Drug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Cheriz LukbanCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Cheriz LukbanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Cheriz LukbanCopyright:
Available Formats
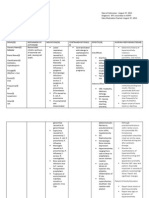
DRUG STUDY
CLASSIFICATION MECHANISM
OF ACTION
INDICATION ADVERSE
REACTION
INTERACTION NURSING
CONSIDERATION
BRAND NAME:
Iselpin
GENERIC
NAME:
Sucralfate
DOSAGE:
tab q6
1 gm/tab
Cytoprotectives Forms a
complex by
binding with
positively
charged
proteins that
adheres to
ulcer site. This
selectively
forms a
protective coat
that protect
the lining
against peptic
acid, pepsin
and bile salts.
Duodenal and
Gastric ulcer
Chronic
gastritis
Constipation,
diarrhea,
nausea, gastric
discomfort,
indigestion,
dry mouth,
rash, pruritus,
back pain,
dizziness,
drowsiness
May decrease
binding of drug
to
gastrodoudenal
mucosa
imparing
effectiveness.
Separate doses
by 30 mins.
Reconstitute
drug before
instillation
through a
nasogastric tube.
Flush tube up
water to ensure
passage into
stomach
Monitor px for
severe persistent
constipation
Tell the px to
take meds on an
empty stomach,
1hr before each
meal.
CLASSIFICA
TION
MECHANISM OF
ACTION
INDICATION ADVERSE
REACTION
INTERACTION NURSING
CONSIDERATION
BRAND NAME:
Paracetamol
GENERIC
NAME:
Biogesic
DOSAGE:
Antibiotic
Antipyretic
Decrease fever
by inhibiting the
effects of
pyrogens on the
hypothalamic
action leading to
sweating and
vasodilation.
Relieves pain by
inhibiting
prostaglandin
synthesis at the
CNS but does
not have anti-
inflammation
action because
of its minimal
effect on
peripheral
prostaglandin
synthesis
Relief of fever,
minor aches
and pains
CONTRAINDIC
ATION:
Hypersensiti
vity to
acetaminop
hen or
phenacin
Long term
alcohol use
(may cause
hepatotoxici
ty)
Children <
3 years old
unless
directed by
a physician
Malnutrition
Thrombocyt
openia
Arthritic or
rheumatoid
conditions
Hepatic
Necrosis,
rash,
urticaria
Chronic
concurrent use
with NSAIDs,
including
aspirin may
increase the
risk of adverse
reactions
Diflunisal
increase
acetaminophen
blood vessels
and may
increases the
risk of
hepatotoxicity
with chronic
concurrent use.
Administer with a full
glass of water
May be taken with food
or on an empty stomach.
Advise patient to take
medication exactly as
directed and not to take
more than the
recommended amount
Avoid alcohol if taking
more than an occasional
1-2 doses
Use liquid form for
children and patients
who have difficulty
swallowing.
In children, dont exceed
five doses in 24 hours.
Advise patient that drug
is only for short term
use and to consult the
physician if giving to
children for longer than
5 days or adults for
affecting
children <
12 years old
longer than 10 days.
Advise patient or
caregiver that many over
the counter products
contain acetaminophen;
be aware of this when
calculating total daily
dose.
Warn patient that high
doses or unsupervised
long term use can cause
liver damage
CLASSIFICATI
ON
MECHANISM
OF ACTION
INDICATION ADVERSE
REACTION
CONTRAINDICA
TION
NURSING CONSIDERATION
BRAND NAME:
Lactated
Ringers
Solution with
5% Dextrose
(D5LR)
- Hypertonic
-
Nonpyrogenic
, parenteral
fluid,
electrolyte
and nutrient
replenisher
Hypertonic
Solutions are
those that have
an effective
osmolarity
greater than
the body fluids.
This pulls the
fluid into the
vascular by
osmosis
resulting in an
increase
vascular
volume. It
raises
intravascular
osmotic
pressure and
provides fluid,
electrolytes and
calories for
energy.
- Treatment
for persons
needing extra
calories who
cannot
tolerate fluid
overload.
- Treatment
of shock
-As a source
of water,
electrolytes
and calories
or as an
alkalinizing
agent
Allergic
reactions or
anaphylactoid
symptoms
such as
localized or
generalized
urticaria and
pruritis;
periorbital,
facial,
and/or laryng
eal edema,
coughing,
sneezing,
and/or
difficulty
with breathing
Administration of
sodium,
potassium,
calcium, chloride
or lactate could
be clinically
detrimental.
Severe metabolic
acidosis or
alkalosis, and in
severe liver
disease or anoxic
states which
affect lactate
metabolism.
Hypersensitivity
to corn products.
> Do not administer unless
solution is clear and
container is undamaged.
> Caution must be exercised
in the administration of
parenteral fluids, especially
those containing sodium
ions to patients receiving
corticosteroids or
corticotrophin.
>Solution containing acetate
should be used with caution
as excess administration
may result in metabolic
alkalosis.
>Solution containing
dextrose should be used
with caution in patients with
known subclinical or overt
diabetes mellitus.
> Discard unused portion.
> In very low birth weight
infants, excessive or rapid
administration of dextrose
injection may result in
increased serum osmolality
and possible intracerebral
hemorrhage.
You might also like
- D5WDocument1 pageD5WBreena Reubee EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Lactulose (Duphalac, Lilac)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Lactulose (Duphalac, Lilac)AgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- Shanti Kumari: Presented byDocument21 pagesShanti Kumari: Presented byDr-Eng Amir ElsafraweyNo ratings yet
- Acfrogas81a C3gdggyv4xgrao Mdfic3te - x187f1 87lztljhozqte1uwyasvd30we4h6qfxqnls Kkx4fhvgdzsyhiidv6ruak2jsebl1ta-o6xhpricpgy55ribskr1dafecu67-RbikzqhDocument126 pagesAcfrogas81a C3gdggyv4xgrao Mdfic3te - x187f1 87lztljhozqte1uwyasvd30we4h6qfxqnls Kkx4fhvgdzsyhiidv6ruak2jsebl1ta-o6xhpricpgy55ribskr1dafecu67-RbikzqhSiseneg Tasma100% (1)
- Industrial Furnaces, 0471387061Document492 pagesIndustrial Furnaces, 0471387061Khin Aung Shwe90% (10)
- Mefenamic AcidDocument3 pagesMefenamic AcidAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of Mannitol RMCDocument1 pageDrug Study of Mannitol RMCAdrian Ardamil0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudySa Dei100% (1)
- UnasynDocument1 pageUnasynrachieeeNo ratings yet
- DRUG Ferrous SulfateDocument1 pageDRUG Ferrous SulfateLovelaine Busto AlaguiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Sudy RowtinexDocument1 pageDrug Sudy RowtinexdollythesheepNo ratings yet
- Drug Study and NCP!Document8 pagesDrug Study and NCP!Abegail Abaygar100% (1)
- Drug Study Potassium ChlorideDocument5 pagesDrug Study Potassium ChlorideKenneth Mark B. TevesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Duavent.Document1 pageDrug Study Duavent.Clariss AlotaNo ratings yet
- CombiventDocument1 pageCombiventleroux2890No ratings yet
- MetronidazoleDocument2 pagesMetronidazoleJm RomancapNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OralDocument1 pageDrug Study OralBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- ItoprideDocument2 pagesItoprideLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocortisone Ointment-Drug StudyDocument1 pageHydrocortisone Ointment-Drug StudyTrisha CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJ.r. MercadoNo ratings yet
- PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesPrednisoloneKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- DRug StudyDocument6 pagesDRug StudyRochell Torres ArtatesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of ChloramphenicolDocument3 pagesDrug Study of Chloramphenicolcasimir1128No ratings yet
- Cues Problem Physiologic Behavioral: Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements Acute Pain Altered ADLDocument3 pagesCues Problem Physiologic Behavioral: Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements Acute Pain Altered ADLAya BolinasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ferrous Sulfate + FADocument3 pagesDrug Study Ferrous Sulfate + FAKristine Champness100% (1)
- Cefuroxime Drug Study ChanDocument5 pagesCefuroxime Drug Study Chanczeremar chanNo ratings yet
- PNSSDocument2 pagesPNSSBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- TrimetazidineDocument2 pagesTrimetazidinemasheennavirgoNo ratings yet
- Aminoleban Drug StudyDocument1 pageAminoleban Drug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudygayskieNo ratings yet
- D5 0.3%Document1 pageD5 0.3%Aloyan Rose Joy0% (1)
- Drug Study Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument5 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing InterventionsYvonne AgathaNo ratings yet
- Ivf StudyDocument2 pagesIvf StudyDanePepitoNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Ceftriaxone ForgramDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Ceftriaxone ForgramJ-lie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- XtendaDocument2 pagesXtendaAlexis CoronadoNo ratings yet
- DRUG LactuloseDocument1 pageDRUG LactuloseJona Phie Domingo MonteroNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Drug SummDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug SummAminah Yue100% (1)
- Paracetamol (Aeknil), Metoclopramide (Plasil), Cotrimoxazole Susp. (Macromed), PedialyteDocument4 pagesParacetamol (Aeknil), Metoclopramide (Plasil), Cotrimoxazole Susp. (Macromed), PedialyteYum C100% (2)
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route & Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side-Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route & Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side-Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDivine Grace Arreglo AbingNo ratings yet
- CoamoxiclavDocument1 pageCoamoxiclavBbhie AntiguaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY AtorvastatinDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY AtorvastatinKyla BeconiaNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument1 pageCEFUROXIMEJose Luis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument18 pagesDrug AnalysisArt Christian RamosNo ratings yet
- Cefipime HCL (AXERA)Document2 pagesCefipime HCL (AXERA)Kristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis, Megacolon and Narrow Angle Glaucoma, Hypersensitivity To HNBB and Other Components of The ProductDocument3 pagesMyasthenia Gravis, Megacolon and Narrow Angle Glaucoma, Hypersensitivity To HNBB and Other Components of The ProductGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Cefaclor, Salbutamol, Paracetamol and NCPDocument13 pagesCefaclor, Salbutamol, Paracetamol and NCPAriane Rose Saria CedronNo ratings yet
- Drug Study QIDocument8 pagesDrug Study QImaeDonitaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SARAHDocument2 pagesDrug Study SARAHirene Joy DigaoNo ratings yet
- Bearse Tablet InsertDocument2 pagesBearse Tablet InsertLeonard Byun100% (1)
- Drug Study Stugeron and Kalium DuruleDocument1 pageDrug Study Stugeron and Kalium DuruleawesomedawnNo ratings yet
- Atropine SulfateDocument1 pageAtropine SulfateTrishaaMayolNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ApidraDocument1 pageDrug Study ApidraChris Denver Bancale100% (1)
- CEFIXIMEDocument2 pagesCEFIXIMEJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- PrefixDocument8 pagesPrefixleian28No ratings yet
- OxacillinDocument2 pagesOxacillinSatinderSinghNo ratings yet
- K PotaDocument2 pagesK PotaJustine May GervacioNo ratings yet
- BNP (C)Document2 pagesBNP (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CaseDocument3 pagesDrug Study CaseKatrina Ponce100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyDick Morgan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFritzie Beatrice NomusNo ratings yet
- Kalium DuruleDocument3 pagesKalium DurulenebuchadnezzarkingheNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyLovely EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology A ReviewDocument13 pagesPharmacology A ReviewCheriz LukbanNo ratings yet
- Bullets PsychDocument9 pagesBullets PsychCheriz LukbanNo ratings yet
- German Keyboard LayoutDocument1 pageGerman Keyboard LayoutCheriz LukbanNo ratings yet
- Mental HealthDocument25 pagesMental HealthCheriz LukbanNo ratings yet
- Ortho PAthoDocument4 pagesOrtho PAthoCheriz LukbanNo ratings yet
- Online NeetDocument36 pagesOnline NeetDR AKASH ADAMSNo ratings yet
- REPSOL Industrial CatalogDocument57 pagesREPSOL Industrial Catalogturbomax7799No ratings yet
- Bio MaterialsDocument127 pagesBio Materialsprathap somuNo ratings yet
- Ovation LabelDocument4 pagesOvation Labeltt cheneyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Organic Derivatives of WaterDocument3 pagesWorksheet Organic Derivatives of WaterVenicer BalaodNo ratings yet
- Abstract: Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography (MEKC), Is ADocument2 pagesAbstract: Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography (MEKC), Is ALohi DasuNo ratings yet
- 0I. Accident Causes and PreventionDocument52 pages0I. Accident Causes and PreventionGregor Clegane100% (1)
- Qcs 2010 Section 20 Part 4 Drainage Pipes in Trenches PDFDocument5 pagesQcs 2010 Section 20 Part 4 Drainage Pipes in Trenches PDFbryanpastor106No ratings yet
- Clinical PharmacologyDocument2 pagesClinical Pharmacology0921pyNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Chromatography PDFDocument14 pagesIon Exchange Chromatography PDFPromita MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Pds SKL sp1Document2 pagesPds SKL sp1bachrul ulumNo ratings yet
- Internship Report Muhammad ArshadDocument95 pagesInternship Report Muhammad ArshadMusama3838 RaoNo ratings yet
- Dunaferr - Cold - RolledDocument12 pagesDunaferr - Cold - RolledMihály PálffyNo ratings yet
- Weldability Test For Thin Sheet MaterialsDocument6 pagesWeldability Test For Thin Sheet MaterialsAnonymous FHkX0ANo ratings yet
- Science CH - 5 - Rasayanik ParivartanDocument17 pagesScience CH - 5 - Rasayanik ParivartanVijay TrivediNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Momentum Edexel Physics Past Papers Questions & Mark Scheme 2001-2009Document53 pagesUltimate Momentum Edexel Physics Past Papers Questions & Mark Scheme 2001-2009kyred100% (2)
- Type of Protection Code: Rating Features Key Description SB SB-P S1 S1-P S2 S3 S4 S5Document6 pagesType of Protection Code: Rating Features Key Description SB SB-P S1 S1-P S2 S3 S4 S5CHAN NYEINNo ratings yet
- Ficks Law in Different CoordinatesDocument21 pagesFicks Law in Different CoordinatesAl-Kawthari As-SunniNo ratings yet
- JIS K2301-1992 - Fuel Gases and Natural Gas. Method For Chemical Analysis and Testing PDFDocument119 pagesJIS K2301-1992 - Fuel Gases and Natural Gas. Method For Chemical Analysis and Testing PDFDianMulyadiNo ratings yet
- SECTION 14560 Trash Chutes Part 1 - General 1.1 Related DocumentsDocument4 pagesSECTION 14560 Trash Chutes Part 1 - General 1.1 Related DocumentsXristell SalutNo ratings yet
- 2015 Reff2020Document11 pages2015 Reff2020Nandkumar PrasadNo ratings yet
- Jindal2021 Article 3DPrintedCompositeMaterialsForDocument19 pagesJindal2021 Article 3DPrintedCompositeMaterialsForabhishek thoteNo ratings yet
- Tabela Winsor NewtonDocument2 pagesTabela Winsor NewtonKrzysztof KowalskiNo ratings yet
- HLL HITES Approved Make ListDocument39 pagesHLL HITES Approved Make ListSUDHEESH KUMAR SNo ratings yet
- 10.1 James Watson and Francis Crick: A Whiz Kid On Quiz KidsDocument5 pages10.1 James Watson and Francis Crick: A Whiz Kid On Quiz KidsDennis JimenezNo ratings yet
- LNG Receiving Terminals: BY CH - Satvika 16021A2545Document24 pagesLNG Receiving Terminals: BY CH - Satvika 16021A2545Ram Charan Konidela100% (2)