Ebs
Ebs
Uploaded by
AbsaACCopyright:
Available Formats
Ebs
Ebs
Uploaded by
AbsaACCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Ebs
Ebs
Uploaded by
AbsaACCopyright:
Available Formats
EBS
Electronically controlled
Brake system
in motor coaches
System and functional
description
1. Edition
Copyright WABCO 2003
Vehicle Control Systems
An American Standard Company
8150004083
The right of amendment is reserved
Version 001/07.01
EBS
Table of Contents
Page
1.
Introduction / Advantages of EBS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.
System structure in buses
System structure 2-axle bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
WABCO EBS construction kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
System variants . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Wiring diagram 2-axle bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Wiring diagram 3-axle bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.
Description of components
Brake signal transmitter 480 00. ... 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
EBS central module 446 135 ... 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Proportional relay valve 480 202 ... 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3/2 relay valve 480 205 ... 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Axle modulator 480 103 ... 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.
Description of EBS function
Function of the electro-pneumatic unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Function of pneumatic redundancy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Additional redundancy on the front axle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Rear axle redundancy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Electrical / electronic structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Control functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Backup functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Halt brake, brake hold and release aid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.
Error recognition and display
Error recognition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Error display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.
EBS emergency modes / EBS test types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
7.
WABCO PC - Diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Diagnostic equipment for WABCO EBS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Diagnostic Software EBS Euro . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
8.
Parameter Setting
Parameter setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Introduction / Advantages of EBS
EBS
1.
Introduction
Increased brake safety
The demands made on braking systems are increasing
steadily. Therefore, the development and introduction of
an electronic braking system (EBS) is a logical step.
WABCO did not only take existing regulations into
consideration while developing EBS. Top priority was
given to safety and user advantages. This is why a
vehicle with EBS can clearly do more than is required by
law.
EBS increases traffic safety through reduced stopping
distance and improved brake stability. The full diagnosis
and surveillance functions as well as the display of brake
lining wear offer an effective fleet logistics.
The high safety quality attributed to EBS is due to
several factors:
Advantages of EBS
Braking time is reduced through shorter response
time and pressure build-up time of the brakes on
the front and rear axle(s).
The improved ABS function increases vehicle
stability when brakes are activated.
The components of the front and rear axle braking
system and brake lining wear are monitored
permanently.
The integrated ASR function also provides
optimum vehicle stability and traction during start
and acceleration.
EBS reduces service costs considerably.
q
The electronic braking system has a lot of
functions. The aim is to maximise braking safety at
reduced costs, for instance by optimising wheel
brake lining wear.
Setting pressure, according to wear criteria, to the
front and rear axle results in uniform lining wear.
Overall wear is minimised by making the load on all
wheel brakes uniform. Moreover, servicing and
lining replacement are done at the same time. This
reduces down-time costs.
Depending on the vehicle utilisation profile and
other factors, this also means considerable savings
for the vehicle user. In terms of wheel brake service
costs alone, a firsthand owner will save more
money with an electronically braked bus than with
a vehicle with a conventional braking system.
2.
EBS
System structure in buses
EBS braking system for buses with no attachment (4S/4M system)
10
11
12
13
14
3
5
Legend:
EBS components:
Other components:
EBS central module
Compressor
Brake signal transmitter
Air dryer
Proportional relay valve
10
Four-circuit protection valve
ABS solenoid valve
11
Air reservoir
Axle modulator
12
Hand brake valve
3/2 relay valve
13
Relay valve FBA
ABS sensors
14
Brake cylinder
System structure in buses
EBS
2.
WABCO EBS construction kit
The design and structure of WABCO EBS allow high
flexibility for vehicle manufacturers during system
construction.
In terms of range
q subsystem or full system
q addition and cut-off redundancy
q electrical interfaces
the most complex demands can, therefore, be met. To
meet the vital needs of the vehicle owner, WABCO
recommends an EBS with an individual pressure control
unit on the front and rear axle, and which provides for
pneumatic redundancies in all brake circuits.
supply
Battery
2P/1E-EBS
AME
BWG
ECAS
EMR
PRV
REDV
RET
RV
S
V
halt brake
third axle
= Axle modulator
= Brake signal transmitter
= Electronically Air Suspension System
= Electronically engine control
= Proportional relay valve
= 3/2 relay valve (redundancy valve)
= Retarder
= Relay valve
= Speed sensor
= Wear indicator
The EBS described here consists of a dual-circuit, purely
pneumatic unit and a superimposed single-circuit,
electro-pneumatic unit. This configuration is described
as 2P/1E system.
The single-circuit, electro-pneumatic unit comprises a
central electronic control device (central module), the
axle modulator with integrated electronic unit for the rear
axle, and, if necessary, the axle modulator for the third
axle, a brake signal transmitter with two integrated
desired value sensors and brake switches, as well as a
proportional relay valve and two ABS valves for the front
axle.
In terms of structure, the dual-circuit pneumatic unit
basically corresponds to that of a conventional braking
system. This unit serves as redundancy and only
becomes active in case of electro-pneumatic circuit
failure.
2.
EBS
System structure in buses
EBS 4S/4M in buses with optional trailer control
Motor
Engine
Retarder
Retarder
NiveauLevel
control
regelung
Getriebe
Gearbox
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
ISO 7638
ISO 11992
Fahrzeugdatenbus
J 1939
vehicle data busSAE
SAE
J 1939
Luftbehlter
air reservoir
WABCO
446 130 XXX 0
EPB 4S/4M
IIII II IIII III
WABCO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Zentralsteuergert EBS
Bremswertgeber
Central
control unit EBS
Prop. signal
Relaisventil
Brake
transmitter
ABS
Magnetregelventil
Proportional Relay valve
Achsmodulator
ABS Solenoid Control valve
Anhngersteuerventil
Axle
modulator
Splus control
Stabsensoren
Trailer
valve
Verschleisensoren
Splus rod sensor
Redundanzventil
Wear indicators
3/2 relay valve (redundancy valve
2
4
WABCO
WABCO
WABCO
WABCO
C
B
4
7
8
7
8
Anhngertrailer
control
steuerventil
valve
EBS 6S/6M in articulated buses
Engine
Motor
NiveauLevel control
regelung
Getriebe
Gearbox
Retarder
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Fahrzeugdatenbus
J 1939
vehicle data busSAE
SAE
J 1939
Central control unit EBS
1
Zentralsteuergert EBS
Brake signal transmitter
2
Bremswertgeber
Proportional Relay
valve
3
Prop. Relaisventil
ABS Solenoid Control valve
4
ABS Magnetregelventil
Axle modulator
5
Achsmodulator
3/2 relay valve6 (redundancy
valve valve
Redundancy
redundanzventil
Splus rod sensor
7
Splus Stabsensoren
Wear indicators
8
Verschleisensoren
Relaisventil
Relay valve 9
WABCO
446 130 XXX 0
EPB 4S/4M
IIII II IIII III
WABCO
1
8
2
4
WABCO
WABCO
WABCO
WABCO
WABCO
WABCO
W A BC O
6
Optional
4
7
8
7
8
7
8
System structure in buses
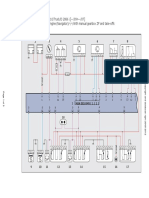
Wiring diagram 841 801 701 0: Dual-axle bus (4S/4M)
EBS
2.
2.
EBS
System structure in buses
Wiring diagram 841 801 702 0: Three-axle bus (6S/6M)
Description of components
EBS
3.
Brake signal transmitter 480 001/ 002 ... 0
The brake signal transmitter is used to produce electrical
and pneumatic signals, and to increase and decrease
the air pressure of the electronically controlled braking
system. The device has a dual-circuit pneumatic and a
dual-circuit electrical structure. Actuation start is recorded electronically by a double switch. The operating tappets route is controlled and transmitted as pulse-width
modulated electrical signal. Further pneumatic redundancy pressure is delivered in circuits 1 and 2. The
pressure in the second circuit is retained slightly in the
process. In case of (electrical or pneumatic) failure of a
circuit, the other circuits remain functional.
Depending on bus type, the brake signal transmitter is
actuated via a running plate (480 002 ... 0) 0) or via a
push pedal using the tappet (480 001 ... 0).
How it works:
3.
EBS
Description of components
EBS central module 446 135 ... 0
The central module is used to control and monitor the
electronically controlled braking system. It determines
the vehicles nominal delay from the signals received by
the brake signal transmitter. The nominal delay and the
wheel velocity measured by the speed sensors are input
signal for the electro-pneumatic control unit, which uses
it to calculate nominal pressure values for the front axle
and rear axle(s). The front axles nominal pressure value
is then compared with the measured actual value, and
any existing deviations corrected with the help of the
proportional relay valve. Moreover, the wheel velocity is
evaluated so that in case of locking, an ABS control can
be carried out by modulating the braking pressure in the
brake cylinders. The central module exchanges EBS
system bus related data with the axle modulators.
The central module communicates with other systems
(engine control unit, retarder, display unit, etc.) via the
vehicle data bus in accordance with SAE J 1939.
KOM-integrated central unit:
10
Description of components
EBS
3.
Proportional relay valve 480 202 ... 0
The proportional relay valve is used in the electronically
controlled braking system to modulate the braking
pressure on the front axle.
It comprises the proportional solenoid valve, relay valve
and pressure sensor. Electrical drive and monitoring
takes place via the central module of the hybrid system
(electro-pneumatically / pneumatically).
The control current impressed by the electronic unit is
transformed via the proportional solenoid valve into a
control pressure for the relay valve. The proportional
relay valves output pressure is proportional to this
pressure. The pneumatic drive on the relay valve takes
place via the brake signal transmitters redundant (backup) pressure.
How it works:
11
3.
EBS
Description of components
3/2 relay valve 480 205 ... 0
The 3/2 relay valve is used to supply air to and remove
air quickly from the brake cylinder on the rear axle in case
of redundancy, and comprises several valve units which
must fulfil the following functions, among others:
q
2/2 solenoid valve for controlling redundancy in
intact electro-pneumatic braking circuit
Relay valve function, to improve the time behaviour
of redundancy,
Pressure retention, to synchronise the beginning of
pressure level control on the front and rear axle, in
case of redundancy .
In case of redundancy, rear axle 1:1 is controlled.
The 3/2 relay valve also has a 3/2 directional control
valve to which current is supplied in case of ABS and is
thus meant to prevent an involuntary drive through of the
rear axle redundancy pressure during ABS control.
How it works:
12
Description of components
EBS
3.
Axle modulator 480 103 ... 0
The axle modulator controls the brake cylinder pressure
on the two sides of a single or dual axle. It has two
pneumatically independent pressure control channels
with an air admission and bleeder valve each, individual
pressure sensors and a joint electronic control unit.
Desired pressure definition and external surveillance
take place via the central module.
Moreover, wheel rotation speed is measured and
evaluated via two speed sensors. In case of wheel-lock
or wheel-spin, the set nominal value is modified.
Provision has been made for the connection of two
sensors to detect brake lining wear.
The axle modulator for the driving axle has an additional
connection for a redundant pneumatic braking circuit. A
two-way check valve on each side drives the higher
pressure (electro-pneumatic or redundant) through to the
brake cylinder.
The axle modulator for the additional axle does not have
three two-way valve.
How it works:
Brake signal transmitter
13
4.
EBS
Description of the EBS function
Function of the electro-pneumatic unit
The electro-pneumatic unit of the EBS system and its
signal path work via
Signals are processed and errors monitored for the rear
axles in the axle modulators, so that the sensor values
can be subsequently transmitted to the central module
via the data bus.
Function of pneumatic redundancy
Brake signal transmitter
two distance sensors determine the nominal value
which is transmitted as pulse-width modulated
signal; two integrated switches are used for nominal
value confirmation, among others
EBS central module
for determining the desired pressure for each axle,
and system control
Proportional relay valve
for pressure control on the front axle
ABS solenoid valves
for the quick ABS pressure control cycles on the left
and right wheel brakes of the front axle
Front and rear axle circuits work with different
redundancy methods. The front axle circuit works
according to the additional redundancy principle, the rear
axle circuit is equipped with a redundancy unit which can
be activated with a valve.
Additional redundancy on the front axle
The front axle circuit which functions pneumatically and
serves as redundancy works via
q
Brake signal transmitter
with 2 pneumatic circuits (front and rear axle)
Proportional relay valve
relay valve with combined pre-control via pneumatic
front axle circuit and the proportional solenoid valve
3/2 relay valve
for restraining the rear axle redundancy pressure
Axle modulators
with integrated control unit for regulating brake
pressures on each side of the rear axle(s).
on the front axle brake cylinder.
EBS can be activated electrically via the driving switch
(pin 15) or by actuating the brake signal transmitter via
the integrated brake switches.
The measured brake pedal distance is interpreted as the
desired delay and converted by the central module into
desired pressure standards for the rear and front axle(s),
using various criteria.
The nominal value standard for the axle modulators is
transmitted by the central module via a central module.
The axle modulators regulate and record the braking
pressures of the rear axles left and right wheel brake.
The braking pressure of the front axle is regulated by the
central module via the proportional relay valve with
integrated pressure sensor.
The wheel rotation speeds are recorded via the sensors
known to the ABS system and serve, among others, as
input quality for the pressure control algorithms, for the
ABS function and for the ASR function.
Before carrying out a wear control operation, the brake
lining wear sensors analyse the brake lining wear on
each wheel brake.
The sensor signals from the front axle are recorded by
the central module whereas those from the rear axle are
recorded by the axle modulators.
14
Electro-pneumatic pressure is delivered via the
proportional valve when the brake signal transmitter is
activated. Depending on the control force, pressure is
supplied to the proportional valve by the brake signal
transmitter in a delayed, pneumatically redundant
manner.
This is added to the pressure delivered already electropneumatically. The pressure delivered by the
proportional valve is adjusted to the set desired pressure
by varying the electro-pneumatic pressure.
In case of electro-pneumatic unit failure, the pneumatic
pressure part alone affects the proportional valve which
can be raised to pmax by actuating the brake pedal
further.
Due to the need to restrain the front axle redundant brake
pressure vis--vis the electro-pneumatic pressure output
(for instance, measures to optimise wear, or integration
of endurance brake), the electrical nominal value
predominates the pneumatic front axle pressure output
on the brake signal transmitter (pneumatic dual circuit of
the brake signal transmitter).
Description of the EBS function
Rear axle redundancy
The pneumatic redundancy of the rear axle works via
q
Brake signal transmitter
with 2 pneumatic circuits (front and rear axle)
3/2 relay valve
with a 3/2 solenoid valve and a relay valve
Relay Valve
for the additional axle
Shuttle valves
integrated in the rear axle modulator
on the brake cylinder of the rear axle(s).
During hitch-free EBS operation, i.e. an electronic
pressure control is possible on the rear axle, the 3/2
solenoid valve in the 3/2 relay valve is set to switch off
redundancy, due to the electronically controlled
pressure.
Electrical / electronic structure
Power is supplied to the electronic braking system
via two separate feed lines.
Clip 30a:
Power supply for the proportional relay valve and the
ABS solenoid valve of the front axle and a brake signal
transmitter circuit.
Clip 30b:
Power supply for the axle modulator(s), 3/2 relay valve,
and the second circuit of the brake signal transmitter.
The central module has a data bus interface for
communication with other vehicle systems (engine, gear
system, retarder).
The axle modulator(s), ABS solenoid valve, and
proportional relay valve of the front axle can be switched
off individually via the short circuit-proof electronic switch
in the central module.
The grounds for the external pressure and wear sensors
are returned to the central module or axle modulator.
Direct connection to the vehicle ground is not allowed.
EBS
4.
Connection between the central module and the axle
modulator(s) is established via an individual CAN system
bus (brake bus).
The brake signal transmitter is separated electrically and
has a dual circuit. The actuation process is recognised
via two switches. The switches have the following
functions:
q
sensing the beginning of the braking process
activating the EBS (if the driving switch is in the off
position)
the offset values of the nominal value sensors are
calibrated and monitored without being activated
The inactivated distance sensors transmit the electrical
brake nominal value as pulse-width modulated signals to
the central module. Both signals of the redundant
electrical transmitter are evaluated equally.
The braking pressure on the front axle is regulated with
an electrically controlled proportional valve. The actualpressure sensors are integrated into the valve
subassemblies. The actual values are transmitted as
analogue signals.
Axle load sensing is not required. The braking pressure
on each axle is determined by a special braking force
distribution function. The valves are actuated by the
central module.
The EBS system status, for instance available errors, is
transmitted by the EBS to a display unit via the vehicle
bus (data line). Alternatively, the display can also take
place via a red and a yellow warning light, as well as via
an TCS light.
Potentiometers must be provided (or possibly alternative
limit switches for drum brakes) for sensing brake lining
wear, and which are read in for the front axle by the
central module.
The activities of each rear axle wear sensor is recorded
by the axle modulator; the results are transmitted via the
system bus brake to the central module. The sensors are
supplied individually and per axle with short circuit-proof
5V.
15
4.
EBS
Description of the EBS function
Control functions
The EBS contains the following renowned functions:
Endurance brake integration
The braking system has an integrated brake
management function which always regulates the
endurance brake when the brake pedal is activated
based on an optimum delay of the vehicle. Optimum
service brake wear is attained through the distribution of
endurance and service brake. This function is an
important part of delay control. The integration of
endurance brake can be deactivated via the switch.
Anti-lock braking system (ABS)
The control logic determines from the wheel rotation
speed whether one or more wheels can be blocked and
decides whether to decrease, maintain, or increase the
braking pressure on it. The rear axle wheels are
controlled in their optimum area in a similar manner
(individual control).
Delay control
Delay control is used to adapt the braking pressure level
to the drivers desired braking rate (def. As z in %).
When the same amount of pressure is applied on the
pedal, the vehicle is often braked in the same manner,
irrespective of the amount of load it is carrying.
If the coefficient of friction on a wheel brake changes (for
instance when the vehicle is moving downhill), the delay
control unit ends every adaptation process when a
predefined, fixed maximum is attained, to enable the
driver to also to feel the deterioration.
Adapting to the braking system hysteresis is also part of
delay control. Each time the brake is released, the
releasing process is chosen in such a way that an
immediate braking force modification is adjusted. This
function results in quick release of the brakes, i.e. car
feeling.
Braking force distribution
The distribution of braking forces on the front and rear
axles depends, among others, on the comparison made
in the program range Delay control between the actual
and nominal value of vehicle delay. The pressure on the
front and rear axles is set in such a way that there is
optimum braking pressure output on these axles.
Brake lining wear control
When the brake is applied partially, the braking pressure
distribution is adjusted, notwithstanding the available
wear signals, i.e. the detected wear difference. The
pressure on the wheel brakes with more lining wear is
reduced slightly, whereas the pressure on the wheel
brakes with less lining wear is increased adequately, so
that there is no change in the overall braking rate
required by the driver.
16
On roads with extremely different adhesion levels
between the right and left sides, vehicles are
uncontrollable or difficult to control using the different
braking forces in ABS (yawning moment development).
As a result, the braking pressure on the front axle brakes
is not adjusted independent of each other, so that the
driver can have a steering reaction (modified individual
control).
If the driving wheels are locked when the endurance
brake is applied on low adhesion levels, possibly
resulting in vehicle instability, the ABS endurance brake
is deactivated via the vehicles CAN bus to maintain
vehicle stability.
Traction control system (TCS)
Just like in the ABS function, while the vehicle is in
motion, the electronic control system determines
whether the wheels are in the stable area of the slip
curve. In case of wheel-spin, the engine output and/or
driving axle wheel braking is adjusted by the axle
modulator via the CAN bus and engine control system.
An activated traction control system is displayed on the
functions display.
Drag torque control
Drag torque occurs in the drive train due to actuation or
change of gas. The resultant braking torque can lead to
driving wheel locking and thus to vehicle instability. Drag
torque control prevents this situation. When a slip state is
exceeded, the engine torque increases and the brake
torque is reduced, irrespective of the driving wheel
velocity. The function of the traction control system ends
when the driving wheel values become stable again.
Description of the EBS function
Backup functions
Generating brake nominal value
The brake pedal distance measured by the sensors in
the brake signal transmitter is transmitted to the central
module where it is processed. The distance is
converted into a nominal delay, based on the
characteristic curve described in the chart.
EBS
4.
Wheel speed sensing and wheel adjustment
Wheel speed sensing corresponds to the sensing
function known to ABS. Automatic wheel adjustment
makes up for the nominal wheel sizes and thus the rolling
circumferences between the axles. If unacceptable
wheel combinations are used, this is recognised as an
error.
If the wheel sizes change, the system requires a change
of parameters.
znominal
z
Halt brake, brake hold and release aid
(Hill holder)
soll
When the halt brake switch in the dashboard is activated,
or if the door control unit so requires, the command
Activate halt brake is transmitted to the central module
via the CAN bus or the halt brake switch. This latter
sends the command to the proportional relay valve and
axle modulator(s), so that 2 bar braking pressure is
exerted on the brake cylinder of the front and rear
axle(s).
Determining the brake nominal value
Pressure control on the front and rear axles
The nominal pressure derived from the brake nominal
value using the higher control algorithms is controlled in
the front and rear axles pressure control circuits. In order
to improve the pressure control properties, the solenoid
current in the solenoid valves are controlled.
If the halt brake command is deactivated via the switch
or via the door electronic unit, and then the driving pedal
activated, the halt brake command is cancelled via the
central module.
17
5.
EBS
Error recognition and display
Failure diagnostics
Error recognition functions are used to avoid the effects
of system failures and/or to inform the driver about
functional problems. The error recognition principles
correspond partly to those of a conventional ABS device
(monitoring the ABS valves, the wheel speed sensors,
the computer hardware).
On the other hand, a big part of the surveillance functions
concerns EBS-specific functions (EBS-specific sensor
analysis, EBS-specific solenoid control, braking pressure
control, data transmission via CAN bus).
In addition to the wheel speed sensor signals, the EBS
evaluates many other sensor signals and checks that
these signals are error-free.
Nominal value sensing (sensors and switches)
The brake signal transmitter provides two sensor and two
switch signals. The (pulse-width modulated) sensor
signals are checked to see whether they conform with
the authorised values, and for mutual deviations. The
correctness of the (digital) switch signals are then tested.
Braking pressure sensing (on the front and rear
axles)
The pressure sensors (analogue) signals in the pressure
control circuits are checked to see whether they
correspond to the authorised values.
Note: The cabling for the two rear axle sensors is not
accessible from outside, since it is an internal axle
modulator cabling.
Rear axle modulators inlet and discharge valve
The rear axles inlet and discharge valves are located
inside the axle modulator. The solenoid cables are not
accessible from outside.
The EBS monitors braking pressure control. The
electrically controlled braking pressure and the
pneumatically redundant pressure are also
monitored.
Too low front axle braking pressure
The availability of minimum braking pressure (on the
front axle at a certain solenoid current supply level) is
checked.
Too high rear axle pressure deviation (from left to
right)
In normal braking processes (neither ABS nor traction
control system TCS -controls) the measured braking
pressure on the left and right sides of the rear axle must
almost be equal. If the braking pressure deviation
exceeds the admissible value, an error is reported.
Rear axle redundancy cannot be switched off
Normally, pneumatic redundancy pressure control in the
rear axle is prevented by the redundancy valve. If an
error makes this deactivation impossible, the rear axle
braking pressure can no longer be reduced during ABS
control, etc. (because there is inlet of non-ABScompatible rear axle redundancy pressure into the rear
axle brake cylinder). Error recognition takes place in this
case.
EBS monitors data transmission
Wear sensing (on the front and rear axles)
The (analogue) signals from the wear sensors are
checked to see whether they correspond to the
admissible values.
between the EBS central module and the axle
modulator (System bus)
between the EBS and other system control devices
(vehicle bus)
The EBS monitors EBS-specific solenoid valve
control.
If communication is impossible or is suddenly cut, an
error is reported.
Front axle proportional relay valve
The frequent solenoid (pressure proportional to the
solenoid current) of the front axle proportional relay valve
is checked to see whether control is carried out correctly.
Rear axle redundancy valve
The rear axle redundancy valves solenoid switch is
monitored to see that control takes place correctly.
18
Error recognition and display
EBS
5.
Error display
Detected errors are transmitted by the EBS central
module to the instrument panel display via the vehicle
data bus, and displayed there.
Alternatively, in vehicles without such a display, errors
can also be reported via a red and a yellow warning light.
A separate TCS light then indicates to the driver the ongoing TCS control activities.
Red Wala:
system deactivated
Yellow Wala:
slight error:
e.g. sensor failure
(emergency mode)
Brake pressure
Supply pressure
19
6.
EBS
Emergency modes/control possibilities
EBS emergency modes
EBS test types
As a rule, certain EBS functions are deactivated when an
error is detected. Functions not impaired by the failure
are maintained. For the EBS-drive with limited functions,
the term emergency mode is used.
The following peculiarities must be observed while
testing the electronically controlled braking system:
q
When the brake is applied > 80% of the pedal
distance and ignition off, the full pressure works on
the front and rear axles.
The following functions can be deactivated if an
error occurs:
Operation without ABS function
The ABS function can be deactivated on a wheel, an
axle, or the entire vehicle. Possible causes: faulty speed
sensor signal, ABS valve error, etc.
Operation without ASR function
The traction control system can be switched off
completely or partially. Complete deactivation means
that both the braking system and the engine control unit
are deactivated.
Partial deactivation means that only the braking system
is deactivated. Possible causes: (faulty speed sensor
signal, etc.)
Pressure control / auxiliary pressure control
Normally, braking pressure control requires braking
pressure sensor signals. When these signals are no
longer available, electrical braking pressure can be
produced. In this case, we talk in terms of pressure
control operation or auxiliary pressure control. However,
the accuracy of this pressure production is limited,
compared to hitch-free pressure control. Possible
causes: Pressure sensor signal failure, etc.)
Redundancy operation
If electrical pressure control becomes impossible, the
corresponding axle is braked with the help of the
pneumatic redundancy pressure. Possible causes:
damaged solenoid, or faulty solenoid cabling, etc.)
20
Maximum pressure level control:
Roller dynanometer test:
(Roller dynanometer function)
A roller dynanometer function was integrated into
the EBS electronic unit so that an electronically
braked KOM can be tested on a roller dynanometer.
This function is used to test the braking pressure at
full load (permitted total weight).
The roller dynanometer function is activated if the
EBS is not switched on via the ignition (class 15)
when the vehicle is braked again, but rather through
activation of the brake signal transmitter via the
integrated brake switches. The front axle and/or
rear axle speed must be < 3 km/h.
Special EBS controls such as endurance brake
integration, delay control and brake lining wear
control are not active when the roller dynanometer
function is active.
The maximum braking pressure can now be
measured. The EBS is working correctly if the
measured braking pressure corresponds to the
basic loaded vehicle design.
WABCO Diagnosis equipment - see: brochure
820 001 029 3
WABCO PC - Diagnosis
EBS
7.
Diagnostic Software
In addition to the familiar diagnosis equipment like
WABCO Compact Tester or the Diagnostic Controller
with program cards, WABCO also offers PC diagnosis.
For all newly integrated WABCO systems such as EBS,
the Diagnostic Software for diagnosis with PCs is offered
in addition to the program card for the Diagnostic
Controller.
The software offers comprehensive and convenient
diagnosis. The program and interface are compatible
with any standard PC or Laptop with the following
characteristics:
Hardware Requirements
The following hardware is required:
notebook / laptop wherever possible
Pentium PC and higher
16 MB main memory, colour display 800x600
approx. 10 MB free hard disk memory
3 " floppy disk drive
1 COM interface (9-pin) for the diagnostic interface
Win95/98/2000, WIN NT
Diagnosis Interface
For establishing diagnosis with the control unit, WABCO
Diagnostic Interface Set, Part No. 446 301 021 0 is
required.
The set contains the interface and a connecting cable to
the PC/laptop (for the COM interface, 9-pin connection).
The vehicle connection on the interface is similar to the
connection for the Diagnostic Controller, permitting the
continued use of connecting cables used in the past.
21
7.
EBS
WABCO PC - Diagnosis
Diagnostic equipment - WABCO EBS
EBS EPB (DaimlerChrysler)
Diagnostic cable
Diagnostic software EPB ACTROS / ATEGO
446 301 517 0 for PC diagnosis
Diagnostic Interface
446 301 021 0 for PC-Diagnostic
Program card EPB ACTROS / ATEGO
446 300 760 0 (D)
Program card EBS CITARO
446 300 766 0 (D)
Diagnostic cable
446 300 340 0
EBS Euro (Motor Vehicle)
Diagnostic cable
Diagnostic software EBS
446 301 548 0 for PC diagnosis
Diagnostic Interface
446 301 021 0 for PC-Diagnostic
Program card EBS Euro
446 300 769 0 (D)
Diagnostic cable
446 300 344 0
22
Diagnostic Software EBS Euro
EBS
7.
Start monitor PC Diagnosis EBS Euro:
Read out diagnosis memory:
23
7.
EBS
Diagnostic Software EBS Euro
Reading out measured values: Pressure sensors
6.88
4.85
6.88
4.96
0.00
5.00
0.00
4.96
Reading out measured values: Wear values
24
51.60
52.00
51.60
51.60
Diagnostic Software EBS Euro
EBS
7.
Reading out measured values: Speed sensors
2.12
0.50
Reading out measured values: Brake signal transmitters
1507.18
1521.92
49.49
26.98
25
7.
EBS
Diagnostic Software EBS Euro
Selection menu Control:
Control: Braking pressure control on front axle
0.00
1.95
26
Diagnostic Software EBS Euro
EBS
7.
Start-up:
Pressure possibility Start-up protocol:
27
7.
EBS
Diagnostic Software EBS Euro
EBS parameter: Input mask No. 1
EBS parameter: Input mask No. 2
28
Diagnostic Software EBS Euro
EBS
7.
Pressure options
29
8.
EBS
Parameter setting
Parameter meaning:
System
Vehicle type
This parameter indicates vehicle type and affects
system configuration.
EBS system:
Indicates the EBS system design.
ASR
the wear area. The value should only be changed
according to the specifications of the vehicle
manufacturer, or by WABCO. These parameters do not
apply if sensors are integrated, and control is active.
Warning light fitted with wear sensors:
If this checkbox is ticked, a warning light or a relay for
switching wear display is monitored.
Start check for warning light wear sensors:
If this checkbox is ticked, the warning light for wear
display is activated during start check.
ASR integrated:
ASR function is permanently activated if this checkbox is
ticked.
Other components
Endurance brake cut-off relay present:
ASR switch type:
You can indicate here whether a switch (in both
positions) or a push-button is fitted.
If this checkbox is ticked, an endurance brake cut-off
relay is controlled and monitored.
Cut-off of Endurance Brake Integration (EBI):
ASR switch function:
You can choose here whether the ASR off-road function
should be activated, or the ASR function deactivated
when the ASR off-road switch is activated.
Wear sensing
Wear control:
If this parameter is not activated, only wear control will
be possible, irrespective of whether or not sensors are
integrated.
Endurance brake integration is activated if the
Endurance Brake Integration checkbox is ticked.
Endurance Brake Integration (EBI) mode:
This parameter is used to adjust the EBI to the city or
tourist coach driving profile. The available vehicle type
parameter settings should only be changed with the
consent of the vehicle manufacturer, or by WABCO.
Trailer control valve present:
If this checkbox is ticked, a trailer control valve is
controlled and monitored.
Wear sensors present:
Tire circumferences:
If wear sensors are fitted on the front and rear axles and
must be evaluated, this checkbox must be ticked.
Standard setting: Wear sensors present.
DV1_15 and DV2_15:
Basic braking pressure settings: VA to HA or HA to ZA in
30
The rolling circumference of the tire equipment must be
entered here according to the vehicle manufacturer or
tire equipment manufacturers specifications. Permitted
values for Pole wheel 100Z is 2550 to 3850, step size 25
mm. Difference between parameter value and tire
circumference: maximum 5%.
Parameter setting
EBS
8.
Settings:
Display ECE R13 Memory error:
If this checkbox is ticked, the error memory bit required
in ECE R13 are displayed when certain errors occur.
Drag torque control released:
Z-soll-Rck:
This parameter is used to coordinate braking force
distribution. The value should only be changed
according to the specifications of the vehicle
manufacturer, or by WABCO.
Drag torque control is released if this checkbox is ticked.
V-Start-Rck
Extended ABS control released:
Extended ABS control is released if this checkbox is
ticked.
This parameter is used to coordinate braking force
distribution. The value should only be changed
according to the specifications of the vehicle
manufacturer, or by WABCO.
AZ1:
Light ASR integrated:
This parameter is used to coordinate braking force
distribution. The value should only be changed
according to the specifications of the vehicle
manufacturer, or by WABCO.
This parameter indicates that the warning light is directly
controlled by the EBS control device, and that the exit is
monitored. Alternatively, the information can be
evaluated on the SAE bus.
BV1 and RBV2:
Yellow warning light present:
This parameter is used to coordinate braking force
distribution. The value should only be changed
according to the specifications of the vehicle
manufacturer, or by WABCO.
This parameter indicates that the warning light is directly
controlled by the EBS control device, and that the exit is
monitored. Alternatively, the warning light information
can be evaluated on the SAE bus.
AV1 and AV2:
This parameter is used to coordinate braking force
distribution. The value should only be changed
according to the specifications of the vehicle
manufacturer, or by WABCO.
Retarder inclination:
Red warning light present:
This parameter indicates that the warning light is directly
controlled by the EBS control device, and that the exit is
monitored. Alternatively, the information can be
evaluated on the SAE bus.
Deactivate roller lock / halt brake:
This parameter is used to lock both functions.
This parameter is used to coordinate braking force
distribution. The value should only be changed
according to the specifications of the vehicle
manufacturer, or by WABCO.
I-Getriebe:
This parameter is used to coordinate braking force
distribution. The value should only be changed
according to the specifications of the vehicle
manufacturer, or by WABCO.
Nominal pressure HSB VA, HA and ZA:
The nominal pressure for the halt brake and roller lock of
the front axle, rear axle, and possibly of the additional
axle is entered here. The value should only be changed
according to the specifications of the vehicle
manufacturer, or by WABCO.
Parameter value x 0.05 bar = nominal pressure.
31
8.
EBS
Parameter setting
Limit speed HSB:
Repeat rate EBC1:
The halt brake and roller lock are not activated by the
EBS if the preset maximum speed is exceeded.
The repeat rate for EBC1 messages can be chosen
here. Only the values 20ms or 100ms are supported.
The value should only be changed according to the
specifications of the vehicle manufacturer.
Axle ratio:
The ratio i of the driving axle control must be entered
here as specified by the vehicle manufacturer.
The value entered is ratio i x 25.
Response pressure VA, HA, ZA:
Repeat rate EBC2:
The repeat rate for EBC2 messages can be chosen
here. The values 20 ms, 50ms or 100ms are supported.
The value should only be changed according to the
specifications of the vehicle manufacturer.
The response pressure of the front axle, rear axle, and
possibly additional axle must be entered here. The value
should only be changed according to the specifications
of the vehicle manufacturer, or by WABCO.
Parameter value x 0.05 bar = response pressure.
Pole wheel teeth number
Front axle, rear axle, and additional axle:
SAE J1939
SAE J1939 monitoring released:
Communication on the SAE J1939 data bus is
monitored if this checkbox is ticked.
32
The Pole wheel teeth number can be entered here for
speed sensing on the corresponding axle. At the
moment only the value 100 is released.
You might also like
- Twin Cylinder OHV BRIGGS & STRATTON PDFDocument101 pagesTwin Cylinder OHV BRIGGS & STRATTON PDFigrekqa100% (13)
- MAN Instructions For Using Wiring DiagramsDocument5 pagesMAN Instructions For Using Wiring DiagramsMircea GilcaNo ratings yet
- Abs ElectricalDocument306 pagesAbs ElectricalYdelkadiasmela Dominguezmorel100% (1)
- MAN EBS 5 Knorr Fault Codes DTCDocument22 pagesMAN EBS 5 Knorr Fault Codes DTCRonit Manojcumar100% (2)
- EBS5 ManDocument370 pagesEBS5 ManBach Nguyen Xuan100% (4)
- MAN EBS Electronic Braking SystemDocument6 pagesMAN EBS Electronic Braking SystemMircea Gilca100% (7)
- Actros Abs EbsDocument32 pagesActros Abs EbsDeleanMihai94% (16)
- MAN PTM CONTROL UNIT Service Information-3Document22 pagesMAN PTM CONTROL UNIT Service Information-3Oroszi Gábor0% (1)
- MAN TGS-TGX Wiring Diagrams Electrical System K100 (2nd Edition) (053-096)Document44 pagesMAN TGS-TGX Wiring Diagrams Electrical System K100 (2nd Edition) (053-096)Myk Voroshchuk100% (1)
- EBS eDocument92 pagesEBS eIan Muhammad67% (3)
- Ecas For Trucks 8150100273 PDFDocument113 pagesEcas For Trucks 8150100273 PDFMircea Gilca86% (7)
- FFR PDFDocument5 pagesFFR PDFmatej1992100% (2)
- Connector C449 - Functions For Automatic Gearbox and Trailer Connection General InformationDocument3 pagesConnector C449 - Functions For Automatic Gearbox and Trailer Connection General InformationmbpajaNo ratings yet
- Daf Ix Ecas4 BlockdiagramDocument46 pagesDaf Ix Ecas4 BlockdiagramMircea Gilca100% (1)
- Ecas 4 PDFDocument66 pagesEcas 4 PDFCarolina83% (6)
- Electronically Controlled Air Suspension (ECAS) For Buses and Trucks With CAN II (SAE 1939) Maintenance 0Document27 pagesElectronically Controlled Air Suspension (ECAS) For Buses and Trucks With CAN II (SAE 1939) Maintenance 0Miller Andres Aroca100% (2)
- SPN FMI Fault Region Fault Reaction Fault Description Remedy Ecas Can2 DTC ListDocument6 pagesSPN FMI Fault Region Fault Reaction Fault Description Remedy Ecas Can2 DTC Listxaime166100% (1)
- Wabco Brakes 2Document35 pagesWabco Brakes 2Shyam Srinivasan100% (3)
- MAN TGA Door Module DiagramDocument10 pagesMAN TGA Door Module DiagramMircea GilcaNo ratings yet
- Overhead Conductor TypesDocument5 pagesOverhead Conductor TypesHumayun Ahsan100% (1)
- 4 PAC InstallationDocument36 pages4 PAC InstallationManuel Espnza50% (2)
- FFR Test Step ListDocument26 pagesFFR Test Step Listumar chNo ratings yet
- ZDR FFR GBDocument26 pagesZDR FFR GBPetru Stefan100% (3)
- Knorr Bremse TebsDocument6 pagesKnorr Bremse Tebsenzo7259No ratings yet
- MAN-Trouble Codes - FFR - 32 A 3527Document28 pagesMAN-Trouble Codes - FFR - 32 A 3527Gastao100% (2)
- T66 2 Ecam 81995985292 EngDocument104 pagesT66 2 Ecam 81995985292 EngGonçalo PereiraNo ratings yet
- EST-42 GearboxDocument64 pagesEST-42 GearboxVilneda77% (13)
- 53 114 An EbsDocument92 pages53 114 An EbsОлег Дочило100% (2)
- EBS e PDFDocument92 pagesEBS e PDFRowan Cornelius100% (2)
- Coduri Man TGXDocument31 pagesCoduri Man TGXMocanu LaurentiuNo ratings yet
- TGX 6x2 Midlift Tractor: Chassis SpecificationDocument4 pagesTGX 6x2 Midlift Tractor: Chassis SpecificationDarNo ratings yet
- N04 - 2 - MAN TeleMatics - Retrofit - TGX - 81991854502 - ENGDocument90 pagesN04 - 2 - MAN TeleMatics - Retrofit - TGX - 81991854502 - ENGAtochkavNo ratings yet
- 53 110 en EbsDocument58 pages53 110 en EbsОлег ДочилоNo ratings yet
- FE - September 2006Document144 pagesFE - September 2006Stefan AslamNo ratings yet
- MANWIS - XSLT - Body Acelerator PedalDocument6 pagesMANWIS - XSLT - Body Acelerator PedalaliNo ratings yet
- Knorr BremseDocument44 pagesKnorr BremseIzz BaharNo ratings yet
- MAN FFR Onboard Computer Fault Codes ListDocument7 pagesMAN FFR Onboard Computer Fault Codes Listhanif khan100% (3)
- MAN TGA FFR Component ListDocument5 pagesMAN TGA FFR Component Listronitmanoj100% (2)
- System Start-Up and Diagnosis: 8.1 GeneralDocument33 pagesSystem Start-Up and Diagnosis: 8.1 GeneralValeriu Dumitrache100% (2)
- Central On-Board Computer 2 (ZBR2) A302Document55 pagesCentral On-Board Computer 2 (ZBR2) A302esam Philipe100% (1)
- ZF Est 48Document98 pagesZF Est 48Андрій ЯвнийNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)Document176 pagesAdaptive Cruise Control (ACC)Tuấn Anh TrươngNo ratings yet
- MAN FFR Onboard Computer Fault Codes ListDocument7 pagesMAN FFR Onboard Computer Fault Codes ListOroszi Gábor100% (1)
- T63 1 M-Tco 1324 81991984832 EngDocument80 pagesT63 1 M-Tco 1324 81991984832 EngGonçalo PereiraNo ratings yet
- SPN (PTM For TGS TGX)Document55 pagesSPN (PTM For TGS TGX)Ihsan SansanNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Management Computer (A403)Document10 pagesVehicle Management Computer (A403)ali100% (3)
- Man Tga 2.Document5 pagesMan Tga 2.Aigars MulisNo ratings yet
- Man EpbDocument4 pagesMan EpbDimaNo ratings yet
- W Wiir Riin NG GD Diia AG GR RA AM M: - English - 9/2016Document586 pagesW Wiir Riin NG GD Diia AG GR RA AM M: - English - 9/2016Pavel100% (1)
- MAN FFR Fault Codes List PDFDocument13 pagesMAN FFR Fault Codes List PDFДмитрий Андрущенко100% (1)
- K100 EwdDocument236 pagesK100 EwdMohamed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Impact - Air Suspension, Component LocationsDocument4 pagesImpact - Air Suspension, Component LocationsAbo FrajNo ratings yet
- ABS 6 System PDFDocument46 pagesABS 6 System PDFVincent Price100% (1)
- Fault Codes: Gearbox (Gearbox - Astronic ZF)Document2 pagesFault Codes: Gearbox (Gearbox - Astronic ZF)Стефан Тасиќ100% (2)
- Man Engine Brake (English)Document8 pagesMan Engine Brake (English)W MoralesNo ratings yet
- Knorr BrakeDocument116 pagesKnorr BrakesengottaiyanNo ratings yet
- ECAS Electronically Controlled Air Suspension/ EFR Electronic Shock Absorber Control 6x2 FNLL (Nordland)Document4 pagesECAS Electronically Controlled Air Suspension/ EFR Electronic Shock Absorber Control 6x2 FNLL (Nordland)Mircea Gilca100% (1)
- Ebs Product Catalogue: ... For Truck & Bus ApplicationsDocument61 pagesEbs Product Catalogue: ... For Truck & Bus ApplicationsjamesNo ratings yet
- MAN TGA FFR Component List PDFDocument5 pagesMAN TGA FFR Component List PDFAlexander Gryshcheniuk100% (1)
- Wabco Tebs eDocument224 pagesWabco Tebs eJelena Tasik100% (4)
- Renault Truck C, D, K, T описаниеDocument259 pagesRenault Truck C, D, K, T описаниеAnatolii100% (3)
- EBS Raid: System and Functional DescriptionDocument40 pagesEBS Raid: System and Functional Descriptionraidhemed100% (1)
- ABS Air Tracks PDFDocument57 pagesABS Air Tracks PDFraidhemed100% (1)
- ECAS TrailerDocument80 pagesECAS TrailerRomica Ciornei100% (1)
- Study of Single Reciprocating Air-CompressorDocument2 pagesStudy of Single Reciprocating Air-Compressorrajivkumardas101No ratings yet
- FZHWDocument6 pagesFZHWЕвгенийNo ratings yet
- 772-f Plano - Vol1 Cab y Vol 2 ChasisDocument21 pages772-f Plano - Vol1 Cab y Vol 2 ChasisAngel Sanchez Vilca100% (1)
- Chart Industries - VS01Document2 pagesChart Industries - VS01criuvosNo ratings yet
- Current Carrying Capacity Table - Calculate Cable Cross SectionDocument7 pagesCurrent Carrying Capacity Table - Calculate Cable Cross SectionRazaqBhat100% (1)
- DGS MU 204 Rev 1Document19 pagesDGS MU 204 Rev 1JOHN DANIALNo ratings yet
- IR Sensor Interfacing With ArduinoDocument10 pagesIR Sensor Interfacing With Arduinoradindra jauharNo ratings yet
- AL4 Pressure Regulation FaultDocument3 pagesAL4 Pressure Regulation FaultHenk Veen100% (2)
- Xerox WC3045 Parts ManualDocument54 pagesXerox WC3045 Parts ManualPaul AlbuNo ratings yet
- Fivalco PDFDocument16 pagesFivalco PDFjhoger2012No ratings yet
- Linear Shaft Motor: Nippon PulseDocument24 pagesLinear Shaft Motor: Nippon PulsemichaelguzziNo ratings yet
- EPIC 950: Thermal Ticket PrinterDocument18 pagesEPIC 950: Thermal Ticket PrinterGabriel RiosNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications For High End Ultrasound Colour Doppler System - 4 June 21Document5 pagesTechnical Specifications For High End Ultrasound Colour Doppler System - 4 June 21pankajNo ratings yet
- Ultrasensor SMX SMO SMPDocument2 pagesUltrasensor SMX SMO SMPyusufbajatNo ratings yet
- VIN Model Designation Order Number License Plate: WDB2030461F130872 Series/model 203.040Document9 pagesVIN Model Designation Order Number License Plate: WDB2030461F130872 Series/model 203.040Ludmila CroitoruNo ratings yet
- 3) TRASMISSIONE T-8450 (Ok) - enDocument15 pages3) TRASMISSIONE T-8450 (Ok) - enЮрийNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Study On A Novel High-Efficiency Bridgeless PFC ConverterDocument9 pagesResearch Article: Study On A Novel High-Efficiency Bridgeless PFC ConverterlordgtyNo ratings yet
- UNIpointDocument6 pagesUNIpointSaroosh MirzaNo ratings yet
- Kenworth AU K220 SpecSheetDocument2 pagesKenworth AU K220 SpecSheetlushnu0% (1)
- Brochure EPP 1665 4 09 Link Box PDFDocument8 pagesBrochure EPP 1665 4 09 Link Box PDFsamsungloverNo ratings yet
- 6FX2001-5QP24 Datasheet enDocument2 pages6FX2001-5QP24 Datasheet enMasoud LotfiNo ratings yet
- Cat HygroGuard E PDFDocument4 pagesCat HygroGuard E PDFWilbur SuandingNo ratings yet
- Experiment No:-: AIM:-To Study The Construction and Working of Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) - TheoryDocument2 pagesExperiment No:-: AIM:-To Study The Construction and Working of Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) - TheoryAnonymous kQpC87iNo ratings yet
- 2014 Mitsubishi Mirage AcDocument13 pages2014 Mitsubishi Mirage AcWilber RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Failure Code Display Algorithm For ECMVDocument4 pagesFailure Code Display Algorithm For ECMValcowo100% (1)
- HAF 922 Product SheetDocument4 pagesHAF 922 Product SheetAlejandro Feliú DiazNo ratings yet