0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
404 viewsCell Signalling Test
This document contains a 20 question quiz on cell signaling for AP Biology. It covers topics like the similarities between plant and bacterial cell signaling systems, the main stages of the cell signaling process, the types of membrane receptors, the roles of ligands, G-proteins and tyrosine kinases in signal transduction, calcium signaling as a secondary messenger, and how cholera causes profuse diarrhea by interfering with cell signaling pathways.
Uploaded by
APbio001Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
404 viewsCell Signalling Test
This document contains a 20 question quiz on cell signaling for AP Biology. It covers topics like the similarities between plant and bacterial cell signaling systems, the main stages of the cell signaling process, the types of membrane receptors, the roles of ligands, G-proteins and tyrosine kinases in signal transduction, calcium signaling as a secondary messenger, and how cholera causes profuse diarrhea by interfering with cell signaling pathways.
Uploaded by
APbio001Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 3
AP BIOLOGY- MR.
MENDOZA 1
Cell Signaling Test
1. Cell signaling systems in plants and bacteria have
a. No similarity, after all they are completely different life
forms
b. A relationship that is similar to that between yeast and
mammals
c. Share only .0009% similarity
d. Are exactly the same
2. The cell signal transduction pathway is
a. the way a signal is converted into energy
b. a series of steps to signaling other cells
c. a series of signals that combine to propagate a message
d. a series of steps by which a signal is converted into a
specific cellular response
3. Paracrine signaling is similar to endocrine signaling except that
paracrine signaling occurs in between
a. Cells that are close to one another
b. Cells that are far away from each other
c. Cells In different organisms
d. Cells of a plant
4. What system transports hormones in animals?
a. Respiratory
b. Circulatory
c. Lymph
d. Endocrine system
5. What are the three stages , in order, of the cell signaling
process?
a. Creation-Response-Expansion
b. Reception-Transduction-Response
c. Receive- Increase-React
d. Recreate-Encompass-Relocate
6. Cells can communicate when they are in direct contact in which
of the following ways?
a. Gap Junctions
b. Plasmodesmata
c. Interaction of cell surface molecules
d. All of the above
7. Which of these is NOT part of the stages of the cell signaling process?
a. Reception
b. Transferring
c. Response
d. They are all part of the process
8. What is a ligand?
a. A small molecule that non-specifically binds to a larger molecule
b. A large molecule that binds to a larger molecule
c. A small molecule that binds to a larger molecule with a high degree
of specificity.
AP BIOLOGY- MR. MENDOZA 1
d. None of the above
9. Which of the following is not a main type of membrane bound receptor?
a. G-protein-linked receptors
b. Tyrosine-kinase receptors
c. Gap Junctions
d. Ligand-gated ion-channel receptors
10. What do the structures of g-proteins look like?
a. Hydrophilic regions
b. There is one B-pleated sheet
c. There are six alpha-helices
d. There are seven alpha-helices
11. Which of these steps in the sequence of steps whereby a signal molecule binding
to a G-protein receptor can cause an intracellular response is wrong?
a. Signal molecule binds to cell membrane receptor
b. binds inactive Tyrosine kinase and causes GTP to replace GDP on
protein thereby activating Tyrosine kinase.
c. activated G-protein binds another protein (usually an enzyme) and
alters the activity of the enzyme
d. get cell response
12. What is the structure of a tyrosine kinase receptor before it binds to the
signal?
a. Double polypeptides
b. Triple polypeptides
c. Individual polypeptides
d. Three individual
13. When the signal binds to the receptor two receptor polypeptides
aggregate forming a dimmer, this aggregation activates the tyrosine-
kinase parts of both polypeptides and these phosphorylate the tyrosines
on the tail of the other polypeptide.
a. G-Protein is activated
b. G-Protein is inactivated
c. Tyrosine Kinase is inactivated
d. Tyrosine Kinase is activated
14. These are enzymes that remove phosphate groups from proteins
a. Protein kinase
b. G-protiens
c. RNAses
d. Protein phosphatase
15. The concentration of Calcium ions within the cytoplasm of the cell is very
low. This allows its use as,
a. conductor of electrical signals
b. Hydrolyser
c. Primary messenger
d. Secondary messenger
AP BIOLOGY- MR. MENDOZA 1
16. Phospholipase C does what in the use of calcium as a
secondary messenger
a. converts a sugar into DAG and IP3
b. converts a protein into a calcium ion channel
c. converts a membrane lipid into a calcium ion channel
d. converts a lipid into DAG and IP3
17.In the Calcium secondary messenger system calcium
a. binds to the G-protein to activate it
b. binds to the ion-gated protein to release more protein
c. binds to the IP3 to activate it
d. interact with proteins to activate them
18. What could be responsible for activating genes in a signaling
pathway?
a. G-proteins
b. Protein kinases
c. Transcription factors
d. DNA
19. Protein A produces 10 molecules which causes protein B to
produce 100 which then makes protein C produce 1000. What is
this process called?
a. Signaling system
b. Signal deamplification
c. Signal amplification
d. IP3 activation
20. In the disease cholera,
a. a bacteria destroys lumen cells cause bloody stool
b. a bacteria causes DNA transcription factors in the lumen
cells to fail
c. a protein produced by bacteria interferes with protein
kinases causing profuse diarrhea
d. a protein produced by the bacteria modifies G-proteins that
then makes them fail causing profuse diarrhea
You might also like
- Molecular Biology of The Cell, Sixth Edition Chapter 11 Membrane Transport of Small Molecules and The Electrical Properties of MembranesNo ratings yetMolecular Biology of The Cell, Sixth Edition Chapter 11 Membrane Transport of Small Molecules and The Electrical Properties of Membranes24 pages
- Kode Icd 10 Tersering Di Poliklinik Obstetri Dan Ginekologi - Edit100% (2)Kode Icd 10 Tersering Di Poliklinik Obstetri Dan Ginekologi - Edit5 pages
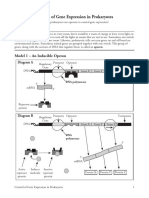
- 17 Control of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes-S PDFNo ratings yet17 Control of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes-S PDF8 pages
- Molecular Biology of The Cell 5th Edition Alberts Test Bank0% (1)Molecular Biology of The Cell 5th Edition Alberts Test Bank10 pages
- Ch07 Test File-Cell Signaling and CommunicationNo ratings yetCh07 Test File-Cell Signaling and Communication39 pages
- Gene Expression and Regulation: Ap BiologyNo ratings yetGene Expression and Regulation: Ap Biology16 pages
- AP Biology Unit 2 - Cell Structure and FunctionNo ratings yetAP Biology Unit 2 - Cell Structure and Function12 pages
- Cell Nuclear Division Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)100% (1)Cell Nuclear Division Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)6 pages
- Chapter 7 Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene Mapping100% (2)Chapter 7 Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene Mapping20 pages
- British Biology Olympiad 2013: Time Allowed 1No ratings yetBritish Biology Olympiad 2013: Time Allowed 125 pages
- CH 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling - Biology in FocusNo ratings yetCH 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling - Biology in Focus8 pages
- Multiple Choice On Proteins - MCQ Biology - Learning Biology Through MCQsNo ratings yetMultiple Choice On Proteins - MCQ Biology - Learning Biology Through MCQs5 pages
- AP Biology Cell Respiration Quiz Study Guide ANSWERSNo ratings yetAP Biology Cell Respiration Quiz Study Guide ANSWERS4 pages
- Chromosomes and Karyotyping: Dr. Nisrine Bissar-TadmouriNo ratings yetChromosomes and Karyotyping: Dr. Nisrine Bissar-Tadmouri21 pages
- Name: - Date: - Period: - AP Biology Genetics Problems PracticeNo ratings yetName: - Date: - Period: - AP Biology Genetics Problems Practice5 pages
- Science behind Non-specific Science: (For Molecular Biologist & Biotechnologist)From EverandScience behind Non-specific Science: (For Molecular Biologist & Biotechnologist)No ratings yet
- Coronavirus Update (Live) : 1,080,846 Cases and 58,120 Deaths From COVID-19 Virus Outbreak - WorldometerNo ratings yetCoronavirus Update (Live) : 1,080,846 Cases and 58,120 Deaths From COVID-19 Virus Outbreak - Worldometer20 pages
- Biomechanical Principles of Tooth Preparation (Esthetic)100% (1)Biomechanical Principles of Tooth Preparation (Esthetic)16 pages
- Read The Following Text and Use The Information To Answer The Questions BelowNo ratings yetRead The Following Text and Use The Information To Answer The Questions Below11 pages
- Buffalo Medical Group, P.C.: Viral ExanthemNo ratings yetBuffalo Medical Group, P.C.: Viral Exanthem1 page
- ANANYA_NANDWANI_YATISH_LAP_24_SR176_S_63787No ratings yetANANYA_NANDWANI_YATISH_LAP_24_SR176_S_637874 pages
- 10 Biology Structural Organization of AnimalsNo ratings yet10 Biology Structural Organization of Animals2 pages