0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
101 viewsAmlodipine CP
Amlodipine CP
Uploaded by
Rose EchevarriaAmlodipine is a calcium channel blocker used to treat hypertension and angina. It works by blocking calcium channels in arterial smooth muscles, causing vasodilation. Common side effects include headache, flushing, edema, and nausea. It can interact with immunosuppressants and simvastatin by increasing their plasma concentrations, and with CYP3A4 inhibitors and inducers by affecting its own plasma concentration. Nurses should monitor blood pressure and heart rate before administration and teach patients about non-pharmacologic control of hypertension.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Amlodipine CP
Amlodipine CP
Uploaded by
Rose Echevarria0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
101 views2 pagesAmlodipine is a calcium channel blocker used to treat hypertension and angina. It works by blocking calcium channels in arterial smooth muscles, causing vasodilation. Common side effects include headache, flushing, edema, and nausea. It can interact with immunosuppressants and simvastatin by increasing their plasma concentrations, and with CYP3A4 inhibitors and inducers by affecting its own plasma concentration. Nurses should monitor blood pressure and heart rate before administration and teach patients about non-pharmacologic control of hypertension.
Original Title
Amlodipine CP.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Amlodipine is a calcium channel blocker used to treat hypertension and angina. It works by blocking calcium channels in arterial smooth muscles, causing vasodilation. Common side effects include headache, flushing, edema, and nausea. It can interact with immunosuppressants and simvastatin by increasing their plasma concentrations, and with CYP3A4 inhibitors and inducers by affecting its own plasma concentration. Nurses should monitor blood pressure and heart rate before administration and teach patients about non-pharmacologic control of hypertension.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
101 views2 pagesAmlodipine CP
Amlodipine CP
Uploaded by
Rose EchevarriaAmlodipine is a calcium channel blocker used to treat hypertension and angina. It works by blocking calcium channels in arterial smooth muscles, causing vasodilation. Common side effects include headache, flushing, edema, and nausea. It can interact with immunosuppressants and simvastatin by increasing their plasma concentrations, and with CYP3A4 inhibitors and inducers by affecting its own plasma concentration. Nurses should monitor blood pressure and heart rate before administration and teach patients about non-pharmacologic control of hypertension.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
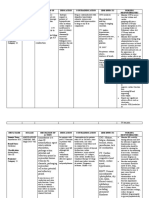
b.
Medications
DRUG MOA: INDICATION: SIDE EFFECTS DRUG INTERACTIONS: NURSING
CLASSIFICATION: Direct Control of hypertension & ADVERSE Increased systemic INTERACTIONS/
Calcium channel vasodilators Also used as anti-anginal EFFECTS: plasma concentration HEALTH
blocker Drug that agent Generalized with TEACHINGS:
block vasodilatory immunosuppressants Monitor BP
DOSAGE: calcium effects; (e.g. ciclosporin, and HR,
5 mg channels of orthostatic tacrolimus) especially
arterial hypotension, Increased serum before
ROUTE: PO smooth headache, concentration of administration
muscles CONTRAINDICATIONS: flushing, simvastatin WOF
GENERIC: that leads to Contraindicated among heat Increased exposure headache and
Amlodipine vasodilation patients with heart failure sensation, with CYP3A4 pedal edema
peripheral enzyme inhibitors Advise patient
BRAND: Norvasc edema (e.g. protease to change
Reflex inhibitors, azole position
tachycardia antifungals, slowly
GI: nausea, erythromycin, Teach patient
vomiting diltiazem) to practice non
Decreased plasma pharmacologic
concentration with control of
CYP3A4 inducers hypertension
(e.g. rifampicin)
b. Medications
You might also like
- Terazosin Hytrin Drug CardDocument1 pageTerazosin Hytrin Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - CORROSION AND NON-FERROUS METALDocument60 pagesChapter 5 - CORROSION AND NON-FERROUS METALتاج نيسها33% (3)
- LOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)Document5 pagesLOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)CHRISTIE MONTANONo ratings yet
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyXio PauNo ratings yet
- Name Mucosta Tablets 100 Description PDFDocument7 pagesName Mucosta Tablets 100 Description PDFnanda RaharjaNo ratings yet
- LacipilDocument2 pagesLacipilianecunarNo ratings yet
- EmpagliflozinDocument2 pagesEmpagliflozinAusaf AhmadNo ratings yet
- BerodualDocument1 pageBerodualAelysa PabloNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: CNS: DizzinessDocument1 pageDrug Study: CNS: Dizzinessmarsh155No ratings yet
- Drug Study PantoprazoleDocument3 pagesDrug Study PantoprazoleIRISH CACAYANNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Document2 pagesDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Primaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)Document2 pagesPrimaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)ENo ratings yet
- TRAMADOLDocument4 pagesTRAMADOLRudie Lee PascualNo ratings yet
- As Pi LetDocument7 pagesAs Pi Letianecunar100% (1)
- Drug Study SpironolactoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study SpironolactoneAina HaravataNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsMarie Kris Chua AbelleraNo ratings yet
- Salazar DsDocument4 pagesSalazar DsDjayNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Reponsibilities Generic NameDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Reponsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbigail BascoNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY AtorvastatinDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY AtorvastatinKyla BeconiaNo ratings yet
- Omacor: Municipal Planning and Development OfficeDocument9 pagesOmacor: Municipal Planning and Development OfficeArthur MericoNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesTramadol Drug StudyJust A Nsg StudentNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyRej Gallien PontalbaNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument1 pageSodium BicarbonateALbinong VelascoNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument10 pagesDrug AnalysisChanel BalinbinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine BesylateDocument2 pagesAmlodipine BesylateYakumaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY OmeprazoleDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY OmeprazoleBRYCE WILLIAM GONo ratings yet
- Drug Study AzithromycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study AzithromycinYamete KudasaiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDrug Study - FurosemideryanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug Studyjho_26100% (2)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MetoprololDocument2 pagesDrug Study MetoprololHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Mucosta: Tablets 100mgDocument4 pagesMucosta: Tablets 100mgInukaicchi TakumichiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Emergency DrugsDocument6 pagesDrug Study Emergency DrugsJhessa Curie PitaganNo ratings yet
- Insulin As PartDocument3 pagesInsulin As PartRezaNo ratings yet
- BisoprololDocument2 pagesBisoprololNovi YulianaNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis: Malaise, Fatigue, Dizziness, Tremors, AtaxiaDocument2 pagesDrug Analysis: Malaise, Fatigue, Dizziness, Tremors, AtaxiaFerdinand Sherwin MorataNo ratings yet
- PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesPrednisoloneKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- NeoblocDocument2 pagesNeoblocianecunar100% (2)
- AldazideDocument2 pagesAldazideianecunarNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyPam RomeroNo ratings yet
- GAT NCP Surgery WardDocument4 pagesGAT NCP Surgery WardDon Richard0% (1)
- Betahistine (DRUG LIST)Document2 pagesBetahistine (DRUG LIST)Bon- BonNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol TartrateDocument1 pageMetoprolol TartrateClifford Estilo100% (1)
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- Captopril Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCaptopril Drug StudyKimzie Joy Basco100% (1)
- Azathioprine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAzathioprine Drug StudyAlexa Lexington Rae Zagado100% (1)
- Drug Study (Ketorolac)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Ketorolac)Andrea De RuedaNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmlodipine Drug StudyRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipinejiglenssNo ratings yet
- Categorize The Treatment Options For Patients With Existing Medical ConditionDocument3 pagesCategorize The Treatment Options For Patients With Existing Medical ConditionMicah LatosaNo ratings yet
- Name OF Drugs Dosage and Route Mechanism and Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesName OF Drugs Dosage and Route Mechanism and Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsAngelyka Abiado AlmodaNo ratings yet
- BHC - Drug StudyDocument3 pagesBHC - Drug Studyboxed juiceNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Omeprazole & LosartanDocument4 pagesDrug Study - Omeprazole & LosartanCarla Tongson MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Ca Plus Vit D CPDocument2 pagesCa Plus Vit D CPRose Echevarria0% (1)
- Ceftriaxone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone Drug StudyRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Metformin Drug StudyDocument1 pageMetformin Drug StudyRose Echevarria67% (3)
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmlodipine Drug StudyRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Nu Tech Catalog 2019 For Website PDFDocument60 pagesNu Tech Catalog 2019 For Website PDFkaranNo ratings yet
- Aib Ga11-30c PDFDocument40 pagesAib Ga11-30c PDFtheloniussherekNo ratings yet
- Defects in Rolled Plates & Sheets: Prepared byDocument14 pagesDefects in Rolled Plates & Sheets: Prepared byMahmoudNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument60 pagesCoordination CompoundsKassandraNo ratings yet
- Fao, Assessment ofDocument160 pagesFao, Assessment ofLisset Valeska Aravena CofréNo ratings yet
- Dna Computing ProposalDocument8 pagesDna Computing ProposalAhmed SaadNo ratings yet
- Stok GenerikDocument7 pagesStok GenerikRifqi KurniaNo ratings yet
- (NATO ASI Series 304) G. M. Idorn (Auth.), Hamlin Jennings, Jörg Kropp, Karen Scrivener (Eds.) - The Modelling of Microstructure and Its Potential For Studying Transport Properties and Durability-SpriDocument554 pages(NATO ASI Series 304) G. M. Idorn (Auth.), Hamlin Jennings, Jörg Kropp, Karen Scrivener (Eds.) - The Modelling of Microstructure and Its Potential For Studying Transport Properties and Durability-SprijdavidospinaNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Cellulose From Some IndustrialDocument121 pagesExtraction of Cellulose From Some IndustrialSathvik PrinceNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics Exam 2018 Wirh SolutionsDocument9 pagesApplied Thermodynamics Exam 2018 Wirh SolutionsFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- Expires: 2012/11/6 CHEMDATA 2011.2 00037B6F-0001BD50 EthyleneDocument2 pagesExpires: 2012/11/6 CHEMDATA 2011.2 00037B6F-0001BD50 Ethylene林淑華No ratings yet
- Ecosystem and Its Components: February 2008Document7 pagesEcosystem and Its Components: February 2008aufaaNo ratings yet
- Adeel Nazeer - Google Scholar Citations PDFDocument2 pagesAdeel Nazeer - Google Scholar Citations PDFAdeel NazeerNo ratings yet
- Loctite PC 5070 Emergency Pipe Repair KitDocument2 pagesLoctite PC 5070 Emergency Pipe Repair KitNs KimNo ratings yet
- A Presentation BY Mbah Chinedu Drilling Engineer Segofs Energy Services LimitedDocument16 pagesA Presentation BY Mbah Chinedu Drilling Engineer Segofs Energy Services LimitedAwani KesterNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NeuroanatomyDocument49 pagesIntroduction To NeuroanatomyPratik Dhakal100% (1)
- 200/300 BAR INERT GAS Fire Suppression SystemsDocument30 pages200/300 BAR INERT GAS Fire Suppression SystemsKamen GrozdanovNo ratings yet
- Guar Gum MachineryDocument14 pagesGuar Gum MachinerySundaresanNo ratings yet
- Properties of Fluorescent Dyes and QuenchersDocument6 pagesProperties of Fluorescent Dyes and QuenchersDummy Tester JrNo ratings yet
- Gpcdoc Gtds Shell Spirax s3 Als 80w-90 (En) TdsDocument2 pagesGpcdoc Gtds Shell Spirax s3 Als 80w-90 (En) TdsFer EmilNo ratings yet
- KBDDocument6 pagesKBDTaufik 'opics' AkbarNo ratings yet
- RefractometerDocument20 pagesRefractometerKimberly WhiteNo ratings yet
- Chemestry English Part-2Document265 pagesChemestry English Part-2devarshiNo ratings yet
- Tomas IndustrialesDocument130 pagesTomas IndustrialesCarlos GomezNo ratings yet
- 03 - Metals & Non-Metals - FDocument42 pages03 - Metals & Non-Metals - FSamveg ClassesNo ratings yet
- Chlorine Institute Emergency KitbDocument4 pagesChlorine Institute Emergency KitbhfguavitaNo ratings yet
- Chromatography+of+Spinach 08Document4 pagesChromatography+of+Spinach 082858keshvi8bNo ratings yet
- Sainik School Chandrapur: There TendencyDocument14 pagesSainik School Chandrapur: There Tendencysiddhantlad01No ratings yet
- Catalog MV PDFDocument58 pagesCatalog MV PDFJS Engineering100% (1)