Matlab-Simulink Controller Design
Uploaded by
Mohamed SomaiMatlab-Simulink Controller Design
Uploaded by
Mohamed SomaiThe 2nd Power and Energy Conversion Symposium (PECS 2014)
Melaka, Malaysia
12 May 2014
MATLAB-SIMULINK CONTROLLER DESIGN
FOR ADRUINO TARGET ON AC MOTOR
CONTROL APPLICATION
Shamsul Aizam Zulkifli
Dept. of Electrical Power Engineering
Faculty of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
86400 Parit Raja, Batu Pahat, Johor, Malaysia
Suhairiyanti Mohd Yusof, Ahmad Hussain Hussian, Ahamd Izzat
Mod Arifin, Mohd Saiful Najib Ismail@Marzuki, Wan Ahmad
Khusairi Wan Chek and Faizul Rizal Mohamed Tazudin
Fakulti Kejuruteraan Elektrik
Universiti Teknologi Mara (Terengganu)
Sura Hujung, 23000 Dungun, Terengganu, Malaysia
Simulink library and then downloaded to the Adruino
microcontroller without changing to C programming in order
to see the performance of the Adruino with the inverter in
MATLAB-Simulink based library.
Due to this reason, a simple control method for ac motor
controller is applied to the modern power electronics
devices. As the results, many of researchers have come out
with various controllers in order to control the parameters of
electric motor such as the speed, voltage and current. The
three phase ac motor also known as a non linear
characteristics and for that reason the nonlinear controller is
needed [2]. From the control parameters of the ac motor, the
current input is important in order to determine the
smoothness rotation of the ac motor. This current regulation
is controlled by controlling the pulse-width-modulated
(PWM) that will be developed in the DSP devices [6][7].
The controller that can be applied to ac motor can be
categorized into two, which are the active and passive
controller [3][4][5]. The active controller is a controller that
responded to the reference target such as Field Oriented
Control (FOC), Direct Torque Control (DTC), Proportional
Integral Derivatives (PID), fuzzy control, nueral network,
Sliding Mode Control (SMC), and Hysteresis control. For
the passive control, it is based on the time control system
response.
At the end of this paper, the dual loop controls that is
combined the hyterisis current control with the PID
controller model has been developed in the MATLABSimulink and will be tested in the experimental by using the
Adruino DSP, the 3-phase inverter and the ac motor in order
to see the current response. As a result the performance
characteristics will be observed in terms of output motor line
current, the switching algorithm for the Adruino and the
inverter output voltage.
AbstractThis paper explains, the implementation of
MATLAB-simulink block diagram with the Adruino DSP
target in order to control the output current of the 3-phase
inverter for ac motor application. There is no programming
code has been involved but only uses the target preferences
blocks that are available in the MATLAB-Adruino library.
The current controller has been developed by using the PIDHyterisis control in order to determine the efficiency of the
controller to control the motor current. The system was been
tested on the 1kW inverter output and was connected to the 3
phase induction motor with rating of 375W.
Index TermsMATLAB,
Hyterisis.
Simulink,
Adruino,
PID,
I. INTRODUCTION
As known, ac motor is the widely used education motors
for non electrical engineering student in order to understand
the concepts of moving object from one direction to another
direction. In doing so, the controller device needs to be
developed. It can be developed by combining the
microcontroller or Digital Signal Processing (DSP) device
with the ac motor. The controller must have high switching
frequency or slow switching frequency. As stated, the DSP
is a device that able to generate miliseconds response that is
needed for the 50Hz AC signal. The Adruino, Rasberry PI,
ezdsp TI board or d-space are the examples of the DSP
platform. Generally, the TI ezdsp and d-space are applied
for high level application such as in power system
application or in high precision application while the
Adruino, Rasberry PI, PIC are for low level application.
The advancement and with the new simple structure of
DSPs have attracted more and more non technical expert to
use and applied the Adruino or Rasberry PI
as a
microcontroller. Due to this advantage, it makes the target
such as the Adruino is easy to install and to troubleshoot
when it been applied to the exsisting power converters that
available today.
Today, the Adruino is capable to communicate with the
MATLAB [1] by using the C programming that is based on
the MATLAB software. Until this paper has been written,
the MATLAB-Simulink for Adruino target never been tested
with the power converters devices such as the inverter. Due
to this finding, this paper is focused to test a simple
controller that will be developed using the MATLAB-
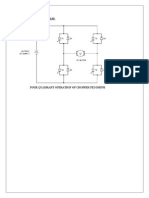
THE PROPOSED TOPOLOGY
Figure 1 shows the block diagram of the project. It
consists of 6 main parts which are the DC source input, the
gate driver circuit, the three phase inverter, the 375W three
phase ac motor as a load, the current sensors and the
Adruino target board. The Adruino is used to test the
controller that has been developed in the MATLABSimulink
327
The 2nd Power and Energy Conversion Symposium (PECS 2014)
Melaka, Malaysia
12 May 2014
The 3-phase inverter was designed to produce 1kW
output that can support about 450V input at the DC source.
The inverter is known as voltage source inverter where it is
the standard used inverter nowadays and it is easy to control
[acul]. The gate driver is needed in order to supply a suitable
voltage for the MOSFET for the inverter. It will produce six
PWM signals that are needed by the inverter.
The ac motor that been used in this project, is a three
phase induction motor rating of 0.37kW, 400V, and 1A
input with maximum rotation speed of 1000rpm. As the
input to the Adruino, the current sensor has been used in
order to give current feedback signal from the ac motor back
to the Adruino.
GATE DRIVER
CIRCUIT
DC POWER SUPPLY
THREE PHASE
INDUCTION
MOTOR
THREE PHASE
INVERTER
Figure 2: Hyterisis band
The function of Analog to Digital (ADC) and Digital to
Analog (DAC) that are shown in Figure 3 are used to change
the input signal from the hardware output to the pc digital
input or vice versa. These bloks are available in the MatlabSimulink where the models are embedded in the
microcontroller by using the Arduino target installer.
PWM
PWM
PWM
HYSTERISIS
CURRENT CONTROL
TECHNIQUE
CURRENT SENSOR
Figure 1: The proposed topology
A. Development of the controller sturcture
The hysteresis control is a nonlinear control that able to
control the nonlinear element such as the ac motor with
simple arrangement or lagging behind condition [13] in
order to have past information for future prediction [14].
There is several methods that can be used for ac motor
control such as Direct torque control (DTC), two hyteresis
comparators [15] and uses the triangle signal in the error
block to minimizes the flux and torque ripple of the ac motor
[16].
Figure 3 : Controller design
In this project the hysteresis current controller is used in
order to generate the PWM signal based on Figure 2. This B. The experimental setup
method has been chosen because the robustness of the
controller to adopt with the changing of the input
The hardware or experimental setup was developed as
control.The hyterisis controller has been designed in
shown in Fig. 4. From Fig.4, the three phase induction
MATLAB-Simulink environment as shown in Figure 3. This
motor has been selected as the test load. The main parts of
project also implements outher loop control by using the PID
this experimental setup are the Adruino, the gate driver and
controller in order to improve the performance of the overall
the 3 phase inverter that have been modelled using Proteus
controller. The general equation of PID control is given in
and changes to 2 layer printed circuit board in order to have
Equation 1.
complete experimental setup. Since the PWM output from
the Adruino is 5 V, the gate driver is needed to increase this
( )
( )
( )
( )
(Eq.1)
( )
voltage before been connected to the 3 phase inverter.
328
The 2nd Power and Energy Conversion Symposium (PECS 2014)
Melaka, Malaysia
12 May 2014
the reference current (red). It indicates that the controller that
has been designed capable to track the reference current.
Figure 4: The experimental setup
Power Transistor (MOSFET SPP11N60C3) and a capacitor
are act as voltage source inverter or full bridge inverter. It is
where the power transistor is capable to handle the
maximum voltage up to 600V or 1kW output.
Figure 6: Reference and feedback current
Figure 7 shows the three phase output line current at the
inverter. It shows that the lines current are balanced where
the three phases are shifted equally. These line currents are
in sinusoidal waveform due to the low pass filter that has
been used at the inverter output.
II. SIMULATION VERIFICATION
From the simulation analysis, the Power System
Blockset and Simulink models were used in order to study
the characteristics of the inverter output with a dummy load.
Figure 5 shows the complete simulation diagram in
MATLAB. It consists of the inverter with six IGBTs which
are connected to the PWM signals at each of the gate pins.
The PWM signal receives from the PID-hysteresis current
controller. For the simulation purpose, the three phase ac
motor is replaced with the 1 resistor and 5mH inductor.
Figure 7: The output current at the inverter
III. HARDWARE VERIFICATION
As seen from Figure 6, the input signal to the Adruino is
in sinusoidal waveform. Due to this, the output that needs to
be generated from the Adruino is in Sinusoidal Pulse Wave
Modulation (SPWM) signal. Figure 8 shows the SPWM
output after the gate driver circuit. These signals will be used
to switch on and off the power MOSFET inside the inverter
circuit.
Figure 5: The Simulink simulation
The detail of the controller is shown in Figure 3 where
for the simulation analysis the ADC and DAC blocks have
been removed.
Figure 6 shows the response of the feedback current from
the load with the current target reference. From this figure,
it shows that the feedback current (green) is followed with
329
The 2nd Power and Energy Conversion Symposium (PECS 2014)
Melaka, Malaysia
12 May 2014
Figure 10 shows the inverter output current. It
indicates that the current waveform is not in sinusoidal
waveform but the motor is still running smoothly. This
problem has been recognized where it is the wrong selection
of the low pass filter sizing. For the next paper the better
design of low pass filter will be used.
IV. CONCLUSION
As a conclusion, the closed loop system for simulation
and hardware results show the function of the Adruino as a
target DSP is able to read the controller design block that
has been developed in the MATLAB-Simulink environment.
This explains that, with the mathematical equations of any
controllers and without to change to programming code, the
Adruino can still works as DSP platform. This will help the
new players of DSP with less experience in programming to
applied the Adruino microcontroller with the power
converters applications as in teaching non electrical
engineering student.
Figure 8: SPWM switching using Adruino
Figure 9 shows the inverter output phase voltage.
This output is measured at the inverter circuit before the
load. It shows the phase voltage is in the square-wave signal
mode. To get the smooth sine wave filtering process must be
done at the output signal.
REFERENCES
[1]
Mathworks
(MATLAB)
Manual,
www.mathworks.com/hardware-support/arduinomatlab.html, excess on Disember 2013
[2] S. Zulkii and M. Ahmad, Linear generator models in
simulink block,in Power and Energy (PECon), 2010 IEEE
International Conference on,pp. 226 231, 292010-dec.1
2010.
[3] Bong-hwan Kwan ,Tac-woo and Jang-hyoun Youm , A
novel SVM-based hystettsis current controller, LEEE Trans.
Ind. Application, vol. 13,no. 2,pp. 297-307,1998.
[4] B.K.Bose,An adaptive hysteresis-band current controller
technique of a voltage-fed PWM inverter for machine drive
system,EEE Trans. Ind. Application, vol. 37, no. 5, pp.
402408,1990.
[5] C.T.Pan and T.Y.Chang, An improved hysteresis cmnt
controller for reducing switching fi-equency, EEE
Trans.Power Electronic, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 97-104, 1994.
[6] D.M.Brod and D.W.Novotny, Current control of VSI PWM
inverter, IEEE Trans. Ind. Application, vol. IA-2, no.4,pp.
562-569,1985
[7] S.Nonaka, New GTO Current source inverter with PWM
control techniques, IEEE Trans. Ind. Application, vol.1A-2,
no. 2, pp. 430436, 1986.
[13] Bertotti, Giorgio (1998). Hysteresis in magnetism: For
physicists, materials scientists, and engineers, Academic
Press. ISBN 978-0-12-093270-2.
[14] Mielke, A.; Roubicek, T. (2003). "A Rate-Independent Model
for Inelastic Behavior of Shape-Memory Alloys". Multiscale
Model. Simul. 1 (4): 571597.
[15] J.Rodri, Guezy, J.Pontty, C.Silvay, S.Kouroy, A.Liendoy, J.
Rebolledoy, Hysteresis current control of a vector controlled
induction motor and DTC: an assessment, Int. J. Electronics,
Vol. 91, No. 11, November 2004, 639651
[16] R.K.Behera and S.P.Das, Improved direct torque of
induction motor with dither injection, Sadhana Vol. 33,
Part 5, October 2008, pp. 551564.
Figure 9 : Inverter output voltage
Figure 10: Inverter current output
330
You might also like
- Dr. Debra Ann Poole PHD - Interviewing Children - The Science of Conversation in Forensic Contexts-American Psychological Association (2016) (Z-Lib - Io)100% (2)Dr. Debra Ann Poole PHD - Interviewing Children - The Science of Conversation in Forensic Contexts-American Psychological Association (2016) (Z-Lib - Io)244 pages
- Closed Loop Control For A Brushless DC Motor To RuNo ratings yetClosed Loop Control For A Brushless DC Motor To Ru1 page
- Integral Cycle Speed Control of Single Phase Induction Motor.50% (2)Integral Cycle Speed Control of Single Phase Induction Motor.47 pages
- Generalized Techniques of Harmonic Elimination and Voltage Control in Thyristor Inverters Part I Harmonic Elimination100% (1)Generalized Techniques of Harmonic Elimination and Voltage Control in Thyristor Inverters Part I Harmonic Elimination8 pages
- Pulsewidth Modulation For Electronic Power Conversion: J. Holtz, Fellow, IEEE Wuppertal University - Germany100% (1)Pulsewidth Modulation For Electronic Power Conversion: J. Holtz, Fellow, IEEE Wuppertal University - Germany18 pages
- Pi Voltage Control Technique For 3 Phase Induuction Motor Using Simulink and ArduinoNo ratings yetPi Voltage Control Technique For 3 Phase Induuction Motor Using Simulink and Arduino37 pages
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- A Case Study for a Single-Phase Inverter Photovoltaic System of a Three-Bedroom Apartment Located in Alexandria, Egypt: building industry, #0From EverandA Case Study for a Single-Phase Inverter Photovoltaic System of a Three-Bedroom Apartment Located in Alexandria, Egypt: building industry, #0No ratings yet
- Fuzzy Logic Control of Three Phase Induction Motor: A Review100% (1)Fuzzy Logic Control of Three Phase Induction Motor: A Review3 pages
- Single Phase Induction Motor Speed Control100% (3)Single Phase Induction Motor Speed Control35 pages
- Microcontroller Based Three Phase InverterNo ratings yetMicrocontroller Based Three Phase Inverter4 pages
- Unit - V Synchronous Drives: 1 Variable Frequency ControlNo ratings yetUnit - V Synchronous Drives: 1 Variable Frequency Control22 pages
- Modeling and Control of A Brushless DC Motor100% (2)Modeling and Control of A Brushless DC Motor66 pages
- Dual-Three Phase Induction Machine Drives Control-A Survey: Extended SummaryNo ratings yetDual-Three Phase Induction Machine Drives Control-A Survey: Extended Summary11 pages
- Load Compensation and Voltage Regulation of Distribution System Using DstatcomNo ratings yetLoad Compensation and Voltage Regulation of Distribution System Using Dstatcom278 pages
- DC Motor Speed Controller Design Using Pulse WidthNo ratings yetDC Motor Speed Controller Design Using Pulse Width12 pages
- MINIDOCUMENTATION - Battery Voltage IndicatorNo ratings yetMINIDOCUMENTATION - Battery Voltage Indicator59 pages
- Speed Control of A DC Motor Using Hand GestureNo ratings yetSpeed Control of A DC Motor Using Hand Gesture4 pages
- TMS320F28335 DSP Programming Using MATLAB Simulink Embedded Coder: Techniques and AdvancementsNo ratings yetTMS320F28335 DSP Programming Using MATLAB Simulink Embedded Coder: Techniques and Advancements7 pages
- AC-DC & DC-DC Converters For DC Motor Drives PDFNo ratings yetAC-DC & DC-DC Converters For DC Motor Drives PDF8 pages
- Speed Control of DC Motor Under Varying Load Using PID Controller100% (1)Speed Control of DC Motor Under Varying Load Using PID Controller11 pages
- Digital Scalar Pulse Width Modulation Methods For Voltage Source Inverter Fed Ac DriveNo ratings yetDigital Scalar Pulse Width Modulation Methods For Voltage Source Inverter Fed Ac Drive7 pages
- Parameter Identification and Modelling of Separately Excited DC MotorNo ratings yetParameter Identification and Modelling of Separately Excited DC Motor8 pages
- Design and Implementation of Water Bill Control System Based GSMNo ratings yetDesign and Implementation of Water Bill Control System Based GSM5 pages
- BLDC Motor Speed Control With RPM DisplayNo ratings yetBLDC Motor Speed Control With RPM Display2 pages
- Vector Control of Induction Motor Without Shaft EncoderNo ratings yetVector Control of Induction Motor Without Shaft Encoder8 pages
- Model Predictive Direct Torque Control Methods For SpeedNo ratings yetModel Predictive Direct Torque Control Methods For Speed25 pages
- Ac Voltage Controller Using Thyristor Project Report by Sandeep100% (1)Ac Voltage Controller Using Thyristor Project Report by Sandeep29 pages
- Project Report On Speed Control of DC Motor by Using PWM TechniqueNo ratings yetProject Report On Speed Control of DC Motor by Using PWM Technique76 pages
- DC Motor Speed Control Using PID ControllerNo ratings yetDC Motor Speed Control Using PID Controller7 pages
- Analysis and Performance Assessment of Six-Pulse Inverter-Fed Three-Phase and Six-Phase Induction MachinesNo ratings yetAnalysis and Performance Assessment of Six-Pulse Inverter-Fed Three-Phase and Six-Phase Induction Machines9 pages
- Chapter 3: Electric Drives and Converters Feeding Electric MotorsNo ratings yetChapter 3: Electric Drives and Converters Feeding Electric Motors11 pages
- Experimental Archaeology in NCU The NewsNo ratings yetExperimental Archaeology in NCU The News17 pages
- No Number of Part Quantity Description Applicability DesignationNo ratings yetNo Number of Part Quantity Description Applicability Designation208 pages
- Sekolah Kluster Kecemerlangan (SKK) : Prepared By: Sitiliyanabtomar NiknurisyabtmohdkamarolzamanNo ratings yetSekolah Kluster Kecemerlangan (SKK) : Prepared By: Sitiliyanabtomar Niknurisyabtmohdkamarolzaman9 pages
- Nueva Ecija 2 District Engineering Office: Required Output/s Deadline Submitted Output/s Date and Time SubmittedNo ratings yetNueva Ecija 2 District Engineering Office: Required Output/s Deadline Submitted Output/s Date and Time Submitted2 pages
- How To Maintain SAP System Alias Entries in Productive Systems - SAP BlogsNo ratings yetHow To Maintain SAP System Alias Entries in Productive Systems - SAP Blogs11 pages
- Algebra Cheat Sheet: Basic Properties & FactsNo ratings yetAlgebra Cheat Sheet: Basic Properties & Facts4 pages
- Chiaroni, D. V. Chiesa & F. Frattini, 2010, Unravelling The Process From Closed To Open Innovation Evidence From MatureNo ratings yetChiaroni, D. V. Chiesa & F. Frattini, 2010, Unravelling The Process From Closed To Open Innovation Evidence From Mature25 pages
- Electronic Resources As Part of Resources in The LibrariesNo ratings yetElectronic Resources As Part of Resources in The Libraries2 pages
- JoelGreenbergThirdSuperseding 30mar 2021No ratings yetJoelGreenbergThirdSuperseding 30mar 202145 pages
- Dr. Debra Ann Poole PHD - Interviewing Children - The Science of Conversation in Forensic Contexts-American Psychological Association (2016) (Z-Lib - Io)Dr. Debra Ann Poole PHD - Interviewing Children - The Science of Conversation in Forensic Contexts-American Psychological Association (2016) (Z-Lib - Io)
- Closed Loop Control For A Brushless DC Motor To RuClosed Loop Control For A Brushless DC Motor To Ru
- Integral Cycle Speed Control of Single Phase Induction Motor.Integral Cycle Speed Control of Single Phase Induction Motor.
- Generalized Techniques of Harmonic Elimination and Voltage Control in Thyristor Inverters Part I Harmonic EliminationGeneralized Techniques of Harmonic Elimination and Voltage Control in Thyristor Inverters Part I Harmonic Elimination
- Pulsewidth Modulation For Electronic Power Conversion: J. Holtz, Fellow, IEEE Wuppertal University - GermanyPulsewidth Modulation For Electronic Power Conversion: J. Holtz, Fellow, IEEE Wuppertal University - Germany
- Pi Voltage Control Technique For 3 Phase Induuction Motor Using Simulink and ArduinoPi Voltage Control Technique For 3 Phase Induuction Motor Using Simulink and Arduino
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld Simulator
- A Case Study for a Single-Phase Inverter Photovoltaic System of a Three-Bedroom Apartment Located in Alexandria, Egypt: building industry, #0From EverandA Case Study for a Single-Phase Inverter Photovoltaic System of a Three-Bedroom Apartment Located in Alexandria, Egypt: building industry, #0
- Fuzzy Logic Control of Three Phase Induction Motor: A ReviewFuzzy Logic Control of Three Phase Induction Motor: A Review
- Unit - V Synchronous Drives: 1 Variable Frequency ControlUnit - V Synchronous Drives: 1 Variable Frequency Control
- Dual-Three Phase Induction Machine Drives Control-A Survey: Extended SummaryDual-Three Phase Induction Machine Drives Control-A Survey: Extended Summary
- Load Compensation and Voltage Regulation of Distribution System Using DstatcomLoad Compensation and Voltage Regulation of Distribution System Using Dstatcom
- DC Motor Speed Controller Design Using Pulse WidthDC Motor Speed Controller Design Using Pulse Width
- TMS320F28335 DSP Programming Using MATLAB Simulink Embedded Coder: Techniques and AdvancementsTMS320F28335 DSP Programming Using MATLAB Simulink Embedded Coder: Techniques and Advancements
- Speed Control of DC Motor Under Varying Load Using PID ControllerSpeed Control of DC Motor Under Varying Load Using PID Controller
- Digital Scalar Pulse Width Modulation Methods For Voltage Source Inverter Fed Ac DriveDigital Scalar Pulse Width Modulation Methods For Voltage Source Inverter Fed Ac Drive
- Parameter Identification and Modelling of Separately Excited DC MotorParameter Identification and Modelling of Separately Excited DC Motor
- Design and Implementation of Water Bill Control System Based GSMDesign and Implementation of Water Bill Control System Based GSM
- Vector Control of Induction Motor Without Shaft EncoderVector Control of Induction Motor Without Shaft Encoder
- Model Predictive Direct Torque Control Methods For SpeedModel Predictive Direct Torque Control Methods For Speed
- Ac Voltage Controller Using Thyristor Project Report by SandeepAc Voltage Controller Using Thyristor Project Report by Sandeep
- Project Report On Speed Control of DC Motor by Using PWM TechniqueProject Report On Speed Control of DC Motor by Using PWM Technique
- Analysis and Performance Assessment of Six-Pulse Inverter-Fed Three-Phase and Six-Phase Induction MachinesAnalysis and Performance Assessment of Six-Pulse Inverter-Fed Three-Phase and Six-Phase Induction Machines
- Chapter 3: Electric Drives and Converters Feeding Electric MotorsChapter 3: Electric Drives and Converters Feeding Electric Motors
- Computer Aided Design of Electrical MachinesFrom EverandComputer Aided Design of Electrical Machines
- Power System Wide-area Stability Analysis and ControlFrom EverandPower System Wide-area Stability Analysis and Control
- Modern Intelligent Instruments - Theory and ApplicationFrom EverandModern Intelligent Instruments - Theory and Application
- No Number of Part Quantity Description Applicability DesignationNo Number of Part Quantity Description Applicability Designation
- Sekolah Kluster Kecemerlangan (SKK) : Prepared By: Sitiliyanabtomar NiknurisyabtmohdkamarolzamanSekolah Kluster Kecemerlangan (SKK) : Prepared By: Sitiliyanabtomar Niknurisyabtmohdkamarolzaman
- Nueva Ecija 2 District Engineering Office: Required Output/s Deadline Submitted Output/s Date and Time SubmittedNueva Ecija 2 District Engineering Office: Required Output/s Deadline Submitted Output/s Date and Time Submitted
- How To Maintain SAP System Alias Entries in Productive Systems - SAP BlogsHow To Maintain SAP System Alias Entries in Productive Systems - SAP Blogs
- Chiaroni, D. V. Chiesa & F. Frattini, 2010, Unravelling The Process From Closed To Open Innovation Evidence From MatureChiaroni, D. V. Chiesa & F. Frattini, 2010, Unravelling The Process From Closed To Open Innovation Evidence From Mature
- Electronic Resources As Part of Resources in The LibrariesElectronic Resources As Part of Resources in The Libraries