Solutions For Assignment - 3
Uploaded by
KarthikeyanKarunSolutions For Assignment - 3
Uploaded by
KarthikeyanKarunDesign of Photovoltaic Systems
Solutions: Assignment 3
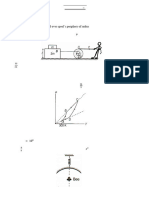
1. The output of a PV cell is 2 W at an insolation of 1 kW/m2 . The area of a cell is
150 × 150 mm2 . If the efficiency of a cell is 15 %, then the angle of incidence of radiation
made with normal to the solar cell is
a) 53.65 deg (X)
b) 36.34
c) 42.28
d) 47.72
(Note: L=1kW/m2*A*eff ; L*cos(theta)=2W)
2. The sensitivity of the solar cell to the spectral irradiance of sun light is maximum at
a) wavelengths less than 400nm
b) wavelengths between 400nm and 700nm (X)
c) wavelength between 700nm and 2000nm
d) wavelength between 2000nm and 5000nm
3. The value of solar constant is approximately:
a) 1 kW/m2
b) 1.37 kW/m2 (X)
c) 1 kWh/m2
d) 1.37 kWh/m2
4. At a given point on earth located on the 30 deg. latitude line, if the solar declination is −20 deg and the hour angle is
45 deg, then the zenith angle is:
a) 44.85 deg
b) 66.15 deg (X)
c) 23.85 deg
d) 45.5 deg
(Note: L.cos(qz)= L.cosd.cosw.cosQ + L.sind.sinQ)
5. On what day approximately the sun will be overhead (noon) at a place located on the latitude 8.57 deg
a) March 12
b) April 12 (X)
c) May 12
d) June 12
(Note: hour angle =0 deg (noon); qz=0 deg (sun overhead), solve for N )
6. On which day zenith angle will be equal to latitude
a) September 21
b) March 21
c) Both A and B (X)
d) June 21
7. The extra terrestrial insolation on March 27 , 1989 is
a) 1.3747 (X)
b) 1.3341
c) 1.3837
d) 1.3447
(Note: find k, and L=Lsc*k = 1.3747 kW/m2)
8. At sunset and sunrise, the zenith angle is
a) 0 deg
b) 90 deg (X)
c) 180 deg
d) 45 deg
9. If the solar declination is 23.5 deg and latitude angle is 45 deg , then the sunrise hour angle is
a) 45 deg
b) −45 deg
c) 90 deg
d) 115 deg (X)
10. The length of the day will be approximately 12 hours on
a) Equator
b) When the angle of declination is zero
c) when the angle of declination is +/- 23.5 deg
d) Both A and B (X)
You might also like
- Principles of Communication Systems by Taub and Schilling73% (41)Principles of Communication Systems by Taub and Schilling119 pages
- (Questions Only) ME 366 ONLINE REGULAR QUIZ 3 2022 - 2023No ratings yet(Questions Only) ME 366 ONLINE REGULAR QUIZ 3 2022 - 202310 pages
- Comp 2025 Grand Btest (Mains) Physics Paper-1No ratings yetComp 2025 Grand Btest (Mains) Physics Paper-112 pages
- Jee Main 2023 PDF Jan 25 Shift 1 Shri Chaitanya PDFNo ratings yetJee Main 2023 PDF Jan 25 Shift 1 Shri Chaitanya PDF10 pages
- Design of Photovoltaic Systems - Unit 4 - EnERGY FROM SUNNo ratings yetDesign of Photovoltaic Systems - Unit 4 - EnERGY FROM SUN3 pages
- Electromagnetic Wave - Optics and Modern Physics - Past Paper PDFNo ratings yetElectromagnetic Wave - Optics and Modern Physics - Past Paper PDF10 pages
- +1 Physics: Adayar - Adambakkam - East Tambaram - Pallavaram - PammalNo ratings yet+1 Physics: Adayar - Adambakkam - East Tambaram - Pallavaram - Pammal18 pages
- Topic 2.1 Oscillatory Motion: Department of Science and Humanities MCQ For Regulations 2017No ratings yetTopic 2.1 Oscillatory Motion: Department of Science and Humanities MCQ For Regulations 201713 pages
- Dept. of Physics, Bangabasi College Kolkata, NPTEL Local ChapterNo ratings yetDept. of Physics, Bangabasi College Kolkata, NPTEL Local Chapter12 pages
- 27 June 2024 Full Syllabus Mock Test 6 Sankalp NEET VedantuNo ratings yet27 June 2024 Full Syllabus Mock Test 6 Sankalp NEET Vedantu77 pages
- Test No-12 - Mock Test Series - NEET - Phy - Chem - BioNo ratings yetTest No-12 - Mock Test Series - NEET - Phy - Chem - Bio25 pages
- T R T R T R T R: PIEAS Test (2016) Subject Part: PhysicsNo ratings yetT R T R T R T R: PIEAS Test (2016) Subject Part: Physics7 pages
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesFrom Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- General Physics (PHY 2140) : Electricity and Magnetism Magnetism Application of Magnetic Forces Ampere's LawNo ratings yetGeneral Physics (PHY 2140) : Electricity and Magnetism Magnetism Application of Magnetic Forces Ampere's Law25 pages
- CADCO Training Brochure AutoCAD Electrical EssentialsNo ratings yetCADCO Training Brochure AutoCAD Electrical Essentials3 pages
- A High Gain Input-Parallel Output-Series DC/DC Converter With Dual Coupled InductorsNo ratings yetA High Gain Input-Parallel Output-Series DC/DC Converter With Dual Coupled Inductors9 pages
- Diffractive Glossmeter For Measurement of DynamicNo ratings yetDiffractive Glossmeter For Measurement of Dynamic239 pages
- EE2201 Measurement and Instrumentation Lecture Notes100% (1)EE2201 Measurement and Instrumentation Lecture Notes73 pages