0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
369 viewsRFBT (Pinnacle Notes)
RFBT (Pinnacle Notes)
Uploaded by
Justz LimThe document discusses the different types of obligations under Philippine law. It defines obligation as the juridical necessity to give, do, or not do something. There are five main sources of obligations: 1) law, 2) contracts, 3) quasi-contracts, 4) delicts, and 5) quasi-delicts. Contracts involve an agreement between two parties where one party binds themselves to give or render a service to the other. Quasi-contracts refer to situations where a person voluntarily takes responsibility for another's property or business without authorization.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
RFBT (Pinnacle Notes)
RFBT (Pinnacle Notes)
Uploaded by
Justz Lim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
369 views1 pageThe document discusses the different types of obligations under Philippine law. It defines obligation as the juridical necessity to give, do, or not do something. There are five main sources of obligations: 1) law, 2) contracts, 3) quasi-contracts, 4) delicts, and 5) quasi-delicts. Contracts involve an agreement between two parties where one party binds themselves to give or render a service to the other. Quasi-contracts refer to situations where a person voluntarily takes responsibility for another's property or business without authorization.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document discusses the different types of obligations under Philippine law. It defines obligation as the juridical necessity to give, do, or not do something. There are five main sources of obligations: 1) law, 2) contracts, 3) quasi-contracts, 4) delicts, and 5) quasi-delicts. Contracts involve an agreement between two parties where one party binds themselves to give or render a service to the other. Quasi-contracts refer to situations where a person voluntarily takes responsibility for another's property or business without authorization.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
369 views1 pageRFBT (Pinnacle Notes)
RFBT (Pinnacle Notes)
Uploaded by
Justz LimThe document discusses the different types of obligations under Philippine law. It defines obligation as the juridical necessity to give, do, or not do something. There are five main sources of obligations: 1) law, 2) contracts, 3) quasi-contracts, 4) delicts, and 5) quasi-delicts. Contracts involve an agreement between two parties where one party binds themselves to give or render a service to the other. Quasi-contracts refer to situations where a person voluntarily takes responsibility for another's property or business without authorization.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
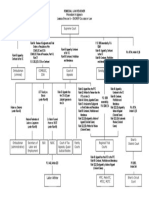
Obligations The meeting of the minds of two or more person,
whereby one binds himself, with respect to the other, to
Art. 1156 – Obligation is the juridical necessity to give, to do or give something or to render some service (Article 1305).
not to do.
3. Quasi-contracts
Elements of Obligations:
Whoever voluntarily takes charge of the agency,
1. Passive Subject (Obligor or Debtor)
business or property of another without any power or
The person who will be giving, doing or not doing the authority from the latter, the former can seek
prestation or the object of the obligation. reimbursement from the latter. Nobody shall be unjustly
enriched at the expense of another.
2. Active Subject (Obligee or Creditor)
a. Negotiorom Gestio (Officious Management)
The person in whose favor the obligation is constituted.
He is known as the active subject because he is the Example: Person A has a farm. A takes a vacation
party with the right to demand performance of the and leaves the farm alone. While on the vacation, B
obligation. worried about the farm or a calamity happened. B
took care of the plants and animals of the farm and
3. Prestation or object incurred expenses while doing so. B can reimburse
the expenses from A.
This subject matter is the act of giving (thing), doing
(act) or not doing (to not act). b. Solutio Indebiti
4. Vinculum Juris (Juridical Tie) Payment not due or payment by mistake. If a person
is paid where there is no right to receive it, he has
Refers to the juridical tie or efficient cause that binds the
the obligation to return what he has received.
parties to the obligation.
4. Delicts
Civil Law vs. Natural Law
If a person commits a crime, he will be criminally and
Civil obligations are based on positive law. It is enforceable in
civilly liable (indemnity for damages). However, criminal
the court of law and there is the juridical necessity to perform it.
liability is separate from the civil liability.
Natural obligations are based on equity or natural law. It is not
5. Quasi-delict
enforceable in the court of law and there is no juridical necessity
to perform it. Performance is because of conscience. A negligence in itself by a person even without a pre-
existing contract.
Sources of Obligations
Three kinds of Negligence
1. Law
1. Culpa contractual - negligence that arises from the
Whatever obligation is imposed by Law, you have to do
breach of a contract.
it. An obligation under the law is never presumed.
2. Culpa aquilliana - negligence that arises with no pre-
2. Contracts existing contract.
3. Culpa criminal - negligence or civil liability that arises
from a crime.
You might also like
- An Open Letter To Teachers Seeking BalanceDocument3 pagesAn Open Letter To Teachers Seeking BalanceAnnya BecerraNo ratings yet
- Appeal Procedure Flowchart PDFDocument1 pageAppeal Procedure Flowchart PDFAudrey100% (1)
- LUZVIMINDA CANLAS v. REPUBLICDocument2 pagesLUZVIMINDA CANLAS v. REPUBLICZusmitha Salcedo100% (3)
- GAD Monitoring & EvaluationDocument13 pagesGAD Monitoring & EvaluationArlene SuetosNo ratings yet
- Consumer Protection Act NotesDocument6 pagesConsumer Protection Act NotesAbarilles, Sherinah Mae P.No ratings yet
- Mock 2nd Eval - TOADocument7 pagesMock 2nd Eval - TOAPatrick Powell100% (1)
- 23 Review Material 23 RFBTDocument21 pages23 Review Material 23 RFBT버니 모지코No ratings yet
- Tax CPAR Final Pre Board2Document5 pagesTax CPAR Final Pre Board2Floyd delMundo100% (1)
- Donors Tax DWCLDocument6 pagesDonors Tax DWCLKyle Jezrel GimaoNo ratings yet
- 18 Special Purpose Audit EngagementDocument2 pages18 Special Purpose Audit EngagementIrish SanchezNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Abc Costing: Cost Accounting AND Control (B. Activity-Based Cost System)Document14 pagesReviewer in Abc Costing: Cost Accounting AND Control (B. Activity-Based Cost System)justine reine cornicoNo ratings yet
- Resa Ip Law Resa RFBT Handouts For Intellectual Property Code LawDocument13 pagesResa Ip Law Resa RFBT Handouts For Intellectual Property Code LawFrances Glei FaminialNo ratings yet
- Recto Law and Maceda Law Part 1Document1 pageRecto Law and Maceda Law Part 1Priscilla DawnNo ratings yet
- Tax Final Notes. 1Document25 pagesTax Final Notes. 1Hannah MeranoNo ratings yet
- Pdic-Example ComputationDocument9 pagesPdic-Example ComputationAndrei Nicole RiveraNo ratings yet
- 301 QuizDocument9 pages301 QuizJames Benedict BantilingNo ratings yet
- PFRS 1 - FIRST-TIME ADOPTION OF PFRSsDocument10 pagesPFRS 1 - FIRST-TIME ADOPTION OF PFRSsHannah TaduranNo ratings yet
- 6.0 Extinguishment of SaleDocument35 pages6.0 Extinguishment of SaleHanna ValerosoNo ratings yet
- Tax 2 Flexible Obtl Midyear 2021Document13 pagesTax 2 Flexible Obtl Midyear 2021Jamaica DavidNo ratings yet
- TAX-303 (Input VAT)Document8 pagesTAX-303 (Input VAT)Fella GultianoNo ratings yet
- AFAR-06 (Revenue From Contracts With Customers - Other Topics)Document26 pagesAFAR-06 (Revenue From Contracts With Customers - Other Topics)MABI ESPENIDONo ratings yet
- 9305 - Corporate LiquidationDocument4 pages9305 - Corporate LiquidationSofiaNo ratings yet
- 7084 Multiple Choice Small Entities Lecture Notes and SolutionDocument4 pages7084 Multiple Choice Small Entities Lecture Notes and SolutionpompomNo ratings yet
- Rfli Midterm ReviewerDocument20 pagesRfli Midterm ReviewerKatrina PaquizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Fundamental Concepts of Donor's Taxation (Notes)Document3 pagesChapter 1 - Fundamental Concepts of Donor's Taxation (Notes)Angela Denisse FranciscoNo ratings yet
- FM112 Student Chapter 1Document15 pagesFM112 Student Chapter 1Thricia Mae IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Donor's Tax (Notes)Document8 pagesChapter 2 - Donor's Tax (Notes)Angela Denisse FranciscoNo ratings yet
- AFAR-06: Revenue From Contracts With Customers: Franchise & ConsignmentDocument12 pagesAFAR-06: Revenue From Contracts With Customers: Franchise & ConsignmentJhekka FerrerNo ratings yet
- Tax RemediesDocument15 pagesTax RemediesChristopher Jan DotimasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Accounting For Disbursements and Related TransactionsDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Accounting For Disbursements and Related TransactionsLeonard CanamoNo ratings yet
- Final Reviewer in RFLIBDocument14 pagesFinal Reviewer in RFLIBMichelle EsternonNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics QuestionnairesDocument26 pagesManagerial Economics QuestionnairesClyde SaladagaNo ratings yet
- FM112 Students Chapter IIDocument12 pagesFM112 Students Chapter IIThricia Mae IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Handouts ConsolidationIntercompany Sale of Plant AssetsDocument3 pagesHandouts ConsolidationIntercompany Sale of Plant AssetsCPANo ratings yet
- Gelinas-Dull 8e Chapter 11 Billing & ReceivableDocument30 pagesGelinas-Dull 8e Chapter 11 Billing & Receivableleen mercado100% (1)
- Other Percentage TaxesDocument9 pagesOther Percentage TaxesLeonard CañamoNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Reporting - PAS No. 18 Accounting For RevenueDocument15 pagesFinancial Accounting and Reporting - PAS No. 18 Accounting For RevenueLuisitoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Non Current Asset Held For SaleDocument1 pageQuiz 1 Non Current Asset Held For SaleLayla SimNo ratings yet
- IA 1 - Chapter 10 - ReviewerDocument4 pagesIA 1 - Chapter 10 - Reviewerkimingyuse1010No ratings yet
- RFBT.O 1602.law On Contracts WithanswersDocument42 pagesRFBT.O 1602.law On Contracts WithanswersDanielle Nicole Marquez0% (1)
- Iueeu CoaDocument4 pagesIueeu Coayes it's kaiNo ratings yet
- CPA Review - BMBE Notes - 2019Document1 pageCPA Review - BMBE Notes - 2019Kenneth Bryan Tegerero TegioNo ratings yet
- Value Added TaxDocument8 pagesValue Added TaxErica VillaruelNo ratings yet
- Article 1582. Primary Obligations of The VendeeDocument8 pagesArticle 1582. Primary Obligations of The Vendeehyunsuk fhebieNo ratings yet
- PFRS 14 15 16Document3 pagesPFRS 14 15 16kara mNo ratings yet
- Preweek Handouts in Business Law May 2014 BatchDocument8 pagesPreweek Handouts in Business Law May 2014 BatchPhilip CastroNo ratings yet
- Qualifying Exam Reviewer: Financial AccountingDocument26 pagesQualifying Exam Reviewer: Financial AccountingJanine AnzanoNo ratings yet
- BAM 242 Credit TransactionsDocument18 pagesBAM 242 Credit TransactionsAndrea GarinNo ratings yet
- 2ND Case StudyDocument8 pages2ND Case StudyAnna Azriffah Janary GuilingNo ratings yet
- Taxation: Far Eastern University - ManilaDocument4 pagesTaxation: Far Eastern University - ManilacamilleNo ratings yet
- AT20Document10 pagesAT20audreyNo ratings yet
- Reo Law On SaleDocument14 pagesReo Law On SaleCzarina JaneNo ratings yet
- Revenue Recognition and Franchise TestbankDocument43 pagesRevenue Recognition and Franchise TestbankBusiness MatterNo ratings yet
- Manalungsung, Kyrell D.Document3 pagesManalungsung, Kyrell D.Chloe Oberlin100% (1)
- ACCTRAN Engage: Kaya Ulit Natin To Partner!Document2 pagesACCTRAN Engage: Kaya Ulit Natin To Partner!Kristine SantanderNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income TaxDocument56 pagesAccounting For Income TaxEau Claire DomingoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Audit Services and Financial Statements AuditDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Audit Services and Financial Statements AuditBryzan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Final Income TaxationDocument15 pagesFinal Income TaxationElizalen MacarilayNo ratings yet
- ReSA B43 RFBT First PB Exam - Questions & AnswersDocument12 pagesReSA B43 RFBT First PB Exam - Questions & AnswersSophia Zavynne Ancheta BuenoNo ratings yet
- Obligation Is Based On Natural Law, But On Equity and Moral Justice. Hence, It IsDocument3 pagesObligation Is Based On Natural Law, But On Equity and Moral Justice. Hence, It IsMae VincentNo ratings yet
- Center For Review and Special Studies - : Practical Accounting 1/theory of Accounts M. B. GuiaDocument13 pagesCenter For Review and Special Studies - : Practical Accounting 1/theory of Accounts M. B. GuiaWilsonNo ratings yet
- RFBT ObligationsDocument10 pagesRFBT Obligationspangtwitterlangto.24No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - General Provisions Art. 1156. An Obligation Is A Juridical Necessity To Give, TodoornottodoDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - General Provisions Art. 1156. An Obligation Is A Juridical Necessity To Give, TodoornottodoNinaNo ratings yet
- ObliCon Provisions1Document64 pagesObliCon Provisions1Kristiana Mikhail FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Suman, Generally, Is Made by People in The Marginalized Sector For SustenanceDocument1 pageSuman, Generally, Is Made by People in The Marginalized Sector For SustenanceJustz LimNo ratings yet
- Post-Employment BenefitsDocument2 pagesPost-Employment BenefitsJustz LimNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management OutlineDocument1 pageSupply Chain Management OutlineJustz LimNo ratings yet
- FWTX, CWTX and CGTX (Points To Remember and Tax Rates)Document2 pagesFWTX, CWTX and CGTX (Points To Remember and Tax Rates)Justz LimNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management (Canteen)Document1 pageSupply Chain Management (Canteen)Justz LimNo ratings yet
- Gross Estate IntroductionDocument2 pagesGross Estate IntroductionJustz LimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management ScienceDocument1 pageIntroduction To Management ScienceJustz LimNo ratings yet
- Revenue Cycle: RL Appliance Inc. 353 Real Street, Downtown, Tacloban City in Front of Mcdonalds Real BranchDocument2 pagesRevenue Cycle: RL Appliance Inc. 353 Real Street, Downtown, Tacloban City in Front of Mcdonalds Real BranchJustz LimNo ratings yet
- Gross Estate IntroductionDocument2 pagesGross Estate IntroductionJustz LimNo ratings yet
- Quiz AuditDocument17 pagesQuiz AuditJustz LimNo ratings yet
- Midterms MADocument10 pagesMidterms MAJustz LimNo ratings yet
- Summary of Part 4 (Risk and Returns)Document3 pagesSummary of Part 4 (Risk and Returns)Justz LimNo ratings yet
- Gross Estate IntroductionDocument2 pagesGross Estate IntroductionJustz LimNo ratings yet
- PPE Problem SetDocument18 pagesPPE Problem SetJustz LimNo ratings yet
- Bali Action Plan 2007 PDFDocument4 pagesBali Action Plan 2007 PDFJustz LimNo ratings yet
- Durban Platform For Enhanced Action PDFDocument4 pagesDurban Platform For Enhanced Action PDFJustz LimNo ratings yet
- Bali Action Plan 2007 PDFDocument4 pagesBali Action Plan 2007 PDFJustz LimNo ratings yet
- Trivia AnswersDocument4 pagesTrivia AnswersJustz LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: The American PeriodDocument6 pagesChapter 6: The American Periodjoseph5689No ratings yet
- PolGov 14Document13 pagesPolGov 14jonbertNo ratings yet
- Holmes 082911Document7 pagesHolmes 082911Lisa BlankenshipNo ratings yet
- Afttp3-10 3Document15 pagesAfttp3-10 3foxbat05No ratings yet
- IMA 101-Chapter 1Document3 pagesIMA 101-Chapter 1csaysalifuNo ratings yet
- Russia Nato The Attempted Coup Against Erdogan and The Asymmetric Ecclesiastical Warfare Between Moscow and Constantinople Ge PDFDocument5 pagesRussia Nato The Attempted Coup Against Erdogan and The Asymmetric Ecclesiastical Warfare Between Moscow and Constantinople Ge PDFAnonymous Pu2x9KV0% (1)
- Collegium SystemDocument6 pagesCollegium SystemVanshika HindujaNo ratings yet
- Intro Case Roe Vs WadeDocument2 pagesIntro Case Roe Vs WadeMark Hiro NakagawaNo ratings yet
- Model Policy: Body-Worn CamerasDocument3 pagesModel Policy: Body-Worn CamerasrandomlyfickleNo ratings yet
- Jarvis JohnsonDocument2 pagesJarvis Johnsoneditorial.onlineNo ratings yet
- Project CHECO Southeast Asia Report ADA486984Document170 pagesProject CHECO Southeast Asia Report ADA486984rongxanhNo ratings yet
- Senate President: Dr. Abubakar Bukola Saraki (Con)Document11 pagesSenate President: Dr. Abubakar Bukola Saraki (Con)Olu Wole OnemolaNo ratings yet
- Tax Midterms EditedDocument113 pagesTax Midterms EditedSabritoNo ratings yet
- Pub Corp Case Digest Page 11-14Document41 pagesPub Corp Case Digest Page 11-14Haze Q.No ratings yet
- Kirk Cheyfitz: Political Schizophrenia in DetroitDocument2 pagesKirk Cheyfitz: Political Schizophrenia in DetroitgmarkusNo ratings yet
- Islam and The West.... Research Proposal by Faiza, Rimsha and ShahzadDocument18 pagesIslam and The West.... Research Proposal by Faiza, Rimsha and ShahzadrimshaNo ratings yet
- Marie Cris VillarinDocument1 pageMarie Cris VillarinFred Nazareno CerezoNo ratings yet
- Miners Association of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesMiners Association of The PhilippinesKarla Kanashii100% (1)
- Corporate Law and Corporate GovernanceDocument30 pagesCorporate Law and Corporate GovernanceNooria YaqubNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Public AdDocument9 pagesSyllabus Public AdPriyanshu SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Sunga V Comelec DigestDocument2 pagesSunga V Comelec Digestilovetwentyonepilots100% (1)
- Us Vs North KoreaDocument16 pagesUs Vs North KoreaAaron ReyesNo ratings yet
- RPC Art. 11-15Document2 pagesRPC Art. 11-15bbysheNo ratings yet
- Citizen Charter of Tamilnadu PoliceDocument2 pagesCitizen Charter of Tamilnadu PoliceMuthur Ramasamy KuppusamyNo ratings yet
- Gujarat OrderDocument2 pagesGujarat OrderNewsinc 24No ratings yet
- Business LawDocument16 pagesBusiness Lawmahum raufNo ratings yet