Flexible Pavement Design
Flexible Pavement Design
Uploaded by
nunajihahCopyright:
Available Formats
Flexible Pavement Design
Flexible Pavement Design
Uploaded by
nunajihahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Flexible Pavement Design
Flexible Pavement Design
Uploaded by
nunajihahCopyright:
Available Formats
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
UNIT
UNIT 14
14
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
OBJECTIVES
General Objective
To know the methods and procedures in designing the flexible pavement for
roads in Malaysia.
Specific Objectives
At the end of the unit you should be able to :
describe the basic layers of road design
calculate the design using the required formula and figure.
design the basic flexible pavement using JKR method.
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
INPUT
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
14.0 INTRODUCTION
A typical section through a pavement is shown in the following sketch ( not to
scale )
Wearing course
Surfacing
Base course
Upper
Road-base
Lower
Sub-base
Capping
Sub-grade
In some type of construction some layers maybe combined.
14.0.1 Foundation
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
Foundation provides uniform support to the pavement through its
life so that maintenance operation is confined to the upper level of the
pavement.
i. Sub-grade
either natural soil or material placed to form
embankment.
ii. Capping
on sub-grade with a low CBR, a capping layer
is required provide working. Platform on which
sub-base construction can proceed with
minimum intersection from wet whether a
minimize effect at weak sub-grade on road
performance.
14.0.2 Sub-base
This layer forms the upper of the pavement foundation and
provides a regulated working platform at a consistent strength on which to
transport, place and compact the bound layers of pavement.
14.0.3 Road Base
Road base is a main structural element that purposes to spread
induced by repeated wheel loads over the foundation and to with stand
internal stresses without excessive deformation.
14.0.4 Surfacing
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
Surfacing is done in order to provide acceptable running surface of
adequate skid resistance and to reduce water penetration to underlying
layer.
14.1 FACTORS FOR DESIGN
14.1.1 Failure Criterion
The definition from Croney, failure as transformation shape or deflection of 20mm
tires lane not speeding that measuring from ground level.
Slow lane
Fast lane
20 mm
14.1.2 Traffic Loading
Protection of the sub-grade from the loading imposed by traffic is one of
the primary functions of a pavement structure. The designer must provide a
pavement that can withstand a large number of repeated applications of a
variable-magnitude loading. The primary loading factors that are important in
flexible pavement design are
1. Magnitude of axle (and wheel) loads.
2. Volume and composition of axle loads.
3. Tire pressure and contact area.
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
The magnitude of maximum loading is commonly controlled by legal load
limits. Traffic survey and loadometer studies are often used to establish the
relative magnitude and occurrence of the various loading to which a pavement
during its design life is a very difficult but obviously important task. Most design
procedures provide for an increase in traffic volume on the basis of experience
by using some estimate growth rate.
14.1.3 Climate or Environment
The climate or environment in which a flexible pavement is to be
established has an important influence on the behavior and performance of the
various materials in the pavement and sub-grade. Probably the two climatic
factors of major significance are temperature and moisture.
The magnitude of temperature and its fluctuation affect the properties of
certain materials. For example, high temperatures cause asphaltic concrete to
lose stability whereas at low temperatures asphaltic concrete becomes very hard
and stiff. Low temperature and temperature fluctuations are also associated with
frost heave and freeze-thaw damage. Granular materials, if not properly graded,
can experience frost heave. Likewise, the sub-grade can exhibit extensive loss in
strength if it becomes frozen. Certain stabilized materials can suffer substantial if
large numbers of freeze-thaw cycles occur in the material.
Moisture also has an important influence on the behavior and performance
of many materials. Sub-grade soils and other paving materials weaken
appreciably when saturated, and certain clayey soils exhibit substantial moistureinduced volume change.
14.2 FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN METHOD
14.2.1 JKR Method
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
This method is a combination of two methods above using a formula and
figures from the result of the testing. A complete guideline for pavement
design can be found in Arahan Teknik (Jalan) 5/85. The thickness of the
pavement depends on the CBR value and the Total Cumulative of
Standard Axle ( JBGP ).
Some data need to be collected before starting any design. They are;
i.
Design life.
ii.
Road hierarchy base of JKR classification.
iii.
Average daily traffic volume.
iv.
Percentage of commercial vehicle.
v.
Yearly rate of traffic growth.
vi.
CBR value for sub-grade.
vii.
Topography condition.
14.2.3.1 Design Life
The design life on JKR Design Method is suggested for 10 years.
The design life begins from the road starts in use for traffic until the
maintenance is required.
14.2.3.2 Road Hierarchy Base Of JKR Classification.
a. Road Classification and its Construction Material.
CLASS
A1
TYPES OF CONSTRUCTION
Concrete Surfacing
A2
Hard Bituminous Metalled
Hard Waterbound Metalled
Hard Bituminous Sealed
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
Gravelled Waterbound
Soil Surfacing
b. Category and its road width.
CATEGORY
WIDTH OF ROAD
RESAVE
01
W (m)
4.5
R (cm)
20.0
02
5.0
30.0
03
6.0
30.0
04
7.0
40.0
05
7.5
40.0
06
3.5 per lane
40.0 or more
Notes : 01 03 Village Roads.
04 06 Urban Roads.
14.2.3.3 Classification by JKR Standard
Road hierarchy
Description
R1U & R1 ( A)U1 ( A) The lowest of hierarchy and geometry design level. Traffic for one
way.
R2U 2
This road hierarchy is same like
level is lowest from
R3
U3
R3
U3
type. Geometry design
type. The lowest hierarchy for single
carriageway.
R3U 3
R4U 4
This road is design for local traffic. Geometry design level low
and non inflow traffic control.
Another road is allowed to intersect in the same level. Geometry
design level is intermediate. Allowed maximum velocity
intermediate.
R5U 5
R6U 6
Inflow control degree half. Distance quite far. Geometry design
level high.
Inflow control degree fully. Distance far. Geometry design level
high
Notes :
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
R Rural
U Urban
14.2.3.3 Traffic Estimation
To design using this method, commercial vehicles without loading
weight more than 1500 kg are to be taken.
The formula is include:
Pc
1
x365 x
100
2
Vo = PLH
Where :
Vo
Total of Yearly Commercial Vehicle for one
direction.( JBKP )
PLH
Average Daily
Traffic Ratio for two directions.
Pc
Commercial Vehicle Percentage.
To determine the Total of Yearly Commercial Vehicle ( JBKP ) for
the one direction for ever lasting Design Life, we have to apply
following formula;
Vc =
Vo 1 r 1
r
Where;
Vc
JBKP at one direction for x year.
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
Rate of Traffic Growth.
Road pavement Design Life ( in years unit )
To determine the Total Cumulative of Standard Axle ( JBGP ) for
traffic mixture, equivalent axle load concept is used.
JBGP = JBKP x equivalent factor
Where ;
JBKP =
Vc
Equivalent Factor
= use the data in Table 10.7 = e
Thus,
JBKP = Vc x e
Using the JKR Method, the traffic volume checklist is used by
comparing the maximum traffic volume. The formula is;
Vx = V 1 ( 1 + r ) X
Where;
Vx
The total traffic volume (commercial and non
commercial) at the end of pavement design life
of one direction after x year.
V1
The Daily Traffic Volume of one direction
Rate of Yearly Traffic Growth.
Life design (in years unit)
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
c=IxRxT
Where;
c
Maxima Traffic Loading per hour for one way.
Absolute Traffic Loading per hour - ( Refer
Table 10.8 )
Road Decreasing Factor ( Refer
Table 10.9 )
Traffic Decreasing Factor ( Refer Table
10.10 )
In JKR Standard, Traffic Loading for an hour is assumed that equal
with 10 % daily loading, as:
C = 10 x c
Where;
C
Daily Traffic Loading ( 24 hours traffic loading
at one direction)
Traffic Loading per hour.
With comparison C value and Vx, we can conclude that;
a). C > Vx
Road still obtain to support the Traffic Volume
at the end of the life design for x years.
b). C < Vx
Road cannot obtain to support the Traffic
volume at the end of the life design for x
years.
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
For (b) condition, this formula are used,
C = V ( 1 + r )n
Where;
n=
log(C / V )
log(1 r )
Daily Traffic Loading for one way ( 24 hours )
Daily Traffic Volume for one way that
assumed loaded for road.
Rate of Yearly Traffic Growth.
Life Design.
14.2.3.4 CBR-Sub-grade Value
To determine the CBR value, 1.0 m sub-grade soil must be taken
from the hard rock level. To get CBR for sub-grade design, this
formula must be applied.
NGC (%) =
Where;
( NGC1)1 / 3 h1 ( NGC 2)1 / 3 h2 ............ ( NGC n)1 / 3 hn
100
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
NGC1, NGC2 ,
= CBR value for layer 1,2 .
h1, h2
= soil deepness from form level for
sample 1,2 .
14.2.3.5 Pavement Thickness Design
Figure 10.8 shows the Nomograph Thickness Design that is used
to design pavement thickness. An early process of design, the
CBR (Sub-grade) and JBGP value must be determined first. To use
the Nomograph, the following steps are normally applied.
Line A value is fixed to 3% and line B is the required JBGP. Draw a
straight crossed line. Then determine C values i.e the thickness
Equivalent, (TA).
a. Insert CBR design value at the line A and draw a line by using
previous C value until crossing line D, Determine D value i.e the
Equivalent Thickness Interval (TA), if all the entire pavement is
constructed from the wearing course or road base.
To determine the thickness of each pavement layer, table 10.11 and
table 10.12 is used with the following formula below i.e to determine
D1, D2 and D3 value of the surface layers, base and road sub-base.
SN = a1D1 + a2D2 + a3D3
Where,
a 1, a 2, a 3
Determine from the table 10.11 based on the
types of pavement requirement at the certain
layers.
Layer Structure Coefficient.
Highway Engineering
D1, D2, D3
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
Approximate thickness design of the certain
layer ( minimum thickness value according to
table 10.12 )
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
ACTIVITY 14
TEST YOUR UNDERSTANDING BEFORE YOU CONTINUE WITH THE NEXT
INPUT
Question
1. State the factors of design that will give impact on to the designing of
flexible pavement.
2. What is the meaning of R2U 2 in road hierarchy outlined by JKR standard.
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
FEEDBACK ON
ACTIVITY 14
Answer
1.
a. Failure Criterion
b. Traffic Loading
c. Climate or Environment
d. Moisture
2.
R2U 2 -
This road hierarchy is same like R3
lowest from R3
U 3 type. Geometry design level is
U 3 type. The lowest hierarchy for single carriageway. R is
for Rural and U is for urban,
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
C3010 / UNIT 14
Question
A road with hierarchy of 05 has a surface width of 7.0 m and road reserve of
40.0m is to be built as a main road in a residential area. It has a initial average
daily traffic of 7000cv/day in both directions. The rate of traffic growth is 7%.
Percentage of commercial vehicle is 25%. Design a flexible pavement for the
road which needs a design life of 10 years. The CBR for sub-grade of the road is
5%. ( Employ the JKR Malaysia Design Method ).
Note:
Requirement of pavement layers:
i.
Wearing Course
= Asphalt Concrete.
ii.
Road-Base Course
= Broken Aggregate.
iii.
Sub-Base Course
= Broken Aggregate.
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
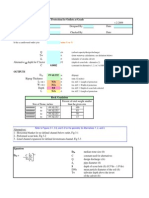
Answer
Pc
1
x365 x
100
2
Vo
PLH
Vo
6800
310250
25
1
x365 x
100
2
Vc
Vo 1 r 1
r
10
Vc
310250 1 0.07 1
0.07
4286552.98
JBGP =
JBKP X EQUAVALENT FACTOR
JBKP =
Vc x e
C3010 / UNIT 14
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
JBKP =
C3010 / UNIT 14
4.29 x 106 x3.0
12.87 x 106
Vx
V1 ( 1 + r ) x
Vx
6800/2( 1 + 0.07 )10
Vx
6689
c=IxRxT
Absolute Traffic Loading per hour - ( Refer
Table 10.8 )
2000/2
1000
Road Decreasing Factor ( Refer
Table 10.9 )
1.0
Traffic Decreasing Factor ( Refer Table
10.10 )
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
100/(100 + 25 )
0.8
IxRxT
1000 x 1.00 x 0.8
800 vec/hr/lane
100c
100(800 vec/hr/lane )
8000 vec/day/lane
From Nomograph Diagram;
43 cm
From table10.11 and table 10.12
a1
1.00
a2
0.32
a3
0.25
C3010 / UNIT 14
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
From table 10.12
Wearing Course
4+5
9 cm
Base Course
10 cm
Sub Base
10 cm granular
SN
a1D1 + a2D2 + a3D3
SN
1D1 + 0.32D2 + 0.25D3
43 cm
Try and Error
1.
2.
3.
D1
D2
10
D3
10
SN
1(9) + 0.32(10) + 0.25(10)
14.7 cm < 43 cm
D1
20
D2
40
D3
50
SN
1(20) + 0.32(40) + 0.25(50)
46 cm > 43 cm
18
D1
C3010 / UNIT 14
Highway Engineering
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
D2
40
D3
50
SN
1(18) + 0.32(40) + 0.25(50)
43.3 cm < 43 cm
OK
C3010 / UNIT 14
You might also like
- Affidavit of Damage To VehicleDocument2 pagesAffidavit of Damage To VehicleMarilen Roque91% (23)
- DSCCDocument11 pagesDSCCRezaNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Transport SystemDocument16 pagesIntelligent Transport SystemMd.imthiyaz90% (10)
- VicRoads Design Final Drawing Presentation Example DrawingsDocument43 pagesVicRoads Design Final Drawing Presentation Example DrawingsAmir SangiNo ratings yet
- Rail Vs Road ComparisonDocument5 pagesRail Vs Road ComparisonAtanu MaityNo ratings yet
- Flexible Pavement Design IRC37 2001 1Document5 pagesFlexible Pavement Design IRC37 2001 1Chatnoir NoirNo ratings yet
- Design Traffic ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDesign Traffic ConsiderationramasamyNo ratings yet
- Embankment Calculation Using C3DDocument25 pagesEmbankment Calculation Using C3DPriyeshBabarNo ratings yet
- Standard Bidding Document KW-4 Road Safety Works: E-Procurement Help Desk No. 080-22485867 E-Mail: Cepramc@kpwd - Gov.inDocument64 pagesStandard Bidding Document KW-4 Road Safety Works: E-Procurement Help Desk No. 080-22485867 E-Mail: Cepramc@kpwd - Gov.inSeshu kvNo ratings yet
- Design Report For Water Works Roads and DrainageDocument6 pagesDesign Report For Water Works Roads and DrainageTayyabah ZafarNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix Design ProcedureDocument9 pagesConcrete Mix Design ProcedureSaroj BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument21 pagesSeminar ReportTheWatchdogs WatchdogNo ratings yet
- DCP Paige Green 2009Document82 pagesDCP Paige Green 2009Joel Johnson KimatareNo ratings yet
- Chp0200 Geometric Design andDocument54 pagesChp0200 Geometric Design andangelbarba100% (2)
- Flexible Pavement Design - Page 3Document1 pageFlexible Pavement Design - Page 3RigonDECNo ratings yet
- Method B18 - The Determination of The Average Least Dimension of Aggregates.Document3 pagesMethod B18 - The Determination of The Average Least Dimension of Aggregates.GUO LEINo ratings yet
- Flexible Pavement DesignDocument4 pagesFlexible Pavement DesignFaisal GulzarNo ratings yet
- Design of Safer Side DrainsDocument22 pagesDesign of Safer Side DrainsSajeebThakurNo ratings yet
- Bearing CapacityDocument4 pagesBearing CapacityahmedNo ratings yet
- Loading To Box-CulvertsDocument20 pagesLoading To Box-CulvertsLjubomir JocicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction of Engineering GeologyDocument21 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction of Engineering GeologyBEENAYEK AdHIKARINo ratings yet
- Culvert Outlet ProtectionDocument12 pagesCulvert Outlet ProtectionjaffnaNo ratings yet
- Continuously Reinforced Concrete PavementDocument7 pagesContinuously Reinforced Concrete Pavementulhas_nakasheNo ratings yet
- Design Flexible ATJ 5I85 2013 2022Document33 pagesDesign Flexible ATJ 5I85 2013 2022Leediya AfrinaNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Report Choon TianDocument35 pagesGeotechnical Report Choon TianAnonymous O404LiV4CNo ratings yet
- Differential Settlement Bh7Document9 pagesDifferential Settlement Bh7Zhi Ming CheahNo ratings yet
- Horizontal AlignmentDocument18 pagesHorizontal AlignmentNur Hazirah SadonNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts: Hour) Peak Within Flow of Rate (Peak V 4 Hour Peak During (PHF) Factor Hour PeakDocument5 pagesBasic Concepts: Hour) Peak Within Flow of Rate (Peak V 4 Hour Peak During (PHF) Factor Hour PeakAbdirizak HussienNo ratings yet
- Highway Engineering Group 1 BSCE-4CDocument30 pagesHighway Engineering Group 1 BSCE-4CMark RipaniNo ratings yet
- Foundation EngineeringDocument45 pagesFoundation EngineeringPhilip NguyenNo ratings yet
- MTENGEKIDocument98 pagesMTENGEKIEmmanuel NdyamukamaNo ratings yet
- Brick CalculatorDocument3 pagesBrick CalculatorP.v.KumarNo ratings yet
- Rigid PavementsDocument5 pagesRigid PavementsvenkateswararaothumaNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity Technical GuidanceDocument10 pagesBearing Capacity Technical GuidanceFarouq SHah0% (1)
- 3.2 Flexible Pavement Design: (JKR Method) - ATJ 5/85Document18 pages3.2 Flexible Pavement Design: (JKR Method) - ATJ 5/85fuad addibNo ratings yet
- CE 353 Transportation Engineering II: Md. Rabiul IslamDocument25 pagesCE 353 Transportation Engineering II: Md. Rabiul IslamMohamed Isak AliNo ratings yet
- Code ListDocument26 pagesCode ListChandra Prakash JyotiNo ratings yet
- Rigid Pavement DesignDocument8 pagesRigid Pavement DesignsagarNo ratings yet
- Current Approach To Pavement DesignDocument25 pagesCurrent Approach To Pavement DesignApril IngramNo ratings yet
- Cement Stablize of SoilDocument10 pagesCement Stablize of Soilالزهور لخدمات الانترنيتNo ratings yet
- CSIR 2016 ImprovementsWinDCPSoftwarePavementDesignLVR FinalDevReport AFCAPDocument33 pagesCSIR 2016 ImprovementsWinDCPSoftwarePavementDesignLVR FinalDevReport AFCAPJoel Johnson KimatareNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Soil Settlement: September 2019Document28 pagesChapter Two Soil Settlement: September 2019NOor AlhoDaNo ratings yet
- Altaf Reg 0950 Cep Flexible Pavement DesignDocument37 pagesAltaf Reg 0950 Cep Flexible Pavement DesignAltaf Hussain 17BNCIV0950No ratings yet
- Step (1) : Determine Storage Volume RequiredDocument12 pagesStep (1) : Determine Storage Volume RequiredYANIshaNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Foundation Settlement and Coefficient of Soil Subgrade ReactionDocument10 pagesCalculation of Foundation Settlement and Coefficient of Soil Subgrade ReactionleodegarioporralNo ratings yet
- Correlations of SPT and DCPT Data For Sandy Soils in Ghana: Lowland Technology International September 2017Document7 pagesCorrelations of SPT and DCPT Data For Sandy Soils in Ghana: Lowland Technology International September 2017SithuAungNo ratings yet
- Development Design Specification D4Document10 pagesDevelopment Design Specification D4Timothy KimemiaNo ratings yet
- Construction Site Earthwork CalculationDocument4 pagesConstruction Site Earthwork CalculationmasteriragaNo ratings yet
- Report-Mauwa DotiDocument140 pagesReport-Mauwa DotiTej Bdr. paliNo ratings yet
- Drain Design (Proag)Document12 pagesDrain Design (Proag)Jeedaran ArshaadNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Brick MasonryDocument21 pagesReinforced Brick MasonryMihaela Batalan100% (1)
- Scour Depth & Stone Apron SizingDocument18 pagesScour Depth & Stone Apron SizingguildkeyNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE CALCULATION - JKR @PWD MethodDocument7 pagesSAMPLE CALCULATION - JKR @PWD MethodyogadarshiniNo ratings yet
- Rankine Earth Pressure Theory PDFDocument4 pagesRankine Earth Pressure Theory PDFgitrixNo ratings yet
- Continuosly Reinforced Concrete Pavement Design For AirportDocument27 pagesContinuosly Reinforced Concrete Pavement Design For AirportDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document30 pagesChapter 1hNo ratings yet
- Rigid Pavement Design PDFDocument14 pagesRigid Pavement Design PDFNaqvi ANo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Flexible Pavement DesignDocument22 pagesTopic 7 Flexible Pavement DesignHanaNo ratings yet
- Road AlignmentDocument17 pagesRoad Alignmentrowaters100% (1)
- 4 CVT1 Two Cell RC Box Culvert Example PDFDocument38 pages4 CVT1 Two Cell RC Box Culvert Example PDFcorrokokoNo ratings yet
- Project PDFDocument14 pagesProject PDFYeshiwondim100% (1)
- Design of Overlay Flexible PavementDocument17 pagesDesign of Overlay Flexible PavementJoseph MathewNo ratings yet
- 2 - Pavement DesignDocument9 pages2 - Pavement DesignG-CAD ENGINEERSNo ratings yet
- 4 Pavement Structure Thickness DesignDocument89 pages4 Pavement Structure Thickness DesignLynas Beh Tahan100% (2)
- The Vehicle Horn Is Used For:: Creating Noise Making Beautiful Sounds Giving Warning To Avoid Accident CorrectDocument7 pagesThe Vehicle Horn Is Used For:: Creating Noise Making Beautiful Sounds Giving Warning To Avoid Accident CorrectNoel TorresNo ratings yet
- Alignment Report (Kolar - Bangarpet)Document25 pagesAlignment Report (Kolar - Bangarpet)Kiran R GowdaNo ratings yet
- E 4 2 Traffic Appraisal Manual Chapter 13 PDFDocument26 pagesE 4 2 Traffic Appraisal Manual Chapter 13 PDFTalha AslamNo ratings yet
- Type 6 - Typical Cross Section at Approach of Rob With Slip RoadDocument11 pagesType 6 - Typical Cross Section at Approach of Rob With Slip RoadSettipalli Ram SuryaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Highway and Railroad EngineeringDocument21 pagesModule 2 Highway and Railroad EngineeringMarlo Nepomuceno100% (1)
- TCS Schedule Table B-1 Typical Cross Sections Schedule: S. No Design Ch. Description TCS Type Length (M) From ToDocument4 pagesTCS Schedule Table B-1 Typical Cross Sections Schedule: S. No Design Ch. Description TCS Type Length (M) From TovivekNo ratings yet
- Light Motor Vehicle Handbook: A Guide To Safe DrivingDocument78 pagesLight Motor Vehicle Handbook: A Guide To Safe DrivingSwati jainNo ratings yet
- Highway Engineering - Unit 2 - Lecture NoteDocument100 pagesHighway Engineering - Unit 2 - Lecture NoteHarsh ParmarNo ratings yet
- 20388EST City Report Indonesia MakassarDocument12 pages20388EST City Report Indonesia MakassarSanty SanNo ratings yet
- Traffic Engineering and Management PDFDocument11 pagesTraffic Engineering and Management PDFjeya50% (2)
- Road Safety Among Medical StudentsDocument10 pagesRoad Safety Among Medical StudentsTengiz VerulavaNo ratings yet
- Road Transport Regulating & Enforcement Bodies - 2006 EditionDocument386 pagesRoad Transport Regulating & Enforcement Bodies - 2006 EditionIRUNo ratings yet
- Road Hazard Management GuideDocument28 pagesRoad Hazard Management GuideXusda GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Sartsm V1 C10-11Document64 pagesSartsm V1 C10-11Et100% (1)
- Provisional Appointment For Driving Skill Test: Rahul Kumar Madan Lal Sri/Smt/KumDocument1 pageProvisional Appointment For Driving Skill Test: Rahul Kumar Madan Lal Sri/Smt/KumAbhishek BhagatNo ratings yet
- Policy ProposalDocument9 pagesPolicy ProposalNatividad GammadNo ratings yet
- Traffic Speed StudyDocument2 pagesTraffic Speed StudyManik GoyalNo ratings yet
- TSPM Assignment 1Document3 pagesTSPM Assignment 1Surya MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Qhse Report GradiDocument4 pagesQhse Report GradimalukuetaNo ratings yet
- Investigating Causes of Pavement Deterioration in Khartoum StateDocument13 pagesInvestigating Causes of Pavement Deterioration in Khartoum Statebereket gNo ratings yet
- Flexible Pavement-Design ReportDocument4 pagesFlexible Pavement-Design ReportPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- DocketDocument1,191 pagesDocketAaron TennysonNo ratings yet
- Arahan Teknik 8-86 R3Document1 pageArahan Teknik 8-86 R3Pipi KNo ratings yet
- Montgomery Fleet Equipment Inventory FA PART 1 ENDDocument4 pagesMontgomery Fleet Equipment Inventory FA PART 1 ENDNayan Moni KalitaNo ratings yet
- Road and ComponentsDocument10 pagesRoad and ComponentsPrakhar patidarNo ratings yet
- TTE4274 - Class 20Document64 pagesTTE4274 - Class 20Logan PatrickNo ratings yet