Solubility of Organic Compounds: Answers To Questions
Solubility of Organic Compounds: Answers To Questions
Uploaded by
Matthew Rei De LeonCopyright:
Available Formats
Solubility of Organic Compounds: Answers To Questions
Solubility of Organic Compounds: Answers To Questions
Uploaded by
Matthew Rei De LeonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Solubility of Organic Compounds: Answers To Questions
Solubility of Organic Compounds: Answers To Questions
Uploaded by
Matthew Rei De LeonCopyright:
Available Formats
M. De Leon / Chemistry 31.
1 (2019) P a g e |1
Solubility of Organic Compounds
Matthew Rei B. De Leona, Avian Faye B. Vitalb
aNational
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, University of the Philippines Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines
bNational
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, University of the Philippines Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines
Performed 15 August 2019; Submitted 22 August 2019
ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS
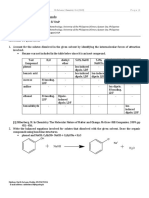
1. Account for the solutes dissolved in the given solvent by identifying the intermolecular forces of attraction
involved.
Hexane was not included in the table below since it is an inert compound.
Test H2O diethyl 5.0% NaOH 5.0% 5.0% HCl Conc.
Compound ether NaHCO3 H2SO4
phenol - - Ion-induced - - -
dipole, LDF
benzoic acid - - Ion-induced Ion-induced - -
dipole, LDF dipole, LDF
sucrose H-bonding, - - - - -
LDF
aniline - - - - Ion-dipole, -
H-bonding,
LDF
ethanol H-bonding, Dipole- - - - -
LDF induced
dipole, LDF
benzaldehyde - - - - - Ion-
induced
dipole, LDF
[1] Silberberg, M. In Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change; McGraw-Hill Companies, 2009; pp
451–456.
2. Write the balanced equations involved for solutes that dissolved with the given solvent. Draw the organic
compounds using bond-line structures.
phenol and NaOH: C6H5OH+ NaOH→ C6H5ONa + H2O
Matthew Rei B. De Leon. Mobile: 09195075924
E-mail address: mbdeleon10@up.edu.ph
M. De Leon / Chemistry 31.1 (2019) P a g e |2
benzoic acid and NaOH: C6H5COOH + NaOH → C6H5COONa + H2O
benzoic acid and NaHCO3: C6H5COOH + NaHCO3 → C6H5COONa + CO2 + H2O
sucrose and H2O: C12H22O11 + H2O → C6H12O6 + C6H12O6
aniline and HCl: C6H5NH2 + HCl → C6H5NH3Cl
ethanol and H2O: C2H5OH(l) + H2O(l) → C2H5OH(aq)
ethanol and diethyl ether: C2H5OH + (C2H5)2O → C6H16O2
Matthew Rei B. De Leon. Mobile: 09195075924
E-mail address: mbdeleon10@up.edu.ph
M. De Leon / Chemistry 31.1 (2019) P a g e |3
benzaldehyde and H2SO4: C7H6O + H2SO4 → C7H6O4S + H2O
[2] Lehman, J. W. Operational Organic Chemistry: A Problem-solving Approach to the Laboratory Course, 4th ed.;
Pearson Prentice Hall, 2009.
[3] Carter, J. The Effect of PH on Ethanol Preserved Muscle Tissue. Collection F 2009, 23 (1-2), 36–45.
[4] Diethyl ether ethanol. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Diethyl-ether-ethanol (accessed Aug
21, 2019).
3. Determine the best solvent to differentiate the following pairs of compounds based on their predicted solubility.
CH3NH2 and CH3(CH2)5NH2 = H2O
phenol and CH3(CH2)5COOH = NaHCO3
p-xylene and benzaldehyde = H2SO4
chloroform and tert-butanol = H2SO4
glucose and n-butanol = diethyl ether
[5] Fieser, L. F.; Williamson, K. L. Organic Experiments, 7th ed.; D.C. Heath, 1992; pp 574.
Matthew Rei B. De Leon. Mobile: 09195075924
E-mail address: mbdeleon10@up.edu.ph
You might also like
- Hildebrand Solubility ParameterDocument8 pagesHildebrand Solubility ParameterDeri Alvian50% (2)
- Chem 31.1 ATQ 1 - FinalDocument2 pagesChem 31.1 ATQ 1 - FinalMikaela BiolenaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Relative Rates of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution QuestionsDocument1 pageExperiment 9 Relative Rates of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution QuestionsElah PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 ATQ 2Document2 pagesChem 31.1 ATQ 2Mikaela BiolenaNo ratings yet
- Chem31.1 ATQ12 Santos PDFDocument3 pagesChem31.1 ATQ12 Santos PDFClaire SantosNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 Unknown Analysis Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesChem 31.1 Unknown Analysis Cheat Sheetฝน เมนโดซาNo ratings yet
- Experiment 13 Results and Discussion Report: Determination of Total Ion Concentration Using Ion Exchange ChromatographyDocument3 pagesExperiment 13 Results and Discussion Report: Determination of Total Ion Concentration Using Ion Exchange ChromatographyNathalie Dagmang100% (3)
- Science6 - q1 - Mod1les3 - Factors Affecting Solubility - EDITEDDocument10 pagesScience6 - q1 - Mod1les3 - Factors Affecting Solubility - EDITEDGene-Beth Cacho Garce50% (2)
- Exp 7 ATQDocument3 pagesExp 7 ATQDean Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 ATQ Chem 31.1Document2 pagesExperiment 4 ATQ Chem 31.1Elah Palaganas100% (1)
- Chem 31.1 Expt 1. SolubilityDocument3 pagesChem 31.1 Expt 1. SolubilityBuiHope100% (2)
- ATQ-1 Solubility of Organic CompoundsDocument2 pagesATQ-1 Solubility of Organic CompoundsAnne Raever BenavidezNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 ATQ Experiment 1Document4 pagesChem 31.1 ATQ Experiment 1Ying YangNo ratings yet
- ATQ 11 Chem 31.1Document2 pagesATQ 11 Chem 31.1BethNo ratings yet
- Relative Rates of Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionDocument2 pagesRelative Rates of Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionAnonymous GO6JVW9Wud100% (4)
- Aliphatic and Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument1 pageAliphatic and Aromatic HydrocarbonsJulian Bato0% (3)
- Chem 31.1 Exp 2 3 4Document2 pagesChem 31.1 Exp 2 3 4qwertyuasiop100% (1)
- Experiment 9 Relative Rates of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution QuestionsDocument2 pagesExperiment 9 Relative Rates of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution QuestionsElah PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Formal Report Chem 31.1Document6 pagesFormal Report Chem 31.1Elah PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Chem 31Document5 pagesNucleophilic Acyl Substitution Chem 31Frances Abegail QuezonNo ratings yet
- Nucleophlic Acyl Substitution - The Synthesis of Ethyl ButanoateDocument5 pagesNucleophlic Acyl Substitution - The Synthesis of Ethyl ButanoateRuther Cabral67% (3)
- Chematq 2Document5 pagesChematq 2Anonymous GO6JVW9Wud100% (5)
- Hinsberg's Method For Characterizing Primary, Secondary and Tertiary AminesDocument2 pagesHinsberg's Method For Characterizing Primary, Secondary and Tertiary AminesGaby de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document5 pagesExperiment 4Ian Joseph Velasco BraganciaNo ratings yet
- Recrystallization and Melting Point Determination of Benzoic AcidDocument6 pagesRecrystallization and Melting Point Determination of Benzoic AcidAnonymous GO6JVW9Wud0% (1)
- CHEM31.1 ATQ3 SantosDocument2 pagesCHEM31.1 ATQ3 SantosClaire SantosNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 Lab ReviewerDocument3 pagesChem 31.1 Lab ReviewerJamie Joice NocheNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Chem 26.1Document2 pagesExperiment 5 Chem 26.1Collin Reyes HuelgasNo ratings yet
- Relative Rates of Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionDocument2 pagesRelative Rates of Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionMatthew ColeNo ratings yet
- Expt. #14 - ATQDocument1 pageExpt. #14 - ATQClarice Mae Dacasin100% (1)
- Quantitative Determination of Dissolved Oxygen Content by Winkler Redox TitrationDocument3 pagesQuantitative Determination of Dissolved Oxygen Content by Winkler Redox TitrationTatocatNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Acid DerivativesDocument2 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Acid DerivativesJuan De FocaNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 Exp 8 and 9Document2 pagesChem 31.1 Exp 8 and 9Dean Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Postlab 3Document6 pagesPostlab 3Ice cream dudeNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 Exp 10Document2 pagesChem 31.1 Exp 10qwertyuasiop100% (1)
- Atq E4Document3 pagesAtq E4BuiHopeNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 Expt 8 Lab ReportDocument30 pagesChem 31.1 Expt 8 Lab ReportJohn Christian LopezNo ratings yet
- UP CHEM 31 Carboxylic Acids and Acid DerivativesDocument3 pagesUP CHEM 31 Carboxylic Acids and Acid DerivativesZsara CampanoNo ratings yet
- Chem 26.1 Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric EDTA TitrationDocument4 pagesChem 26.1 Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric EDTA TitrationBuiHopeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - ATQDocument2 pagesExperiment 1 - ATQAndrea Nicole RocafortNo ratings yet
- AtqDocument3 pagesAtqElah PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 Expt 2Document1 pageChem 31.1 Expt 2Kelvin LabarezNo ratings yet
- Atq 9Document2 pagesAtq 9Justin Brian MariñasNo ratings yet
- Extraction and Purification of CaffeineDocument3 pagesExtraction and Purification of CaffeineAnonymous GO6JVW9Wud100% (2)
- Recrystallization and Melting Point Determination of Benzoic AcidDocument3 pagesRecrystallization and Melting Point Determination of Benzoic AcidKarl Brylle CablaidaNo ratings yet
- ATQ 6 Chem 28.1Document2 pagesATQ 6 Chem 28.1ho-humhumdrumNo ratings yet
- Atq Experiment 8 Chem 26.1Document7 pagesAtq Experiment 8 Chem 26.1Rei Diaz Apalla100% (1)
- Experiment 5 Chem 26 AtqDocument2 pagesExperiment 5 Chem 26 AtqAbi ANo ratings yet
- Chem 31 AtqE1Document3 pagesChem 31 AtqE1Anonymous GO6JVW9WudNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 Formal Report Expt 16Document6 pagesChem 31.1 Formal Report Expt 16Angelo VillaranteNo ratings yet
- Chem 26.1 FR E11Document7 pagesChem 26.1 FR E11smile fireNo ratings yet
- E15 AtqDocument1 pageE15 Atqariblueleaf100% (2)
- Synthesis of 1-Phenylazo 'Sudan 1'Document5 pagesSynthesis of 1-Phenylazo 'Sudan 1'seryuyuyu100% (2)
- Postalb 16-Synthesis of Sudan 1Document2 pagesPostalb 16-Synthesis of Sudan 1edcalumpitNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 - FR2 CastroDocument4 pagesChem 31.1 - FR2 CastroMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- Expt. 10 Chem 26.1Document3 pagesExpt. 10 Chem 26.1Jeannelle TanNo ratings yet
- Expt. #4 - RDRDocument7 pagesExpt. #4 - RDRClarice Mae DacasinNo ratings yet
- (Ablang) Experiment 4 AtqDocument2 pages(Ablang) Experiment 4 AtqAbi ANo ratings yet
- Expt 8 26.1Document7 pagesExpt 8 26.1Kyle CortezNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones: Answers To QuestionsDocument3 pagesAldehydes and Ketones: Answers To Questionsmark pascuaNo ratings yet
- Solubility of Organic Compounds: Answers To QuestionsDocument3 pagesSolubility of Organic Compounds: Answers To QuestionsMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- Solubility of Organic CompoundsDocument3 pagesSolubility of Organic CompoundsdeleonmatthewreiNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 - FR2 CastroDocument4 pagesChem 31.1 - FR2 CastroMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- The 26 Annual Biosciences Quiz BeeDocument3 pagesThe 26 Annual Biosciences Quiz BeeMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument9 pagesOperations ManagementMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- Rubrics For Formal ReportDocument1 pageRubrics For Formal ReportMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- Solubility of Organic Compounds: Answers To QuestionsDocument3 pagesSolubility of Organic Compounds: Answers To QuestionsMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- Letter of Invitation For Judges - MBBDocument1 pageLetter of Invitation For Judges - MBBMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- The Thomasian Hospitality Cup 2019: Recipe FormDocument4 pagesThe Thomasian Hospitality Cup 2019: Recipe FormMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- L4 Travel MotivationDocument35 pagesL4 Travel MotivationMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- Macro: III. Terminologies For Travel & TourismDocument7 pagesMacro: III. Terminologies For Travel & TourismMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- Tourism Risk Management: Key PointsDocument10 pagesTourism Risk Management: Key PointsMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- Table 2. Absorbance of The UnknownDocument2 pagesTable 2. Absorbance of The UnknownMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- Chem 26.1 Experiment 11 Atq Questions and Data SheetDocument4 pagesChem 26.1 Experiment 11 Atq Questions and Data SheetMatthew Rei De LeonNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 NotesDocument14 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 NotessharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Properties of MaterialsDocument26 pagesChapter 2 Properties of Materialssrujanpm2012No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Liquid-Liquid ExtractionDocument29 pagesChapter 3 - Liquid-Liquid Extractiond20221103362No ratings yet
- Chemistry_Solution Answer Key_Grade 12 _2024C-1Document20 pagesChemistry_Solution Answer Key_Grade 12 _2024C-1Prepert knowledgeNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of Nonelectrolyte Solutions - Boundless ChemistryDocument15 pagesColligative Properties of Nonelectrolyte Solutions - Boundless Chemistryprashant_cool_4_uNo ratings yet
- Reverse OsmosisDocument4 pagesReverse OsmosisKiran ShresthaNo ratings yet
- In Class Exercise For Chapter 13 KeyDocument2 pagesIn Class Exercise For Chapter 13 KeyJennifer TabitaNo ratings yet
- Work_Sheet_12th_NEET_SolutionsDocument8 pagesWork_Sheet_12th_NEET_SolutionsbreegrayNo ratings yet
- Medicine Data With Lumped Quantity and MeasureDocument102 pagesMedicine Data With Lumped Quantity and MeasureGoutham RajNo ratings yet
- QUEST 3 Product SearchDocument2 pagesQUEST 3 Product Searchbegone thotNo ratings yet
- Apendice 2Document12 pagesApendice 2JA UMAN1No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2Document15 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2Marianne67% (3)
- AP PPT CH 11Document68 pagesAP PPT CH 11Канат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Solutions Solvents SolutesDocument14 pagesSolutions Solvents Solutesapi-267079239No ratings yet
- Andhra Bank Clerk Paper 2007 Part IIDocument8 pagesAndhra Bank Clerk Paper 2007 Part IIRaghava Reddy AmmireddyNo ratings yet
- Effects of Various Liquid Organic Solvents On Solvent-Induced Crystallization of Amorphous Poly (Lactic Acid) FilmDocument11 pagesEffects of Various Liquid Organic Solvents On Solvent-Induced Crystallization of Amorphous Poly (Lactic Acid) FilmqueteimportaNo ratings yet
- 8.4 Solvents in Organic Chemistry: A. Classification of SolventsDocument8 pages8.4 Solvents in Organic Chemistry: A. Classification of SolventsjacNo ratings yet
- 7aed7d83 457f 4522 9c06 40e9f10536d6 Introduction To SolutionsDocument3 pages7aed7d83 457f 4522 9c06 40e9f10536d6 Introduction To SolutionsHarvexxNo ratings yet
- Exercise - 1: Basic Objective Questions: Concentration TermsDocument14 pagesExercise - 1: Basic Objective Questions: Concentration TermsJohn WickNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin Calcium Trihydrate Farmacopea BPDocument3 pagesAtorvastatin Calcium Trihydrate Farmacopea BPGuadalupe EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Ch1. Solutions Type 3. Multiple Choice Questions RememberingDocument9 pagesCh1. Solutions Type 3. Multiple Choice Questions RememberingAakriti JainNo ratings yet
- (PDF - Io)Document86 pages(PDF - Io)gxk9822czqNo ratings yet
- Preparation 2: Calcium Hydroxide Topical Solution: Dds LabDocument4 pagesPreparation 2: Calcium Hydroxide Topical Solution: Dds LabKate MendozaNo ratings yet
- 2.solutions 2ndPUC PYQsDocument3 pages2.solutions 2ndPUC PYQsDarshan M100% (1)
- Drug Calculations VI - Diluting SolutionsDocument3 pagesDrug Calculations VI - Diluting Solutionsnthmy.vnNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of SolutionsDocument2 pagesPhysical Properties of SolutionsRochelleCasador180No ratings yet
- Lecture30 f05Document27 pagesLecture30 f05احمد الدلالNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument3 pagesSolutionsmanjulamanju6996No ratings yet