4 D 16 D 32 D 64 D : ELTP-GATE-2013 Engineering Mechanics: (PAPER-SET-1)
4 D 16 D 32 D 64 D : ELTP-GATE-2013 Engineering Mechanics: (PAPER-SET-1)
Uploaded by
pragyanCopyright:
Available Formats
4 D 16 D 32 D 64 D : ELTP-GATE-2013 Engineering Mechanics: (PAPER-SET-1)
4 D 16 D 32 D 64 D : ELTP-GATE-2013 Engineering Mechanics: (PAPER-SET-1)
Uploaded by
pragyanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
4 D 16 D 32 D 64 D : ELTP-GATE-2013 Engineering Mechanics: (PAPER-SET-1)
4 D 16 D 32 D 64 D : ELTP-GATE-2013 Engineering Mechanics: (PAPER-SET-1)
Uploaded by
pragyanCopyright:
Available Formats
ELTP-Group ELTP-GATE
ELTP-GATE-2013
Engineering Mechanics: (PAPER-SET-1)
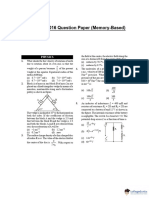
1. The second moment of a circular area about the diameter is given by (D is the diameter).
D4 D4 D4 D4
(a) (b) (c) (d)
4 16 32 64
2. A cylindrical body of cross-sectional area A, height H and density s, is immersed to a depth h in a liquid of density ,
and tied to the bottom with a string. The tension in the string is
(a) ghA (b) (s - )ghA (c) ( - s) ghA (d) (h - s H)gA
3. A truss consists of horizontal members (AC, CD, DB and EF) and vertical members (CE and DE) having length /
each. The members AE, DE and BF are inclined at 45° to the horizontal. For the uniformly distributed load "P" per unit
length on the member EF of the truss shown in figure given below, the force in the member CE is
pl 2 pl
(a) (b) pl (c) 0 (d)
2 3
4. A bullet of mass "m" travels at a very high velocity v (as shown in the Figure) and gets embedded inside the block of
mass "M" initially at rest on a rough horizontal floor. The block with the bullet is seen to move a distance "s" along the
floor. Assuming u to be the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the floor and "j" the acceleration due to
gravity what is the velocity v of the bullet?
Mm Mm M m M
(a) 2 gs (b) 2 gs (c) 2 gs (d) 2 gs
m m m m
5. A water container is kept on a weighing balance. Water from a tap is falling vertically into the container with a volume
flow rate of Q; the velocity of the water when it hits the water surface is U. At a particular instant of time the total mass
of the container and water is m. The force registered by the weighing balance at this instant of time is
(a) mg + QU (b) mg + 2 QU (c) mg + QU2/2 (d) QU2/2
Data for Q. 6 – 7 are given below. Solve the problems and choose correct answers.
A real of mass "m" and radius of gyration “k” is rolling down smoothly from rest with one end of the thread wound on it
held in the ceiling as depicted in the figure Consider the thickness of the thread and its mass negligible in comparison
with the radius “r” of the hub and the reel mass "m". Symbol "S" represents the acceleration due to gravity.
6. The linear acceleration of the real is
gr 2 gk 2 grk mgr 2
(a)
r 2
k2 (b)
r 2
k2 (c)
r 2
k2 (d)
r 2
k2
Ph.9302649096 Page 1 COMMITTED FOR SUCCESS!!!
ELTP-Group ELTP-GATE
7. The tension in the tread is
mgr 2 mgrk mgk 2 mg
(a)
r 2
k 2
(b)
r 2
k 2
(c)
r 2
k 2
(d)
r 2
k2
Data for Q. 8 - 9 are given below. Solve the problems and choose correct answers.
The circular disc shown in its plan view in the figure rotates in a plane parallel to the horizontal plane about the point
Oat a uniform angular velocity to. Two other points A and B are located on the line OZ at distances rA and rB from O
respectively.
8. The velocity of point B with respect lo point A is a vector of magnitude
(a) 0
(b) (rn – rA) and direction opposite to the direction of motion of point B
(c) (rB – rA) and direction same as the direction of motion of point B
(d) (rB – rA) and direction being from O to Z,
9. The acceleration of point B with respect to point A is a vector of magnitude
(a) 0
(b) (rB – rA) and direction same as the direction of motion of point B
(c) 2 (rB – rA) and direction opposite to be direction of motion of point B
(d) 2 (rB – rA) and direction being from Z to 0.
10. A uniform stiff rod of length 300 mm and having a weight of 300 N is pivoted at one end and connected to a spring
at the other end. For keeping the rod vertical in a stable position the minimum value of spring constant K needed is
(a) 300 N/m (b) 400 N/m (c) 500 N/m (d) 1000 N/m
11. An ejector mechanism consists of a helical compression spring having a spring constant of K = 981 x 10 3 N/m. It is
pre-compressed by 100 mm from its free state. If it is used to eject a mass of 100 kg held on it, the mass will move up
through a distance of
(a) 100 mm (b) 500 mm (c) 981 mm (d) 1000 mm
12. A rigid body shown in the Fig. (a) has a mass of 10 kg. II rotates with a uniform angular velocity ‘’. A
balancing mass of 20 kg is attached as shown in Fig. (b). The percentage increase in mass moment of inertia as a
result of this addition is
(a) 25% (6) 50% (c) 100% (d) 200%
Ph.9302649096 Page 2 COMMITTED FOR SUCCESS!!!
ELTP-Group ELTP-GATE
13. The figure shows a pair of pin-jointed gripper-tongs holding an object weighting 2000 N. The co-efficient of friction
() at the gripping surface is 0.1 XX is the line of action of the input force and YY is the line of application of gripping
force. If the pin-joint is assumed to be friction loss, then magnitude of force F required to hold the weight is
(a) 1000 N (b) 2000 N (c) 2500 N (d) 5000 N
14. A simple pendulum of length 5 m, with a bob of mass 1 kg, is in simple harmonic motion, as it passes through its
mean position, the bob has a speed of 5 m/s. The net force on the bob at the mean position is
(a) zero (b) 2.5 N (c) 5 N (d) 25 N
15. Two identical cantilever beams are supported as shown, with their free ends in contact through a rigid roller. After
the load P is applied, the free ends will have
(a) equal deflections but not equal slopes (b) equal slopes but not equal deflections
(c) equal slopes as well as equal deflections (d) neither equal slopes nor equal deflections
16. An elevator (lift) consists of the elevator cage and a counter weight, of mass m each. The cage and the
counterweight are connected by a chain that passes over a pulley, the pulley is coupled to a motor, it is desired that the
elevator should have a maximum stopping time of t seconds from a peak speed v. If the inertias of the pulley and the
chain are neglected, the minimum power that the motor must have is
1 mv 2 mv 2 2 mv 2
mv 2
2 2t t t
(a) (b) (c) (d)
17. A shell is fired from a cannon. At the instant the shell is just about to leave the barrel, its velocity relative to the barrel
is 3m/s, while the barrel is swinging upwards with a constant angular velocity of 2 rad/s. The magnitude of the absolute
velocity of the shell is
(a) 3 m/s (b) 4 m/s (c) 5 m/s (d) 7 m/s
18. Two books of mass 1 kg each are kept on a table, one over the other. The coefficient of friction on every pair of
contacting surfaces is 0.3. the lower book is pulled with a horizontal force F. The minimum value of F for which slip
occurs between the two books is
Ph.9302649096 Page 3 COMMITTED FOR SUCCESS!!!
ELTP-Group ELTP-GATE
(a) zero (b) 1.06 N (c) 5.74 N (d) 3.83 N
19. A 1 kg mass of clay, moving with a velocity of 10 m/s, strikes a stationary wheel and sucks to it. The sold wheel has
a mass of 20 kg and a radius of 1 m. Assuming that the wheel and the ground are both rigid and that the wheel is set
into pure rolling motion, the angular velocity of the wheel immediately after the impact is approximately
1 10 10
(a) zero (b) rad s (c) rad s (d) rad s
3 3 3
Statement for Linked Answer Questions 20 and 21
A band brake consists of a lever attached to one end of the band. The other end of the band is fixed to the ground. The
wheel has a radius of 200 mm and the wrap angle of the band is 270°. The braking force applied to the lever
is limited to 100 N, and the coefficient of friction between the band and the wheel is 0.5. No other information is given.
20. The maximum tension that can be generated in the band during braking is
(a) 1200 N (b) 2110 N (c) 3224 N (d) 4420 N
21. The maximum wheel torque, that can be completely braked is
(a) 200 N.m (b) 382 N.m (c) 604 N.m (d) 844 N.m
22. The differential equation governing the vibrating system is
k x y 0
(a) m x c x (b) m x y c x kx 0
y
(c) m x c x kx 0
y (d) m x y c x k x y 0
y
23. If a system is in equilibrium and the position of the system depends upon many independent variables, the principle
of virtual work states that the partial derivatives of its total potential energy with respect to each o/ the independent
variable must be
(a) -1.0 (b) 0 (c) 1.0 (d)
24. If point A is in equilibrium under the action of the applied forces, the values of tension TAB and TAC are respectively
Ph.9302649096 Page 4 COMMITTED FOR SUCCESS!!!
ELTP-Group ELTP-GATE
(a) 520 K and 300 N (b) 300 N and 520 N (c) 450 N and 150 N (d) 150 N and 450 N
25. During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved?
(a) total linear momentum only (b) total kinetic energy only
(c) both linear momentum and kinetic energy (d) neither linear momentum nor kinetic energy
26. A block of mass M is released from point P on a rough inclined plane with inclination angle , shown in the figure
below. The co-efficient of friction is . If < tan , then the time taken by the block to reach another point Q on the
inclined plane, where PQ = s, is
2s 2s 2s
(a) (b) (c)
g cos tan g cos tan g sin tan
2s
(d)
g sin tan
27. The input link O2P of a four bar linkage is rotated at 2 rad/s counter clockwise direction as shown below. The
angular velocity of the coupler PQ in rad/s, at an instant when O4O2P = 180°, is
1
(a) 4 (b) 2 2 (c) 1 (d)
2
28. The natural frequency of the system shown below is
k k 2k 3k
(a) (b) (c) (d)
2m m m m
29. A straight rod of length L(t), hinged at one end and freely extensible at the other end, rotates through an angle (t)
about the hinge. At time t, L(t) = 1 m, L(t) = 1 m/s, (t) = /4 rad and (t) = 1 rad/s. The magnitude of the velocity at the
other end of the rod is
Ph.9302649096 Page 5 COMMITTED FOR SUCCESS!!!
ELTP-Group ELTP-GATE
(a) 1 m/s (b) 2 m s (c) 3 m s (d) 2 m/s
30. A solid circular shaft of diameter 100 mm is subjected to an axial stress of 50MPa.It is further subjected to a torque
of 10 kNm. The maximum principal stress experienced on the shaft is closest to
(a) 41 MPa (b) 82 MPa (c) 164 MPa (d) 204 MPa
31. A circular disk of radius R rolls without slipping at a velocity v. The magnitude of the velocity at point P (see figure) is
(a) 3v (b) 3v 2 (c) v/2 (d) 2 v 3
32. The natural frequency of the spring mass system shown in the figure is closest to
(a) 8 Hz (b) 10 Hz (c) 12 Hz (d) 14 Hz
33. Consider a truss PQR loaded at P with a force F as shown in the figure. The tension in the member QR is
(a) 0.5 F (b) 0.63 F (c) 0.73 F (d) 0.87 F
34. A uniform rigid rod of mass m = 1 kg and length L = 1 m is hinged at its centre and laterally supported at one end by
a spring of spring constant k = 300 N/m. The natural frequency n in rad/s is
(a) 10 (b) 20 (c) 30 (d) 40
35. The natural frequency of a spring-mass system on earth is n. The natural frequency of this system on the moon
(gmoon = gearth/6) is
(A) n (B) 0.408n (c) 0.204n (d) 0.167n
36. A mass m attached to a spring is subjected to a harmonic force as shown in figure. The amplitude of the forced
motion is observed to be 50mm. the value of m (in kg) is
(a) 0.1 (b) 1.0 (c) 0.3 (d) 0.5
37. A simple supported beam PQ is loaded by a moment of 1 kN-m at the mid-span of the beam as shown in the figure.
The reaction forces RP and RQ at supports P and Q respectively are
(a) 1 kN downward, 1 kN upward (b) 0.5 kN upward, 0.5 kN downward
(c) 0.5 kN downward, 0.5 kN upward (d) 1 kN upward, 1 kN upward
Ph.9302649096 Page 6 COMMITTED FOR SUCCESS!!!
ELTP-Group ELTP-GATE
38. An ideal Brayton cycle, operating between the pressure limits of 1 bar and 6 bar, has minimum and maximum
temperatures of 300 K and 1500 K. The ratio of specific heats of the working fluid is 1.4. The approximate final
temperatures in Kelvin at the end of the compression and expansion processes are respectively
(a) 500 and 900 (b) 900 and 500 (c) 500 and 500 (d) 900 and 900
39. For the four-bar linkage shown in the figure, the angular velocity of link AB is 1 rad/s. The length of link CD is 1.5
times the length of link AB. In the configuration shown, the angular velocity of link CD in rad/s is
(a) 3 (b) 3/2 (c) 1 (d) 2/3
40. If the length of the cantilever beam is halved, then natural frequency of the mass M at the end fo this cantilever
beam of negligible mass is increased by a factor of
(a) 2 (b) 4 (c) 6 (d) 8
41. The coefficient of restitution of a perfectly plastic impact is
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d)
42. A mass of 1 kg is attached to two identical springs each with stiffness k = 20 kN/m as shown in the figure. Under
frictionless condition, the natural frequency of the system in Hz is close to
(a) 32 (b) 23 (c) 16 (d) 11
43. An unbiased coin is tossed five times. The outcome of each toss is either a head or a tail. The probability of getting
at least one head is
(a) 1/32 (b) 13/32 (c) 16/32 (d) 31/32
44. A stone with mass of 0.1 kg is catapulted as shown in the figure. The total force Fx (in N) exerted by the rubber band
as a function of distance x (in m) is given by Fx = 300x2 . If the stone is displaced by 0.1 m from the un-stretched
position (x = 0) of the rubber band, the energy stored in the rubber band is
(a) 0.01 J (b) 0.1 J (c) 1 J (d) 10 J
Ph.9302649096 Page 7 COMMITTED FOR SUCCESS!!!
You might also like
- Sample For Instructor Solution Manual For Matter and Interactions Vol 2 by Chabay and SherwoodDocument25 pagesSample For Instructor Solution Manual For Matter and Interactions Vol 2 by Chabay and Sherwoodomar burak100% (2)
- Lecture2 PDFDocument21 pagesLecture2 PDFAni HairaniNo ratings yet
- H2 Physic 2007 A Level SolutionsDocument19 pagesH2 Physic 2007 A Level SolutionsonnoezNo ratings yet
- O Q (Gate, Ies, Ias) : Moment of Inertia (Second Moment of An Area)Document4 pagesO Q (Gate, Ies, Ias) : Moment of Inertia (Second Moment of An Area)harshdeepNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 01-02-2024 (Morning Shift) : QuestionsDocument41 pagesJEE Main 01-02-2024 (Morning Shift) : QuestionsMahir KachwalaNo ratings yet
- CLASS 12 REPEATER BATCH PHYSICS PAPER_15-12-24Document5 pagesCLASS 12 REPEATER BATCH PHYSICS PAPER_15-12-24pankajsingh.electrical.mnnitNo ratings yet
- Tifr - 2017Document10 pagesTifr - 2017sampannkumarNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanical ModelDocument3 pagesQuantum Mechanical Modelshalini.yadav19No ratings yet
- Physics - Xii - Test 5: Topic - Electric Flux & Gauss LawDocument1 pagePhysics - Xii - Test 5: Topic - Electric Flux & Gauss LawManoj GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1523959087MU OET Physics Section PaperDocument6 pages1523959087MU OET Physics Section PapernoobsuniteNo ratings yet
- 100 MCQSDocument10 pages100 MCQSshiviNo ratings yet
- DPP VectorsDocument3 pagesDPP VectorsNight KingerNo ratings yet
- 2024 11 17 20 17 SolutionDocument23 pages2024 11 17 20 17 SolutionVEDANT SUTARNo ratings yet
- Iit Jam Physics 2007 PDFDocument6 pagesIit Jam Physics 2007 PDFKritiraj KalitaNo ratings yet
- Jest 2014 PhysicsDocument7 pagesJest 2014 PhysicsKritiraj KalitaNo ratings yet
- Ntse QuizDocument9 pagesNtse QuizTEJA SINGHNo ratings yet
- 2020 Question PaperDocument16 pages2020 Question Paperlittledash15No ratings yet
- 31-12-2323 - JR - Star Co-Sc (Model-B) - Jee - Main - CTM-28 - QP FinalDocument22 pages31-12-2323 - JR - Star Co-Sc (Model-B) - Jee - Main - CTM-28 - QP Finalholaheg352No ratings yet
- DV 12 Physics Hy Set A Final After CorrectionDocument9 pagesDV 12 Physics Hy Set A Final After Correctionsangeetapanwar1000No ratings yet
- BITSAT 2020 Question PaperDocument14 pagesBITSAT 2020 Question PaperBhumi PundhirNo ratings yet
- BITSAT 2016 Question Paper (Memory-Based)Document14 pagesBITSAT 2016 Question Paper (Memory-Based)rirov78741No ratings yet
- Download JEE Main 2024 Question Paper PDF ExpectedDocument14 pagesDownload JEE Main 2024 Question Paper PDF ExpectedemailidofsamratNo ratings yet
- Ugee 2018 Official Question PaperDocument10 pagesUgee 2018 Official Question PaperCreative me inspiring youNo ratings yet
- Full Test 1 Paper 1 PDFDocument19 pagesFull Test 1 Paper 1 PDFChandaNo ratings yet
- Electric Field & Force - FinalDocument12 pagesElectric Field & Force - FinalVaidik DubeyNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics MCQDocument4 pagesQuantum Mechanics MCQkrishna prasad ghanta0% (1)
- Properties of Matter - Question PaperDocument10 pagesProperties of Matter - Question PaperBhawna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Magnetics 08 AnswersDocument5 pagesMagnetics 08 AnswersRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- KLEEE Old Question Paper PDFDocument27 pagesKLEEE Old Question Paper PDFkattukoluNo ratings yet
- Net Dec. 2016 Physical ChemistryDocument32 pagesNet Dec. 2016 Physical ChemistryEswara SaiNo ratings yet
- 13 - ElectrostaticsDocument8 pages13 - Electrostaticsp_k_soni_iit_physics78% (9)
- HK - 90 101 2Document10 pagesHK - 90 101 2cosmist.officialNo ratings yet
- Vectors 2 PDFDocument3 pagesVectors 2 PDFtrannyNo ratings yet
- Model Test Paper 1 PDFDocument5 pagesModel Test Paper 1 PDFShaunak ThakarNo ratings yet
- A Car Accelerates Uniformly From Rest To A Speed V For Time T. Find TheDocument11 pagesA Car Accelerates Uniformly From Rest To A Speed V For Time T. Find TheDiana paredes acostaNo ratings yet
- Exerciselist5 Eja2022 PhysicsDocument5 pagesExerciselist5 Eja2022 PhysicsfelicioNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper - 2 (Question Paper) - 6Document10 pagesPhysics Paper - 2 (Question Paper) - 6Saumya MundraNo ratings yet
- Iit Jam Physics 2009Document6 pagesIit Jam Physics 2009Subha NayakNo ratings yet
- Physics Chemistry Mathematics IITJEE TestDocument17 pagesPhysics Chemistry Mathematics IITJEE TestAbhay Kumar Nayak100% (5)
- Class XI Physics DPP Set (23) - Previous Chaps + Rotational MotionDocument21 pagesClass XI Physics DPP Set (23) - Previous Chaps + Rotational MotionNilabha DasNo ratings yet
- AIIMS 2011 QuestionsDocument13 pagesAIIMS 2011 QuestionsSomitha Sree.SNo ratings yet
- Selfstudys Com FileDocument28 pagesSelfstudys Com Filedhariharan38No ratings yet
- Main Paper 02-04-17Document19 pagesMain Paper 02-04-17anjuNo ratings yet
- ALPS 2317 Physics Assignment PaperDocument16 pagesALPS 2317 Physics Assignment PaperVaibhav DixitNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Solved Paper 2015Document64 pagesAIIMS Solved Paper 2015pinky sisodiya0% (1)
- 5_6266924834727401406Document6 pages5_6266924834727401406navrenNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion (Question Paper)Document6 pagesCircular Motion (Question Paper)anchlia12345No ratings yet
- Ashadeep International School STD 11: Physics Worksheet: Chapters: 6 Date: 21/08/24Document58 pagesAshadeep International School STD 11: Physics Worksheet: Chapters: 6 Date: 21/08/24nirmitchovatiya17No ratings yet
- DPP - 02 - ElectrostaticsDocument4 pagesDPP - 02 - ElectrostaticsstudyvishalsinghNo ratings yet
- STAR CO-SC (MODEL-B) - Jee-Main - CTM-34 - QP FINALDocument20 pagesSTAR CO-SC (MODEL-B) - Jee-Main - CTM-34 - QP FINALnobihav525No ratings yet
- Arjuna JEE Main Test 13 - Physics (Only PDFS) - Test No.13 - 13.02.2022 - Physics - Arjuna JEE - 1.0Document10 pagesArjuna JEE Main Test 13 - Physics (Only PDFS) - Test No.13 - 13.02.2022 - Physics - Arjuna JEE - 1.0rjackthe142No ratings yet
- 13-Comp-2012-13-14-15-Aits Pt+otDocument6 pages13-Comp-2012-13-14-15-Aits Pt+otShreyaNo ratings yet
- Test - Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocument2 pagesTest - Magnetic Effect of Currentbhavnoor singh 9th c 24No ratings yet
- Ecat Entrance Test - 2: PhysicsDocument12 pagesEcat Entrance Test - 2: PhysicsXXXNo ratings yet
- Mock JEE Main-2 JEE 2025_SolutionsDocument17 pagesMock JEE Main-2 JEE 2025_SolutionsDivyanshuMittalNo ratings yet
- Education: JEST 2021Document12 pagesEducation: JEST 2021Main DdNo ratings yet
- BITSAT 2022 Question Paper PDFDocument13 pagesBITSAT 2022 Question Paper PDFagrawaluma60No ratings yet
- JAM Test Series 3 of Career EndeavourDocument11 pagesJAM Test Series 3 of Career EndeavourSouradip DasNo ratings yet
- Vedantu - JEE Main Simulator: and TDocument51 pagesVedantu - JEE Main Simulator: and TnvarnidhiNo ratings yet
- 2012Document20 pages2012rajangrNo ratings yet
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryFrom EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillNo ratings yet
- BS Physics - Scheme of StudiesDocument28 pagesBS Physics - Scheme of StudiesTanawushNo ratings yet
- 1966 - Berry - J Chem Educ - V - Atomic OrbitalsDocument17 pages1966 - Berry - J Chem Educ - V - Atomic Orbitalsvitoribeiro90No ratings yet
- Applied Mechanics - Kinetic Energy & MomentumDocument15 pagesApplied Mechanics - Kinetic Energy & MomentumfinopectradingNo ratings yet
- Physics Edexcel SummaryDocument56 pagesPhysics Edexcel SummaryworadejpoNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of A System of ParticlesDocument3 pagesDynamics of A System of ParticlesAyush YadavNo ratings yet
- CLASS XI Holiday Homework (PHYSICS) 2023-24Document3 pagesCLASS XI Holiday Homework (PHYSICS) 2023-24Aditya VishnoiNo ratings yet
- Tugas I - FTF - Annisa Vada Febriani - 2307054003Document23 pagesTugas I - FTF - Annisa Vada Febriani - 2307054003annisavada02No ratings yet
- Intro Propulsion Lect 1 39Document1,061 pagesIntro Propulsion Lect 1 39ashriveNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument7 pagesPhysics Reviewerrmgc1003No ratings yet
- Phys12 SM 05 5Document15 pagesPhys12 SM 05 5Junseo KimNo ratings yet
- Transport Properties of Fluids Their Correlation Prediction and EstimationDocument497 pagesTransport Properties of Fluids Their Correlation Prediction and Estimationvamsi_m100% (1)
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Calculation OF Centre of MassDocument26 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Calculation OF Centre of MassBalaji Classes washimNo ratings yet
- Joel Franklin-Classical Field TheoryDocument218 pagesJoel Franklin-Classical Field TheoryGerman ChiappeNo ratings yet
- 2 ch05 LQ eDocument19 pages2 ch05 LQ eCHANNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument90 pagesHydraulicsilhammkaNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document24 pagesCH 12api-314383788No ratings yet
- Department of Physics - IIT MadrasDocument7 pagesDepartment of Physics - IIT MadrasDarrenLovelockNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE Phys Revision WorksheetsDocument35 pagesCIE IGCSE Phys Revision Worksheetsv.michaeljg1No ratings yet
- SQA Higher Physics Summary NotesDocument115 pagesSQA Higher Physics Summary Noteshhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhf100% (2)
- MCQ in Engineering Mechanics - 1Document16 pagesMCQ in Engineering Mechanics - 1Rovina Lacuna100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Fluid Flow: Cengr 3260 - HydraulicsDocument17 pagesFundamentals of Fluid Flow: Cengr 3260 - HydraulicsBry RamosNo ratings yet
- Motion Under Central ForcesDocument1 pageMotion Under Central ForcesSaptangshu RoyNo ratings yet
- Relativistic MechanicsDocument4 pagesRelativistic Mechanicsnikita bajpaiNo ratings yet
- IB PHYSICS 2.4 Presentation All UnitDocument34 pagesIB PHYSICS 2.4 Presentation All UnitJustCallMeLarryNo ratings yet
- Bingham Reiner EquationDocument6 pagesBingham Reiner EquationSaad Ahmed100% (2)
- ConceptMap PDFDocument8 pagesConceptMap PDFWongXinXinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Revision) Force and Momentum: Bakliwal Tutorials - IITDocument6 pagesChapter 2 (Revision) Force and Momentum: Bakliwal Tutorials - IITMihica KhareNo ratings yet