Resistance To Fuels of Exteriors Automotive Materials and Components
Resistance To Fuels of Exteriors Automotive Materials and Components
Uploaded by
Anvarbek KarimovCopyright:
Available Formats
Resistance To Fuels of Exteriors Automotive Materials and Components
Resistance To Fuels of Exteriors Automotive Materials and Components
Uploaded by
Anvarbek KarimovOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Resistance To Fuels of Exteriors Automotive Materials and Components
Resistance To Fuels of Exteriors Automotive Materials and Components
Uploaded by
Anvarbek KarimovCopyright:
Available Formats
WORLDWIDE
ENGINEERING Test Procedure GMW14333
STANDARDS
Resistance to Fuels of Exteriors Automotive Materials and
Components
1 Introduction
Note: Nothing in this standard supercedes applicable laws and regulations.
Note: In the event of conflict between the English and domestic language, the English language shall take
precedence.
1.1 Purpose. The objective of this standard is to determine the effects of fuels on exterior automotive materials
and components.
1.1.1 Summary of Test Procedure. Using this method, resistance of sample parts to automotive fuels is
determined by evaluation after repeated short immersions.
1.2 Applicability. Painted or mold-in-color vehicle components in locations with potential fuel exposure.
Typically, this test is included as part of the performance requirements for painted plastic components.
1.3 Remarks. Using this method, resistance of sample parts to automotive fuels is determined by evaluation
after repeated short immersions.
2 References
Note: Only the latest approved standards are applicable unless otherwise specified.
2.1 External Standards/Specifications.
ASTM D1744 DIN 51777-1 ISO 1817 ISO 10336
2.2 GM Standards/Specifications.
GMW3221 GMW14914
3 Resources
3.1 Facilities. Not applicable.
3.1.1 Calibration. The test facilities and equipment shall be in good working order and shall have a valid
calibration label.
3.1.2 Alternatives. Alternative test facilities and equipment may also be used. However, all measuring
variables as specified in this standard shall be determined correctly with respect to their physical definition.
3.2 Equipment.
3.2.1 Apparatus for conditioning according to GMW3221.
3.2.2 Stop watch with 0.1 s divisions.
3.2.3 Suitable glass beakers to allow immersion of sample.
3.2.4 Sharp knife.
3.2.5 Test fuel composition per the following:
ISO 1817 Liquid 2 with additional 20 ppm formic acid.
25.35%, 2.2.4-trimethylpentane (analytical grade).
42.25% toluene (analytical grade).
12.68% di-isobutylene (analytical grade).
4.22% ethanol (analytical grade).
© Copyright 2014 General Motors Company All Rights Reserved
September 2014 Page 1 of 6
--`,,,,``,,,``,`,```````-`-``,```,,,`---
Copyright General Motors Company Order Number: 02198911
Provided by IHS Markit under license with General Motors Company Sold to:LLC 'UZ-KORAM KO' [700166107173] - SHPARK@CANDH.BIZ,
Reproduction, distribution or publication of these standards is expressly prohib Not for Resale,2018-05-15 09:18:35 UTC
GM WORLDWIDE ENGINEERING STANDARDS GMW14333
15.00% methanol (analytical grade).
0.50% water.
20 ppm formic acid (analytical grade).
Note: Also refer to GMW14914, Test Fuels for Global Applications.
3.2.5.1 This fuel composition must be used for all technology approvals. Additional applications of this
procedure must be agreed upon by the responsible engineer. (i.e., Production Part Approval Process (PPAP)
testing or problem solving, etc.)
3.2.6 Preparation of Fuel Test Fluid (Gasoline).
3.2.6.1 Mixture A. In a first step, the components trimethylpentane, toluene, and/or di-isobutylene, have to be
mixed in a way that the final composition of the fluid corresponds to the composition as given in 3.2.5.
3.2.6.2 Water Content. Since the final fuel test fluid contains a specified amount of water, the primary water
content of Mixture A shall be determined using the Karl Fischer Titration method (ISO 10336, ASTM D1744 or
DIN 51777-1).
3.2.6.3 Mixture B. The volume parts of methanol and/or ethanol respectively shall be added to Mixture A with
the appropriate volume parts of test fluid blend to give a composition approximating to that specified in 3.2.5.
3.2.6.4 Water Content (if Applicable). The water content of Mixture B shall be determined using the
Karl Fischer Titration. Afterwards, distilled or deionised water shall be added to attain the required
concentration.
3.2.6.5 Mixture C (Additives). Lastly, the acid (dissolved in absolute ethanol) or corrosive content shall be
added to reach the final fuel test fluid (Mixture C).
3.2.6.6 Water Content (if Applicable). Water content of Mixture C shall again be determined to ensure
compliance per 3.2.5. The test fluid shall be stored in a sealed brown or opaque glass bottle or suitable metal
container.
Note: During the use of the test fluid, all orders and regulations concerned with safety must be observed i.e.,
flammability of fluids regulations and those relating to dangerous work materials.
3.3 Test Vehicle/Test Piece.
3.3.1 Plastic Parts. Wherever possible, complete components shall be tested. Where size, configuration, etc.,
restricts testing, sections of convenient size, cut from the components, shall be used. In such cases, the cut
edges produced during preparation shall be suitably masked by the use of tape etc., prior to testing.
3.3.2 Organic Coatings. For organic coatings, specially prepared test panels can be used. The test panels
shall be 250 mm ± 5 mm × 20 mm ± 2 mm × 1 mm ± 0.5 mm and should be made from substrate
representative of production intent. The quality of the organic coating and its procedure of application shall be
as per current final finish procedures appropriate to the envisaged application of the material under test. The
organic coating shall be in accordance to the relevant material specification.
3.3.3 Self Adhesive Films. For self-adhesive films, the film shall be applied, as per production procedures to
production intent surfaces prepared per 4.1.1, unless otherwise previously agreed.
3.3.4 Number of Test Pieces. A minimum of three (3) test pieces shall be tested.
Note: Samples shall be free from visual defects which could add to the severity of the test.
3.4 Test Time. Not applicable.
3.5 Test Required Information. Not applicable.
3.6 Personnel/Skills. Not applicable.
4 Procedure
4.1 Preparation.
4.1.1 Test Sample Conditioning and Preparation. Test pieces shall be tested after conditioning to
GMW3221 for periods as defined per 4.1.1.1.1 through 4.1.1.4.
4.1.1.1 Metallic Substrates.
4.1.1.1.1 For oven dried organic coatings, minimum of 24 h after coating and baking.
© Copyright 2014 General Motors Company All Rights Reserved
September 2014 Page 2 of 6
--`,,,,``,,,``,`,```````-`-``,```,,,`---
Copyright General Motors Company Order Number: 02198911
Provided by IHS Markit under license with General Motors Company Sold to:LLC 'UZ-KORAM KO' [700166107173] - SHPARK@CANDH.BIZ,
Reproduction, distribution or publication of these standards is expressly prohib Not for Resale,2018-05-15 09:18:35 UTC
GM WORLDWIDE ENGINEERING STANDARDS GMW14333
4.1.1.1.2 For air dried organic coatings, minimum of 72 h after coating and drying.
4.1.1.1.3 For components from the supplier, to be tested as received.
4.1.1.2 Self Adhesive Parts. Minimum 24 h after adhering.
4.1.1.3 Plastic Parts. Minimum of 24 h.
4.1.1.4 Conditioning and Testing. Conditioning and testing shall not be carried out within 72 h after
manufacturing.
4.2 Conditions.
4.2.1 Environmental Conditions. Not applicable.
4.2.2 Test Conditions. Deviations from the requirements of this standard shall have been agreed upon. Such
requirements shall be specified on component drawings, test certificates, reports, etc.
4.3 Instructions.
4.3.1 Test Procedure.
4.3.1.1 Test Cycles. The number of test cycles to which test pieces shall be subjected. (See Table 1.)
Table 1: Test Cycles
Method Number of Test Cycles
A 10 (see 4.4.1)
B Continuous for 1 h (See 4.4.2)
C As specified
4.3.2 Test Temperature. The test shall be performed at 23 °C ± 5 °C.
4.4 Instructions.
4.4.1 Method A (Dip).
--`,,,,``,,,``,`,```````-`-``,```,,,`---
4.4.1.1 Conditioned test pieces shall be immersed in the test fluid contained in a beaker, for 10 s ± 1 s and
allowed to dry over the beaker for 20 s ± 1 s (this full sequence consists of one (1) cycle). This procedure shall
be repeated for the specified number of cycles. See 4.3.1.1.
4.4.1.2 Organic Coatings Only. Immediately after the 5th immersion, the painted surface shall be checked for
thumbnail hardness by attempting to mar the surface by scraping with the thumbnail with moderate pressure
across the surface in a straight line, 2.5 cm minimum length. Visually examine the resulting surface and record
as marred or not marred. A surface shall be considered marred if any paint has been removed, or the
appearance has been significantly changed. Samples showing marring effects shall not be considered
acceptable. Thumbnail test shall be run in a different area each time.
Note: Disorientation of metal flakes in metallic coatings is not considered a failure (marred).
4.4.1.3 Repeat 4.4.1.1 and 4.4.1.2 for total of ten (10) immersions.
4.4.1.4 Record rating after each thumbnail hardness check.
4.4.1.5 After completion of the required number of test cycles, the test pieces shall then be allowed to
recondition for 1 h at 23 °C ± 5 °C and evaluated. Test pieces shall remain in a vertical position.
4.4.2 Method B (Continuous Immersion). For painted parts, samples shall be scribed with a sharp knife. The
scribe pattern shall be two (2) series of eleven (11) parallel lines intersecting at an angle of 90 degrees. The
distance between the lines shall be 3 mm to 4 mm. See Figure 1.
© Copyright 2014 General Motors Company All Rights Reserved
September 2014 Page 3 of 6
Copyright General Motors Company Order Number: 02198911
Provided by IHS Markit under license with General Motors Company Sold to:LLC 'UZ-KORAM KO' [700166107173] - SHPARK@CANDH.BIZ,
Reproduction, distribution or publication of these standards is expressly prohib Not for Resale,2018-05-15 09:18:35 UTC
GM WORLDWIDE ENGINEERING STANDARDS GMW14333
Scribe Pattern
Figure 1: Method B
4.4.2.1 Conditioned test pieces shall be completely immersed in the test fluid contained in a beaker. The
beaker shall then be covered to prevent evaporation during testing.
4.4.2.2 After 15 minutes immersion, the test samples shall be removed and the number of cells that have
blistered or lifted from the substrate quickly counted. The area of each affected cell should be estimated to the
nearest 25%.
4.4.2.3 The test samples shall be immediately returned to immersion in the test fluid. Total time out of the fluid
shall not exceed 1 minute.
4.4.2.4 The evaluation previously described shall be repeated every 15 minutes until 60 minutes of total
immersion has been reached.
5 Data
5.1 Calculations.
5.1.1 Evaluation and Rating.
5.1.1.1 Method A (Dip). Test pieces shall be examined with the naked eye and compared with untested
reference samples, taken either from the same component or test sample, or from the same batch of
components or test samples. The visual examination shall determine whether or not the requirements of the
following ratings, dependent upon the nature of the material under test, are complied with, and shall be
reported accordingly.
5.1.1.1.1 Rating 1 for Plastics. No change of surface, e.g., change in gloss, shrinkage, discoloration, swelling,
dissolution, wrinkling or creasing, blistering, distortion, cracking, etc.
5.1.1.1.2 Rating 2 for Organic Coated Surfaces. No change of surface, e.g., change in gloss, shrinkage,
discoloration, swelling, dissolution, wrinkling or creasing, blistering, distortion, cracking etc. Thumbnail
hardness to meet the requirements per 4.4.1.2 of this standard.
© Copyright 2014 General Motors Company All Rights Reserved
September 2014 Page 4 of 6
--`,,,,``,,,``,`,```````-`-``,```,,,`---
Copyright General Motors Company Order Number: 02198911
Provided by IHS Markit under license with General Motors Company Sold to:LLC 'UZ-KORAM KO' [700166107173] - SHPARK@CANDH.BIZ,
Reproduction, distribution or publication of these standards is expressly prohib Not for Resale,2018-05-15 09:18:35 UTC
GM WORLDWIDE ENGINEERING STANDARDS GMW14333
5.1.1.1.3 Rating 3 for Self-Adhesive Films. No deterioration of adhesive strength in the adhered area. No
change of surface, e.g., change in gloss, shrinkage, discoloration, swelling, dissolution, wrinkling or creasing,
blistering, distortion, cracking etc. Swelling of the adhered edges, up to 1 mm penetration shall be permitted.
5.1.1.1.4 Rating 4 as Specified. Any other specified properties which are deemed necessary, and are defined
separately.
5.1.1.2 Method B (Continuous Immersion).
5.1.1.2.1 The percentage of paint removed or blistered at each evaluation shall be reported.
5.1.1.2.2 Rating 1 for Plastics. No change of surface, e.g., change in gloss, shrinkage, discoloration, swelling,
dissolution, wrinkling or creasing, blistering, distortion, cracking, etc.
5.1.1.2.3 Rating 2 for Organic Coated Surfaces. No change of surface, e.g., change in gloss, shrinkage,
discoloration, swelling, dissolution, wrinkling or creasing, blistering, distortion, cracking etc.
5.1.1.2.4 Rating 3 as Specified. Any other specified properties which are deemed necessary, and are defined
separately.
5.1.1.3 Method C (as Specified).
5.1.1.3.1 Evaluation and rating shall be as agreed between the design release engineer and the supplier.
5.2 Interpretation of Results. Not applicable.
5.3 Test Documentation.
5.3.1 The report shall completely describe the materials tested.
5.3.2 Deviations from this standard shall have been agreed upon between supplier and vehicle manufacturer.
All deviations shall be specified on the component drawings, material specifications, etc., and shall be
indicated on test certificates, reports, etc.
--`,,,,``,,,``,`,```````-`-``,```,,,`---
6 Safety
This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not propose to
address all the safety problems associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
to use.
7 Notes
7.1 Glossary. Not applicable.
7.2 Acronyms, Abbreviations, and Symbols.
ASTM ASTM International
ISO International Organization for Standardization
PPAP Production Part Approval Process
ppm parts per million
8 Coding System
This standard shall be referenced in other documents, drawings, etc., as follows:
Test to GMW14333
© Copyright 2014 General Motors Company All Rights Reserved
September 2014 Page 5 of 6
Copyright General Motors Company Order Number: 02198911
Provided by IHS Markit under license with General Motors Company Sold to:LLC 'UZ-KORAM KO' [700166107173] - SHPARK@CANDH.BIZ,
Reproduction, distribution or publication of these standards is expressly prohib Not for Resale,2018-05-15 09:18:35 UTC
GM WORLDWIDE ENGINEERING STANDARDS GMW14333
9 Release and Revisions
This standard was originated in September 2005. It was first approved by Global Paint and Materials
Engineering in May 2006. It was first published in July 2006.
Issue Publication Date Description (Organization)
1 JUL 2006 Initial publication.
2 OCT 2006 Revised to include the continuous immersion test derived from GM9501P as
Code B. The previous Code B (As Specified) is now designated as Code C.
(Global Paint and Materials Engineering)
3 MAY 2009 Revised to show 11 line scribe pattern. Removed callout for adhesion testing in
paragraphs 5.1.1.1.2 and 5.1.1.2.2. Specific fuel composition added in section
3.2.5. Preparation of test fuel added in section 3.2.6. Added paragraphs 4.4.1.2,
4.4.1.3, 4.4.1.4, 4.4.1.5 thumbnail after dip. (Global Paint and Polymers Center)
4 SEP 2014 Updated to current template. Removed inactive specifications from Section.2.
Removed specifications referencing test fuel described in 3.2.5. Description of
thumbnail test added to 4.4.1.2. Paragraph 5.1.1.1.2 references 4.4.1.2 instead of
GM9507P. (Paint-Finishes and Coatings Global Subsystem Leadership Team)
--`,,,,``,,,``,`,```````-`-``,```,,,`---
© Copyright 2014 General Motors Company All Rights Reserved
September 2014 Page 6 of 6
Copyright General Motors Company Order Number: 02198911
Provided by IHS Markit under license with General Motors Company Sold to:LLC 'UZ-KORAM KO' [700166107173] - SHPARK@CANDH.BIZ,
Reproduction, distribution or publication of these standards is expressly prohib Not for Resale,2018-05-15 09:18:35 UTC
You might also like
- GORE Automotive Vents Exterior Lighting Datasheet ENNo ratings yetGORE Automotive Vents Exterior Lighting Datasheet EN4 pages
- Worldwide Engineering Standards: Stone Impact Resistance of CoatingsNo ratings yetWorldwide Engineering Standards: Stone Impact Resistance of Coatings3 pages
- Worldwide Engineering Standards: Tape Adhesion Test For Paint FinishesNo ratings yetWorldwide Engineering Standards: Tape Adhesion Test For Paint Finishes9 pages
- Determination of Volatile and Semi-Volatile Organic Compounds From Vehicle Interior MaterialsNo ratings yetDetermination of Volatile and Semi-Volatile Organic Compounds From Vehicle Interior Materials19 pages
- Worldwide Engineering Standards: Neutral Salt Spray (NSS) TestNo ratings yetWorldwide Engineering Standards: Neutral Salt Spray (NSS) Test4 pages
- GMW16717 - Decorative Interior Laminates and FilmsNo ratings yetGMW16717 - Decorative Interior Laminates and Films16 pages
- CS.00056 Environmental Spec For Electrical - Electronic ComponentsNo ratings yetCS.00056 Environmental Spec For Electrical - Electronic Components84 pages
- ES-X83244 - G - B - E Standard Test Method Molded Plastics (For Exterior Parts)No ratings yetES-X83244 - G - B - E Standard Test Method Molded Plastics (For Exterior Parts)9 pages
- Film Hardness by Pencil Test: Standard Test Method ForNo ratings yetFilm Hardness by Pencil Test: Standard Test Method For3 pages
- 9.55460-2009 - Needle Punched and Nonwoven Fabrics For Interior Vehicle LiningsNo ratings yet9.55460-2009 - Needle Punched and Nonwoven Fabrics For Interior Vehicle Linings14 pages
- FLTM BI 168-01 (2006) Fluid Resistance of Chassis and Exterior Materials For Incidential ExposureNo ratings yetFLTM BI 168-01 (2006) Fluid Resistance of Chassis and Exterior Materials For Incidential Exposure2 pages
- F659-10 Standard Specification For Ski and Snowboard Goggles100% (2)F659-10 Standard Specification For Ski and Snowboard Goggles8 pages
- Minimum Performance Requirements For Decorative Chromium Plated Plastic PartsNo ratings yetMinimum Performance Requirements For Decorative Chromium Plated Plastic Parts20 pages
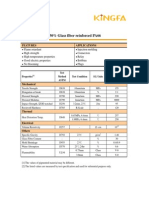
- PA66-RG301: Flame Retardant, 30% Glass Fiber Reinforced PA66No ratings yetPA66-RG301: Flame Retardant, 30% Glass Fiber Reinforced PA662 pages
- ASTM D256-23 Standard Test Methods For Determining The Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of PlasticsNo ratings yetASTM D256-23 Standard Test Methods For Determining The Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics11 pages
- Sae J 1767 Instrumental Color Difference Measurements For Colorfastness of Automotive Interior Trim Materials - 1995.01No ratings yetSae J 1767 Instrumental Color Difference Measurements For Colorfastness of Automotive Interior Trim Materials - 1995.014 pages
- Organic Coating Performance for Underhood and Underbody Component 14671No ratings yetOrganic Coating Performance for Underhood and Underbody Component 146719 pages
- Strength Characteristics of Soil Fly Ash Mixtures Reinforced With Randomly Oriented Polypropylene FibersNo ratings yetStrength Characteristics of Soil Fly Ash Mixtures Reinforced With Randomly Oriented Polypropylene Fibers6 pages
- Green and Blue Illustrative Technology Product Development PresentationNo ratings yetGreen and Blue Illustrative Technology Product Development Presentation10 pages
- Complete Download The Quest for Therapy in Lower Zaire John M. Janzen PDF All ChaptersNo ratings yetComplete Download The Quest for Therapy in Lower Zaire John M. Janzen PDF All Chapters43 pages
- Chapter Three Proposal From Melaku Group (10) TheNo ratings yetChapter Three Proposal From Melaku Group (10) The30 pages
- Laporan Akhir M3 - Ridho Aulia Ahmad - 120150079 - GeotekNo ratings yetLaporan Akhir M3 - Ridho Aulia Ahmad - 120150079 - Geotek22 pages
- Targeted electric vehicle procurement incentives facilitate efficient abatement cost outcomesNo ratings yetTargeted electric vehicle procurement incentives facilitate efficient abatement cost outcomes66 pages
- Mid-Western University School of Management Annual Report 2019-20 (2076-77 B.S)No ratings yetMid-Western University School of Management Annual Report 2019-20 (2076-77 B.S)49 pages
- Photo Warehouse Film Development Chart Push Processing (B/W)No ratings yetPhoto Warehouse Film Development Chart Push Processing (B/W)1 page
- GORE Automotive Vents Exterior Lighting Datasheet ENGORE Automotive Vents Exterior Lighting Datasheet EN
- Worldwide Engineering Standards: Stone Impact Resistance of CoatingsWorldwide Engineering Standards: Stone Impact Resistance of Coatings
- Worldwide Engineering Standards: Tape Adhesion Test For Paint FinishesWorldwide Engineering Standards: Tape Adhesion Test For Paint Finishes
- Determination of Volatile and Semi-Volatile Organic Compounds From Vehicle Interior MaterialsDetermination of Volatile and Semi-Volatile Organic Compounds From Vehicle Interior Materials
- Worldwide Engineering Standards: Neutral Salt Spray (NSS) TestWorldwide Engineering Standards: Neutral Salt Spray (NSS) Test
- GMW16717 - Decorative Interior Laminates and FilmsGMW16717 - Decorative Interior Laminates and Films
- CS.00056 Environmental Spec For Electrical - Electronic ComponentsCS.00056 Environmental Spec For Electrical - Electronic Components
- ES-X83244 - G - B - E Standard Test Method Molded Plastics (For Exterior Parts)ES-X83244 - G - B - E Standard Test Method Molded Plastics (For Exterior Parts)
- Film Hardness by Pencil Test: Standard Test Method ForFilm Hardness by Pencil Test: Standard Test Method For
- 9.55460-2009 - Needle Punched and Nonwoven Fabrics For Interior Vehicle Linings9.55460-2009 - Needle Punched and Nonwoven Fabrics For Interior Vehicle Linings
- FLTM BI 168-01 (2006) Fluid Resistance of Chassis and Exterior Materials For Incidential ExposureFLTM BI 168-01 (2006) Fluid Resistance of Chassis and Exterior Materials For Incidential Exposure
- F659-10 Standard Specification For Ski and Snowboard GogglesF659-10 Standard Specification For Ski and Snowboard Goggles
- Minimum Performance Requirements For Decorative Chromium Plated Plastic PartsMinimum Performance Requirements For Decorative Chromium Plated Plastic Parts
- PA66-RG301: Flame Retardant, 30% Glass Fiber Reinforced PA66PA66-RG301: Flame Retardant, 30% Glass Fiber Reinforced PA66
- ASTM D256-23 Standard Test Methods For Determining The Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of PlasticsASTM D256-23 Standard Test Methods For Determining The Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics
- Sae J 1767 Instrumental Color Difference Measurements For Colorfastness of Automotive Interior Trim Materials - 1995.01Sae J 1767 Instrumental Color Difference Measurements For Colorfastness of Automotive Interior Trim Materials - 1995.01
- Organic Coating Performance for Underhood and Underbody Component 14671Organic Coating Performance for Underhood and Underbody Component 14671
- Strength Characteristics of Soil Fly Ash Mixtures Reinforced With Randomly Oriented Polypropylene FibersStrength Characteristics of Soil Fly Ash Mixtures Reinforced With Randomly Oriented Polypropylene Fibers
- Green and Blue Illustrative Technology Product Development PresentationGreen and Blue Illustrative Technology Product Development Presentation
- Complete Download The Quest for Therapy in Lower Zaire John M. Janzen PDF All ChaptersComplete Download The Quest for Therapy in Lower Zaire John M. Janzen PDF All Chapters
- Laporan Akhir M3 - Ridho Aulia Ahmad - 120150079 - GeotekLaporan Akhir M3 - Ridho Aulia Ahmad - 120150079 - Geotek
- Targeted electric vehicle procurement incentives facilitate efficient abatement cost outcomesTargeted electric vehicle procurement incentives facilitate efficient abatement cost outcomes
- Mid-Western University School of Management Annual Report 2019-20 (2076-77 B.S)Mid-Western University School of Management Annual Report 2019-20 (2076-77 B.S)
- Photo Warehouse Film Development Chart Push Processing (B/W)Photo Warehouse Film Development Chart Push Processing (B/W)