Valves
Valves
Uploaded by
eng_ebrahim_2000Copyright:
Available Formats
Valves
Valves
Uploaded by
eng_ebrahim_2000Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Valves
Valves
Uploaded by
eng_ebrahim_2000Copyright:
Available Formats
Lion DVD
AFA I
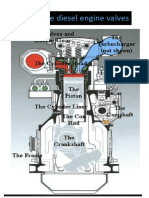
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Engine Valves
Service Training Malaga
In this module we will learn how to analyze valve failures.
Lion DVD
AFA I
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
In This Presentation
Nomenclature
Function
Materials
Manufacturing
Operation
Normal Appearance
Failure Analysis
Service Training Malaga
During operation con rods experience compressive and tensile loads during
combustion and intake strokes.
Lion DVD
AFA I
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Nomenclature
Service Training Malaga
Valve nomenclature includes stem, keeper grooves,
inertial weld, fillet radius, head and hardfacing.
Lion DVD
AFA I
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Valve Functions
Control Gas Flow
Seal Pressure
Withstand Heat
Withstand Acid
Endure Cyclic Loading
Provide Replacement
Service Training Malaga
Valves are primarily used to control the flow of air and exhaust gasses into and out
of the cylinder.
They must be able to withstand high temperatures and corrosive conditions during
millions of load cycles and they are a maintenance item which may need to be
remanufactured at certain maintenance intervals.
Lion DVD
AFA I
Material
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Two Piece Valves
Head austenitic stainless steel
Stem consists mild low carbon steel
Service Training Malaga
Almost all Caterpillar valves in use today are friction welded two piece valves
consisting of a head made from special alloy steel and a stem consisting of a low
alloy steel. This etched cross section shows the different materials.
Lion DVD
AFA I
Manufacturing
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Hardening
Stems hardened to Rc 40
Keeper groove induction
hardened to Rc 55
Service Training Malaga
A closer look at the tip end shows the keeper grooves on a typical valve. Valve
stems are heat treated to about Rc 40 to prevent wear and the keeper grooves are
then induction hardened to Rc 55 to provide extra fatigue strength and wear life.
Lion DVD
Manufacturing
AFA I
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Hard Facing
Forged stainless
steel
Hard facing high
alloy material
Service Training Malaga
The valve head is made from austenitic stainless steel by forging. The flow lines
five the head increased toughness. The head is then heat treated to final hardness
and strength. Notice the area of hard facing surrounding the circumference of the
valve head.This is a welded deposit of high alloy material that resists wear against
the valve seat.
Lion DVD
Manufacturing
AFA I
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Friction Welding
Service Training Malaga
The stem and head are joined by a process called friction welding. The acid etch
shows the joint very clearly.
The darker metal is magnetic while the lighter material is only very slightly
magnetic.
Lion DVD
Manufacturing
Service Training Malaga
AFA I
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Friction Welding
The stem is inertial or friction welded to the head. In
this process a free spinning flywheel containing a fixed
amount of energy holds the stem that is then pushed
against the valve head. The energy of the flywheel is
transferred into frictional heat and causes melting and
adhesion of the stem to the head. The weld is completed
when the flywheel stops. All inertial welds are checked
for soundness.
Lion DVD
Manufacturing
AFA I
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Friction Welding
Find the weld with
the help of a Magnet
Service Training Malaga
10
A magnet can be used to determine the weld location on a new or used valve. This
is also a good way to determine if a valve failed at the weld.
If one side is magnetic and the other side is not, the weld failed.
10
Lion DVD
AFA I
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Operation
Service Training Malaga
11
Valves will function correctly only if they are installed properly and aligned with
the valve seat inserts in the cylinder head.
This means the valve guides must be properly positioned in the cylinder head.
During operation the welded area of the valve stem remains inside the valve guide
as it cannot withstand the higher exhaust temperatures and corrosive exhaust
conditions.
11
Lion DVD
AFA I
Operation
Service Training Malaga
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Spring Force
12
Valves experience loading from the valve spring.
This produces tension in the stem on closing and compression at the keeper grooves
on opening.
12
Lion DVD
Operation
AFA I
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Valve Closing
Tensile load in
valve stem
Service Training Malaga
13
When the valve sits down on the seat upon closing it produces a tensile load
throughout the entire length.This is why it is important to keep valve lash adjusted
properly. This prevents shock loading the valve on seating.
13
Lion DVD
Operation
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
AFA I
Combustion Pressure
Bending stresses
in under head fillet
Service Training Malaga
14
Probably the most severe stress the valve experiences is bending due to combustion
gas loading.
This causes a lot of stress on the valve under head fillet.
14
Lion DVD
AFA I
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
High Temperature Road signs
Thermal Cracks in Fillet Radius
Dished Valve Head
Oxidation, Scale Buildup
Many Valves Damaged
Service Training Malaga
15
Probably the single largest cause of valve failures is overheating. This leads to loss
of strength in the under head fillet which is a high stressed area.
Lets see what the road signs of high temperature operation look like.
15
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
High Temperature
Thermal Fatigue Crack
Service Training Malaga
16
Notice the cracking in the under head fillet. These cracks are caused by excessive
exhaust temperatures. They are thermal fatigue cracks and can lead to a valve head
failing. We should attempt to discover what is causing the excessive temperature.
16
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
High Temperature
Dishing or tuliping
Service Training Malaga
17
Some inlet valves are not made of the type of alloy metal that is used in exhaust
valves.These valves will not withstand excessive temperatures for very long without
drooping. This valve is actually dish shaped or curved due to high temperature
operation.
17
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
High Temperature
Oxidation and
Decomposition
Service Training Malaga
18
This valve head shows oxidation and decomposition of the valve head alloy. This
indicates excessive high temperature operation for extended periods.
18
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
High Temperature
Discoloring
Service Training Malaga
19
If severe temperatures persist, sometimes the valve cannot remove the heat and it
travels up the stem into the valve guide discoloring most of the valve stem.
19
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
High Temperature
Chordal Fractures
Service Training Malaga
20
As valves continue to operate at excessive temperatures the under head fillet starts
to weaken and may experience fracture.
This type of failure is called chordal fracture.
20
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
High Temperature
Chordal Fractures
Service Training Malaga
21
We can see a smooth fracture with beach marks indicating this is a fatigue fracture
which grew over time.
The initiation site is at the top.
21
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
High Temperature
Chordal Fractures
Service Training Malaga
22
Looking at the other side of the fracture we see some ratchet marks extending to the
surface indicating fatigue started on the valve surface.
The oxide deposits on the surface are indicators of excessive high temperature
operation.
Most chordal fracture is caused high temperature operation for extended periods.
22
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Misalignment
Rotating bending stresses
Service Training Malaga
23
Remember that valves must be properly aligned to work correctly. Lets examine
what could happen if the valve guide and the valve seat insert are not on the same
central axis. The valve face will contact the insert harder on one side as it
rotates.This will produce rotating bending stress in the valve stem. Under these
conditions, the valve usually fractures in the stem.
23
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Misalignment
Ratchet Marks
Ratchet
marks
Service Training Malaga
24
Looking at this fracture we see ratchet marks around the valve stem circumference
and beach marks growing inwards.
Final fracture is in the center.
This is typical rotating bending fatigue caused by misalignment between the valve
and valve seat insert.
24
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Bending Fatigue
Ratchet Marks
Beach Marks
Service Training Malaga
25
Looking at this fracture what do we see? Beach marks and ratchet marks indicating
a fatigue crack started at lower right and grew to final fracture at upper left.This is
typical bending fatigue.What might cause this.If the valve head becomes bent, the
valve face only contacts the seat at one point putting a constant bending load on the
stem.
25
Lion DVD
AFA I
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Camshaft Nomenclature
Service Training Malaga
26
To prevent the valve from seating too rapidly or not at all, the cam lobe is designed
to gently lift the valve off the seat.
Accelerate it rapidly to full open position, slow it down until it stops at full open,
and then reverse the process.
This requires careful and accurate valve lash adjustment and good maintenance
practices.
If valve lash is not adjusted correctly, shock loading of the valve on the seat can
occur leading to fracture in the valve stem.
26
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
Service Training Malaga
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Lash Adjustment
27
This is the typical appearance of a valve stem fractured due to improper lash
adjustment.
27
Lion DVD
AFA I
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Improper Lubrication Root Causes
Guide to Loose
Guide to Tight
Wrong Oil Type/Viscosity
Valve to Hot/ Cold
To Much/Little Oil
Service Training Malaga
28
There are many reasons why improper lubrication of the valve in the guide may
occur.
The end result is usually valve sticking.
28
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Piston Contact
Bent valve may indicate valve
was sticking in guide
Service Training Malaga
29
When valves are bent but not broken, this may indicate the valve was sticking in the
guide and hit by the piston.
29
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Piston Contact
Ductile or Brittle fracture
due to impact load
Service Training Malaga
30
Valves broken due to impact by the piston should show a ductile or brittle fracture
due to the impact load.
30
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Piston Contact
Brittle fracture
Service Training Malaga
31
What do we see here? Sparkles, rough surface, no plastic deformation. This is a
brittle fracture due to a single impact load.
The valve and piston collided. We need to discover why the valve was open when
the piston came up.
31
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Piston Contact
The rest of the parts
Service Training Malaga
32
We should inspect the remainder of the valve train.
Bent push rods, broken lifters and valve spring coil contact all indicate the valve
was struck hard by a piston.
32
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Piston Contact
Brittle fracture
Service Training Malaga
33
Note the road signs of brittle fracture and impact load on this follower.
33
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Piston Contact
Keeper may be damaged
made of low carbon steel
Service Training Malaga
34
Keepers may be damaged also due to impact since they are made from soft low
carbon steel.
34
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Piston Contact
Cracks in retainers
Service Training Malaga
35
Cracks may be found in retainers too if impact or shock loading of the valve train
occurred.
35
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Piston Contact
Full coil contact
Service Training Malaga
36
Full coil contact of valve springs are good indications of shock load on the valve
train but may also be evidence of over speed.
36
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
Service Training Malaga
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Piston Contact
37
Most springs have paint markings to identify the spring supplier. Note how the paint
has been removed where the spring coils contact. This indicates the spring was
compressed solid and we should attempt to find out why.
37
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Guttering
Caused by valve face deposits
Mostly common in Gas engines
Service Training Malaga
38
Another way valves fail is by guttering. This is more common in gas engine valves
but occurs anytime valve face deposits form. Deposits often are brittle, crack and
form leakage paths for hot exhaust gasses.
38
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Guttering
Right OIL must be used to
prevent deposit formation
Service Training Malaga
39
Eventually the gasses act like a cutting torch and gutter the valve. This is why it is
extremely critical to keep valve faces and seat inserts free of deposits. The right oil
must be used to prevent deposit formation.
39
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Guide Wear
Improper Lubrication
Poor lube oil quality
Corrosive environment
Service Training Malaga
40
Improper guide lubrication or poor lube oil quality can lead to excessive guide wear.
Worn guides allow valves to slap against seats and can contribute to valve failure.
40
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
Service Training Malaga
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Corrosive Environment
41
Splitting open the guide in the previous picture shows the severe corrosive attack
that has removed all the knurling in the guide and left oxide deposits.
41
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
Service Training Malaga
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Corrosive Environment
42
This same corrosive condition can lead to accelerated valve face and seat wear.
42
Lion DVD
AFA I
Abnormal Conditions
Service Training Malaga
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Foreign Material
43
Another abnormal condition sometimes seen on valves occurs only on the head area
facing the piston.
This appearance is caused by foreign material between the valve and the piston.
Look for the material embedded into the piston top if the engine has aluminum
pistons.
43
Lion DVD
AFA I
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Parts Problem
Friction Weld Failure
Handling Damage
Material Strength
Service Training Malaga
44
Very few valve failures are due to parts problems but lets look at some of the more
common ones.
44
Lion DVD
Parts Problem
AFA I
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Friction Weld Failure
Service Training Malaga
45
This valve failed at the friction weld due to poor weld quality.
Note the swirled condition of the metal.
Remember that a magnet can be used to quickly confirm that this is a weld failure.
45
Lion DVD
Parts Problem
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
AFA I
Valve head and stem not aligned
Service Training Malaga
46
Once in a while the valve head is not correctly aligned with the stem.
This will be obvious if the seat will not grind completely.
46
Lion DVD
AFA I
Parts Problem
CHAPTER: Engine Valves
Spring Problems
Fail along the inner diameter
Due to load is highest there
Service Training Malaga
47
Occasionally valve spring wire may have inclusions present. This can lead to
smooth fatigue fracture of the valve spring. The spring load is highest along the
inner diameter of the spring and this is the place where most fatigue failures will
start.
47
You might also like
- Federal Mogul Valve BulletinDocument18 pagesFederal Mogul Valve BulletinJoe Torren100% (2)
- Introductory Fabrication and Applications PDFDocument447 pagesIntroductory Fabrication and Applications PDFJody HuangNo ratings yet
- API 602 Forged Steel Gate, Globe & Check Valves (Vel-Sfv-Web) PDFDocument22 pagesAPI 602 Forged Steel Gate, Globe & Check Valves (Vel-Sfv-Web) PDFThomasFrenchNo ratings yet
- Valve Guide TypesDocument1 pageValve Guide Typeseng_ebrahim_200067% (3)
- (Oto-Hui - Com) Caterpillar 966H Wheel Loader HYDRAULIC SYSTEMDocument33 pages(Oto-Hui - Com) Caterpillar 966H Wheel Loader HYDRAULIC SYSTEMeng_ebrahim_200090% (21)
- Problem 1 PDFDocument67 pagesProblem 1 PDFStanley ChenNo ratings yet
- Ariel E. Valves 3.2Document48 pagesAriel E. Valves 3.2Manuel Liñeiro100% (1)
- 445دلايل خرابي سوپاپ PDFDocument7 pages445دلايل خرابي سوپاپ PDFmehdi kamaliNo ratings yet
- Valve Failure of Diesel EngineDocument17 pagesValve Failure of Diesel EnginejhpandiNo ratings yet
- Engine Disassembling and ReassemblingDocument6 pagesEngine Disassembling and ReassemblingtselothaiilemariamNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Relief Valve InformationDocument2 pagesCylinder Relief Valve InformationKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- ValvesDocument40 pagesValvesMizta KunaNo ratings yet
- Valve AnalysisDocument5 pagesValve AnalysisghostrpgNo ratings yet
- Cam TerminologyDocument8 pagesCam TerminologychasestarNo ratings yet
- HLADocument6 pagesHLAdhe2dbaseNo ratings yet
- Camshaft - TerminologyDocument7 pagesCamshaft - Terminologyvmgobinath67% (3)
- Epq320 84-94Document5 pagesEpq320 84-94L.No ratings yet
- General Twin Seal 06Document24 pagesGeneral Twin Seal 06Gk GaneshNo ratings yet
- Cooling System DiagnosticsDocument17 pagesCooling System DiagnosticsWakhileNo ratings yet
- P250-250S Cap 06 (CYLINDER HEADVALVES)Document12 pagesP250-250S Cap 06 (CYLINDER HEADVALVES)Minh ChuNo ratings yet
- BW125 - 150 Cap 06 (Testa Valvole)Document12 pagesBW125 - 150 Cap 06 (Testa Valvole)Franckie HyacintheNo ratings yet
- Marine Valvas 1Document4 pagesMarine Valvas 1h1a2s3s4n5h1a2s3s4n5No ratings yet
- Agility125 07Document12 pagesAgility125 07bryan cervantesNo ratings yet
- Valve Twin SealDocument28 pagesValve Twin SealVinay Korekar100% (2)
- 4000 Series Indexing Valve Installation and Troubleshooting GuideDocument6 pages4000 Series Indexing Valve Installation and Troubleshooting GuideClaudio SilvaggiNo ratings yet
- Val-Matic Rubber-Seated Ball Valve: Operation, Maintenance and Installation ManualDocument12 pagesVal-Matic Rubber-Seated Ball Valve: Operation, Maintenance and Installation ManualDhim131267No ratings yet
- SV010203 Safety Valve ManualDocument14 pagesSV010203 Safety Valve ManualwinhlaingooNo ratings yet
- Solenoid ValveDocument3 pagesSolenoid ValveHasanka MadhurangaNo ratings yet
- PLUG VALVES SPVDocument16 pagesPLUG VALVES SPVJorge Hanna AkouriNo ratings yet
- Fausto - TALLER Y PDLDocument12 pagesFausto - TALLER Y PDLromina_montes_1No ratings yet
- Cylinder HeadDocument55 pagesCylinder Headmadhav sai100% (2)
- Study of Automobile ValveDocument6 pagesStudy of Automobile Valvepsmonu54No ratings yet
- Trouble ShootingDocument20 pagesTrouble ShootingSarah FrazierNo ratings yet
- Answer:-T Is A Known Fact That Every Running Machine Has A Tendency To VibrateDocument92 pagesAnswer:-T Is A Known Fact That Every Running Machine Has A Tendency To VibrateSri VasanNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine ValvesDocument2 pagesDiesel Engine ValvesLaxman Singh SankhlaNo ratings yet
- MEO Class 4 Oral Questions With Answers PDFDocument46 pagesMEO Class 4 Oral Questions With Answers PDFArvind Sugumaran85% (13)
- Cameron CatalogueDocument28 pagesCameron CatalogueDaniel Quijada LucarioNo ratings yet
- TM 5-1100 Roller Road, Gasoline Driven, 3-Wheel, 10-Ton, Galion, Model ChiefDocument245 pagesTM 5-1100 Roller Road, Gasoline Driven, 3-Wheel, 10-Ton, Galion, Model ChiefddlevyNo ratings yet
- M 16 Piston 1sect. A Part 2Document67 pagesM 16 Piston 1sect. A Part 2Arief SambestNo ratings yet
- Swing-Flex Check Valve: Operation, Maintenance and Installation ManualDocument8 pagesSwing-Flex Check Valve: Operation, Maintenance and Installation ManualAhmed ShawkyNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips - Gy6 Engine Service ManualDocument39 pagesQdoc - Tips - Gy6 Engine Service ManualAislan ScaravattoNo ratings yet
- MI-259 - Rev. ADocument11 pagesMI-259 - Rev. Aamir barekatiNo ratings yet
- 4 Stroke Diesel Engine Meo Class 2 OralDocument10 pages4 Stroke Diesel Engine Meo Class 2 OralSarath KnNo ratings yet
- Valve - Lash Technical InformationDocument3 pagesValve - Lash Technical Informationborreg12No ratings yet
- Valves HandbookDocument51 pagesValves Handbookedhy_0367% (3)
- MEO Class 2 Orals Function 4 & 6 Q & ADocument8 pagesMEO Class 2 Orals Function 4 & 6 Q & Aneeraj118578% (9)
- Valve Spring Preparation and InstallationDocument18 pagesValve Spring Preparation and InstallationCarloss CastroNo ratings yet
- Sebf9050 01Document16 pagesSebf9050 01faisal ali khanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Gate Valves and Gate Valve TypesDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Gate Valves and Gate Valve Typesramyatan SinghNo ratings yet
- Valves PresentationDocument36 pagesValves PresentationFareedee100% (3)
- Virgo Coker ValvesDocument4 pagesVirgo Coker Valvessoftechq1809100% (1)
- 1.me Components InspectionDocument5 pages1.me Components InspectionAayush AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Gate Valve Troubleshoot-2Document33 pagesGate Valve Troubleshoot-2Trushar GhosalkarNo ratings yet
- A Book of Helpful Tips on Overhauling a Vintage Engine - Including Car, Motorbike and Lawn Mower EnginesFrom EverandA Book of Helpful Tips on Overhauling a Vintage Engine - Including Car, Motorbike and Lawn Mower EnginesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- And Come Back For More Questions: Home User Forums MMD Orals MMD ObjectiveDocument44 pagesAnd Come Back For More Questions: Home User Forums MMD Orals MMD ObjectiveReginNo ratings yet
- 9 Most Common Clutch FailuresDocument3 pages9 Most Common Clutch FailuresJohn StephenNo ratings yet
- 5r55n How-To-Fix-ItDocument87 pages5r55n How-To-Fix-ItDavid Chalker100% (16)
- Yarway Blow Off Valves Operation ManualDocument4 pagesYarway Blow Off Valves Operation ManualLeoNo ratings yet
- LT Valves Gate Globe Check Valves API 600Document28 pagesLT Valves Gate Globe Check Valves API 600yusufNo ratings yet
- 7 StrotDocument16 pages7 StrotLkp. AlfarizqyNo ratings yet
- Exhaust Valves: Rocker Operation of Valves Presents Certain ProblemsDocument4 pagesExhaust Valves: Rocker Operation of Valves Presents Certain ProblemscamalielNo ratings yet
- Valves Gate DamperDocument54 pagesValves Gate DamperLalit MeenaNo ratings yet
- AFA CHAPTER: Engine ValvesDocument26 pagesAFA CHAPTER: Engine ValvesMohamed HamdallahNo ratings yet
- 7.load EstimationDocument35 pages7.load EstimationkrmcharigdcNo ratings yet
- Piston Ring FunctionDocument1 pagePiston Ring Functioneng_ebrahim_2000No ratings yet
- Valve Seat Ring TypesDocument1 pageValve Seat Ring Typeseng_ebrahim_2000No ratings yet
- Types: Piston Rings Cylinder Liners/finned Cylinders AssemblyDocument3 pagesTypes: Piston Rings Cylinder Liners/finned Cylinders Assemblyeng_ebrahim_20000% (1)
- Steering SystemDocument236 pagesSteering Systemeng_ebrahim_2000100% (1)
- PDF C 3 DocumentDocument17 pagesPDF C 3 Documenteng_ebrahim_2000100% (2)
- Fuel, Intake and Exhaust SystemsDocument242 pagesFuel, Intake and Exhaust Systemseng_ebrahim_2000100% (4)
- Pdfcdocum 2 EntDocument14 pagesPdfcdocum 2 Enteng_ebrahim_2000100% (2)
- (Oto-Hui - Com) Doosan Hydraulic BasicDocument76 pages(Oto-Hui - Com) Doosan Hydraulic Basiceng_ebrahim_2000100% (2)
- Rear AxlesDocument228 pagesRear Axleseng_ebrahim_2000100% (1)
- Braking SystemDocument204 pagesBraking Systemeng_ebrahim_2000No ratings yet
- 2659 SldeDocument44 pages2659 Sldeeng_ebrahim_2000100% (1)
- SERV2633 - Monitor & Implement - Text - 992GDocument103 pagesSERV2633 - Monitor & Implement - Text - 992Geng_ebrahim_2000100% (2)
- Acert Technology c9Document71 pagesAcert Technology c9eng_ebrahim_200075% (4)
- Serv1830 TXTDocument269 pagesServ1830 TXTeng_ebrahim_2000100% (3)
- Sk200-6 Pump & Regulator ExplainingDocument17 pagesSk200-6 Pump & Regulator Explainingeng_ebrahim_200096% (74)
- (Oto-Hui - Com) en - Hydraulic CoursesDocument47 pages(Oto-Hui - Com) en - Hydraulic Courseseng_ebrahim_2000100% (1)
- LS الاختبار الاول (النهائي) 2023-2024 physics grade 12Document3 pagesLS الاختبار الاول (النهائي) 2023-2024 physics grade 12jourymestrah3182019No ratings yet
- UST College of Science Analytical Chemistry 3 Laboratory:, 36 PagesDocument3 pagesUST College of Science Analytical Chemistry 3 Laboratory:, 36 PagesKENT BENEDICT PERALESNo ratings yet
- Modified Windkessel Model Applied in A Tubular Pulsation Dampener AnalysisDocument11 pagesModified Windkessel Model Applied in A Tubular Pulsation Dampener AnalysisFrancesca CoattiNo ratings yet
- Laser Plasma InteractionDocument22 pagesLaser Plasma InteractionrabeaNo ratings yet
- KupdfDocument7 pagesKupdfKayezelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Convective Mass TransferDocument34 pagesConvective Mass TransferRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration CircuitDocument32 pagesRefrigeration CircuitHassan Iftekhar Ahmed50% (2)
- 10.1016@0008 8846 (96) 82365 9Document2 pages10.1016@0008 8846 (96) 82365 9nimabsnNo ratings yet
- ME201 Material Science & Engineering: Imperfections in SolidsDocument30 pagesME201 Material Science & Engineering: Imperfections in SolidsAmar BeheraNo ratings yet
- PART VI, Chapter 8, DetailingDocument25 pagesPART VI, Chapter 8, DetailingLutfor RahmanNo ratings yet
- Soluble Oakflo 800Document2 pagesSoluble Oakflo 800slpampcpoNo ratings yet
- Form Six Series OneDocument3 pagesForm Six Series OneSabrina LinuxNo ratings yet
- Memoria de Cálculo CorreasDocument7 pagesMemoria de Cálculo CorreasAbner Ramos ApazaNo ratings yet
- AISC Channel Design 360-16Document6 pagesAISC Channel Design 360-16Pankaj_Taneja_9684No ratings yet
- Boiler Water Wall Tube Inspection With or Without ScaffoldingDocument3 pagesBoiler Water Wall Tube Inspection With or Without ScaffoldingHyujeii MceNo ratings yet
- Generator Space HeatersDocument3 pagesGenerator Space Heaterslinkangjun0621No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 OxidationDocument49 pagesChapter 3 OxidationsunNo ratings yet
- Directions: Choose The Best Answer For Each Multiple Choice Question. Write The Best Answer On The BlankDocument3 pagesDirections: Choose The Best Answer For Each Multiple Choice Question. Write The Best Answer On The BlankRanulfo Mayol100% (1)
- Biosensor PresentationDocument30 pagesBiosensor PresentationvjpatilkaradNo ratings yet
- Janun HXDocument8 pagesJanun HXTHE SEZARNo ratings yet
- Hadron Spectroscopy With Lattice QCDDocument35 pagesHadron Spectroscopy With Lattice QCDSajjad MarriNo ratings yet
- 2 Grillage Analysis of Bridge DecksDocument11 pages2 Grillage Analysis of Bridge Decksahmad fakhruddinNo ratings yet
- 14 3302013ShearStrengthDocument55 pages14 3302013ShearStrengthGeorgeNo ratings yet
- What Is EmulgelDocument8 pagesWhat Is EmulgelTeha RedloverzNo ratings yet
- Steam Trap DatasheetDocument1 pageSteam Trap DatasheetAkram VhoraNo ratings yet
- 16-11-24 - Jr.C-120 - Jee-Main - WTM-21 - Key & Sol'sDocument19 pages16-11-24 - Jr.C-120 - Jee-Main - WTM-21 - Key & Sol'sRamuNo ratings yet
- Seismic Evaluation of Existing BLDGDocument33 pagesSeismic Evaluation of Existing BLDGMunna BhaiNo ratings yet
- GFD I Problem Set 2 SolutionsDocument4 pagesGFD I Problem Set 2 SolutionskazoncaNo ratings yet