Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planning
Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planning
Uploaded by
Papellero Villamor GlendaCopyright:
Available Formats
Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planning
Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planning
Uploaded by
Papellero Villamor GlendaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planning
Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planning
Uploaded by
Papellero Villamor GlendaCopyright:
Available Formats
Instructional Planning
(The process of systematically planning, developing, evaluating and managing the instructional
process by using principles of teaching and learning - D.O. 42, s. 2016)k
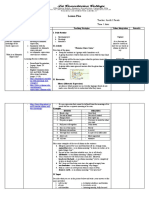
Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format
DLP No.: Learning Area: Grade Level: Quarter: Duration: Date:
ENGLISH 7- St. Philomena 4th 60 02/28/20
(11:00-12:00 a.m.)
Learning Competency/ies: Give the various meanings of identified homonymous or polysemous Code:
(Taken from the Curriculum Guide) words or expressions EN7V-IV-e-9
Key Concepts / Homonyms (or multiple meaning words)- are words that share the same spelling and the same
Understandings to be pronunciation but have different meanings.
Homophones(or sound-alike words)- are words that are pronounced identically although they
Developed have different meanings and are often pronounced differently as well.
Homographs- are words that are spelled the same, but have different meanings and are often
pronounced differently as well.
Domain Adapted Cognitive Process Dimensions (D.O. No. 8, s. 2015) 1. Objectives
Knowledge Categories: Behavioral Verbs:
The fact or condition identify, retrieve, recognize, duplicate, list,
Remembering
of knowing memorize, repeat, describe, reproduce
The learner can recall information and
something with
retrieve relevant knowledge from long-term
familiarity gained
memory
through experience
Understanding interpret, exemplify, classify, summarize, Discuss homonymous or polysemous
or association
The learner can construct meaning from oral, infer, compare, explain, paraphrase, discuss
words or expressions
written and graphic messages
Skills Applying execute, implement, demonstrate,
The ability and The learner can use information to undertake a dramatize, interpret, solve, use,
capacity acquired procedure in familiar situations or in a new way illustrate, convert, discover
through deliberate, Analyzing differentiate, distinguish, compare,
systematic, and The learner can distinguish between parts and contrast, organize, outline, attribute,
sustained effort to determine how they relate to one another, and to the deconstruct
smoothly and overall structure and purpose
adaptively carryout coordinate, measure, detect, defend,
complex activities or
Evaluating
The learner can make judgments and justify decisions judge, argue, debate, describe,
the ability, coming critique, appraise, evaluate
from one's
Creating generate, hypothesize, plan, design, Generate the various meanings of identified
knowledge, practice, develop, produce, construct, homonymous or polysemous in a given
aptitude, etc., to do The learner can put elements together to form a
functional whole, create a new product or point of view formulate, assemble, devise sentence.
something
Attitude Categories: List of Attitudes:
Growth in 1. Receiving Phenomena - Awareness, willingness to hear, selected attention Self-esteem, Self-confidence,
feelings or Behavioral Verbs: ask, choose, describe, erect, follow, give, hold, identify, locate, name, Wellness, Respect, Honesty, Personal
emotional point to, reply, select, sit, Study, use discipline, Perseverance, Sincerity,
areas. 2. Responding to Phenomena - Active participation on the part of the learners. Attends and Patience, Critical thinking, Open-
A settled reacts to a particular phenomenon. Learning outcomes may emphasize compliance in mindedness, Interest, Courteous,
way of responding, willingness to respond, or satisfaction in responding (motivation). Obedience, Hope, Charity, Fortitude,
thinking Behavioral Verbs: aid, answer, assist, comply, conform, discuss, greet, help, label, Resiliency, Positive vision,
or feeling perform, practice, present, read, recite, report, select, tell, write Acceptance, Determined,
about 3. Valuing - Attaches to a particular object, phenomenon, or behavior. This ranges from simple Independent , Gratitude, Tolerant,
someone acceptance to the more complex state of commitment. Valuing is based on the internalization Cautious, Decisive, Self-Control,
or of a set of specified values, while clues to these values are expressed in the learner's overt Calmness, Responsibility,
something behavior and are often identifiable. Accountability, Industriousness,
, typically Industry, Cooperation, Optimism,
one that is
Behavioral Verbs: work, complete, demonstrate, differentiate, explain, follow, form, Satisfaction, Persistent, Cheerful,
reflected initiate, invite, join, justify, propose, read, report, select, share, study Reliable, Gentle, Appreciation of
in a 4. Organization - Organizes values into priorities by contrasting different values, resolving one’s culture, Globalism,
person’s conflicts between them, and creating a unique value system. The emphasis is on comparing, Compassion, Work Ethics, Creativity,
behavior relating, and synthesizing values. Entrepreneurial Spirit, Financial
Behavioral Verbs: adhere, alter, arrange, combine, compare, complete, defend, explain, Literacy, Global, Solidarity, Making a
formulate, generalize, identify, integrate, modify, order, organize, prepare, relate, synthesize stand for the good, Voluntariness of
5. Internalizing values - (Characterization): Has a value system that controls their behavior. The human act, Appreciation of one’s Display critical
behavior is pervasive, consistent, predictable, and most importantly, characteristic of the rights, Inclusiveness, Thoughtful, thinking
learner. Instructional objectives are concerned with the student's general patterns of Seriousness, Generous, Happiness,
adjustment (personal, social, emotional). Modest, Authority, Hardworking,
through the use
Behavioral Verbs: act, discriminate, display, influence, listen, modify, perform, practice, Realistic, Flexible, Considerate, of words or
propose, qualify, question, revise, serve, solve, verify Sympathetic, Frankness expressions
such as
homonymous
and
polysemous
words.
Values Categories: List of Values:
A 1. Receiving Phenomena - Awareness, willingness to hear, selected attention 1. Maka-Diyos
learner's Behavioral Verbs: ask, choose, describe, erect, follow, give, hold, identify, locate, Love of God, Faith, Trusting,
principles name, point to, reply, select, sit, Study, use Spirituality, Inner Peace, Love of
or 2. Responding to Phenomena - Active participation on the part of the learners. Attends and truth, Kindness, Humble
standards reacts to a particular phenomenon. Learning outcomes may emphasize compliance in
of responding, willingness to respond, or satisfaction in responding (motivation).
behavior;
Behavioral Verbs: aid, answer, assist, comply, conform, discuss, greet, help, label,
one's 2. Maka-tao
perform, practice, present, read, recite, report, select, tell, write
judgment Concern for Others, Respect for Initiate productivity in
3. Valuing - Attaches to a particular object, phenomenon, or behavior. This ranges from
of what is human rights, Gender equality, using homonymous
simple acceptance to the more complex state of commitment. Valuing is based on the
important Family Solidarity, Generosity, and polysemous
internalization of a set of specified values, while clues to these values are expressed in the
in life. Helping, Oneness words
learner's overt behavior and are often identifiable.
Go
beyond Behavioral Verbs: work, complete, demonstrate, differentiate, explain, follow, form,
learner’s initiate, invite, join, justify, propose, read, report, select, share, study 3. Makakalikasan
life on 4. Organization - Organizes values into priorities by contrasting different values, resolving Care of the environment, Disaster
earth, conflicts between them, and creating a unique value system. The emphasis is on Risk Management, Protection of
include comparing, relating, and synthesizing values. the Environment, Responsible
more Behavioral Verbs: adhere, alter, arrange, combine, compare, complete, defend, Consumerism, Cleanliness,
than explain, formulate, generalize, identify, integrate, modify, order, organize, prepare, Orderliness, Saving the
wealth relate, synthesize ecosystem, Environmental
and fame, 5. Internalizing values - (Characterization): Has a value system that controls their behavior. sustainability
and would The behavior is pervasive, consistent, predictable, and most importantly, characteristic of 4. Makabansa
affect the the learner. Instructional objectives are concerned with the student's general patterns of Peace and order, Heroism and
eternal adjustment (personal, social, emotional). Appreciation of Heroes, National
destiny of Behavioral Verbs: act, discriminate, display, influence, listen, modify, perform, Unity, Civic Consciousness, Social
millions. practice, propose, qualify, question, revise, serve, solve, verify responsibility, Harmony,
(Intention Patriotism, Productivity
ally add
value to
people
everyday.
)
2. Content HOMONYMS, HOMOPHONES AND HOMOGRAPHS
3. Learning Resources
4. Procedures
4.1 Introductory Activity (____ minutes). This part introduces the lesson Curriculum
content. Although at times optional, it is usually included to serve as a warm-up Contextualization Preliminary Activities
activity to give the learners zest for the incoming lesson and an idea about what Opening Prayer
Localization:
it to follow. One principle in learning is that learning occurs when it is conducted
in a pleasurable and comfortable atmosphere.
Consider/include here Greetings
the appropriate Local Checking of attendance
Heritage Themes: Presentation of learning objectives
1. Annual Rites,
Festivals, and
Review the previous lesson
Rituals (Ask questions from the past lesson)
(Historical/Religious Motivation: JUMBLED WORDS
Festivals, Local The teacher presents jumbled words. All
Cultural Festivals, learners are encourage to pair words which sound
Local
Delicacies/Products
most alike. The learners read the words aloud after
Festivals, Rituals, the teacher.
Wedding Ritual,
Palihi Ritual, Burial
Ritual,
B Literary Anthologies
4.2 Activity/Strategy (____ minutes). This is an interactive strategy to
Written In Local
The teacher shows a video and discusses
elicit learner’s prior learning experience. It serves as a springboard for new Language (BALITAW, about “HOMOPHONES,HOMOGRAPHS
learning. It illustrates the principle that learning starts where the learners are.
Carefully structured activities such as individual or group reflective exercises,
BALAK, Folktales/ AND HOMONYMS.
Short Stories, Local
group discussion, self-or group assessment, dyadic or triadic interactions, Heroes
puzzles, simulations or role-play, cybernetics exercise, gallery walk and the like C. Historical Events,
may be created. Clear instructions should be considered in this part of the Enduring Values,
lesson. Indigenous Materials,
4.3 Analysis (____ minutes). Essential questions are included to serve as a Indigenous Cultural Process Questions:
guide for the teacher in clarifying key understandings about the topic at hand. Communities/Indigeno
Critical points are organized to structure the discussions allowing the learners to us People, Indigenous 1. What have you learned after watching the video?
maximize interactions and sharing of ideas and opinions about expected issues. Games
Affective questions are included to elicit the feelings of the learners about the D. Topography, Flora/
activity or the topic. The last questions or points taken should lead the learners Fauna (Falls, 2.Do you understand the differences among
to understand the new concepts or skills that are to be presented in the next Mountains, River, homonyms, homophones and homographs? If yes,
part of the lesson. Cave, Trees, Flower,
Fauna describe each of them and give examples.
E. Food & Local
products 3. What do all of these words have common? How
G. Role Model Family. are they the same?
4. As a learner, why do we have to know the correct
usage of those words?
4.4 Abstraction (____ minutes). This outlines the key concepts, important Process Questions:
skills that should be enhanced, and the proper attitude that should be 1.What are homophones, homonyms and
emphasized. This is organized as a lecturette that summarizes the learning
homographs?
emphasized from the activity, analysis and new inputs in this part of the lesson.
2. Why do we need to know about homonyms,
homophones, and homographs?
4.5 Application (____ minutes). This part is structured to ensure the Direction: You will be divided into three groups according to
commitment of the learners to do something to apply their new learning in their your interest like Singing, Reading a Poem and Acting. Pick the
own environment. correct homophones, homographs and homonyms for the given
lines in the poem entitled “I’m All Mixed Up.
I’m All Mixed Up
I’m All Mixed Up.
I need help from you.
How do I no/know.
Why the sky is blue/blew?
I do not no/know.
I wish I new/knew.
Is my sister aged for/four or too/to/two?
Eye/I am named Marie
She is named Be/Bee/Bea.
We eat red/read berries
By the water at the see/sea.
I have a lot of work to do/due!
I’ll so/sew a button
On the coat you wear/where.
I’ll sit on that chair.
I’ll wait right/write over there/their.
I’m All Mixed Up.
I need help from you.
Can you choose the right words?
See what you can do!
4.6 Assessment (___ minutes). For the Teacher to: a) Assess whether
learning objectives have been met for a specified duration, b) Remediate
and/or enrich with appropriate strategies as needed, and c) Evaluate whether
learning intentions and success criteria have been met. (Reminder: Formative
Assessment may be given before, during, or after the lesson). Choose any from
the Assessment Methods below:
Assessment Method Possible Activities
a) Observation Investigation, Role
(Formal and informal observations of learners’ performance or behaviors are Play, Oral
recorded, based on assessment criteria) Presentation, Dance,
Musical Performance,
Skill Demonstration,
Group Activity (e.g.
Choral Reading),
Debate, Motor &
Psychomotor Games,
Simulation Activities,
Science Experiment
b) Talking to Learners / Conferencing Hands-on Math
(Teachers talk to and question learners about their learning to gain insights on Activities, Written
their understanding and to progress and clarify their thinking) Work and Essay,
Picture Analysis,
Comic Strip, Panel
Discussion, Interview,
Think-Pair-Share,
Reading
c) Analysis of Learners’ Products Worksheets for all
(Teachers judge the quality of products produced by learners according to subjects, Essay,
agreed criteria) Concept
Maps/Graphic
Organizer, Project,
Model, Artwork,
Multi-media
Presentation, Product
made in technical-
vocational subjects
d) Tests Skill Performance
(Teachers set tests or quizzes to determine learners’ ability to demonstrate Test, Open-Ended Direction. Choose (a) or (b) that fits to the correct
mastery of a skill or knowledge of content) Question, Practicum,
Pen and Paper Test, meaning of the highlighted word in the given
Pre and Post Test, sentence.
Diagnostic Test, Oral
Test, Quiz
1.The kids are going to watch ___ TV tonight.
What time is it? I have to set my watch____.
(a) small clock worn on the wrist
(b) look at
2. The singer made a low bow ___ to the audience.
Maria placed a red bow ___ on the birthday gift.
(a) decorative ribbon (rhymes with so)
(b) bend at the waist (rhymes with how)
3. Please try not to waste____ paper.
He put his arm around her waist_____.
(a) the typically narrowed part of the body between
the hips and chest or upper back.
(b) to spend or use carelessly
4. I don’t know if I will live ___ or die.
Last night I saw the band play live ___ in concert.
(a) to have life (rhymes with give)
(b) in real time performance (rhymes with hive)
5. Let’s play ___ soccer after school
The author wrote a new play ___.
(a) participate in a sport
(b) theater piece
4.7 Assignment (____ minutes). Fill-in below any of the four purposes:
Reinforcing / strengthening the day’s lesson
Enriching / inspiring the day’s lesson
Enhancing / improving the day’s lesson
Preparing for the new lesson
4.8 Concluding Activity (____ minutes).
This is usually a brief but affective closing activity such as a strong quotation, a short song, an anecdote,
parable or a letter that inspires the learners to do something to practice their new learning.
5. Remarks Indicate below special cases including but not limited to continuation of lesson plan to the following day in case of re-teaching or lack of time,
transfer of lesson to the following day, in cases of class suspension, etc.
6. Reflections Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your student’s progress this week. What works? What else needs to be done
to help the students learn? Identify what help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them relevant
questions. Indicate below whichever is/are appropriate.
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
evaluation.
B. No. of learners who
require additional
activities for
remediation.
C. Did the remedial
lessons work? No.
of learners who
have caught up
with the lesson.
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation.
E. Which of my
learning strategies
worked well? Why
did these work?
F. What difficulties did
I encounter which
my principal or
supervisor can help
me solve?
G. What innovation or
localized materials
did I use/discover
which I wish to
share with other
teachers?
Prepared by:
Name: Glenda V. Papellero School: AWIHAO NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Position/Designation: TEACHER I Division: TOLEDO CITY
Contact Number: 09260559641 Email address: glenda.papellero071@deped.gov.ph
Bibliography
Appendices: (attach all materials that will be used)
1. Activity Sheet …
2. Formative Assessment …
3. Answer Key …
4. Handouts …
5. PowerPoint Presentation …
6. Others
You might also like
- 14 Working With Groups 2015 by TLMendoza PDFDocument19 pages14 Working With Groups 2015 by TLMendoza PDFJoseph Giducos Jumantoc83% (12)
- Example of Motivation LetterDocument2 pagesExample of Motivation LetterJuliana Gomes de Oliveira25% (4)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningPapellero Villamor Glenda100% (1)
- DLL11 Verb ComplementationDocument8 pagesDLL11 Verb ComplementationNolibhele BahanNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Human Resource Planning On Organizational Performance 1Document17 pagesThe Impact of Human Resource Planning On Organizational Performance 1musab100% (1)
- Anik Singal Success PDFDocument197 pagesAnik Singal Success PDFpatelpuri75% (8)
- Learning Planeng7editedDocument13 pagesLearning Planeng7editedRoseAntonetteOrtizNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 3Document27 pagesStudy Guide 3Darlene Joy CambayNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Grade 7 Learning Competency: Express Ideas and Opinions Based The Text Listened To. Competency Code: EN7OL-III-f-2.4.1 I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesLesson Plan For Grade 7 Learning Competency: Express Ideas and Opinions Based The Text Listened To. Competency Code: EN7OL-III-f-2.4.1 I. ObjectivesJose Dominic GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in 21 Century LiteratureDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in 21 Century LiteratureRomel BearsNo ratings yet
- LP 1 The Conflict and Its TypesDocument11 pagesLP 1 The Conflict and Its TypesLaura Lae Venzon VillescoNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson PlanLezleih Shane TalisicNo ratings yet
- Rhodora P. Rosco Bsed Ii - EnglishDocument13 pagesRhodora P. Rosco Bsed Ii - EnglishRhodora RoscoNo ratings yet
- Rubrics For RoleplayDocument5 pagesRubrics For RoleplayEvan Maagad LutchaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan For DemoDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan For DemoMelyang IntongNo ratings yet
- Where's The Patis - DLPDocument5 pagesWhere's The Patis - DLPMAY DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- School Grade Level: I. ObjectivesDocument8 pagesSchool Grade Level: I. ObjectivesJerome BautistaNo ratings yet
- English 8 Noting Cultural DifferencesDocument40 pagesEnglish 8 Noting Cultural DifferencesDahlia Galvan- MaglasangNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: School: Grade Level: Learning Area: ENGLISH Quarter: TeacherDocument4 pagesI. Objectives: School: Grade Level: Learning Area: ENGLISH Quarter: TeacherClaire BalaneNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN IN ENGLISH 7 AlliterationDocument9 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN IN ENGLISH 7 AlliterationArnel MameNo ratings yet
- CG-4TH QuarterDocument31 pagesCG-4TH QuarterPatricia Carla UndangNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in Eng 7Document2 pagesDiagnostic Test in Eng 7LAIZA SOJONNo ratings yet
- Paradox, Irony and Paradox (Evaluative Demo)Document4 pagesParadox, Irony and Paradox (Evaluative Demo)DezmeinNo ratings yet
- Idioms Eng 7 Melc 1Document7 pagesIdioms Eng 7 Melc 1Gladiola DelimNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing Imagery, Diction, and Figures of Speech Week 4 Performance Task ORIGINAL POEM (30 PTS.)Document2 pagesCreative Writing Imagery, Diction, and Figures of Speech Week 4 Performance Task ORIGINAL POEM (30 PTS.)Roxanne LomandasNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan English7 Q3Document5 pagesInstructional Plan English7 Q3Imelda QuintosNo ratings yet
- Unit PlanDocument40 pagesUnit Planapi-257586514100% (1)
- Rem. 2Document2 pagesRem. 2LadyNareth MierdoNo ratings yet
- GRADE7Document121 pagesGRADE7Ariane del RosarioNo ratings yet
- INFORMATIVE - DLL AutoRecoveredDocument6 pagesINFORMATIVE - DLL AutoRecoveredmarinel de claroNo ratings yet
- G7 Q1 Lesson1Document3 pagesG7 Q1 Lesson1Jed GalvezNo ratings yet
- Figurative Language Class Discussion Writing Realization: En7V-Iic-10.1.2Document10 pagesFigurative Language Class Discussion Writing Realization: En7V-Iic-10.1.2Harly DavidsonNo ratings yet
- LP English 9 Lesson 1Document13 pagesLP English 9 Lesson 1ERIC BAAYNo ratings yet
- ENG10Document36 pagesENG10DaveNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Eng LPDocument6 pagesWeek 2 Eng LPflorlijosol0% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan G7 GENERAL REFERENCESDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan G7 GENERAL REFERENCESYra Valenzuela100% (1)
- 1q Reading ComprehensionDocument1 page1q Reading Comprehensionapi-407221957No ratings yet
- Stages 1-2 (Literature) (Print Me)Document4 pagesStages 1-2 (Literature) (Print Me)Charm PosadasNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in English 7 DECEMBER 5, 2019 I. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in English 7 DECEMBER 5, 2019 I. ObjectivesEljien Lumbayo100% (1)
- Quarter 1-Week 6 - Day 4.revisedDocument5 pagesQuarter 1-Week 6 - Day 4.revisedJigz FamulaganNo ratings yet
- EN8V-Ib-10.2: Determine The Meaning of Idiomatic Expressions by Noting Context Clues and CollocationsDocument6 pagesEN8V-Ib-10.2: Determine The Meaning of Idiomatic Expressions by Noting Context Clues and CollocationsDorothy Joy NadelaNo ratings yet
- LPDocument20 pagesLPMorris CarrealNo ratings yet
- For ClinicalDocument4 pagesFor ClinicalJinkai FernandezNo ratings yet
- React To The Falsity or Soundness of An ArgumentDocument7 pagesReact To The Falsity or Soundness of An ArgumentShawn MikeNo ratings yet
- Odato - LP - The Cracked PotDocument5 pagesOdato - LP - The Cracked PotIvy OdatoNo ratings yet
- Understand The Concept of Maxims, Universal Truths, and Philosophies in LiteratureDocument3 pagesUnderstand The Concept of Maxims, Universal Truths, and Philosophies in LiteratureNiña Marie CorsigaNo ratings yet
- DLP IntonationDocument7 pagesDLP IntonationLyka Mae BunagNo ratings yet
- English8 Q2 L1-2Document23 pagesEnglish8 Q2 L1-2Jane Drelle AgustinNo ratings yet
- LP Day 4 (Figure of Speech)Document6 pagesLP Day 4 (Figure of Speech)BelmerDagdagNo ratings yet
- Final Collocation - Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesFinal Collocation - Lesson PlanIAm RegieNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Lesson PlanstellamariceNo ratings yet
- Readers Theater Chamber Theater and One Act PlayDocument42 pagesReaders Theater Chamber Theater and One Act PlayAliza Jean Delarosa BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Philippine Literature During The Period of ApprenticeshipDocument12 pagesPhilippine Literature During The Period of ApprenticeshipJanrhey Dar0% (1)
- Herrera, Hazel Mae M. LPDocument2 pagesHerrera, Hazel Mae M. LPHazel Mae HerreraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Idiomatic Expression - Joseth Pasalo - (ENG 23)Document5 pagesLesson Plan - Idiomatic Expression - Joseth Pasalo - (ENG 23)Joseth100% (1)
- TABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS - Grade-10 (4th Grading)Document4 pagesTABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS - Grade-10 (4th Grading)Aljon Jay Sulit SiadanNo ratings yet
- Emeterio-Federica Gerez National High School: Jhs Learning Activity SheetDocument3 pagesEmeterio-Federica Gerez National High School: Jhs Learning Activity SheetChelleyOllitroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Intonation Sep 14Document4 pagesLesson Plan - Intonation Sep 14aria jen05No ratings yet
- Poetry Semi Detailed Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesPoetry Semi Detailed Lesson PlanAlexis Dan Aquino MendozaNo ratings yet
- Checked Detailed Lesson Plan in English 9 Q4M3Document9 pagesChecked Detailed Lesson Plan in English 9 Q4M3christianlovehernandezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Arts and Creativity LiteracyDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Arts and Creativity LiteracyChristine Mae BacomoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 5 - Types of TextDocument1 pageQuiz 5 - Types of TextLorna T. OrdizNo ratings yet
- English CG WordDocument122 pagesEnglish CG WordNanaths Su100% (2)
- DLP - TYPES OF IRONY - RevisedDocument5 pagesDLP - TYPES OF IRONY - RevisedFrensey JynethNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningPapellero Villamor GlendaNo ratings yet
- Attentive Listening: Name: Glenda V. Papellero DATE: FEBRUARY 8,2020 Reflection: 4 Subject: Eng 512 (Tesl)Document1 pageAttentive Listening: Name: Glenda V. Papellero DATE: FEBRUARY 8,2020 Reflection: 4 Subject: Eng 512 (Tesl)Papellero Villamor GlendaNo ratings yet
- Let's Get Started!Document15 pagesLet's Get Started!Papellero Villamor GlendaNo ratings yet
- English 7Document19 pagesEnglish 7Papellero Villamor GlendaNo ratings yet
- Process Approach Writing:Part 1Document21 pagesProcess Approach Writing:Part 1Papellero Villamor GlendaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningPapellero Villamor GlendaNo ratings yet
- Writing Correction CodeDocument7 pagesWriting Correction CodeJack PoleskiNo ratings yet
- 10 Journals LEADERSHIPDocument27 pages10 Journals LEADERSHIPNewgleer WengNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence and Teacher Effectiveness Sept 2013Document5 pagesEmotional Intelligence and Teacher Effectiveness Sept 2013Maria IrinaNo ratings yet
- KM - WalmartDocument6 pagesKM - Walmartricha928No ratings yet
- Edu 201 Lesson Plan FinalDocument3 pagesEdu 201 Lesson Plan Finalapi-571252616No ratings yet
- INSIDE THE GURU MIND - Heller - Jack Welch PDFDocument16 pagesINSIDE THE GURU MIND - Heller - Jack Welch PDFCris_eu09No ratings yet
- Chen Self Determination TheoryDocument12 pagesChen Self Determination TheoryAiona AlmogueraNo ratings yet
- Faiza - 1334 - 16064 - 2 - Lecture 3 - Organization - Individual Relations and RetentionsDocument20 pagesFaiza - 1334 - 16064 - 2 - Lecture 3 - Organization - Individual Relations and RetentionsUrooj MustafaNo ratings yet
- Transformational Transactional and Laissez-Faire Leadership Styles - A Meta-Analysis Comparing Women and MenDocument23 pagesTransformational Transactional and Laissez-Faire Leadership Styles - A Meta-Analysis Comparing Women and Menabdulaziz90No ratings yet
- INTRO TO COMM MEDIA - Module 2Document9 pagesINTRO TO COMM MEDIA - Module 2Christianne VenturaNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Positive Thinking and Individual Characteristics: Development of The Soccer Positive Thinking ScaleDocument10 pagesThe Relationship Between Positive Thinking and Individual Characteristics: Development of The Soccer Positive Thinking ScaleIrinNo ratings yet
- What Makes Accounting Students Choose Their Career A Case in Indonesian Major UniversitiesDocument30 pagesWhat Makes Accounting Students Choose Their Career A Case in Indonesian Major UniversitiesNgọc TrânNo ratings yet
- The Social and Affective Dimensions of Early Second Language Acquisition: A Case StudyDocument12 pagesThe Social and Affective Dimensions of Early Second Language Acquisition: A Case Studymary christi mondigoNo ratings yet
- Peak: Secrets From The New Science of ExpertiseDocument7 pagesPeak: Secrets From The New Science of ExpertiseAman DanishNo ratings yet
- Lu - VersaillesDocument23 pagesLu - Versailleswhiskyagogo1No ratings yet
- Optimism, Explanatory Style, and Hope: Positive PsychologyDocument25 pagesOptimism, Explanatory Style, and Hope: Positive PsychologyJay Mark Samson CabreraNo ratings yet
- A STUDY ON EMPLOYEES JOB SATISFACTION IN NEEPCO LTDDocument63 pagesA STUDY ON EMPLOYEES JOB SATISFACTION IN NEEPCO LTDShahzad SaifNo ratings yet
- How To Write A CVDocument2 pagesHow To Write A CVJaydeepSachdevNo ratings yet
- Article IJBSS BahrulDocument9 pagesArticle IJBSS BahrulJohn Paul XavierNo ratings yet
- Functions Human Resource Management Functions: Managerial, Operative and Advisory FunctionDocument4 pagesFunctions Human Resource Management Functions: Managerial, Operative and Advisory FunctionGAYATHRI HARIKUMARNo ratings yet
- Les Donaldson, Edward Scannell, Edward S. Scannell-Human Resource Development - The New Trainer's Guide-Basic Books (2000) PDFDocument209 pagesLes Donaldson, Edward Scannell, Edward S. Scannell-Human Resource Development - The New Trainer's Guide-Basic Books (2000) PDFsaurabh887100% (1)
- Assignment Feedback Form Holiday RepDocument4 pagesAssignment Feedback Form Holiday RepThom de GrootNo ratings yet
- BBA MPP Unit 1 SEM 1Document143 pagesBBA MPP Unit 1 SEM 1Rohit ChandraNo ratings yet
- Advanced Teacher's Support Book 5 Iii: Rod FlickerDocument227 pagesAdvanced Teacher's Support Book 5 Iii: Rod FlickerVukan Jokic100% (1)
- Reflection From Teachers and Students On Speaking Anxiety in An Efl ClassroomDocument2 pagesReflection From Teachers and Students On Speaking Anxiety in An Efl Classroomafriwani susantiNo ratings yet
- 0 Tandon2020 Sleepless Due To Social Media Investigating Problematic Sleep Due To Social Media and Social Media Sleep Hygiene Q1Document12 pages0 Tandon2020 Sleepless Due To Social Media Investigating Problematic Sleep Due To Social Media and Social Media Sleep Hygiene Q1QUYNH NGUYEN LE DIEMNo ratings yet