0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
473 viewsDNA Teacher V.
This document provides information about DNA and its structure. It defines DNA as deoxyribonucleic acid and notes that DNA contains genes which code for proteins. The document explains that DNA has a double helix shape with sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base pairs forming the structure. It identifies that Watson and Crick established the DNA structure and that DNA can be found in the nucleus and mitochondria of cells. The document also summarizes several other key aspects of DNA including its role in determining cell types from the same DNA and why it is considered the blueprint of life.
Uploaded by
Angela Joan YedersbergerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
473 viewsDNA Teacher V.
This document provides information about DNA and its structure. It defines DNA as deoxyribonucleic acid and notes that DNA contains genes which code for proteins. The document explains that DNA has a double helix shape with sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base pairs forming the structure. It identifies that Watson and Crick established the DNA structure and that DNA can be found in the nucleus and mitochondria of cells. The document also summarizes several other key aspects of DNA including its role in determining cell types from the same DNA and why it is considered the blueprint of life.
Uploaded by
Angela Joan YedersbergerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 3
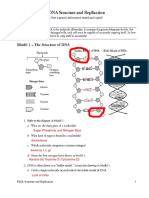
DNA Molecule
Summary Questions
1. Write out the full name for DNA.
deoxyribonucleic acid
2. What is a gene?
a segment of DNA that codes for a particular protein
3. Where in the cell are chromosomes located? nucleus
4. DNA can be found in what organelles in the cell? Mitochondria and
chloroplasts
5. What two scientists established the structure of DNA? Watson and Crick
6. What is the shape of DNA? Double helix
7. The sides of the DNA ladder are composed of what?Sugar (deoxyribose) &
phosphate
8. The "rungs" of the DNA ladder are made of what? Nitrogenous bases
9. What sugar is found in DNA? In RNA? Deoxyribose & ribose
10. How do the bases bond together?
A bonds with __T__
G bonds with ___ C ___
11. The two purines in DNA are__adenine____ and _guanine___.
12. DNA is made of repeating units called _nucleotides___.
13. Why is RNA necessary to act as a messenger? Why can't the code be taken
directly from the DNA? DNA is too big to leave the nucleus
14. Proteins are made where in the cell? On the ribosome in the cytoplasm
15. How do some cells become brain cells and others become skin cells, when the
DNA in ALL the cells is exactly the same? most genes are turned off
16. Why is the DNA molecule referred to as the "blueprint of life"? It tells the
cell how to build the organism
You might also like
- Meiosis Square Dance Lyrics Your Description Picture of PhaseNo ratings yetMeiosis Square Dance Lyrics Your Description Picture of Phase3 pages
- Lesson 1 - 1A - Introduction To Genetics - NotesNo ratings yetLesson 1 - 1A - Introduction To Genetics - Notes6 pages
- 08 Lion Elephant Energy From MacromoleculesNo ratings yet08 Lion Elephant Energy From Macromolecules8 pages
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationNo ratings yetPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration57 pages
- Chromosome Number Worksheet Meiosis MitosisNo ratings yetChromosome Number Worksheet Meiosis Mitosis3 pages
- General Biology Mid Exam Summary Semester One100% (1)General Biology Mid Exam Summary Semester One26 pages
- Laboratory Manual Activity No. 2 Observing BacteriaNo ratings yetLaboratory Manual Activity No. 2 Observing Bacteria9 pages
- The Chemistry of Life of The Chemistry of Life Assessments of CK 12 Biology Quizzes and Test S v5 8bm s1No ratings yetThe Chemistry of Life of The Chemistry of Life Assessments of CK 12 Biology Quizzes and Test S v5 8bm s15 pages
- Fossil Evidence of Evolution Guided Notes Part 1No ratings yetFossil Evidence of Evolution Guided Notes Part 15 pages
- Student Exploration: Human Karyotyping: Vocabulary: Autosome, Chromosomal Disorder, Chromosome, Genome, Karyotype, SexNo ratings yetStudent Exploration: Human Karyotyping: Vocabulary: Autosome, Chromosomal Disorder, Chromosome, Genome, Karyotype, Sex5 pages
- Inquiry Into Genetic Disorders Case StudiesNo ratings yetInquiry Into Genetic Disorders Case Studies10 pages
- Evidence For The Theory of Evolution (CER) HOT Lab100% (1)Evidence For The Theory of Evolution (CER) HOT Lab13 pages
- Ds72-Review Summative Mitosis AssessmentNo ratings yetDs72-Review Summative Mitosis Assessment4 pages
- Lesson 1 - 1A - Introduction To GeneticsNo ratings yetLesson 1 - 1A - Introduction To Genetics26 pages
- Slope Intercept, Point Slope, General Form TestNo ratings yetSlope Intercept, Point Slope, General Form Test14 pages
- Planning An Adventure - Assessment RubricNo ratings yetPlanning An Adventure - Assessment Rubric2 pages
- Reproduction and Human Development Test 2 AnswersNo ratings yetReproduction and Human Development Test 2 Answers8 pages
- Reproduction and Human Development Test For Practice AnswersNo ratings yetReproduction and Human Development Test For Practice Answers7 pages
- Grade 8B - Dalmeny High School 2015/2016: Dear Students and FamiliesNo ratings yetGrade 8B - Dalmeny High School 2015/2016: Dear Students and Families2 pages
- Classifying Organisms in An Ecosystem - Fill in The BlankNo ratings yetClassifying Organisms in An Ecosystem - Fill in The Blank4 pages