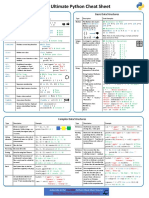
Python Basics Cheat Sheet 1
Uploaded by
srikanth patilPython Basics Cheat Sheet 1
Uploaded by
srikanth patilPYTHON FOR DATA List Operations
Operations Flow Control Method Generic Operations
SCIENCE
• if-else (Conditional Statement) • range(5): 0,1,2,3,4
• List=[]: Defines an empty list
• list[i]=a: Stores a at the ith position
if price>=700: • S=input(“Enter:”)
CHEAT SHEET
print(“Buy.”)
• list[i]: Retrieves the character at the ith position else: • Len(a): Gives item count in a
print(“Don’t buy.”)
• list[i:j]: Retrieves characters in the range i to j • For loop (Iterative Loop Statement) • min(a): Gives minimum value in a
Python Basics • list.append(val): Adds item at the end a=“New Text”
• max(a): Gives minimum value in a
count=0
• list.pop([i]): Removes and returns item at index i for i in a: • sum(a): Adds up items of an iterable and returns
if i==‘e’:
String Operations count=count+1 sum
Datatypes • String[i]: Retrieves the character at the ith position print(count)
• sorted(a): Sorted list copy of a
• While loop (Conditional Loop Statement)
• String[i:j]: Retrieves characters in the range i to j
a=0 • importing modules: import random
• Numbers: a=2(Integer), • String: a=“New String” Dictionary Operations i=1
while i <10:
b=2.0(Float), c=1+2j(Complex)
• Sets: a= {2,3,4,5} • dict={} : Defines an empty dictionary a=a*2
• List: a=[1,2,3,’Word’] i=i+1
File Operations
• dict[i]=a: stores “a” to the key “i”
• Dictionary: x= {‘a’: print(a)
• Tuple: a= (1,2,4) • dict[i]: Retrieves the item with the key “i” • Loop Control: Break, Pass and continue f= open(“File Name”,“opening mode”)
[1,2],‘b’: [4,6]}
• dict.key: Gives all the key items
(Opening modes: r: read, w: write, a: append, r+: both read
• dict.values: Gives all the values Functions
Operators and write)
def new_function():
Numeric Operator: (Say, a holds 5, b holds 10) OOPS print("Hello World") Try & Except Block
• a + b = 15 • b/a = 2 Inheritance: try:
• a – b = -5 new_function()
• b%a=0 A process of using details from a new class without
• a * b = 50 modifying existing class. [Statement body block]
• a**b =9765625
• 7.0//2.0 = 3.0, -11//3 = -4 Polymorphism: Lambda Function raise Exception()
Comparison Operator: A concept of using common operation in different ways for except Exception as e:
different data input. lambda a,b: a+b
• (a == b): not true • (a > b): not true [Error processing block]
Encapsulation:
• (a!= b): true • (a >= b): not true lambda a,b: a*b
Hiding the private details of a class from other objects.
• (a > b): not true • (a <= b) is true
Boolean Operator: Comments
Class/object
• a and b
Class: class Pen: # Single Line Comment
• a or b
pass """
• not a
Multi-line comment
Object: obj=Pen() FURTHERMORE:
"""
Python for Data Science Certification Training Course
You might also like
- Python Challenge!: Learn To Program Fast in100% (1)Python Challenge!: Learn To Program Fast in24 pages
- Python Cheat Sheet: Print Print ("Hello World") Input Input ("What's Your Name")100% (1)Python Cheat Sheet: Print Print ("Hello World") Input Input ("What's Your Name")16 pages
- Python Interview Questions and Answers For 2019 - IntellipaatNo ratings yetPython Interview Questions and Answers For 2019 - Intellipaat25 pages
- Basic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To FalseNo ratings yetBasic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To False8 pages
- Beginners Python Cheat Sheet PCC ClassesNo ratings yetBeginners Python Cheat Sheet PCC Classes2 pages
- UT-AUSTIN Data-Analytics-Essentials-Online-CourseNo ratings yetUT-AUSTIN Data-Analytics-Essentials-Online-Course16 pages
- Built-In Functions - Python 3.10.1 DocumentationNo ratings yetBuilt-In Functions - Python 3.10.1 Documentation27 pages
- Python Test - 2: Time: 1Hr Max. Marks 30No ratings yetPython Test - 2: Time: 1Hr Max. Marks 302 pages
- R Programming Cheat Sheet: Ata TructuresNo ratings yetR Programming Cheat Sheet: Ata Tructures2 pages
- 1 - Power BI - Query Editor - IntroductionNo ratings yet1 - Power BI - Query Editor - Introduction43 pages
- Python Notes: Invented By: Guido Van Rossum (1991)No ratings yetPython Notes: Invented By: Guido Van Rossum (1991)2 pages
- Preparing Data For Analysis Using ExcelNo ratings yetPreparing Data For Analysis Using Excel10 pages
- Python by Example Book 1 (Fundamentals and Basics)100% (1)Python by Example Book 1 (Fundamentals and Basics)57 pages
- Cleaning Dirty Data With Pandas & Python - DevelopIntelligence Blog PDFNo ratings yetCleaning Dirty Data With Pandas & Python - DevelopIntelligence Blog PDF8 pages
- Boolean Algebra: Name Reads As Logic Gate OCR Notation Alternative Notation Examples Truth Table NotesNo ratings yetBoolean Algebra: Name Reads As Logic Gate OCR Notation Alternative Notation Examples Truth Table Notes2 pages
- AIML%20Short%20Term%20Internship%20Session%2013%20Summary-1719637291003No ratings yetAIML%20Short%20Term%20Internship%20Session%2013%20Summary-17196372910037 pages
- Hashing - Datastructures and AlgorithmsNo ratings yetHashing - Datastructures and Algorithms32 pages
- Working With Files and Directories: Chapter 11No ratings yetWorking With Files and Directories: Chapter 1162 pages
- HP Z420 Memory Configurations and Optimization: Supported Memory Modules Memory FeaturesNo ratings yetHP Z420 Memory Configurations and Optimization: Supported Memory Modules Memory Features2 pages
- Computer Science Issues in Ubiquitous Computing: Mark WeiserNo ratings yetComputer Science Issues in Ubiquitous Computing: Mark Weiser17 pages
- Certified Mikrotik Training Basic ClassNo ratings yetCertified Mikrotik Training Basic Class445 pages
- Active Directory Installation: © N. Ganesan, PH.D., All Rights ReservedNo ratings yetActive Directory Installation: © N. Ganesan, PH.D., All Rights Reserved65 pages
- Data Structures Bit Bank Unit-I 1 Mark Questions InformationNo ratings yetData Structures Bit Bank Unit-I 1 Mark Questions Information4 pages