0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 viewsHerpes NCP
Herpes NCP
Uploaded by
Sanny L Asim Jr. The patient's temperature was 38.6°C. The nursing care plan aimed to decrease the patient's temperature to 37.5°C within 1 hour and return vital signs to normal range within 4 hours through interventions like tepid sponge baths, oral fluids, and antipyretics as needed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Herpes NCP
Herpes NCP
Uploaded by
Sanny L Asim Jr.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 views3 pages The patient's temperature was 38.6°C. The nursing care plan aimed to decrease the patient's temperature to 37.5°C within 1 hour and return vital signs to normal range within 4 hours through interventions like tepid sponge baths, oral fluids, and antipyretics as needed.
Original Title
herpes-ncp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The patient's temperature was 38.6°C. The nursing care plan aimed to decrease the patient's temperature to 37.5°C within 1 hour and return vital signs to normal range within 4 hours through interventions like tepid sponge baths, oral fluids, and antipyretics as needed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 views3 pagesHerpes NCP
Herpes NCP
Uploaded by
Sanny L Asim Jr. The patient's temperature was 38.6°C. The nursing care plan aimed to decrease the patient's temperature to 37.5°C within 1 hour and return vital signs to normal range within 4 hours through interventions like tepid sponge baths, oral fluids, and antipyretics as needed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
JH CERILLES STATE COLLEGE
in consortium with
Western Mindanao State University
West Capitol Road, Balangasan District, Pagadian City
PATIENT INITIALS : DATE :
STUDENT NURSE : AREA of ROTATION :
YEAR LEVEL and BATCH : CLINICAL INSTRUCTOR :
NURSING CARE PLAN
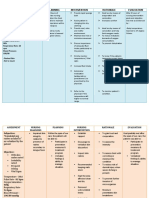
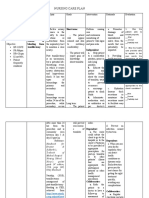
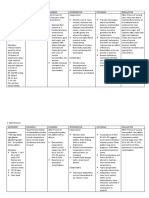
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective Short Term Independent Short Term
”Nurse, murag gihilantan After 1 hour of 1. Monitor vital signs. Vital signs provide After 1 hour of
akong anak” as Elevated body appropriate nursing more accurate appropriate nursing
verbalized by the temperature intervention the indication of core intervention the
significant other. patient’s temperature temperature. patient’s temperature
related to disease
will decrease to decreases to 37.5oC.
Objective process 37.5oC. 2. Provide tepid sponge TSB helps in
Temperature: 38.6C bath. Do not use lowering the body Long Term
RR: 26cycle per Long Term alcohol. temperature and After 4 hours of
minute After 4 hours of alcohol cools the appropriate nursing
appropriate nursing skin too rapidly, intervention the
Hot, flushed skin intervention the causing shivering. patient’s vital signs
Increased respiratory patient’s vital signs Shivering increases has returned to normal
rate will return to normal metabolic rate and range; with a
Diaphoresis range; with a body temperature temperature of 36.5-
temperature of 36.5- 37.5oC,pulse rate of
Warm to touch
37.5oC,pulse rate of 60-100bpm and
60-100bpm and 3. Remove excess These decrease respiratory rate of 12-
respiratory rate of clothing and covers. warmth and increase 20 cycles per min.
12-20 cycles per evaporative cooling.
min.
4. Promote a well- To promote clear
ventilated area to flow of air in the
patient. patient’s area. One
way of promoting
heat loss.
5. Advise patient to Additional fluids
increase oral fluid help prevent elevated
intake. temperature
associated with
dehydration.
6. Maintain bed rest. Reduce metabolic
demands/ oxygen
consumption
7. Provide high-calorie To meet increased
diet. metabolic demands.
8. Educate and advise Teaching the
support system Support system the
(relative) to do TSB right way to do TSB
when patient feels will help in knowing
hot. what to do in case
- Luke warm water the patient’s
only. temperature
- Make sure that increases
armpits and groins
were included in
doing TSB.
9. Monitored VS and To know the
recheck. effectiveness of
nursing
interventions done
and to know the
progress of
patient’s condition.
Dependent These drugs inhibit
10. Provide antipyretic the prostaglandin
medications as that serve as
indicated. mediators of pain
and fever.
You might also like
- NCP 3rd YearDocument6 pagesNCP 3rd YearTotoro AblogNo ratings yet
- TFN - Week 8 Kristen SwansonDocument4 pagesTFN - Week 8 Kristen SwansonJoy PelpinosasNo ratings yet
- Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesCamarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationEdelweiss Marie CayetanoNo ratings yet
- PRS Ear Instillation - GlovaDocument3 pagesPRS Ear Instillation - GlovaAndrea Colleen GlovaNo ratings yet
- NCP Cavernous Sinus ThrombosisDocument3 pagesNCP Cavernous Sinus ThrombosisVencel Mae Famas Villahermosa50% (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAriaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument14 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaNo ratings yet
- Preop Appendectomy NCPDocument3 pagesPreop Appendectomy NCPMyra AtuleNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPKrizia TepootNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial InfarctionDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan For Myocardial InfarctionRocelyn CristobalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocument3 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Outline of Nursing Care Plan: 1. Hyperthermia Hyperthermia Associated With High FeverDocument2 pagesOutline of Nursing Care Plan: 1. Hyperthermia Hyperthermia Associated With High FeverFarah FildzahNo ratings yet
- NCP DIarrheaDocument8 pagesNCP DIarrheakamini ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Feliciano, Troy Ivan Silva, Queenie Rose V. BSN 3-C: Rationale: To Track The Changes of Client's ConditionDocument4 pagesFeliciano, Troy Ivan Silva, Queenie Rose V. BSN 3-C: Rationale: To Track The Changes of Client's ConditionQueenie SilvaNo ratings yet
- Femur FractureDocument19 pagesFemur FractureMadx VNo ratings yet
- Gensurvey SJMCDocument2 pagesGensurvey SJMCMariKeith AcostaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDocument16 pagesNursing Care Plan FinalErickson OcialNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Concept MapDocument1 pagePneumonia Concept MapsekwetNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Impetigo: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Impetigo: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On Ischemic Cardiomyopathy & Ccf-1-1Document18 pagesCase Presentation On Ischemic Cardiomyopathy & Ccf-1-1Maliha aliNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan AMLDocument2 pagesHealth Teaching Plan AMLInah Floresta BesasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On Platelet DisordersDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan On Platelet DisordersbhavanaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain..Document2 pagesAcute Pain..Melody Kaye MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Case Pres (NCP-Hyperthermia)Document2 pagesCase Pres (NCP-Hyperthermia)Trixia DiazNo ratings yet
- TB Nursing CareplanDocument14 pagesTB Nursing CareplanEstherThompson100% (1)
- NCM 114 - NCPDocument3 pagesNCM 114 - NCPReysiela Mae ValinoNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus 9Document9 pagesHydrocephalus 9Shesly PhilominaNo ratings yet
- NCP TB MeningitisDocument1 pageNCP TB MeningitisMark Adrian D. DizorNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objective of Care Intervention RationaleDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Objective of Care Intervention Rationaleahmad ryanNo ratings yet
- Copd - NCPDocument6 pagesCopd - NCPMonique Sacherow BacherNo ratings yet
- 11 - NCPsDocument6 pages11 - NCPsellian3leiNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- NCP (Coronary Artery Disease)Document7 pagesNCP (Coronary Artery Disease)Kristile Ann PacateNo ratings yet
- Primaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)Document2 pagesPrimaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)ENo ratings yet
- Case Study: Acute Exacarbation Chronic Obstructive Aspiration Disease (Aecoad)Document5 pagesCase Study: Acute Exacarbation Chronic Obstructive Aspiration Disease (Aecoad)Muhammad Alif100% (1)
- Community Health Nursing Vol. 2: Christian Parabuac Bachelor of Sciene in Nursing Level 3. Prof. Cherry Ann DuranteDocument50 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Vol. 2: Christian Parabuac Bachelor of Sciene in Nursing Level 3. Prof. Cherry Ann DuranteLeya Thaobunyuen100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance NCPDocument1 pageIneffective Airway Clearance NCPBenz ParCoNo ratings yet
- Community Teaching Plan and Evaluation Submission, Assignment Week 6Document10 pagesCommunity Teaching Plan and Evaluation Submission, Assignment Week 6taniaNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPyupipsjamNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusionkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Febrile SeizuresDocument4 pagesFebrile Seizuresmgonzalez_29No ratings yet
- NCP Case Analysis GastritisDocument7 pagesNCP Case Analysis GastritisSteffi GolezNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument1 pageNCP Painsitz04No ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPChe2x^^100% (2)
- Mushtaq Ahmad: Running Head: REFLECTIVE LOG 1Document5 pagesMushtaq Ahmad: Running Head: REFLECTIVE LOG 1Shafiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Application of Eye Patch, Eye Shield and Pressure Dressing To The EyeDocument2 pagesApplication of Eye Patch, Eye Shield and Pressure Dressing To The EyeissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- 4th Yr. Med Cardio Module Question - Copy-1Document11 pages4th Yr. Med Cardio Module Question - Copy-1Sheda BondNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedDocument5 pagesAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangNo ratings yet
- Child - Major Burn PDFDocument3 pagesChild - Major Burn PDFAldith GrahamNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs TPRDocument21 pagesVital Signs TPRfloremer guimalanNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Ludwig’s Angina, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLudwig’s Angina, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentMoi Valdoz100% (1)