Roche Midiprep
Roche Midiprep
Uploaded by
Bee CarbonellCopyright:
Available Formats
Roche Midiprep
Roche Midiprep
Uploaded by
Bee CarbonellOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Roche Midiprep
Roche Midiprep
Uploaded by
Bee CarbonellCopyright:
Available Formats
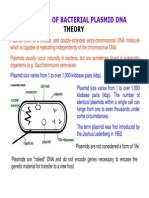
Genopure Plasmid Midi Kit
Genopure Plasmid Midi Kit
for up to 20 preparations of plasmid DNA in medium scale
Cat. No. 03 143 414 001
Principle
The isolation procedure is based on a modied alkaline lysis protocol and can be divided
into the following steps:
The bacteria are partially lysed, allowing the plasmid DNA to escape the cell wall into the
supernatant. The larger E. coli chromosomal DNA is trapped in the cell wall. The lysate is
cleared of cellular debris and the plasmid DNA containing fraction is added to the
column. The bound plasmid DNA is washed to remove contaminating bacterial components. The plasmid DNA is eluted and precipitated to remove salt and to concentrate the
eluate.
This is a commonly used method that generates highly puried plasmid DNA (free of
RNA contamination).
Starting material
5 30 ml E. coli cultures transformed with a high copy number plasmid.
10 100 ml E. coli cultures transformed with a low copy number plasmid
(at a density of 2 6.0 A600 units per ml bacterial culture).
Application
This kit is used to prepare plasmid DNA in medium quantities known as midi preps.
Using a modied alkaline lysis method highly puried plasmid DNA is generated. The
kit is designed for the isolation of up to 100 g of plasmid DNA from bacterial culture.
Depending on the copy number of the plasmids use either 5 to 30 ml (high copy
number) or 10 to 100 ml (low copy number) bacterial suspension. The quality of the
plasmid DNA is better than plasmid DNA obtained by 2 x CsCl gradient centrifugation.
As a result, the plasmid DNA is suitable for all molecular biology applications e.g.,
transfection, PCR, restriction analysis/Southern blotting, sequencing and cloning.
Time required
Total time: 60 min including a ltration step after the alkaline lysis.
Hands-on time: Minimal hands-on time required (about 10 min).
Results
Purity: Plasmid DNA is free of all other bacterial components, including RNA,
shown by gel electrophoresis
Yield: Depending on E. coli strain and density of the cell culture. Comparable to
traditional purication methods
Application: The puried plasmid has been used for PCR, sequencing and transfection with excellent results
Benets
Avoids organic or toxic materials as no phenol or chloroform, CsCl and ethidium
bromide needed
Ready to use because all reagents provided with the kit
Reliable quality because better than 2 x CsCl
Parallel processing because of use of high speed gravity ow columns
All plasmid sizes can be isolated even BAC DNA
122
Nucleic Acid Isolation and Purication Manual
Genopure Plasmid Midi Kit
How to use the kit
How to use the kit
I.
Flow diagram
Centrifuge 5 30 ml E. coli
culture, at 3000 5000 x g
at 2 to 8C for 10 min
Resuspend pellet in 4 ml
Suspension Buffer/RNase
Add 4 ml Lysis Buffer
Discard supernatant
Mix gently, incubate
at 15 to 25C
2 3 min
Add 4 ml chilled
Neutralization Buffer
Mix gently by inversion,
incubate 5 min on ice
Clear bacterial lysate by
filtration (or by centrifugation), transfer flowthrough
(or supernatant) to preequilibrated column
Add 5 ml Wash Buffer
Discard pellet
Allow the column to empty
by gravity flow and repeat
this wash step
Discard flowthrough
Add 5 ml Elution Buffer
Allow the column to empty
by gravity flow and collect
flowthrough
Add 3.6 ml isopropanol
equilibrated to 15 to 25C
Centrifuge at 15,000 x g
at 2 to 8C for 30 min
Add 3 ml chilled
70% ethanol
Discard supernatant
Centrifuge at 15,000 x g
at 2 to 8C for 10 min
Discard supernatant
Briefly air-dry the pellet
(10 min) and redissolve
the pellet
Ion Exchange Chromatography
Add 20 100 l TE Buffer
or H2O double dist
123
Genopure Plasmid Midi Kit
How to use the kit
II.
Kit contents
Suspension Buffer (100 ml) for suspension of bacterial cell pellets
RNAse A (12 mg) for dissolution in Suspension Buffer
Lysis Buffer (100 ml) for bacterial cell lysis
Neutralization Buffer (100 ml) to form a stable cellular debris precipitate
Equilibration Buffer (70 ml) for equilibrating the columns prior to use
Wash Buffer (250 ml) for removal of residual impurities
Elution Buffer (125 ml) for plasmid elution
NucleoBond AX 100 Columns (20 columns) for the isolation step
Folded lters (20 lters) to eliminate a centrifugation step and to remove cellular
debris
Sealing rings (10 rings) to station the columns in test tubes
III.
Additional materials needed
Centrifuge and tubes for harvesting bacterial cultures, capable of 15,000 x g
Isopropanol
70% ethanol
TE Buffer or other low salt buffer
Tube for collecting and precipitating eluted plasmid DNA
Funnel for clearing of lysates by folded lters
124
Nucleic Acid Isolation and Purication Manual
Genopure Plasmid Midi Kit
How to use the kit
IV.
Protocol for preparing high copy number plasmid DNA
Step Action
Time / x g /
Temperature
Centrifuge bacterial cells from 5 30 ml E. coli culture grown in LB
medium.
Discard the supernatant.
Carefully resuspend the pellet in 4 ml Suspension Buffer + RNase and mix
well.
Add 4 ml Lysis Buffer to the suspension and mix gently by inverting the
tube 6 to 8 times and incubate.
5 10 min/
3000 5000 x g/ 2 to 8C
2 3 min at 15 to 25C
Do not vortex in order to avoid shearing and release of genomic
DNA. Do not incubate for more than 5 min to prevent the release of
chromosomal DNA from the cell debris.
Add 4 ml chilled Neutralization Buffer to the suspension.
Immediately mix the suspension gently by inverting the tube 6 to 8 times
until a homogeneous suspension is formed.
Incubate the tube.
5 min on ice
The solution becomes cloudy and occulent precipitate will form.
Clear the lysate by either centrifugation (4a) or by ltration (4b).
V Centrifuge at high speed
Directly after centrifugation carefully remove the supernatant from the
white precipitate and proceed with step 5.
W Put a folded lter into a funnel inserted in a 50 ml plastic tube.
>30 min/ >12,000 x g/
2 to 8C
Moisten the lter with a few drops of Equilibration Buffer or sterile double
dist. water.
Load the lysate onto the wet folded lter and collect the owthrough.
The SDS is removed with the Neutralization Buffer (white precipitate) and should not be loaded onto the column. If the supernatant
is not clear, load it again onto a folded lter to prevent clogging of
the column.
Mount the sealing ring to the column as shown in Figure 36 to x the
column in the Collection Tube.
Figure 36
Insert one column into one Collection Tube.
Equilibrate the column with 2.5 ml Equilibration Buffer.
Allow the column to empty by gravity ow.
Discard the owthrough.
Load the cleared lysate of step 4 onto the equilibrated column.
Allow the column to empty by gravity ow.
Discard the owthrough.
Wash the column with 5 ml Wash Buffer.
Allow the column to empty by gravity ow.
Discard the owthrough.
Repeat step 7.
Discard owthrough and Collection Tube.
Ion Exchange Chromatography
125
Genopure Plasmid Midi Kit
How to use the kit
IV.
Protocol for preparing high copy number plasmid DNA,
continued
Step Action
Time / x g /
Temperature
Re-insert the column into a new Collection Tube capable of withstanding
high speed centrifugation (15,000 x g).
Elute the plasmid with 5 ml Elution Buffer.
Allow the column to empty by gravity ow.
The collected owthrough contains the plasmid.
Precipitate the eluted plasmid DNA with 3.6 ml isopropanol equilibrated to
15 to 25C.
Centrifuge immediately at high speed.
30 min/ 15,000 x g/2 to 8C
Carefully discard the supernatant.
Wash the plasmid DNA with 3 ml chilled 70% ethanol.
2 to 8C
Centrifuge at high speed.
10 min/ >15,000 x g/2 to 8C
Carefully remove ethanol from the tube with pipet tip.
Air-dry the plasmid DNA pellet.
Carefully redissolve the plasmid DNA pellet in 20 100 l TE Buffer or
sterile double dist. H2O.
10 min
V.
Troubleshooting the Genopure Plasmid Midi protocol
If you get...
Then, the
cause may be...
And you should...
Low nucleic acid
yield or purity
Kit stored under
non-optimal
conditions
Store kit at 15 to 25C at all times upon arrival.
Buffers or other
reagents were
exposed to
conditions that
reduced their
effectiveness
Store all buffers at 15 to 25C.
Reagents and
samples not
completely
mixed
Always mix the sample tube well after addition of each reagent.
Low recovery
of nucleic acids
after elution
After reconstitution of RNase with Suspension Buffer store
aliquots at 2 to 8C.
Close all reagent bottles tightly after each use to preserve pH,
stability and freedom from contamination.
Ensure Lysis Buffer and Neutralization Buffer are free of
precipitates.
Non-optimal
Use the Elution Buffer of the kit.
reagent has been
used for elution. Salt
is required
for optimal
elution
126
Nucleic Acid Isolation and Purication Manual
Genopure Plasmid Midi Kit
How to use the kit
V.
Troubleshooting the Genopure Plasmid Midi protocol,
continued
If you get...
Then, the
cause may be...
And you should...
Low plasmid
yield
Too few cells in
starting material
Grow E. coli to an absorbency (A600) of 2 6 before harvest.
Incomplete
cell lysis
Ensure the E. coli pellet is completely resuspended in Suspension Buffer.
Make sure the lysate is clear and viscous after the lysis step
(incubation with Lysis Buffer).
Ensure a cloudy white precipitate forms when Binding Buffer
is added to the lysate.
Lysate did not bind Pre-equilibrate the column by adding Equilibration Buffer
completely
before adding sample.
to column
RNA is present
in nal product
RNase not
completely
dissolved
To reconstitute the lyophilized RNase completely:
1. Pipette 1 ml of Suspension Buffer into the glass vial containing lyophilized RNase.
2. Stopper and invert the vial until all the lyophilizate (including any stuck to the rubber stopper) is dissolved.
3. Transfer all the reconstituted RNase back into the Suspension Buffer and mix thoroughly
4. Mark the reconstituted mixture (enzyme and buffer) with
the date of reconstitution and store at 2 to 8C.
Reconstituted mixture is stable for 6 months when stored
properly.
Genomic DNA
present in nal
product
Genomic DNA
sheared during
lysis step
Vortexing the preparation after addition of Lysis Buffer should
be avoided.
RNase present
in nal product
RNase not
completely
dissolved
See suggestions under RNA present in nal product above.
Too many
cells in
starting material
Do not overload the column.
Denatured
plasmid in nal
product
Reduce the incubation time during step 2 (lysis step) of the
protocol.
Additional
band running
slightly faster
than supercoiled plasmid
is seen on gels
Ion Exchange Chromatography
127
Genopure Plasmid Midi Kit
Typical results with the kit
Puried Plasma
Digested with
Eco R1/Ssp1
Elution
2nd Washing Step
1st Washing Step
MWM
Flowthrough
Typical results with the kit
Figure 37: The purication process
results in contamination-free plasmid
DNA.
Plasmid Preparation
Method
Endotoxin
(EU/g)
Transfection efciency
(%)
Genopure
4 10
100
2-fold CsCl
0.7 3
~95
Alternative Commercial
Source (Anion Exchange)
9.3
80
Silica-Matrix/Gel Slurry
> 1000
> 30
Table 2: Mean values from several experiments.
Figure 38: Western blot analysis of GFP after
expression in RTS 500 HY reactions. Equal volumes
of diluted reaction solutions were separated by SDSPAGE, then blotted. Detection was performed with the
anti-His6 peroxidase-conjugated antibody.
Molecular Weight
Marker [kD]
100
75
45
30
GFP
20
Genopure
Genopure
Plasmid Maxi Plasmid Midi
References
Ausubel, F. M. et al. (eds.) (1991) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, Wiley Interscience, New York
Birnboim, H. C. and Doly, J, (1979) Nucl. Acids Res. 7, 1513 1522
Darby, R. A. J. and Hine, A. V. (2005) The FASEB Journal, 10.1096/fj.04-2812fje
Kuwano, Y. et al. (2006) Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290, C433 C443
Sambrook, J. et al. (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd Edition, Cold
Spring Harbour Laboratory Press
Song, S. et al. (2005) Cancer 103: 1606 1614
Waga, S. and Zembutsu, A. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281, 10926 10934
Zembutsu, A. and Waga, S. (2006) Nucl. Acids Res. 34, e91
128
Nucleic Acid Isolation and Purication Manual
You might also like
- Pharmacy Calculation Workbook: 250 Questions to Prepare for the NAPLEX and PTCB ExamFrom EverandPharmacy Calculation Workbook: 250 Questions to Prepare for the NAPLEX and PTCB ExamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- This Study Resource Was: Chapter 3 Exploring Proteins and ProteomesDocument8 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Chapter 3 Exploring Proteins and ProteomesGamze SakallıNo ratings yet
- Plasmid DNA Isolation PDFDocument3 pagesPlasmid DNA Isolation PDF9001 Trisha BakshiBBT2No ratings yet
- Purelink Quick Plasmid QRCDocument4 pagesPurelink Quick Plasmid QRCEvelyn LiuNo ratings yet
- Purification of Plasmid DNA: MaterialsDocument3 pagesPurification of Plasmid DNA: MaterialsTham Su MingNo ratings yet
- High Yield Miniprep ProtocolDocument2 pagesHigh Yield Miniprep ProtocolAdison WongNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Protocols: Plasmid DNA IsolationDocument7 pagesLaboratory Protocols: Plasmid DNA Isolationone kilometerNo ratings yet
- Mini PrepDocument6 pagesMini PrepWilson GomargaNo ratings yet
- Routine Culturing Plasmodium Falciparum - Edinburgh 2Document6 pagesRoutine Culturing Plasmodium Falciparum - Edinburgh 2NeelutpalGogoiNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Bacterial Plasmid DNA (Compatibility Mode)Document18 pagesIsolation of Bacterial Plasmid DNA (Compatibility Mode)Khandoker Faisal100% (1)
- Plant Genomic DNA Extraction by CTAB - 2 - FionaDocument5 pagesPlant Genomic DNA Extraction by CTAB - 2 - FionayomnayasminNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Genomic DNA Miniprep KitsDocument6 pagesMammalian Genomic DNA Miniprep KitsRajan RawalNo ratings yet
- Glycerol Stocks and DNA shRNA CRISPR ORF Sept2015Document5 pagesGlycerol Stocks and DNA shRNA CRISPR ORF Sept2015Azb 711No ratings yet
- CH1801 C5 Plasmid IsolationDocument7 pagesCH1801 C5 Plasmid IsolationTanisha ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- MEGAclear™ KitDocument12 pagesMEGAclear™ KitXiaojie LiuNo ratings yet
- Applied Biotechnology CatalogueDocument18 pagesApplied Biotechnology CatalogueMohamed Salem SoltanNo ratings yet
- Plasmidextraction 2002Document2 pagesPlasmidextraction 2002Sahithi KotcherlakotaNo ratings yet
- JetQuick Plasmid Miniprep - GenomedDocument4 pagesJetQuick Plasmid Miniprep - GenomedCarlos de PazNo ratings yet
- (Intended Use) : Instruction ManualDocument8 pages(Intended Use) : Instruction ManualTPNo ratings yet
- Elisa MethodDocument7 pagesElisa MethodNandia SeptiyoriniNo ratings yet
- DNA Extraction ProtocolsDocument13 pagesDNA Extraction Protocolsdr.samakaNo ratings yet
- Human DSP (Dentin Sialoprotein) ELISA KitDocument9 pagesHuman DSP (Dentin Sialoprotein) ELISA Kitmsk adiwiryaNo ratings yet
- Definitive Guide To Western BlotDocument13 pagesDefinitive Guide To Western BlotmllboxNo ratings yet
- RNA Extraction Using TRIzol ReagentDocument5 pagesRNA Extraction Using TRIzol ReagentAliza JafriNo ratings yet
- Western Blot (ABCAM)Document5 pagesWestern Blot (ABCAM)강지영No ratings yet
- Protocol: 190989 Dentin Sialoprotein (DSP) Bioassay™ Elisa Kit (Human)Document4 pagesProtocol: 190989 Dentin Sialoprotein (DSP) Bioassay™ Elisa Kit (Human)MSKANo ratings yet
- Sandwich ELISA Kit For Dysferlin: ABIN6955479Document11 pagesSandwich ELISA Kit For Dysferlin: ABIN6955479Trd FFNo ratings yet
- Rat PDGF (Platelet-Derived Growth Factor) ELISA Kit: Instruction ManualDocument9 pagesRat PDGF (Platelet-Derived Growth Factor) ELISA Kit: Instruction ManualSigit Harya HutamaNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Dog TSHB / Tsh-Beta Elisa Kit (Sandwich ELISA)Document22 pagesUser Manual: Dog TSHB / Tsh-Beta Elisa Kit (Sandwich ELISA)Julio Cesar MaceNo ratings yet
- Wizard SV Genomic DNA Purification System Quick Protocol PDFDocument4 pagesWizard SV Genomic DNA Purification System Quick Protocol PDFPramusita Yoga DaniswaraNo ratings yet
- Protocolo de Extracción de ADN Bacteriano - AusubelDocument5 pagesProtocolo de Extracción de ADN Bacteriano - AusubelLesly CastilloNo ratings yet
- DNA Xpress ReagentDocument7 pagesDNA Xpress Reagenthar2dikNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Aberrations 19 4 23Document50 pagesChromosomal Aberrations 19 4 23Richa MishraNo ratings yet
- Easy Tissue & Cell Genomic DNA Purification Kit: Cat. # DP021E/ DP021E-150 Size 50/150 ReactionsDocument8 pagesEasy Tissue & Cell Genomic DNA Purification Kit: Cat. # DP021E/ DP021E-150 Size 50/150 ReactionsTam LyNo ratings yet
- Lab 4.isolation of PlasmidDocument7 pagesLab 4.isolation of PlasmidJane MargarethaNo ratings yet
- Plasmid DNA IsolationDocument2 pagesPlasmid DNA Isolation9001 Trisha BakshiBBT2No ratings yet
- Mouse IL-8 (Interleukin 8) ELISA Kit: Instruction ManualDocument9 pagesMouse IL-8 (Interleukin 8) ELISA Kit: Instruction ManualAak An NasherNo ratings yet
- (Intended Use) : Instruction ManualDocument8 pages(Intended Use) : Instruction ManualTPNo ratings yet
- Prosedur Isolasi DNA HPV Dari Swab VaginaDocument2 pagesProsedur Isolasi DNA HPV Dari Swab Vaginadinda akhiraniNo ratings yet
- QQ05 Extraction of DNA Fragments From Polyacrylamide Gels Using The QIAquick Gel Extraction KitDocument2 pagesQQ05 Extraction of DNA Fragments From Polyacrylamide Gels Using The QIAquick Gel Extraction KitBogdan HateganNo ratings yet
- ABIN6975603 ManualDocument12 pagesABIN6975603 ManualAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Haccp Procedures and Micro TestingDocument20 pagesHaccp Procedures and Micro TestingUttam Kumar DashNo ratings yet
- Trizol ReagentDocument4 pagesTrizol ReagentDean JanetNo ratings yet
- MDA Kits For Rat For Researcher OnlyDocument14 pagesMDA Kits For Rat For Researcher OnlyPritta TaradipaNo ratings yet
- 3bsmt1 Bobier, Ashwelldonne Molbio PCRDocument9 pages3bsmt1 Bobier, Ashwelldonne Molbio PCRAshwell Donne BobierNo ratings yet
- Dna07 2Document2 pagesDna07 2Sabesan TNo ratings yet
- DNA Purification KitDocument8 pagesDNA Purification KitSukara RatkoNo ratings yet
- Ctab Protocol For Isolating Dna From Plant TissueDocument4 pagesCtab Protocol For Isolating Dna From Plant Tissuemitalimaithani596No ratings yet
- Lab Manual Molecular BiologyDocument19 pagesLab Manual Molecular BiologyLockerLingNo ratings yet
- Mol Bio FinalDocument16 pagesMol Bio FinalBoka PolaNo ratings yet
- KIT 9040 50 PrimeWay Plasmid DNA Extraction Kit ManualDocument7 pagesKIT 9040 50 PrimeWay Plasmid DNA Extraction Kit ManualSn SabrinaNo ratings yet
- ELISA Kit For Angiotensin II (AngII) E90005RaDocument8 pagesELISA Kit For Angiotensin II (AngII) E90005RaTan Jie HuiNo ratings yet
- C5 Plasmid Isolation Formal ReportDocument9 pagesC5 Plasmid Isolation Formal ReportTanisha ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Expression of Recombinant Proteins in The Methylotrophic Yeast Pichia PastorisDocument5 pagesExpression of Recombinant Proteins in The Methylotrophic Yeast Pichia PastorisAlexis TorresNo ratings yet
- DNA Lab 1Document4 pagesDNA Lab 1Abdul Mueez LoneNo ratings yet
- Protocol, Isolation of High Molecular Weight Genomic DNA (CTAB) A1aDocument4 pagesProtocol, Isolation of High Molecular Weight Genomic DNA (CTAB) A1aahmed.mo.22555417No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterFrom EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNo ratings yet
- Practical Handbook of Pharmaceutical Chemistry for M.PharmFrom EverandPractical Handbook of Pharmaceutical Chemistry for M.PharmNo ratings yet
- The Fundamentals of Scientific Research: An Introductory Laboratory ManualFrom EverandThe Fundamentals of Scientific Research: An Introductory Laboratory ManualNo ratings yet
- The Sanger Method: Background InformationDocument5 pagesThe Sanger Method: Background InformationSâthí SàthîNo ratings yet
- Purification Table InstructionDocument1 pagePurification Table Instructionapi-3744715100% (3)
- Non-Complex Active Drug ProductsDocument5 pagesNon-Complex Active Drug Productsmehrdarou.qaNo ratings yet
- Purification of ProteinsDocument28 pagesPurification of ProteinsaasthaNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrometryDocument19 pagesMass SpectrometryArchieNo ratings yet
- Liquid Chromatography HPLC/UPLCDocument42 pagesLiquid Chromatography HPLC/UPLCJohnNo ratings yet
- 2100 Expert - High Sensitivity DNA Assay - DE04105470 - 2019-07-11 - 10-20-58Document18 pages2100 Expert - High Sensitivity DNA Assay - DE04105470 - 2019-07-11 - 10-20-58Pavithra MohanNo ratings yet
- SARS COV 2 (Covid 19) Cycle Threshold Value (CT Value)Document1 pageSARS COV 2 (Covid 19) Cycle Threshold Value (CT Value)mr copy xeroxNo ratings yet
- Student Handout 01 - Cell StructureDocument6 pagesStudent Handout 01 - Cell StructureJoslynn SlaytonNo ratings yet
- Brochure, CAMAG Linomat 5Document2 pagesBrochure, CAMAG Linomat 5Fajar Aji LumaksoNo ratings yet
- Albumin-Indirect Antiglobulin TestDocument2 pagesAlbumin-Indirect Antiglobulin TestCatia CorreaNo ratings yet
- Principle:: Intermolecular Forces Between The Component and The Silica GelDocument32 pagesPrinciple:: Intermolecular Forces Between The Component and The Silica GelKrishnan GiribabuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 (Bacte)Document7 pagesChapter 7 (Bacte)Jessica PontanaresNo ratings yet
- AN LS 001 DNA MeasurementDocument3 pagesAN LS 001 DNA MeasurementLufia CeruleanNo ratings yet
- BoxCar Data Dependent Acquisition Improves The MS MS Cover - 2023 - Arabian JourDocument13 pagesBoxCar Data Dependent Acquisition Improves The MS MS Cover - 2023 - Arabian JourLaboratorium BCPekanbaruNo ratings yet
- BIO107 Laboratory Exercise 8Document5 pagesBIO107 Laboratory Exercise 8Kent Harold GenonNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 6 Fall 2018 With SolutionsDocument5 pagesProblem Set 6 Fall 2018 With SolutionsrickNo ratings yet
- Illumina Dye SequencingDocument5 pagesIllumina Dye SequencingNguyen TaNo ratings yet
- 4.9 Spectroscopy and Chromatography-2Document45 pages4.9 Spectroscopy and Chromatography-2Michael Angelo FilomenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Concept 6.1 Microscopy: The Use of MicroscopesDocument3 pagesChapter 6 Concept 6.1 Microscopy: The Use of MicroscopesksalvadorNo ratings yet
- Af9Pim500 0418M500 : Gotaq Hot Start PolymeraseDocument2 pagesAf9Pim500 0418M500 : Gotaq Hot Start Polymerasenbiolab6659No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Products of Primary Distillation Separation by Vacuum DistillationDocument36 pagesChapter 6 Products of Primary Distillation Separation by Vacuum DistillationAbdurabu AL-MontaserNo ratings yet
- Distillation ColumnsDocument40 pagesDistillation ColumnsSantiagoOrtizLdsNo ratings yet
- Types and Range of Applications For Liquid ChromatographyDocument24 pagesTypes and Range of Applications For Liquid ChromatographyHưng Trần VănNo ratings yet
- Tugas TLC MHSDocument2 pagesTugas TLC MHSCipoxz ParicukNo ratings yet
- Analytical Transmissions Electron Microscopy (TEM) : The Microscope Sample Preparation ImagingDocument54 pagesAnalytical Transmissions Electron Microscopy (TEM) : The Microscope Sample Preparation Imagingshirley rajNo ratings yet
- HB-0986-S41-001 PS QS Casework 1000 V8 0219 WWDocument7 pagesHB-0986-S41-001 PS QS Casework 1000 V8 0219 WWJoshue RosalesNo ratings yet
- CHM 260 Experiment 5Document8 pagesCHM 260 Experiment 5MOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRI0% (1)
- Data Sheet 3 - Bromelain Extraction and CharacterizationDocument2 pagesData Sheet 3 - Bromelain Extraction and Characterizationkatieduong2002No ratings yet