0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
Acids and Bases
Uploaded by
thaboAcids and bases can be identified using litmus paper tests. Acids turn litmus paper red and bases turn litmus paper blue. Common acids include lemon juice and vinegar, while common bases include sodium hydroxide, bicarbonate of soda, and toothpaste. Acids and bases have a variety of uses, such as toothpaste neutralizing acids in the mouth to prevent tooth decay and bicarbonate of soda neutralizing bee stings.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
Acids and Bases
Uploaded by
thabo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
Acids and bases can be identified using litmus paper tests. Acids turn litmus paper red and bases turn litmus paper blue. Common acids include lemon juice and vinegar, while common bases include sodium hydroxide, bicarbonate of soda, and toothpaste. Acids and bases have a variety of uses, such as toothpaste neutralizing acids in the mouth to prevent tooth decay and bicarbonate of soda neutralizing bee stings.
Original Title
science
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Acids and bases can be identified using litmus paper tests. Acids turn litmus paper red and bases turn litmus paper blue. Common acids include lemon juice and vinegar, while common bases include sodium hydroxide, bicarbonate of soda, and toothpaste. Acids and bases have a variety of uses, such as toothpaste neutralizing acids in the mouth to prevent tooth decay and bicarbonate of soda neutralizing bee stings.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
Acids and Bases
Uploaded by
thaboAcids and bases can be identified using litmus paper tests. Acids turn litmus paper red and bases turn litmus paper blue. Common acids include lemon juice and vinegar, while common bases include sodium hydroxide, bicarbonate of soda, and toothpaste. Acids and bases have a variety of uses, such as toothpaste neutralizing acids in the mouth to prevent tooth decay and bicarbonate of soda neutralizing bee stings.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1/ 4
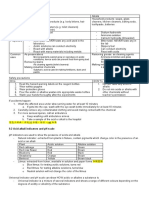
ACIDS AND BASES
Acid
- a substance that turns blue litmus paper red
- has a sour taste
- soluble in water and form an acidic solution
- very corrosive
- examples, hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, nitric acid, citric acid
Bases
- a substance that reacts with an acid to give a neutral solution
- turns red litmus paper blue
- react with acids and remove the sour taste
- some bases dissolve in water to form an alkaline solution
- bases that dissolve in water are called alkalis
- examples sodium hydroxide, ammonia, sodium carbonate
Neutral substances
- substances that are neither acidic nor basic
- have no effect on litmus paper
Litmus paper test for acids and bases
- a litmus paper changes between red and blue
- a blue litmus paper turns red in the presence of an acid
- a red litmus paper turns blue in the presence of a base
Experiment : to investigate the effect of acids and bases on litmus paper
Method
Dip a litmus paper in a solution of the following substances and record
observations
Results
Substance Red litmus paper Blue litmus paper Type of substance
Sodium hydroxide Turns blue No effect alkali
Lemon juice No effect Turns red acid
Colgate Turns blue No effect alkali
Bicarbonate of Turns blue No effect alkali
soda
Tap water No effect No effect neutral
Handy andy Turns blue No effect alkali
Vinegar No effect Turns red acid
Properties of acids and bases
Acids and bases can be strong or weak
Strong acids and bases are very corrosive and dangerous e. sulphuric
acid, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide
These cause serious burns
In the labs, we use dilute acids dissolved in water
Weak acids are for example citric acid found in citrus fruits, acetic acid in
vinegar and these are not dangerous
Weak bases are for example the bases found in toothpaste, bicarbonate
of soda and detergents
Uses of acids and bases
i. Acids formed in the mouth by bacteria cause tooth decay. The
alkali in toothpaste removes the acids preventing tooth decay
ii. Our stomachs contain hydrochloric acid needed for digestion of
food. A person with excess acid in the stomach takes anti acids
which contain an alkali that removes the excess acids
iii. The acid in a bee sting can be neutralised by bicarbonate of soda
iv. The alkaline sting of a wasp can be neutralised using vinegar
You might also like
- Acids, Bases, & Salts: Presentation by Navaneeth.S VII DNo ratings yetAcids, Bases, & Salts: Presentation by Navaneeth.S VII D14 pages
- Acids & Bases (New) Ntse Module Class 6No ratings yetAcids & Bases (New) Ntse Module Class 616 pages
- Acids Bases and Salts-Handout: Subject: Science Class ViiNo ratings yetAcids Bases and Salts-Handout: Subject: Science Class Vii4 pages
- Chapter 6 - Acids, Bases and Salts - NotesNo ratings yetChapter 6 - Acids, Bases and Salts - Notes6 pages
- Ch12 Kitabcd Class 8 MSBHSE Science NotesNo ratings yetCh12 Kitabcd Class 8 MSBHSE Science Notes6 pages
- Aqua Regia or "Kingly Water" and Has The Ability To Dissolve GoldNo ratings yetAqua Regia or "Kingly Water" and Has The Ability To Dissolve Gold6 pages
- Chapter 6 Acid and Alkali: Learning OutcomesNo ratings yetChapter 6 Acid and Alkali: Learning Outcomes5 pages
- The Chemistry of Soaps and Salts - Chemistry Book for Beginners | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Soaps and Salts - Chemistry Book for Beginners | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- S D ' C H S: T Ominic S Hishawasha IGH ChoolNo ratings yetS D ' C H S: T Ominic S Hishawasha IGH Chool8 pages
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelNo ratings yetZimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level12 pages
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level100% (3)Zimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level24 pages
- PPT1 - Cambridge - IX - Chem - Unit17 - Chemistry of Our EnvironmentNo ratings yetPPT1 - Cambridge - IX - Chem - Unit17 - Chemistry of Our Environment19 pages
- WS - MCQ - X - Chem - Acids Bases and SaltsNo ratings yetWS - MCQ - X - Chem - Acids Bases and Salts5 pages
- Chapter Two General Inorganic Chemistry: Characteristics of S Block ElementsNo ratings yetChapter Two General Inorganic Chemistry: Characteristics of S Block Elements32 pages
- Experimental Investigation of Effect of TIG and MIG Welding Parameters On Ti6Al4VNo ratings yetExperimental Investigation of Effect of TIG and MIG Welding Parameters On Ti6Al4V4 pages
- Determination of Phosphorus in Plant Food and Similar Samples - Gravimetric Method (MGNH Po - 6H O Precipitation)No ratings yetDetermination of Phosphorus in Plant Food and Similar Samples - Gravimetric Method (MGNH Po - 6H O Precipitation)9 pages
- Chemistry of Group 16 in P Block ElementsNo ratings yetChemistry of Group 16 in P Block Elements4 pages
- Estimation of Glucose by Folin Wu MethodNo ratings yetEstimation of Glucose by Folin Wu Method3 pages
- High-Temperature Metals and Alloys Chlorine Corrosion ofNo ratings yetHigh-Temperature Metals and Alloys Chlorine Corrosion of6 pages
- Acids, Bases, & Salts: Presentation by Navaneeth.S VII DAcids, Bases, & Salts: Presentation by Navaneeth.S VII D
- Acids Bases and Salts-Handout: Subject: Science Class ViiAcids Bases and Salts-Handout: Subject: Science Class Vii
- Aqua Regia or "Kingly Water" and Has The Ability To Dissolve GoldAqua Regia or "Kingly Water" and Has The Ability To Dissolve Gold
- The Chemistry of Soaps and Salts - Chemistry Book for Beginners | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Soaps and Salts - Chemistry Book for Beginners | Children's Chemistry Books
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelZimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelZimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
- PPT1 - Cambridge - IX - Chem - Unit17 - Chemistry of Our EnvironmentPPT1 - Cambridge - IX - Chem - Unit17 - Chemistry of Our Environment
- Chapter Two General Inorganic Chemistry: Characteristics of S Block ElementsChapter Two General Inorganic Chemistry: Characteristics of S Block Elements
- Experimental Investigation of Effect of TIG and MIG Welding Parameters On Ti6Al4VExperimental Investigation of Effect of TIG and MIG Welding Parameters On Ti6Al4V
- Determination of Phosphorus in Plant Food and Similar Samples - Gravimetric Method (MGNH Po - 6H O Precipitation)Determination of Phosphorus in Plant Food and Similar Samples - Gravimetric Method (MGNH Po - 6H O Precipitation)
- High-Temperature Metals and Alloys Chlorine Corrosion ofHigh-Temperature Metals and Alloys Chlorine Corrosion of