts of MotherboardKurt Balani100% (2)
- Fanless Full Flat Touch Screen POS TerminalDocument2 pagesFanless Full Flat Touch Screen POS Terminalerol isNo ratings yet
- RefreshRateService ReleaseNote v2.0.3Document4 pagesRefreshRateService ReleaseNote v2.0.3Yaroslav NNo ratings yet
- The Lenovo C225 Desktop.: Reshaping The Affordable Home ComputerDocument2 pagesThe Lenovo C225 Desktop.: Reshaping The Affordable Home ComputerChandraNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Teknis Laboratorium Micro TeachingDocument5 pagesSpesifikasi Teknis Laboratorium Micro TeachingHana sakuraNo ratings yet
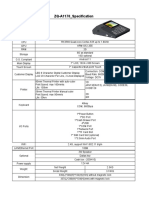
- ZQ-A1170 - Details SpecificationDocument1 pageZQ-A1170 - Details SpecificationBryan PascuaNo ratings yet
- Hardware TroubleshootingDocument13 pagesHardware TroubleshootingAamirPathanNo ratings yet
- Computer Shortcut KeysDocument11 pagesComputer Shortcut Keyseeeabhi9100% (1)
- Adventure Pack I - Manual PDFDocument4 pagesAdventure Pack I - Manual PDFtelengard_tNo ratings yet
- Professional Laptop Battery Store-Battery4us-ComDocument8 pagesProfessional Laptop Battery Store-Battery4us-ComAndy LawNo ratings yet
- TLE-TE 10 - Q1 - W5 - Mod5 - ICT CSS WorksheetDocument2 pagesTLE-TE 10 - Q1 - W5 - Mod5 - ICT CSS WorksheetJohn King johnking.monderinNo ratings yet
- TI41MDocument4 pagesTI41MMourad SemidaNo ratings yet
- Gigabyte Manual k8n51gmf-Rh eDocument88 pagesGigabyte Manual k8n51gmf-Rh eenergiculNo ratings yet
- SK600 Series Bluetooth SetupDocument1 pageSK600 Series Bluetooth Setupjohnnydangerous034No ratings yet
- Manual Book HP Revolve 810Document116 pagesManual Book HP Revolve 810SK DATO' ABDUL HAMID (2)-CM1 KPM-SK-LamanNo ratings yet
- Yoga 9i 14 2 in 1 Laptops Built On Intel Evo Lenovo USDocument1 pageYoga 9i 14 2 in 1 Laptops Built On Intel Evo Lenovo USfewap73153No ratings yet
- Manette x3Document1 pageManette x3Jean Pierre MARTINEAUNo ratings yet
- C-Zone SDN BHD: Price List Effective 10 AUG 2019Document2 pagesC-Zone SDN BHD: Price List Effective 10 AUG 2019Cikgu AlNo ratings yet
- Notebook Packages 4 10 23Document4 pagesNotebook Packages 4 10 23Gilfred PetancioNo ratings yet
- SynKernelDiag2020 07 02 - 21 08 09Document1,623 pagesSynKernelDiag2020 07 02 - 21 08 09Kryss Clyde TabliganNo ratings yet
- RK96-User ManualDocument1 pageRK96-User ManualFonz PalomaNo ratings yet
- ChosenArchitect's PCDocument2 pagesChosenArchitect's PCJessey LuijcksNo ratings yet
- Reliable Tech - Cherubim and Seraphim Church Yoruba HymnDocument12 pagesReliable Tech - Cherubim and Seraphim Church Yoruba HymnMaderich John AdebayoNo ratings yet
- Basic Keyboarding: Introduction To The Computer KeyboardDocument9 pagesBasic Keyboarding: Introduction To The Computer KeyboardIrrone Castro100% (1)
- New DevicesaaDocument101 pagesNew Devicesaajorakom263No ratings yet
- Screencast 0Document3 pagesScreencast 0Nicolás Durán GarcésNo ratings yet
- 00 Versiune BiosDocument2 pages00 Versiune BiosionicoNo ratings yet
- Thinkpad E490: Business Devices That Are A Class ApartDocument2 pagesThinkpad E490: Business Devices That Are A Class ApartFelipe DussanNo ratings yet
- MKBTDocument4 pagesMKBTAtique RehmanNo ratings yet