Kami Export - POGIL 1 DNA Structure
Kami Export - POGIL 1 DNA Structure
Uploaded by
Eva EllisCopyright:
Available Formats
Kami Export - POGIL 1 DNA Structure
Kami Export - POGIL 1 DNA Structure
Uploaded by
Eva EllisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Kami Export - POGIL 1 DNA Structure
Kami Export - POGIL 1 DNA Structure
Uploaded by
Eva EllisCopyright:
Available Formats
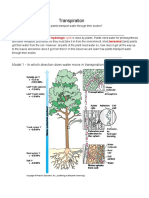
DNA Structure and Replication
HOV.' is genetic information stored and copied?
Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA is the molecule of heredity. It contains the genetic blueprint for life. For
organisms to grow and repair damaged cells, each cell must be capable of accurately copying itself. So how
does die structure of DNA
allow it to copy itselfso accura
Model 1 —The Structure of DNA
Model ofDNA Helix Model ofDNA
Nucleotide
C G
Phosphate
T A
D •oxyn%oe Nitrogen-
sugar contmmng
base
A T
Nitrogen Bases
G C
Thymine
C G
Guamne
D Cytosine T A
l. Refer to the diagram in Model l.
What are the thlee parts ofa nucleotide?
Sugar, Phosphate, and Nitrogen Base
b. What kind of sugar is found in a nucleotide?
deoxyribose
c. Which nucleotide. component contains nitrogen?
bases (a, t, c, g)
d Name the four nitrogen bases shown in Model l.
Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosmine (C)
2. DNA is often drawn in a "ladder model." Locate this drawing in Model l.
Circle a single nucleotide on each side of the ladder model of DNA
Look at latter
DNA Structure and Replication 1
b. What part(s) ofthe nucleotides make up the rungs of the "ladder"?
bases
c. What parts ofthe nucleotides makeup the sides (backbone) of the "ladder"?
Sugar and phosphate
d Look at the bottom and top ofthe "ladder" in Model l. Are die rungs parallel (the ends of
the strands match) or antiparallel (the ends of the strands are opposites)?
Antiparallel, one side ends in sugar and the other side ends in phosphate
3. On dae ladder model of DNA label each ofthe bases with the letterA. T, C or G.
Look at latter
4. Refer to Model l. When one nucleotide contains adenine, what type of base is the adenine
attached to on the opposite nucleotide strand?
Thymine
5. The two strands of DNA are held together with hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen bases.
These are weak bonds between polar molecules. How many hydrogen bonds connect the two
bases from Question 4?
two
6. Refer to Model l. When one nucleotide contains cytosine, what type of base is the cytosine
attached to on the opposite nucleotide strand?
Guanine
7. How many hydrogen bonds connect the two bases from Question 6?
Three
8. With your group, use a complete sentence to write a rule for how the bases are arranged in the
laåder model of DNA.
The Adenine and Thymine bases connect and then Cytosine and Guanine connect
Read This!
Elwin Chargaff (1905—2002), an Austrian-American biochemist, investigated the ratio of nucleotide bases
found in the DNA from a variety of organisms. From his research, as well as reseacch by Rosalind Frank*
lin and Maurice Wilkins, Watson and Crick developed the oomplementary base-pair rule during their
race to discover the structure of DNA. The complementuy base-pair rule states that adenine and thymine
form pairs across two strands, and guanine and cytosine form pairs across tv.'0 strands,
9. Fill in the complementary bases on the strand below according to the base-pair rule.
c
T A G G T C
10. The ladder model ofDNAis asimplified representation ofthe actual structure and shape ofa
DNA molecule. In reality, the strands of DNA form a double helix. Refer to the double helix
diagram in Model I and describe its shape using a complete sentence.
A double helix is two back bones made of alternating phosphate and sugar. The bases connect
the back bones in the middle of the double helix.
You might also like
- Cell Biology Biochemistry - 4th EdDocument152 pagesCell Biology Biochemistry - 4th EdBlitzen BusaingNo ratings yet
- Ebook Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7Th Edition Karp Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument68 pagesEbook Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7Th Edition Karp Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDavidLeekemt100% (13)
- DNA StructureDocument6 pagesDNA StructureSebastian RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Transpiration POGIL Answer KeyDocument8 pagesTranspiration POGIL Answer KeyJade Tapper50% (2)
- Killing Chloroplasts:: Herbicides Targeting PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesKilling Chloroplasts:: Herbicides Targeting PhotosynthesisAhmed MohsenNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument12 pagesBiology ProjectAtharva Dalvi86% (7)
- Intro To Genetics WebQuestDocument3 pagesIntro To Genetics WebQuestFRANKLIN Ofori100% (2)
- Jacob Gutierrez - Gizmos DNAAnalysisDocument4 pagesJacob Gutierrez - Gizmos DNAAnalysisJacob GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Selection and Speciation POGILDocument3 pagesSelection and Speciation POGILCody PalmerNo ratings yet
- Biomes of North America: Average Temperature (°C)Document6 pagesBiomes of North America: Average Temperature (°C)Victoria AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- 11.4 Meiosis: Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pages11.4 Meiosis: Multiple ChoiceMING ZHUNo ratings yet
- AP Biology - Worksheet - Pedigrees 2 PDFDocument3 pagesAP Biology - Worksheet - Pedigrees 2 PDFVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- As OCR Biology Unit F212 Learning Grids Module 1 Nucleic Acids and EnzymesDocument16 pagesAs OCR Biology Unit F212 Learning Grids Module 1 Nucleic Acids and EnzymesJordanGabrielNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Cambridge AS Level Biology Biological Molecules: 2 N 2 N 2 2 N N 2Document19 pagesTest 1 Cambridge AS Level Biology Biological Molecules: 2 N 2 N 2 2 N N 2Kajana Sivarasa ShenthanNo ratings yet
- Human GeneticsDocument32 pagesHuman GeneticsLorenzo Maria CerviNo ratings yet
- Eoc ReviewDocument33 pagesEoc Reviewapi-237316144No ratings yet
- IB MYP U7 Peppered Moth Activity SolutionsDocument2 pagesIB MYP U7 Peppered Moth Activity SolutionsCoco LocoNo ratings yet
- Biology SQP-01 2024 ExamDocument8 pagesBiology SQP-01 2024 ExamananyainwydNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Document6 pagesGene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Camila CorvalanNo ratings yet
- Paper Practice Test With KEY AttachedDocument8 pagesPaper Practice Test With KEY AttachedmspallardNo ratings yet
- Transport in Cells POGILDocument6 pagesTransport in Cells POGILAaliyah AdenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26Document2 pagesChapter 26araneyaNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab: Natural Selection and Allele FrequencyDocument3 pagesBiology Lab: Natural Selection and Allele FrequencynazrimuhsinNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions 1 EvolutionDocument14 pagesPractice Questions 1 EvolutioncindyjiacaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 203 Spring 2015 Mock FinalDocument6 pagesBIOL 203 Spring 2015 Mock FinalMASNo ratings yet
- Cells ExamDocument13 pagesCells Examwafa eliasNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Life Long TestDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Life Long TestMichelle Ramirez Co-GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 2008 Entrance Exam Q62-80Document9 pages2008 Entrance Exam Q62-80SciOlympiad2345100% (1)
- DNA RAN Prot Syn Web PracticeDocument11 pagesDNA RAN Prot Syn Web PracticeTimothy MacdonaldNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression and Regulation: Ap BiologyDocument16 pagesGene Expression and Regulation: Ap BiologyFb EyeNo ratings yet
- BioEOC PracticekeyDocument21 pagesBioEOC PracticekeyEnerya AbalosNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells - PeTa2Document6 pagesProkaryote and Eukaryote Cells - PeTa2Robin-chwan100% (1)
- N5 Biology 2014Document41 pagesN5 Biology 2014FarooqAhmadLashariNo ratings yet
- H2 Evolution QuestionsDocument27 pagesH2 Evolution QuestionsWesley Tan100% (1)
- 9 Glycolysis and The Krebs Cycle-S PDFDocument8 pages9 Glycolysis and The Krebs Cycle-S PDFmadhavi goswamiNo ratings yet
- 28 Control of Blood Sugar Levels-SDocument5 pages28 Control of Blood Sugar Levels-SAaliya Nagori100% (1)
- Cell Cycle POGILDocument4 pagesCell Cycle POGILRemuo33% (3)
- DNA and RNA Practice QuestionsDocument13 pagesDNA and RNA Practice QuestionsAngeleena ANTONo ratings yet
- 2008 Biology: InsightDocument23 pages2008 Biology: InsightXavier GavinNo ratings yet
- Beano LabDocument12 pagesBeano Labapi-284496286No ratings yet
- 1.4 DNA and Protein SynthesisDocument46 pages1.4 DNA and Protein SynthesisHuseyn Agazade100% (1)
- Section Assignement 1 - Graphing and StatsDocument7 pagesSection Assignement 1 - Graphing and StatsDavina SuseloNo ratings yet
- s6 Biology Paper 1Document19 pagess6 Biology Paper 1Tusiime RobertNo ratings yet
- Biology Life On Earth NotesDocument10 pagesBiology Life On Earth NotesEmmanuel Onyebuchi ObinwanorNo ratings yet
- Science SQP-01 2024Document13 pagesScience SQP-01 2024badasserytechNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA, Part 2Document15 pagesDNA and RNA, Part 2shiyiNo ratings yet
- Genetics Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesGenetics Practice ProblemsCatalinaCardenasNo ratings yet
- 22 Nutrient Cycles-SDocument7 pages22 Nutrient Cycles-SChanceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Organization of The CellDocument15 pagesChapter 4-Organization of The CellKevin Ang100% (1)
- Ecology Practice Questions 2Document19 pagesEcology Practice Questions 2Fares ElgalladNo ratings yet
- NucleiacidsDocument89 pagesNucleiacidsdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- 21 Evolution and Selection-SDocument6 pages21 Evolution and Selection-SSSSSSSSSSS100% (1)
- Dna and Rna A Must ReadDocument11 pagesDna and Rna A Must ReadBonny Ya SakeusNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Dna Class 12Document30 pagesWorksheet Dna Class 12BrindhaVasudevan100% (1)
- Worksheet - Enzymes - ReviewDocument3 pagesWorksheet - Enzymes - Reviewapi-270403367100% (1)
- 2006 Assessment 2006 Biology GA 3: Written Examination General CommentsDocument7 pages2006 Assessment 2006 Biology GA 3: Written Examination General Commentspjb_94No ratings yet
- 19 Evidence For Evolution-S PDFDocument6 pages19 Evidence For Evolution-S PDFstlcajun55No ratings yet
- DNA Structure and Repliation, Transcription and Replication and PhotosynthesisDocument67 pagesDNA Structure and Repliation, Transcription and Replication and Photosynthesisdiahema100% (1)
- 2019 Human Biology Unit 1Document41 pages2019 Human Biology Unit 1Ralph Rezin Moore100% (1)
- Name - Date - Period - Mutations WorksheetDocument4 pagesName - Date - Period - Mutations WorksheetEric CalderónNo ratings yet
- British Biology Olympiad 2012 Round Two Question Paper: Time Allowed 1Document24 pagesBritish Biology Olympiad 2012 Round Two Question Paper: Time Allowed 1Malvina Yuan0% (1)
- Kami Export - ALEXA CADENA - Copy of 04 DNA Structure - POGILDocument2 pagesKami Export - ALEXA CADENA - Copy of 04 DNA Structure - POGILALEXA CADENANo ratings yet
- Mitochondria: Structure and FunctionDocument7 pagesMitochondria: Structure and FunctionHariniNo ratings yet
- From Gene To ProteinDocument9 pagesFrom Gene To ProteincrookedspookNo ratings yet
- (Premna Oblongifolia Merr) Pada Mencit C3H Yang Ditransplantasi Sel Tumor Payudara. Bogor: Institut Pertanian Bogor (IPB)Document5 pages(Premna Oblongifolia Merr) Pada Mencit C3H Yang Ditransplantasi Sel Tumor Payudara. Bogor: Institut Pertanian Bogor (IPB)karinNo ratings yet
- General Introduction and Basic Biochemical PrinciplesDocument6 pagesGeneral Introduction and Basic Biochemical PrinciplescelecosibNo ratings yet
- RiboflavinDocument29 pagesRiboflavinDR JIJIN J UNo ratings yet
- Han 2010Document14 pagesHan 2010julia rossoNo ratings yet
- Adapters N LinkersDocument17 pagesAdapters N LinkersGeetika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ligand Gated Ion ChannelDocument12 pagesLigand Gated Ion ChannelShoaib Patel0% (1)
- IELTS Academic Reading Practice Sample - IELTS-upDocument10 pagesIELTS Academic Reading Practice Sample - IELTS-upChalee YanaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGoDocument8 pagesBiomolecules - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGoRoshan AhamedNo ratings yet
- Harga Tayang Afifarma Jamkesnas 2023Document4 pagesHarga Tayang Afifarma Jamkesnas 2023Fadly AsriNo ratings yet
- Study of Lipid Profile in AnemiaDocument140 pagesStudy of Lipid Profile in AnemiaGoto Lalu100% (1)
- Biology STD 12: Biology MCQ: Section A //X Choose Correct Answer From The Given Options. (Each Carries 1 Mark)Document19 pagesBiology STD 12: Biology MCQ: Section A //X Choose Correct Answer From The Given Options. (Each Carries 1 Mark)Darshil MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis: BiochemistryDocument10 pagesGluconeogenesis: BiochemistryManila Med100% (1)
- Nextera™ DNA Sample Prep Kit EpicentreDocument12 pagesNextera™ DNA Sample Prep Kit Epicentrekomissar27No ratings yet
- Biologically Important Molecules Chemical Tests LabDocument8 pagesBiologically Important Molecules Chemical Tests LabJames DaurayNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec Midterm TransesDocument17 pagesBiochem Lec Midterm Transescathryna gaylanNo ratings yet
- What Is Epigenetics?Document34 pagesWhat Is Epigenetics?jhhjjh100% (1)
- Microbial Genetics: DNA Replication and The Central DogmaDocument27 pagesMicrobial Genetics: DNA Replication and The Central DogmawijayantiNo ratings yet
- Pgy 3419 2amino Acid Metabolism 2021 PDFDocument47 pagesPgy 3419 2amino Acid Metabolism 2021 PDFDesmond BwalyaNo ratings yet
- Chp12.odt 1Document4 pagesChp12.odt 1Devin ParkerNo ratings yet
- Macromolecule InfographicDocument1 pageMacromolecule InfographicKorah PichonNo ratings yet
- Bio103L, Expt 3 & 4 (Revised)Document10 pagesBio103L, Expt 3 & 4 (Revised)Piya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Glucose HomeostasisDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Glucose Homeostasistliviu334066No ratings yet
- MODULE 2-BIOMOLECULES PETA-WORKSHEET-answer KeyDocument4 pagesMODULE 2-BIOMOLECULES PETA-WORKSHEET-answer Keyromavin guillermoNo ratings yet
- Genome Editing With CRISPR-Cas Nucleases, Base Editors, Transposases and Prime EditorsDocument21 pagesGenome Editing With CRISPR-Cas Nucleases, Base Editors, Transposases and Prime EditorsTomer ChenNo ratings yet