0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
442 viewsTo The States, Are Reserved To The States Respectively, or To The People."
To The States, Are Reserved To The States Respectively, or To The People."
Uploaded by
Brat Wurst1) The 10th Amendment reserves powers not delegated to the federal government nor prohibited by the Constitution to the states or people.
2) There are two views of the 10th Amendment - as a limit on federal power protecting state sovereignty, or as a simple reminder of enumerated powers.
3) The Supreme Court has ruled that federal laws cannot commandeer or compel states by forcing them to enact laws or implement federal programs. However, generally applicable laws are allowed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
To The States, Are Reserved To The States Respectively, or To The People."
To The States, Are Reserved To The States Respectively, or To The People."
Uploaded by
Brat Wurst0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
442 views1 page1) The 10th Amendment reserves powers not delegated to the federal government nor prohibited by the Constitution to the states or people.
2) There are two views of the 10th Amendment - as a limit on federal power protecting state sovereignty, or as a simple reminder of enumerated powers.
3) The Supreme Court has ruled that federal laws cannot commandeer or compel states by forcing them to enact laws or implement federal programs. However, generally applicable laws are allowed.
Original Description:
1L Flow Charts by blondebarrister of reddit
Original Title
10A
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
1) The 10th Amendment reserves powers not delegated to the federal government nor prohibited by the Constitution to the states or people.
2) There are two views of the 10th Amendment - as a limit on federal power protecting state sovereignty, or as a simple reminder of enumerated powers.
3) The Supreme Court has ruled that federal laws cannot commandeer or compel states by forcing them to enact laws or implement federal programs. However, generally applicable laws are allowed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
442 views1 pageTo The States, Are Reserved To The States Respectively, or To The People."
To The States, Are Reserved To The States Respectively, or To The People."
Uploaded by
Brat Wurst1) The 10th Amendment reserves powers not delegated to the federal government nor prohibited by the Constitution to the states or people.
2) There are two views of the 10th Amendment - as a limit on federal power protecting state sovereignty, or as a simple reminder of enumerated powers.
3) The Supreme Court has ruled that federal laws cannot commandeer or compel states by forcing them to enact laws or implement federal programs. However, generally applicable laws are allowed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
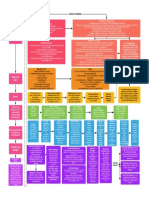
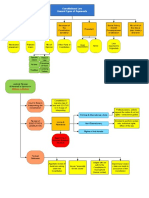
The 10th Amendment - "The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it This
This dispute concerns 2 interrelated issues of constitutional
policy -
to the states, are reserved to the states respectively, or to the people."
1 - how imporant is the protection of state sovereignty &
federalism?
Two competing readings of the 10th amendment - 2 - should it be the role of the judiciary to protect state
prerogatives, or should this be left to the political process?
- 10th as a simple reminder Congress can only
legislate within Constitutional authority - laws are not
- 10th as important limit on Congressional power
unconstitutional for violating the 10th; laws Federalism benefits - decreasing likelihood of federal
that protects state sovereignty from federal
constitutional so long as they are within scope of power tyranny, division of power reduces it, state/local govts -
intrusion & reserved a zone of activity to the
granted by the Constitution - 10th not a basis for political process insufficient to protect state sovereignty
states for their exclusive control, federal laws
invalidating federal law. - Enhances democratic rule by providing govt close to people
intruding on the zone are unconstitutional.
-Federal laws could be unconstitutional for violating - Allows states to be laboratories for new ideas
another Constitutional provision.
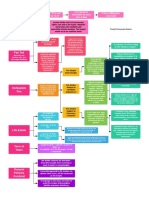
10th as reserving zone of Bailey v. Drexel - Reiteration of doctrine of enumerated powers not
activities to states for Furniture - Congress individual limit of Congressional authority.
exclusive control - Hammer attempting to control
specifically control over production & intrduce Two Direct Methods of Regulation of States -
production like manufacturing into zone Ct saw Darby - 10th but a truism Laws of General Application [Garcia] - To make states
Gibbons - so long as
was for states - Child Labor reserved to states that all is retained which has susceptible to same regulation as private parties. OK.
congress acted within
Case - regulating hours of labor Butler - impermissibly not been surrendered. Commandeering of state officials - forcing states to
scope of CC, law
of children entrusted purely to controlled production, -Law constitutional so long implement federal policy; this is not OK.
wouldn't be
state authority, state police area left to states by as within scope of
unconstitutional as
power 10th Constitutional power.
violating state
Expressly overtturned
sovereignty. CC no
National League - ct declared unconstitutional Hammer; made clear 10th Political accountability - voters don't know where to point
limitations other than
application of fair labor standards act requiring state & wouldn't be based for finger during political process if state official does something
prescribed in
local employees be paid min wage invalidating federal laws. the federal govt has forced them to do rather than something
Constitution.
- "there are limits upon power of Congress to override the state has decided to do; federalism is to protect
state sovereignty even when exercising otherwise individual liberty; to do so; fed govt needs to be politically
plenary powers to regulate commerce." violated 10th bc Garcia - overruled NLC; responsible
"operated to directly displace states freedom to structure -NLC approach unworkable -
integral operations in areas of traditional govt functions." "traditional" or "integral" - any rule of
state immunity looking to traditional
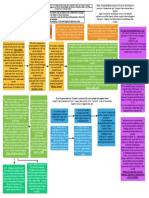
NY v. U.S. [all states must clean up waste or Printz v. U.S. nature of govt functions invites
take title & be liable for any harm waste [state/local LEO unelected fed judiciary to make
caused] - Unconstitutional - take title gave must conduct decisions about what state policies it
state govts choice bt accepting ownership of background checks favors & what it doesn't
waste or regulating according to before issuing -protection of state prorgatives should
Congressional instructions firearms] - be thru political process not from
Congress was commandeering states, Unconstitutional, judiciary.
conscripting the states, forcing them to Congress was
enact a law or regulation, violating the 10th - commandeering
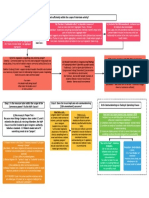
cannot compel states to enact or administer states - cannot Garcia v. NY/Printz -
a federal regulatory program, would compel state · Garcia seems to apply mainly to
undermine govt accountability bc congress executive officials to generally applicable federal
could make a decision, but states would administer a federal lawmaking -when Congress passes a
take political heat & be held responsible for mandate, cannot generally applicable law, 10th doesn?t
a decision not theirs compel state entitle state?s own operations to
*Majority explictly rejected argument that officers to act, exemption merely because it is a
compelling govt interest sufficient to permit a violates 10th state being regulated along with all
law that otherwise would violate the 10th amendment. other private entities.
-Central Holding - unconstitutional to compel -Also SoP violation - -Where federal tries to force state or
state leg to adopt laws or state agencies to Congress local govt to enact legislation or
adopt regulations; but Congress could set impermissible gave regulation or tries to force state or
standards state/local govts must meet, executive authority local officials to perform particular
preempt state & local actions; may attach to implment law to govt functions- not part of generally
strings on grants to state & local govts to state/local LEOs applicable scheme & instead directed
induce specifically at states?basic exercise
of sovereignty- right to carry out
business of govt- federal government
HOWEVER - Congress can try to induce state/local may not use such coercion
govts to act by conditioning grants of money so long
as they are clearly stated, related to the purpose or
program, & are not unduly coercive
-NY & Printz 0 affirmative mandates, not restrictions
on conduct
You might also like
- ConLaw PreWrites 2018 PDFDocument12 pagesConLaw PreWrites 2018 PDFMaria M100% (1)
- ContractsDocument1 pageContractsBrat Wurst100% (2)
- Joinder DiagramsDocument1 pageJoinder DiagramsBrat Wurst100% (3)
- Negligence AnalysisDocument1 pageNegligence AnalysisBrat Wurst100% (3)
- Future InterestsDocument1 pageFuture InterestsBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Restrictions On Land UseDocument1 pageRestrictions On Land UseBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Restrictions On Land UseDocument1 pageRestrictions On Land UseBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Ucc 2-207Document1 pageUcc 2-207Brat Wurst100% (1)
- Con Law Master ChartDocument1 pageCon Law Master ChartBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Property Present EstatesDocument1 pageProperty Present EstatesBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Property Present EstatesDocument1 pageProperty Present EstatesBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Answering A Con Law QuestionDocument1 pageAnswering A Con Law QuestionBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Con Law Commerce Clause Flow ChartDocument1 pageCon Law Commerce Clause Flow ChartJ Alexander VernonNo ratings yet
- Answering A Con Law QuestionDocument1 pageAnswering A Con Law QuestionBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Commerce Clause FlowchartDocument1 pageCommerce Clause FlowchartMark Adamson100% (1)
- 1st A - Speech Flowchart # CasesDocument2 pages1st A - Speech Flowchart # Casessmuldersam100% (1)
- Property 1L Outline - 2021Document67 pagesProperty 1L Outline - 2021AmandaNo ratings yet
- SSI Under 11thDocument1 pageSSI Under 11thBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Basic Commerce Clause FrameworkDocument1 pageBasic Commerce Clause FrameworkBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- DCCDocument1 pageDCCBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Commerce ClauseDocument1 pageCommerce ClauseBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Powers & Limitations of The Judiciary Step 1: Can/will The Supreme Court Hear The Case?Document1 pagePowers & Limitations of The Judiciary Step 1: Can/will The Supreme Court Hear The Case?Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- Dormant Commerce Clause FCDocument1 pageDormant Commerce Clause FCslbernstein100% (1)
- SMJDocument1 pageSMJBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Con Law II OutlineDocument44 pagesCon Law II OutlineCharlene Soleimani100% (10)
- P JoiningDocument1 pageP JoiningBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Takings FlowchartDocument1 pageTakings FlowchartAmanda100% (1)
- Contracts 2 OutlineDocument37 pagesContracts 2 OutlineBrandon YeboahNo ratings yet
- Basic Commerce Clause FrameworkDocument1 pageBasic Commerce Clause FrameworkBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Commerce ClauseDocument1 pageCommerce ClauseBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Lead With Emotional IntelligenceDocument15 pagesLead With Emotional IntelligenceElay CalinaoNo ratings yet
- Con Law OutlineDocument14 pagesCon Law Outlinetm05101No ratings yet
- Con Law Outline For 1 and 2 Good OutlineDocument35 pagesCon Law Outline For 1 and 2 Good Outlinetyler505No ratings yet
- Allocation of Foreign Policy PowerDocument1 pageAllocation of Foreign Policy PowerBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Executive Powers - Page 1Document1 pageExecutive Powers - Page 1Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- Steel Seizure FrameworkDocument1 pageSteel Seizure FrameworkBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Civil War Enforcement PowersDocument1 pageCivil War Enforcement PowersBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Property ChecklistDocument30 pagesProperty ChecklistHeather Kinsaul FosterNo ratings yet
- Con Law SkeletalDocument20 pagesCon Law Skeletalnatashan1985No ratings yet
- Impleader DiagramDocument1 pageImpleader DiagramBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Con Law AttackDocument6 pagesCon Law Attackthisfadednight100% (2)
- Civil Procedure RoadmapsDocument15 pagesCivil Procedure RoadmapsCarolina JordanNo ratings yet
- Business OrganizationsDocument71 pagesBusiness Organizationsjdadas100% (2)
- Commerce Clause Flow ChartDocument1 pageCommerce Clause Flow Chartrad108100% (1)
- My Con Law I Outline (Charts & Bones)Document13 pagesMy Con Law I Outline (Charts & Bones)Priscilla QuansahNo ratings yet
- Present and Future Estates OutlineDocument4 pagesPresent and Future Estates OutlineTripp Rush100% (2)
- ENS CivPro Attack OutlineDocument4 pagesENS CivPro Attack OutlineseabreezeNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law II Zietlow Outline VillanuevaDocument49 pagesConstitutional Law II Zietlow Outline VillanuevaCatNo ratings yet
- Con Law 2 Gulasekaram 1Document10 pagesCon Law 2 Gulasekaram 1Big BearNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law OutlineDocument55 pagesConstitutional Law OutlineIsabella Levy100% (1)
- Supplemental Jurisdiction 2Document1 pageSupplemental Jurisdiction 2Vince DePalmaNo ratings yet
- Crim Law Attack OutlineDocument12 pagesCrim Law Attack OutlineRick Coyle100% (1)
- Business Associations (Corporations) - Duty of Care FlowchartDocument1 pageBusiness Associations (Corporations) - Duty of Care FlowchartBill Brasky0% (2)
- Constitutional Law I Outline 2013Document29 pagesConstitutional Law I Outline 2013The Lotus Eater100% (2)
- P ReclusionDocument1 pageP ReclusionBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- ConLaw Exam Q With Model ADocument32 pagesConLaw Exam Q With Model ALouis Carlos100% (1)
- Con Law TestsDocument4 pagesCon Law Testschristell Casey50% (6)
- Criminal Law Pre-WritesDocument1 pageCriminal Law Pre-WritesAlex HardenNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Jurisdiction FlowchartDocument1 pageSupplemental Jurisdiction FlowchartAmandaNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law Outline Swartzwelder Standards of Review Intro Issue: RuleDocument37 pagesConstitutional Law Outline Swartzwelder Standards of Review Intro Issue: RuleKylee Colwell100% (2)
- Con LawDocument34 pagesCon LawNathan Breen100% (1)
- EPC, DPC Attack PlansDocument6 pagesEPC, DPC Attack PlansEl100% (3)
- Con Law I Outline - WeaverDocument62 pagesCon Law I Outline - WeaverJasonNo ratings yet
- Con Law Flow ChartsDocument6 pagesCon Law Flow ChartsBrady WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Con Law OutlineDocument22 pagesCon Law OutlineslavichorseNo ratings yet
- Class Action - Rule 23 To Be Certified, Must Meet 23A Requirements & Fit Into A 23B - Not Class Action Until Court Certifies It As SuchDocument1 pageClass Action - Rule 23 To Be Certified, Must Meet 23A Requirements & Fit Into A 23B - Not Class Action Until Court Certifies It As SuchBrat Wurst100% (1)
- Leg Reg ChecklistDocument5 pagesLeg Reg ChecklistChristopher Pedro100% (1)
- Con Structs Review Document 11.21.22Document21 pagesCon Structs Review Document 11.21.22Maya El CheikhNo ratings yet
- Consti and Local Gov Notes HayzDocument20 pagesConsti and Local Gov Notes HayzFantaxiaNo ratings yet
- Gimkit Spreadsheet Import Template 2Document1 pageGimkit Spreadsheet Import Template 2mega36tbNo ratings yet
- Executive Powers - Page 1Document1 pageExecutive Powers - Page 1Brat WurstNo ratings yet
- Steel Seizure FrameworkDocument1 pageSteel Seizure FrameworkBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Civil War Enforcement PowersDocument1 pageCivil War Enforcement PowersBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Class Action - Rule 23 To Be Certified, Must Meet 23A Requirements & Fit Into A 23B - Not Class Action Until Court Certifies It As SuchDocument1 pageClass Action - Rule 23 To Be Certified, Must Meet 23A Requirements & Fit Into A 23B - Not Class Action Until Court Certifies It As SuchBrat Wurst100% (1)
- YsealDocument4 pagesYsealMuhammad Reza Agung SadewaNo ratings yet
- Circular No. 102-2012-TT-BTC - Per-Diem For Overseas Business Trip - ENGDocument20 pagesCircular No. 102-2012-TT-BTC - Per-Diem For Overseas Business Trip - ENGLê Đình ChinhNo ratings yet
- Release Waiver and Quitclaim: Signed in The Presence ofDocument1 pageRelease Waiver and Quitclaim: Signed in The Presence ofVerscel Malalis GuisadioNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE - Smooth Stones - Joe Coffey - CruciformPressDocument40 pagesSAMPLE - Smooth Stones - Joe Coffey - CruciformPressCruciform PressNo ratings yet
- CB9 Story Ave Proposal ResponseDocument2 pagesCB9 Story Ave Proposal ResponseGersh KuntzmanNo ratings yet
- Contents FinalDocument48 pagesContents FinalDaisy Jane BrionesNo ratings yet
- Scribd Publication Abridged - Benter Owino - The Leader's Role in Effective Policy Advocacy For Increased Domestic Health Financing in KenyaDocument17 pagesScribd Publication Abridged - Benter Owino - The Leader's Role in Effective Policy Advocacy For Increased Domestic Health Financing in KenyaBenter OwinoNo ratings yet
- Dear Canyon View Families,: Geography BeeDocument8 pagesDear Canyon View Families,: Geography BeeCTIVVCVNo ratings yet
- Business English: by Mr. Pablo Cardenas Pi English SchoolDocument37 pagesBusiness English: by Mr. Pablo Cardenas Pi English SchoolPablo Cárdenas100% (6)
- Track Events: Training Guide For CommissairesDocument20 pagesTrack Events: Training Guide For CommissairesMinor MirandaNo ratings yet
- Senate - 2021 May 26Document2 pagesSenate - 2021 May 26BernewsAdminNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ProjectDocument4 pagesEntrepreneurship Projecthuzaifa anwarNo ratings yet
- Forum ScriptDocument2 pagesForum ScriptAina ZhrhNo ratings yet
- JuNO Slide DeckDocument28 pagesJuNO Slide DeckWestSeattleBlogNo ratings yet
- Tan Et Al., 2008, Correlates of Academic Procrastination and Students' Grade GoalsDocument12 pagesTan Et Al., 2008, Correlates of Academic Procrastination and Students' Grade GoalsThanh TuyềnNo ratings yet
- BB 4332 Project Management 1Document4 pagesBB 4332 Project Management 1farzanahrazakNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Learning, Assessment For Learning, and Assessment As LearningDocument11 pagesAssessment of Learning, Assessment For Learning, and Assessment As LearningAnonymous kiom0L1FqsNo ratings yet
- In The High Court of South Africa Gauteng Local Division, JohannesburgDocument9 pagesIn The High Court of South Africa Gauteng Local Division, JohannesburgColias DubeNo ratings yet
- JUGAAD-The Indian Way of BusinessDocument3 pagesJUGAAD-The Indian Way of BusinessKrishnamurthy PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Domain Project TitleDocument23 pagesCyber Security Domain Project TitleKishore GNo ratings yet
- Letter of Intent JadiDocument1 pageLetter of Intent JadiRichlatul QurbaNo ratings yet
- Six Principles of Ensuring AchievementDocument15 pagesSix Principles of Ensuring AchievementBarry FeldmanNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Entp6398.501.08s Taught by Joseph Picken (jcp016300)Document9 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Entp6398.501.08s Taught by Joseph Picken (jcp016300)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. A. C. D. A. C. D. A. B. D. A. B. C.: Trang 1Document7 pagesA. B. C. A. C. D. A. C. D. A. B. D. A. B. C.: Trang 1Hai DoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 (Compatibility Mode)Document4 pagesCHAPTER 2 (Compatibility Mode)Shohana Naz IslamNo ratings yet
- The War On White Australia - Brenton Sanderson (2016)Document103 pagesThe War On White Australia - Brenton Sanderson (2016)Anonymous hNtVmwMJYNo ratings yet
- Abolish ICTY by Milan TepavacDocument8 pagesAbolish ICTY by Milan TepavacDusko_MirkovicNo ratings yet
- A DisertationDocument120 pagesA DisertationMohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Arnis 1Document6 pagesArnis 1Rochelle NimrefNo ratings yet