Pregnancy Uterus Fetus Embryo: Morbidity Selectively Reduce Multiple Pregnancy
Pregnancy Uterus Fetus Embryo: Morbidity Selectively Reduce Multiple Pregnancy
Uploaded by
nyzgirl17Copyright:
Available Formats
Pregnancy Uterus Fetus Embryo: Morbidity Selectively Reduce Multiple Pregnancy
Pregnancy Uterus Fetus Embryo: Morbidity Selectively Reduce Multiple Pregnancy
Uploaded by
nyzgirl17Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Pregnancy Uterus Fetus Embryo: Morbidity Selectively Reduce Multiple Pregnancy
Pregnancy Uterus Fetus Embryo: Morbidity Selectively Reduce Multiple Pregnancy
Uploaded by
nyzgirl17Copyright:
Available Formats
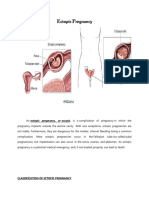
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by the removal or expulsion from
the uterus of a fetus or embryo, resulting in or caused by its death.
The termination of pregnancy before fetus is viable.
Fetus is viable is defined as fetus of 20 weeks AOG, weighing <350 grams.
May be elective (planned, medical termination of pregnancy) or reproductive
problem.
Types of Abortion:
complete abortion - one in which all the products of conception are expelled from the
uterus and identified.
habitual abortion - spontaneous abortion occurring in three or more successive
pregnancies, at about the same level of development.
incomplete abortion - with retention of parts of the products of conception.
induced abortion - brought on intentionally by medication or instrumentation.
The manner selected depends chiefly upon the gestational age of the embryo or fetus,
which increases in size as it ages. Specific procedures may also be selected due to legality,
regional availability, and doctor-patient preference. Reasons for procuring induced abortions are
typically characterized as either therapeutic or elective. An abortion is medically referred to
as therapeutic when it is performed to:
save the life of the pregnant woman.
preserve the woman's physical or mental health;
terminate pregnancy that would result in a child born with a congenital disorder that
would be fatal or associated with significant morbidity; or
selectively reduce the number of fetuses to lessen health risks associated with multiple
pregnancy.
inevitable abortion - a condition in which vaginal bleeding has been profuse and the
cervix has become dilated, and abortion will invariably occur.
infected abortion -associated with infection of the genital tract.
missed abortion - retention in the uterus of an abortus that has been dead for at least
eight weeks.
septic abortion - associated with serious infection of the uterus leading to generalized
infection.
spontaneous abortion - occurring naturally.
Spontaneous abortion (also known as miscarriage) is the expulsion of an embryo or fetus
due to accidental trauma or natural causes before approximately the 22nd week of gestation; the
definition by gestational age varies by country. Most miscarriages are due to incorrect replication
of chromosomes; they can also be caused by environmental factors. A pregnancy that ends
before 37 weeks of gestation resulting in a live-born infant is known as a "premature birth". When
a fetus diesin utero after about 22 weeks, or during delivery, it is usually termed "stillborn".
Premature births and stillbirths are generally not considered to be miscarriages although usage of
these terms can sometimes overlap.
therapeutic abortion - induced for medical considerations. Medical abortions are non-
surgical abortions that use pharmaceutical drugs, and are only effective in the first trimester of
pregnancy.
threatened abortion - a condition in which vaginal bleeding is less than in inevitable
abortion and the cervix is not dilated, and abortion may or may not occur.
Surgical abortion
In the first 12 weeks, suction-aspiration or vacuum abortion is the most common method.
Manual Vacuum aspiration (MVA) abortion consists of removing
the fetus or embryo, placenta and membranes by suction using a manual syringe,
while electric vacuum aspiration (EVA) abortion uses an electric pump. These techniques are
comparable, and differ in the mechanism used to apply suction, how early in pregnancy they can
be used, and whether cervical dilation is necessary. MVA, also known as "mini-suction" and
"menstrual extraction", can be used in very early pregnancy, and does not require cervical
dilation. Surgical techniques are sometimes referred to as 'Suction (or surgical) Termination Of
Pregnancy' (STOP). From the 15th week until approximately the 26th,dilation and
evacuation (D&E) is used. D&E consists of opening the cervix of the uterus and emptying it using
surgical instruments and suction.
Dilation and curettage (D&C)
The second most common method of abortion is a standard gynecological procedure
performed for a variety of reasons, including examination of the uterine lining for possible
malignancy, investigation of abnormal bleeding, and abortion. Curettage refers to cleaning the
walls of the uterus with a curette. The World Health Organization recommends this procedure,
also called sharp curettage, only when MVA is unavailable.] The term D and C, or
sometimes suction curette, is used as a euphemism for the first trimester abortion procedure,
whichever the method used
Signs of Abortion (Assessment findings)
1. Vaginal Bleeding – observe carefully for accurate determination of amount saving
all perineal pads.
2. Contractions, pelvic cramping, backache
3. Passage of tissues/fetus
4. Cervical dilatation
5. Lowered hemoglobin if blood loss is significant.(less than 10.5mg/dL)
6. Signs related to blood loss- pallor, tachycardia, tachypnea, cold clammy skin,
restless, oliguria, hypotension, air hunger.
Complications of Abortion
1. Hemorrhage
2. Infection
3. Infertility
4. Uterine perforation from curettage
5. PID (Pelvic Inflammatory disease).
6. Retained products of conception, may lead to H-mole
7. Anemia
Exams and Tests
Abdominal or vaginal ultrasound may be done to check the baby's development, heart
beat, and amount of bleeding. A pelvic exam will be done to check the cervix.
The following blood tests may be performed:
* Complete blood count (CBC) to determine amount of blood loss
* Serum HCG to ccheck pregnancy
* White blood count (WBC) with differential to rule out infection
* Ultrasound
You might also like
- Networking Assignment1 Fontsheet 1Document43 pagesNetworking Assignment1 Fontsheet 1Dương Bùi Thái100% (1)
- Abnormal Labor: Ina S. Irabon, MD, Fpogs, FPSRM, FpsgeDocument51 pagesAbnormal Labor: Ina S. Irabon, MD, Fpogs, FPSRM, FpsgeMa. Bernadette PinedaNo ratings yet
- SCGX Fino UserguideDocument189 pagesSCGX Fino UserguideWashington JohnNo ratings yet
- Abortion and Ectopic PregnancyDocument3 pagesAbortion and Ectopic PregnancyJefelson Eu Palaña NahidNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandGastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- And Vaginal Bleeding (In Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy)Document9 pagesAnd Vaginal Bleeding (In Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy)Clareen JuanicoNo ratings yet
- Cervical IncompetenceDocument30 pagesCervical IncompetenceSignor ArasNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument4 pagesGestational Trophoblastic DiseasePrincess PlateroNo ratings yet
- 68 Abnormal PeuperiumDocument44 pages68 Abnormal PeuperiumGodsonYeboah-AwudziNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders of PregnancyDocument66 pagesBleeding Disorders of PregnancyDivine Flores-CamposNo ratings yet
- Septic Abortion PhysioDocument66 pagesSeptic Abortion PhysioChristiemae_An_6363No ratings yet
- The Incompetent Cervix 2Document30 pagesThe Incompetent Cervix 2api-3705046100% (3)
- Hiv in Pregnancy FinalDocument73 pagesHiv in Pregnancy Finalapi-3797079No ratings yet
- Case Report AUBDocument15 pagesCase Report AUBRirinAdinda0% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy - OMDocument9 pagesEctopic Pregnancy - OMrheind100% (1)
- PATHO OB DystociaDocument14 pagesPATHO OB Dystociasailor MoonNo ratings yet
- Pyloric StenosisDocument5 pagesPyloric Stenosisensoooooooooo100% (1)
- 5 - Abortion or MiscarriageDocument43 pages5 - Abortion or Miscarriageasifdawar2011No ratings yet
- Φ PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesΦ PathophysiologyMariah AshooriyanNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia and EclampsiaDocument23 pagesPreeclampsia and Eclampsiaapi-3705046100% (6)
- Spontaneous AbortionDocument17 pagesSpontaneous Abortionanon_985338331No ratings yet
- Postpartum ComplicationsDocument21 pagesPostpartum ComplicationsRoccabeth Villanueva100% (1)
- Evaluation of Fetal DeathDocument9 pagesEvaluation of Fetal DeathVinisia TakaraiNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placentae: ALCANTARA, Eduardo L. Ms. Analinda R. Sese, RN, MANDocument45 pagesAbruptio Placentae: ALCANTARA, Eduardo L. Ms. Analinda R. Sese, RN, MANinscenekivir100% (1)
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument45 pagesAbruptio PlacentaJosef Kevin ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors of Cesarean Delivery Due To Cephalopelvic Disproportion in Nulliparous Women at Sisaket HospitalDocument7 pagesRisk Factors of Cesarean Delivery Due To Cephalopelvic Disproportion in Nulliparous Women at Sisaket HospitalManangioma ManNo ratings yet
- Endometriosis PresentationDocument58 pagesEndometriosis PresentationBRI KU100% (1)
- RH Disease and ABO IncompatibilityDocument21 pagesRH Disease and ABO Incompatibilityjeezislove617No ratings yet
- PROM SANJIDA FInal 2Document32 pagesPROM SANJIDA FInal 2Saiful islam RonyNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Induction and Augmentation of LaborDocument17 pagesModule 5 Induction and Augmentation of LaborZyrene RiveraNo ratings yet
- Antepartum HaemorrhageDocument48 pagesAntepartum HaemorrhageDuncan JacksonNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument52 pagesPregnancy Induced HypertensionJoy GloryNo ratings yet
- Apolonio, JC - Postpartum Assessment ActivityDocument3 pagesApolonio, JC - Postpartum Assessment ActivityJustin ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Antenatal CareDocument26 pagesAntenatal CarepluiedecielNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument3 pagesAbruptio Placentachichilovesyou100% (1)
- HypertensionDocument6 pagesHypertensionTj Kevin P-DoctorNo ratings yet
- Obstructed Labor-Bandl's RingDocument43 pagesObstructed Labor-Bandl's RingJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Presentation: "Ectopic Pregnancy"Document8 pagesCase Study Presentation: "Ectopic Pregnancy"Sherwina Alih-BieberNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument26 pagesEctopic PregnancyDavid SitinjakNo ratings yet
- GTD Case StudyDocument9 pagesGTD Case StudyZnarf Izlah Sadanreb100% (1)
- Labor DystociaDocument100 pagesLabor DystociaAnonymous kChMIy7tXNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument5 pagesAbruptio PlacentaJuan Carlo Z. SolidumNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia Eclampsia and Hellp SyndromeDocument24 pagesPreeclampsia Eclampsia and Hellp Syndromeapi-403416350100% (1)
- DR - Group CaseDocument62 pagesDR - Group CaseRon Lucernas MayugaNo ratings yet
- OSCE Sp1 Feto Breech PresentationDocument7 pagesOSCE Sp1 Feto Breech PresentationobbyNo ratings yet
- GDM (Gestational Diabetes Mellitus) PresentationDocument32 pagesGDM (Gestational Diabetes Mellitus) PresentationMovies 4 YouNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa PathoDocument2 pagesPlacenta Previa Pathoshakira0% (1)
- Cesarean Section Report Richard LimDocument48 pagesCesarean Section Report Richard LimEj PogiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Findings: ACOG - Cervical Insufficiency As "Document5 pagesClinical Findings: ACOG - Cervical Insufficiency As "lllNo ratings yet
- NSVDDocument48 pagesNSVDchiqui14100% (2)
- #3 Cesarean SectionDocument20 pages#3 Cesarean SectionDunice Lloyd Mata100% (1)
- NCM - Pregancy Induced HypertensionDocument5 pagesNCM - Pregancy Induced HypertensionZam PamateNo ratings yet
- Case Pres AutosavedDocument21 pagesCase Pres AutosavedJaysellePuguonTabijeNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument31 pagesGestational Diabetes MellitusLidya BintangNo ratings yet
- MastitisDocument8 pagesMastitisAmalia Putri100% (1)
- 05 DystociaDocument10 pages05 DystociaRiantiara PutrizaNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Growth RestrictionDocument10 pagesIntrauterine Growth RestrictionNoelia D PenaNo ratings yet
- Case PresDocument100 pagesCase PresJoj BagnateNo ratings yet
- HERNIA - Case StudyDocument8 pagesHERNIA - Case StudyMa Jaimeliz Mae MuñizNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Case Study of MiscarriageDocument25 pagesPowerpoint Case Study of MiscarriageAngel CauilanNo ratings yet
- CC CC: YY YYDocument54 pagesCC CC: YY YYnyzgirl17No ratings yet
- Infertility: They Can't Have Bab IesDocument10 pagesInfertility: They Can't Have Bab Iesnyzgirl17No ratings yet
- Cozaar 25 MG: What Is Losartan (Cozaar) ?Document25 pagesCozaar 25 MG: What Is Losartan (Cozaar) ?nyzgirl17No ratings yet
- By: Tiffany M. AustriaDocument10 pagesBy: Tiffany M. Austrianyzgirl17No ratings yet
- By: Tiffany M. AustriaDocument10 pagesBy: Tiffany M. Austrianyzgirl17No ratings yet
- Neonatal Assessment Guide - TiffDocument7 pagesNeonatal Assessment Guide - Tiffnyzgirl17No ratings yet
- Causes of Spontaneous Abortion 2Document23 pagesCauses of Spontaneous Abortion 2kenNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering in Ancient Sri LankaDocument10 pagesCivil Engineering in Ancient Sri LankaBimal FernandoNo ratings yet
- DAF XF105 Infosheet Cab enDocument5 pagesDAF XF105 Infosheet Cab enMarko PajićNo ratings yet
- Publication 1 1129 24Document14 pagesPublication 1 1129 24Marwan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Name Those Notes Treble ClefDocument6 pagesName Those Notes Treble Clefapi-602219205No ratings yet
- Synopsis-Jasmin KhatriDocument10 pagesSynopsis-Jasmin KhatrinpkarambelkarNo ratings yet
- Doctor of Medicine (MD) ProgramDocument16 pagesDoctor of Medicine (MD) ProgramKSU LibraryNo ratings yet
- What Is 2pl, 3pl, and 4pl?Document2 pagesWhat Is 2pl, 3pl, and 4pl?Ahmed AbdiwahabNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument20 pagesReadmemiskoajkulaNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth ToolsDocument30 pagesBluetooth ToolsMarco Antonio Martinez AndradeNo ratings yet
- SAGE Profile V6.3.2 User Manual - Volume 3Document55 pagesSAGE Profile V6.3.2 User Manual - Volume 3GodwinNo ratings yet
- The Grenz Zone: Ossama Abbas, MD, and Meera Mahalingam, MD, PHD, FrcpathDocument9 pagesThe Grenz Zone: Ossama Abbas, MD, and Meera Mahalingam, MD, PHD, FrcpathDaniel FilizzolaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics After Shoulder Joint Replacement by TENDAI MUTSOPOTSIDocument2 pagesAntibiotics After Shoulder Joint Replacement by TENDAI MUTSOPOTSIPhysiotherapy Care SpecialistsNo ratings yet
- National Rail Policy Green PaperDocument95 pagesNational Rail Policy Green PaperNicholas FeatherstonNo ratings yet
- Ucsp 1Document1 pageUcsp 1Ian Karl BuclaoNo ratings yet
- JurisprudenceDocument13 pagesJurisprudencen9821531759No ratings yet
- The Integrating A/D Converter (ICL7135) : Application Note February 1999Document5 pagesThe Integrating A/D Converter (ICL7135) : Application Note February 1999ytnateNo ratings yet
- FMG90 Series: With PVDF and 316L ConstructionDocument2 pagesFMG90 Series: With PVDF and 316L ConstructionRavi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Waves and em Spectrum Work SheetDocument2 pagesWaves and em Spectrum Work SheetSenpai ChibiNo ratings yet
- Shobhit Nirwan Chemistry Class 11Document246 pagesShobhit Nirwan Chemistry Class 11KiraNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and Diagnostics of PV Plants by A Wireless Self-Powered Sensor For Individual PanelsDocument9 pagesMonitoring and Diagnostics of PV Plants by A Wireless Self-Powered Sensor For Individual PanelsDevil faNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Past Year Questions April 2011Document3 pagesAssignment 1 - Past Year Questions April 2011aiman_safianNo ratings yet
- Pedalpower ppg2 3 1Document7 pagesPedalpower ppg2 3 1ramsinghNo ratings yet
- Helen of Troy Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesHelen of Troy Lesson PlanJF Mamjjasond SupanNo ratings yet
- Electrical SafetyDocument43 pagesElectrical SafetyRamanujam O SNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Quantitatave and Qualitative ResearchDocument6 pagesComparison of Quantitatave and Qualitative Researchkristine collins YambaoNo ratings yet
- Đề số 6Document6 pagesĐề số 6minhhanhnguyen790No ratings yet
- My Biology HomeworkDocument7 pagesMy Biology HomeworkDumissa MelvilleNo ratings yet