Sonia PDF
Sonia PDF
Uploaded by
MurthyCopyright:
Available Formats
Sonia PDF
Sonia PDF
Uploaded by
MurthyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Sonia PDF
Sonia PDF
Uploaded by
MurthyCopyright:
Available Formats
ISSN : 2230-7109(Online) | ISSN : 2230-9543(Print) IJECT Vol. 2, Issue 3, Sept.
2011
Reconfigurable Antennae: A Review
1
Sonia Sharma, 2Monish Gupta, 3C.C. Tripathi
1,2,3
UIET, University Institute of Engineering and Technology, Kurukshetra, Haryana, India
Abstract This paper is divided into six sections. Section II introduces the
This paper provides a complete state-of-the-art of reconfigurable concept of frequency reconfigurable antennae. This section
antennae viz. frequency reconfigurable antennae, radiation provides the geometry of frequency reconfigurable antenna
pattern reconfigurable antennae, polarization reconfigurable which concludes that the operating frequency of antenna
antennae, and combination of radiation and frequency could be modified by modifying patch’s resonating length with
reconfigurable antennae from the literature. Of late, the help of RF MEMS switches. In dual frequency microstrip
reconfigurable antennae have received a lot of attention for patch antenna, a PIN diode is positioned in the center of
their applications in diversified areas like communication, the slot which changes the current path on the patch hence
surveillance etc. This is owing to their ability to modify their antenna’s electrical length is modified with the help of PIN diode
radiation characteristics, frequency of operation, polarization condition i.e. ON or OFF. Section III elaborates the concept of
or even a combination of these features in real time. radiation pattern/beam reconfigurable antenna. This proposed
Reconfigurable antennae have the potential to add substantial reconfigurable scheme is based on the modification of the
degrees of freedom and functionality to mobile communication EM propagation characteristics of the surface waves by the
and phase array systems. Reconfigurability in antennae allows use of metallic switch-loaded parasitic structure and thus the
us for spectrum reallocation in multi-band communication radiation pattern could be modified which modify the main
systems, dynamic spectrum management, therefore reducing beam pattern in a controlled fashion. Section IV deals with the
the number and size of antennae in a system. concept of polarization reconfigurable antennae. It provides
an overview of the patch antennae with suitable slots for
Keywords RHCP/LHCP diversity. By activating the switches in the slot,
Reconfigurability, patch antenna, polarization reconfigurable, antenna radiates with either (RHCP) or (LHCP) by sharing the
frequency reconfigurable, MEMS switch, slot antenna, mobile same feeding probe. Section V presents reconfigurable single
communications turn square spiral printed antennae capable of both radiation
pattern and frequency reconfiguration. Section VI concludes
I. Introduction the paper.
Wireless communication systems are evolving toward multi-
functionality. This multi functionality provides users with options II. Frequency Reconfigurable Antennae
of connecting to different kinds of wireless services for different Modern communication systems demand transmitters and
purposes at different times. Large numbers of antennae are receivers with multi-band operation, as a result, numerous
mounted on ships, aircrafts or other vehicles; it is highly desirable techniques for achieving frequency reconfigurability have
to develop single radiating element having capabilities of been proposed in system where weight and area are critical
performing different functions and/or multi-band operation in issues.
order to minimize the antennae's weight and area. An antenna The reconfigurable patch module (RPM) proposed by J. T.
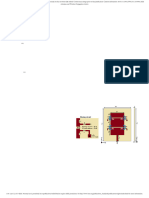
that possesses the ability to modify its characteristics, such Bernhard et al. [1] consists of a 3x3 array of square patches
as operating frequency, polarization or radiation pattern, in connected together by the RF MEMS switches as depicted in
real time condition is referred to as a reconfigurable antenna. Fig. 1. Ideally, the RF MEMS switch has two operational states,
Reconfigurable antennae have the potential to add substantial ON and OFF. The ON state represents a short circuit, while the
degrees of freedom and functionality to mobile communication OFF state exhibits an open circuit. When all the switches are
and phase array systems. Reconfigurable antennae can be in the OFF state, the total radiation pattern is formed by the
simply used to reduces the number of antennae necessary pattern radiated by each small patch as shown in Fig. 1(a). As
for intended system function, but they can also be designed a result, the antenna resonates at a higher frequency band. On
to serve much more complex roles. Examples of emerging the other hand, when all switches are turned ON, the antenna
applications include software defined radio, cognitive radio, effective area is clearly larger than the area of a singular patch
MIMO systems, multifunction consumer wireless devices, and array. The antenna accordingly resonates at a lower frequency
high performance phased arrays. In addition, reconfigurable band as shown in Fig. 1(b).
antennae can be a cheaper alternative to traditional adaptive
arrays or they can be incorporated into adaptive arrays to
improve their performance by providing additional degrees
of freedom. Reconfigurability in antennae allows us for
spectrum reallocation in multi-band communication systems,
dynamic spectrum management, reduces the number and
size of antennae in a system. Generally reconfigurability can
be obtained using following techniques: Tunable elements in
the feeding networks, adaptive matching networks, phase Fig. 1: (a) Antennae geometry when switches are turned OFF
shifters and tunable filters, tunable elements embedded such (b) Antennae geometry when switches are turned ON [1]
as PIN diodes, MEMS (switches, varactors, moveable parts)
and optical switching in the radiating elements, mechanically
moveable radiating elements.
w w w. i j e c t. o r g International Journal of Electronics & Communication Technology 131
IJECT Vol. 2, Issue 3, Sept. 2011 ISSN : 2230-7109(Online) | ISSN : 2230-9543(Print)
Furthermore, it has been observed that the total radiation allows for the continuous tuning of the operating frequency
patterns are nearly identical between the two states of the (though not typically of the instantaneous bandwidth) over a
switch operation. large band, which has been shown to be 20–30% depending
In the work by Y. Qian et al. [2] the frequency reconfigurable on the type of micro strip antennae used.
antenna consists of a linear array of micro strip-based leaky-
mode antennas as shown in Fig. 2. By activating the switches III. Radiation Pattern or Beam Reconfigurable
connected on the radiating patches, the resonant frequency Antennae
can be modified. Clearly, the operating frequency is controlled The antenna is designed to be able to reconfigure its radiation
by the state of the switch operation. This technique reduces pattern during real time operation such that it maintains its
the number and size of the antennas mounted on board broad pattern in the absence of interferences, and is capable of
tremendously, especially in a multi-band communication. narrowing its pattern beam width, when the interfering signals
arrive at the antennae, to suppress these undesired signals
as much as possible.
In addition, reconfigurable antennae can be a cheaper
alternative to traditional adaptive arrays or they can be
incorporated into adaptive arrays to improve their performance
by providing additional degrees of freedom. The radiation
pattern reconfigurability is needed to steer the radiation pattern
away from noise sources or to reduce interference.
It is well known that the total radiation pattern from the
microstrip antennae originates mostly from three contributions:
Fig. 2: Geometry of a frequency reconfigurable leaky mode/ direct space wave, edge diffracted space wave and edge
multifunction printed antenna [2] diffracted surface wave. R. G. Rojas et al. [5] considered that
the contribution comes from the surface wave that is diffracted
Another way to affect discrete changes in a microstrip antennae’s at the edges, as a loss mechanism because they travel along
electrical length is to change the path of radiating currents the substrate and radiate to free space at the truncation/edge
without changing the overall footprint of the antennae. An of the substrate. The surface waves usually distort the main
example of this approach was proposed by Yang and Rahmat- beam radiation pattern and increasing the level of the side
Samii et al. [3] for micro strip antennae. Starting with standard lobes as well as the back lobes. For the particular application
rectangular micro strip antennae, a slot is etched in the patch under consideration, the control of the surface waves is crucial
so that it is perpendicular to the direction of the main current to achieve pattern reconfigurability. To reconfigure the radiation
of the patch’s first resonance, as shown in Fig. 3. A PIN diode is pattern, some researchers have used shorting pins and in-
positioned in the center of the slot to change the current paths line open tuning elements. Low cost antennae that can alter
on the patch. If the diode is OFF, then currents travel around their radiation patterns during real time operating conditions
the slot and the antennae operates in a lower fr frequency. are required in response to intentional interferences. S.
Zhang, G. H. Huff, J. Feng et al. [6] designed radiation pattern
reconfigurable antennae for this they designed a microstrip
patch antenna which radiates a broad field pattern i.e. in the
broadside direction from which the desired GPS signals from
the satellites arrive as shown in Fig. 4.
Fig. 3: Geometry of a dual-frequency microstrip patch antennae
with a switchable slot (PASS) [3] band, while when the diode
is ON, the effective length of the patch is shorter and the
antennae operates in a higher frequency band. The frequency
ratio between the upper and lower operating frequencies are
controlled by the length of the slot, and as long as the slot length Fig. 4: Scenario of radiation pattern reconfigurable antennae
is not too long, the radiation pattern of the original antennae in the presence of intentional interferences [6]
is largely preserved.
In another work by Bhartia and Bahl et al. [4] the operating They also assumes the presence of interfering signals, in the
frequency range of a micro strip patch antennae was form of jamming signals, which incident at the antennae in
continuously tuned by using varactor diodes (varactors) at horizontal directions approximately +100 ± to -150 ± from the
the radiating edges of the structure. The varactors operated end fire direction. This is a common scenario for antennae on
with a reverse bias between 0 and 30 volts that corresponded airborne platforms. The designed antenna is able to reconfigure
to capacitances of 2.4-0.4 pF. With a change in bias, the its radiation pattern during real time operation such that it
capacitance induced at the radiating edge is changed, resulting maintains its broad pattern in the absence of interferences, and
in a change in the effective electrical length of the patch. This is capable of narrowing its pattern beam width, in the presence
132 International Journal of Electronics & Communication Technology w w w. i j e c t. o r g
ISSN : 2230-7109(Online) | ISSN : 2230-9543(Print) IJECT Vol. 2, Issue 3, Sept. 2011
of interferences. Hence in the presence of jamming signals, [7]
the reconfigurable microstrip antennae is required to adjust its
antennae beam width to suppress these unwanted signals as IV. Polarization Reconfigurable Antennae
much as possible. In most conventional microstrip antennas, Antennae with polarization diversity are gaining popularity due
the substrate is thin to minimize the strength of the surfaces to the tremendous growth of wireless communications and
waves. However, electrically thick microstrip antennae have radar systems. A design of microstrip antennae with switchable
the advantage of providing a larger operational bandwidth over slots (PASS) was introduced to accomplish circular polarization
microstrip antennae mounted on thin substrates. Microstrip diversity by Yang et al. [8]. Two orthogonal slots are introduced
antenna proposed by R. G. Rojas and K. W. Lee et al. [5] into the radiating patch and two pin diodes are used to switch
for the design and analysis of pattern reconfigurable antenna the slots on as shown in Fig.7.
mounted on electrically thick substrates so that edge-diffracted
surface wave field can be strong and have a magnitude larger
than the diffracted space wave field. The designed passive
microstrip antenna element is surrounded with a parasitic
ring loaded with switches as shown in Fig. 5. This proposed
reconfigurable scheme is based on the modification of the EM
propagation characteristics of the surface waves, and thus
the radiation pattern could be modified through the use of
a metallic switch-loaded parasitic structure. Now, modified
radiated surface waves contribute to the main beam pattern
in a controlled fashion, hence beam reconfigurability achieved.
The switches provide two different ring configurations and
pattern reconfigurability is controlled by the two states of the
switches (ON/OFF). Although the switches can be either RF Fig. 7 A patch antennae with switchable slots (PASS) for RHCP/
MEMS, electronic or photonic-controlled, diode switches. LHCP diversity [8]
By activating the switches on the antennae radiates with either
right hand circular polarization (RHCP) or left hand circular
polarization (LHCP) by sharing the same feeding probe. The
feeding probe is located on the diagonal line of the patch.
Note that the antenna radiates either RHCP or LHCP at a time,
depending upon the operating state of the diode switches.
Therefore, there is no coupling is induced between the two
Fig. 5: Geometry of a radiation pattern reconfigurable patch polarizations.
antennae surrounded by a switch-loaded parasitic structure
[5]
In another example J.C. Chiao et al. [7], proposed a
reconfigurable scheme based on the modification of the
characteristics of the surface waves by mechanical movable
Vee antennae connected to the actuators, and thus the
radiation pattern can be modified through the use the switch
loaded parasitic structure. The surface waves are modified
simply by activating the switches. Unlike the previous example,
the switches could also be employed to alter the mechanical
property of the antennae. The proposed antenna consists of
a movable planar Vee antennae connected to the actuators Fig. 8: Geometry of a polarization reconfigurable patch antennae
as represented in Fig. 6. The direction of the Vee antennae is [9].
controlled by the operating state of the actuators. The beam
steering and shaping capacities can be achieved by running An antennae that can alternate its radiation pattern between
different states of the actuators. circular and linear polarization at a fixed operating frequency
has been proposed by Simons et al. [9] .The antenna shown in
Fig. 8 consists of a square micro strip antenna integrated with
RF MEMS actuator for switching the polarization state. When
the RF MEMS actuator is in the OFF state, the perturbation of
the modes is negligible and thus the patch radiates a circularly
polarized pattern. Similarly when the RF MEMS actuator is
turned ON, the phase relation between the two current modes
on the patch surface is disturbed, as a result, patch radiates
a dual linearly polarized pattern.
Fig. 6: Geometry of RF MEMS reconfigurable Vee antennae In another example by M.K Fries, M. Grani et al. [10] designed
w w w. i j e c t. o r g International Journal of Electronics & Communication Technology 133
IJECT Vol. 2, Issue 3, Sept. 2011 ISSN : 2230-7109(Online) | ISSN : 2230-9543(Print)
a slot-ring antenna in which PIN diodes are used to reconfigure
the polarization state between linear to circular polarization
and LHCP to RHCP. For the switching between linear to circular Another example of the frequency and pattern reconfigurable
polarization state as shown in Fig. 9(a), when the diodes placed antennae can also be found in the work of J. T. Bernhard et
at 45° and −135° relative to the feed point are forward-biased al.[1]. The stacked balanced bowtie antennae structure is
than the antenna produces linear polarization state, while when shown in Fig. 11. The lower bowtie antennae locate on the
the diodes are reverse biased than the antenna delivers the substrate, while the upper ones are on the top of the super
circular polarization state. The design in Fig. 9(b) goes one substrate. Note that the lower bowtie antennae are electrically
step further and it adds additional symmetric discontinuities larger than the upper ones in size. Consequently, they resonate
to support switching between left and right handed circular at a lower frequency band. Note that each antenna feed point
polarizations. In both designs, care is taken to divide the ground is connected to the source via the RF MEMS switch, and only
planes carefully to support proper DC biasing for the diodes one antennae arrays radiate at a time. The operating frequency
while providing RF continuity through capacitors connected is thus determined by the states of the RF MEMS switches. In
between ground plane sections. This antenna is a good other words, if the lower band is chosen, the RF MEMS switches
example of the factor that when transitioning from a fixed to a connected to the lower bowtie antennae will be activated, and
reconfigurable antenna, the fundamental structure may remain vice versa. It is also worth noticing that when the lower bowtie
the same, but critical adjustments are required to enable proper antennae are radiating, the upper bowtie antennae are virtually
DC connections and RF performance. the floating parasitic elements for the lower ones, and thus
slightly broadening the impedance bandwidth. On the other
hand, an operation of the upper bowtie antennae requires
that the lower antennae must be grounded via the RF MEMS
switches. In this case, the lower bowtie antennae are simply
an equivalent ground plane for the upper ones.
Fig. 9: Polarization reconfigurable slot ring antennae: (a)
switchable between linear and left hand circular polarization
and (b) switchable between LHCP to RHCP [10]
V. Radiation and Frequency Reconfigurable Antennae
In general, most antennae are capable of either frequency or
pattern reconfigurability; however they can be made combination
of both frequency and pattern reconfigurable simultaneously. Fig. 11: Stacked reconfigurable array of balanced bowtie
G. H Huff et al. [11] proposed a frequency and pattern antennae: Lower and upper band elements are alternatively
reconfigurable micro strip antennae using multiple switch activated using MEMS switches [1]
connections. Fig. 10 illustrates geometry of a switch loaded
single turn square spiral printed antenna which resonates at VI. Conclusion
3.7 GHz with a linear polarized pattern. One set of the switch Reconfigurable antennae have their applications in diversified
connections redirects its main beam radiation pattern away areas like communications, surveillance etc. They possess the
from the broadside, whilst maintaining a common impedance properties to modify their radiation characteristics, frequency of
bandwidth with the baseline configuration. The second set of operation, polarization or even a combination of these features
the switch connections, however, shifts the operating frequency in real time. Reconfigurable antennae have the potential to add
from 3.7 GHz to 6 GHz, while preserving a broadside radiation substantial degrees of freedom and functionality to mobile
pattern. communications and phase array systems. The present
paper provided a survey of various reconfigurable antennae.
It attempted to classify the various types of reconfigurable
antennae.
References
[1] J. T. Bernhard, R. Wang., R. Clark, and P. Mayes, “Stacked
reconfigurable antenna elements for space-based radar
applications”, IEEE AP-S International Symposium, 1:158-
161, 2001.
[2] Y. Qian, B. C. C. Chang, M. F. Chang, T.Itoh, “Reconfigurable
leaky mode/ multifunction patch antenna structure”
Electron. Lett., 35:104-105, 1999.
[3] F. Yang, Y. Rahmat-Samii, “Patch Antenna with Switchable
Fig. 10: Geometry of a reconfigurable antenna capable of both Slot (PASS) for Dual frequency Operation,” Microwave and
radiation pattern and frequency reconfigurability [2]. Optical Technology Letters, vol. 31, November 2001
134 International Journal of Electronics & Communication Technology w w w. i j e c t. o r g
ISSN : 2230-7109(Online) | ISSN : 2230-9543(Print) IJECT Vol. 2, Issue 3, Sept. 2011
[4] P. Bhartia, I. J. Bahl, “Frequency Agile Microstrip Antennas,”
Microwave J., vol. 25: 67–70, October 1982
[5] R.G. Rojas, K.W. Lee., “Control of Surface Waves in Planar
Printed Antennas”, Technical Report 735571-1, The Ohio
State University Electro Science Lab.
[6] S. Zhang, G. H. Huff, J. Feng, J. T. Bernhard, “A Pattern
Reconfigurable Microstrip Parasitic Array,” IEEE Trans.
Antennas Propagation, vol. 52:2773–2776, Oct 2004
[7] J.C. Chiao, Y. Fu, I. M. Chio, M. DeLisio, L.Y. Lin, “MEMS
reconfigurable Vee antenna” Microwave Symposium
Digest, 1999 IEEE MTT-S International, 4:1515-1518,
1999.
[8] F. Yang, Y. Rahmat-Samii, “A reconfigurable patch antenna
using switchable slots for circular polarization diversity”,
IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letter, 12(3):96-
98, March 2002.
[9] R. N. Simons, D. Chun, L. P. B. Katehi “Polarization
reconfigurable patch antenna using MEMS actuators”,
IEEE AP-S International Symposium, 2:6-9, 2002.
[10] M.K Fries, M. Grani, R. vahldieck, “A Reconfigurable Slot
Antenna with Switchable Polarizations”, IEEE Microwave
and wireless components letter, vol.13: 490-492,Nov
2003,
[11] G. H. Huff, J. Feng, J. T. Bernhard,“A novel radiation
pattern and frequency reconfigurable single turn square
spiral microstrip antenna”, IEEE Microwave and Wireless
Components Letter, 13(2):57-59, February 2003.
w w w. i j e c t. o r g International Journal of Electronics & Communication Technology 135
You might also like
- Eton Grundig M400 ManualDocument21 pagesEton Grundig M400 ManualBlack Onion0% (1)
- A Novel Reconfigurable Multiband Patch Antenna: Rahul Agrawal, M.K. Meshram, S.P. SinghDocument3 pagesA Novel Reconfigurable Multiband Patch Antenna: Rahul Agrawal, M.K. Meshram, S.P. SinghmanojNo ratings yet
- Communication Patch AntennaDocument5 pagesCommunication Patch AntennaManjunatha KurugoduNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Reconfigurable Antennas: Zhang Jiajie, Wang Anguo, Wang Peng Tianjin University Tianjin 300072 ChinaDocument4 pagesA Survey On Reconfigurable Antennas: Zhang Jiajie, Wang Anguo, Wang Peng Tianjin University Tianjin 300072 ChinaMurthyNo ratings yet
- Rahim 2016 ReconfigDocument6 pagesRahim 2016 ReconfigFathima Thasleema NNo ratings yet
- Journal AntennaDocument3 pagesJournal Antennaنورول نضيره رشديNo ratings yet
- RF MEMS Integrated Frequency Reconfigurable Annular Slot Antenna-Hsr PDFDocument7 pagesRF MEMS Integrated Frequency Reconfigurable Annular Slot Antenna-Hsr PDFjulio perezNo ratings yet
- Reconfigurable Multifunctional AntennasDocument4 pagesReconfigurable Multifunctional AntennasMohammed AliNo ratings yet
- 1.4 PeanoDocument4 pages1.4 PeanoanilNo ratings yet
- A Low Profile Freq Pattern ReconfigDocument4 pagesA Low Profile Freq Pattern ReconfigKarthika KandasamyNo ratings yet
- 8922-Article Text-15994-1-10-20210614Document6 pages8922-Article Text-15994-1-10-20210614madhavineha5No ratings yet
- RF Mems For: Fractal Antenna With Switches Multiple Frequency ApplicationsDocument4 pagesRF Mems For: Fractal Antenna With Switches Multiple Frequency ApplicationsKriky LimaNo ratings yet
- The Investigation of The Varactor Diode As Tuning Element On Reconfigurable AntennaDocument2 pagesThe Investigation of The Varactor Diode As Tuning Element On Reconfigurable AntennaTayyabNo ratings yet
- Log-Periodic Patch Antenna With Tunable Frequency: M. F. Ismail, M. K. A. Rahim, F. Zubir, O. AyopDocument5 pagesLog-Periodic Patch Antenna With Tunable Frequency: M. F. Ismail, M. K. A. Rahim, F. Zubir, O. AyopZayar HeinNo ratings yet
- Frequency Reconfigurable Microstrip Patch Antenna For Multiband ApplicationsDocument11 pagesFrequency Reconfigurable Microstrip Patch Antenna For Multiband ApplicationsIJRES teamNo ratings yet
- Pixel Reconfigurable Antennas: Towards Low-Complexity Full ReconfigurationDocument5 pagesPixel Reconfigurable Antennas: Towards Low-Complexity Full ReconfigurationMurthyNo ratings yet
- Literature Review-AntennaDocument8 pagesLiterature Review-AntennaSifat UllahNo ratings yet
- Automatic Antenna-Tuning Unit For Software-Defined and Cognitive RadioDocument13 pagesAutomatic Antenna-Tuning Unit For Software-Defined and Cognitive RadioSamiNo ratings yet
- Wideband Smart Antenna Theory Using Rectangular Array StructuresDocument9 pagesWideband Smart Antenna Theory Using Rectangular Array StructuresRadhika SethuNo ratings yet
- Adaptive MicroantennasDocument8 pagesAdaptive MicroantennasHòa TrầnNo ratings yet
- A Frequency-Reconfigurable Series-Fed Microstrip Patch Array With Interconnecting CRLH Transmission LinesDocument4 pagesA Frequency-Reconfigurable Series-Fed Microstrip Patch Array With Interconnecting CRLH Transmission LinesGurulakshmi A BNo ratings yet
- Spatial DivisionDocument4 pagesSpatial DivisionbaruaeeeNo ratings yet
- B V Ramana Research PaperDocument8 pagesB V Ramana Research PaperECE HOD AmalapuramNo ratings yet
- For Group 16,41,45,53Document11 pagesFor Group 16,41,45,53sulemanmy998No ratings yet
- Multiband Reconfigurable Filtering Monopole Antenna For Cognitive Radio ApplicationsDocument5 pagesMultiband Reconfigurable Filtering Monopole Antenna For Cognitive Radio Applicationsabinaya_359109181No ratings yet
- Mak 2007Document10 pagesMak 2007Anubhab BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Icee 2018Document3 pagesIcee 2018aaaretNo ratings yet
- A Study of Reconfigurable Multiband Antenna For Wireless ApplicationDocument11 pagesA Study of Reconfigurable Multiband Antenna For Wireless Applicationsuresh sangamNo ratings yet
- AWP 4 UnitDocument24 pagesAWP 4 Unit23f2000268No ratings yet
- Design of Dual-Band Reconfigurable Smart AntennaDocument1 pageDesign of Dual-Band Reconfigurable Smart Antennasree479No ratings yet
- qin2010Document4 pagesqin2010Devansh RamdurgekarNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Microstrip Phased Array Antenna DesignDocument5 pagesComparative Analysis of Microstrip Phased Array Antenna DesignHAPURNo ratings yet
- Beamwidth Reconfigurable Magneto-Electric Dipole Antenna Based On Tunable Strip Grating ReflectorDocument7 pagesBeamwidth Reconfigurable Magneto-Electric Dipole Antenna Based On Tunable Strip Grating ReflectorAkanksha SinghNo ratings yet
- A Simple Frequency Reconfigurable Microstrip Patch Antenna For Wireless CommunicationDocument5 pagesA Simple Frequency Reconfigurable Microstrip Patch Antenna For Wireless CommunicationMes TAREKNo ratings yet
- Antenas Fractais ProgramaDocument50 pagesAntenas Fractais ProgramaAml LimaNo ratings yet
- Multi-Layered Coating Metasurfaces Enabling Frequency Reconfigurability in Wire AntennaDocument11 pagesMulti-Layered Coating Metasurfaces Enabling Frequency Reconfigurability in Wire AntennaLalaNo ratings yet
- Resumo BoomDocument4 pagesResumo BoomAml LimaNo ratings yet
- Wide-Band Circular Patch Antenna For Pattern Diversity ApplicationDocument4 pagesWide-Band Circular Patch Antenna For Pattern Diversity ApplicationSowmya RajendranNo ratings yet
- Group 27Document5 pagesGroup 27jagacon689No ratings yet
- A Study of Reconfigurable Multiband AnteDocument10 pagesA Study of Reconfigurable Multiband AnteAnubhab BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- A Gain Enhancement and Flexible Control of Beam Numbers Antenna Based On Frequency Selective SurfacesDocument10 pagesA Gain Enhancement and Flexible Control of Beam Numbers Antenna Based On Frequency Selective SurfacesAnurag PalNo ratings yet
- A Reconfigurable Antenna Is An Antenna Capable of Modifying Dynamically Its Frequency and Radiation Properties in A Controlled and Reversible MannerDocument2 pagesA Reconfigurable Antenna Is An Antenna Capable of Modifying Dynamically Its Frequency and Radiation Properties in A Controlled and Reversible MannerRamesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Frequency-Reconfigurable Low-Profile Circular Monopolar Patch AntennaDocument7 pagesFrequency-Reconfigurable Low-Profile Circular Monopolar Patch AntennaSnehasis HotaNo ratings yet
- Antenna Simulation Horn Pyr PDFDocument4 pagesAntenna Simulation Horn Pyr PDFEshwarNo ratings yet
- Wideband Reconfigurable Rolled Planar Monopole AntennaDocument8 pagesWideband Reconfigurable Rolled Planar Monopole Antennakirisawa.1125No ratings yet
- A 6-Port Two-Dimensional 3 × 3 Series-Fed Planar Array Antenna For Dual-Polarized X-Band Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar ApplicationsDocument7 pagesA 6-Port Two-Dimensional 3 × 3 Series-Fed Planar Array Antenna For Dual-Polarized X-Band Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar ApplicationsROHIT PRAMOD PEDNEKARNo ratings yet
- Smart Antenna TechnologyDocument19 pagesSmart Antenna TechnologyanusrisaraswathiNo ratings yet
- A Rotatable Reconfigurable Antenna For Cognitive Radio ApplicationsDocument4 pagesA Rotatable Reconfigurable Antenna For Cognitive Radio ApplicationsPeshal NayakNo ratings yet
- Reconfigurable Antennas and Their Applications: Harish Chandra Mohanta, Abbas Z. Kouzani, Sushanta K. MandalDocument20 pagesReconfigurable Antennas and Their Applications: Harish Chandra Mohanta, Abbas Z. Kouzani, Sushanta K. MandalAdnan ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Broadband Antenna For Cognitive Radio ApplicationsDocument9 pagesBroadband Antenna For Cognitive Radio Applicationsiramchocolate8No ratings yet
- Design and Test of A Mobile Antenna System With Tri-Band Operation For Broadband Satellite Communications and DBS ReceptionDocument11 pagesDesign and Test of A Mobile Antenna System With Tri-Band Operation For Broadband Satellite Communications and DBS ReceptionAdiNo ratings yet
- Reduction in Transmission Power of Base Transceiver StationDocument5 pagesReduction in Transmission Power of Base Transceiver StationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Wideband-to-Narrowband Tunable Monopole Antenna With Integrated Bandpass Filters For UWB/WLAN ApplicationsDocument4 pagesWideband-to-Narrowband Tunable Monopole Antenna With Integrated Bandpass Filters For UWB/WLAN Applicationsabinaya_359109181No ratings yet
- Investigation of A New Idea For Antipodal Vivaldi Antenna DesignDocument5 pagesInvestigation of A New Idea For Antipodal Vivaldi Antenna DesignhimansuNo ratings yet
- dinesh_abstractDocument2 pagesdinesh_abstractPedro Vargas ChabléNo ratings yet
- A Wideband Filtering Dielectric Patch Antenna WithDocument8 pagesA Wideband Filtering Dielectric Patch Antenna WithMahalakshmi ArjunanNo ratings yet
- A Cellular Base Station Antenna Configuration For Variable CoverageDocument7 pagesA Cellular Base Station Antenna Configuration For Variable CoverageABD SHNo ratings yet
- Dubal 2020Document5 pagesDubal 2020Thao Hoang PhuongNo ratings yet
- Amateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileFrom EverandAmateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- mgmt-maharaj-vijayaram-gajapathi-raj-college-of-engineering20240104-Document3 pagesmgmt-maharaj-vijayaram-gajapathi-raj-college-of-engineering20240104-MurthyNo ratings yet
- Probability and Stochastic Processes A FDocument83 pagesProbability and Stochastic Processes A FMurthyNo ratings yet
- Radar Engineering Notes - Unit2Document21 pagesRadar Engineering Notes - Unit2MurthyNo ratings yet
- WideBand Star-Shaped Microstrip Patch AntennaDocument9 pagesWideBand Star-Shaped Microstrip Patch AntennaMurthyNo ratings yet
- 5A942K723Document38 pages5A942K723MurthyNo ratings yet
- GaddaDocument119 pagesGaddaMurthyNo ratings yet
- Transmission Electromagnetic: W. L. BarrowDocument31 pagesTransmission Electromagnetic: W. L. BarrowMurthyNo ratings yet
- MPMC - Notes T ApparaoDocument105 pagesMPMC - Notes T ApparaoMurthyNo ratings yet
- Research: Research Is The Process of Solving Problems and Finding Facts in An OrganisedDocument2 pagesResearch: Research Is The Process of Solving Problems and Finding Facts in An OrganisedMurthyNo ratings yet
- Kennedy Bit QuestionsDocument26 pagesKennedy Bit QuestionsMurthyNo ratings yet
- Periodicity: There Exists T 0 TDocument6 pagesPeriodicity: There Exists T 0 TMurthyNo ratings yet
- Daily Planner Template 12Document1 pageDaily Planner Template 12MurthyNo ratings yet
- Mju Pee PDFDocument17 pagesMju Pee PDFMurthyNo ratings yet
- Properties of The Fourier TransformDocument6 pagesProperties of The Fourier TransformMurthyNo ratings yet
- Seven Habits of Highly Effective People This Book Lists 7 Life Changing HabitsDocument6 pagesSeven Habits of Highly Effective People This Book Lists 7 Life Changing HabitsMurthyNo ratings yet
- Pixel Reconfigurable Antennas: Towards Low-Complexity Full ReconfigurationDocument5 pagesPixel Reconfigurable Antennas: Towards Low-Complexity Full ReconfigurationMurthyNo ratings yet
- Padava PrayanamDocument11 pagesPadava PrayanamMurthyNo ratings yet
- MID TERM TESTDocument8 pagesMID TERM TESTvuankhe1No ratings yet
- BC Alumni Newsletter November 2024 - FinalDocument29 pagesBC Alumni Newsletter November 2024 - FinalkarenNo ratings yet
- I Am A Gummy Bear Theme Chords by Misc Cartoons Tabs at Ultimate Guitar ArchiveDocument3 pagesI Am A Gummy Bear Theme Chords by Misc Cartoons Tabs at Ultimate Guitar Archivelilama45-1No ratings yet
- DS ANT TNA990A00Rx 190801 ENDocument3 pagesDS ANT TNA990A00Rx 190801 ENMario Alvarez GarciaNo ratings yet
- (Clarinet Institute) Tchaikovsky - Nutcracker For 10 Clarinets PDFDocument48 pages(Clarinet Institute) Tchaikovsky - Nutcracker For 10 Clarinets PDFAgnė DaniulėNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 DCDocument88 pagesUnit 3 DCNEHA BHUJBALNo ratings yet
- A Slumber Did My Spirit Seal (Litcharts)Document9 pagesA Slumber Did My Spirit Seal (Litcharts)Zenith RoyNo ratings yet
- Guion Shrek El Musical FinalDocument24 pagesGuion Shrek El Musical FinalLouis AgrestNo ratings yet
- How To Design A Dolby Atmos Mix RoomDocument10 pagesHow To Design A Dolby Atmos Mix RoomingborislNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 (Mapeh)Document13 pagesGrade 3 (Mapeh)krissia.cernalNo ratings yet
- ArtsDocument17 pagesArtsJaycon Baquial IINo ratings yet
- Abbey Road ChordsDocument10 pagesAbbey Road ChordsNoe ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Examen Ingles Tercero Eso InglesDocument5 pagesExamen Ingles Tercero Eso InglesMaría MirallesNo ratings yet
- Sound DesignDocument7 pagesSound Designapi-432165820No ratings yet
- 1 Arquivo - Giannini International Catalog WebDocument70 pages1 Arquivo - Giannini International Catalog WebAntonio MemoliNo ratings yet
- Black History Month Concert SeriesDocument24 pagesBlack History Month Concert SeriesM. LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Heat Capacity Mapping Mission Press KitDocument48 pagesHeat Capacity Mapping Mission Press KitBob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- Best Ways 20 HackDocument19 pagesBest Ways 20 HackRed X YassinNo ratings yet
- Michael Jackson - Kids, Thriller & Songs - BiographyDocument10 pagesMichael Jackson - Kids, Thriller & Songs - BiographyJiminie JikookieNo ratings yet
- JPSC Mains SyllabusDocument17 pagesJPSC Mains Syllabusamir faisalNo ratings yet
- Massive MIMO SeminarDocument26 pagesMassive MIMO SeminarelsadigsaeidNo ratings yet
- SMALLTOWN BOY Accordi 100% Corretti - Bronski BeatDocument4 pagesSMALLTOWN BOY Accordi 100% Corretti - Bronski BeatAurora StamerraNo ratings yet
- I Talk To The Wind (Lyrics)Document1 pageI Talk To The Wind (Lyrics)Ben DollionNo ratings yet
- Bass Fundamentals-Column 1 - A Little JazzDocument3 pagesBass Fundamentals-Column 1 - A Little JazzdizzybeeNo ratings yet
- The Best of Keren CytterDocument328 pagesThe Best of Keren Cytterkeren cytterNo ratings yet
- Surfans F20 MP3 Player User ManualDocument66 pagesSurfans F20 MP3 Player User ManualepaqgzNo ratings yet
- Twentieth Sunday in Ordinary Time - Year C: Music RecommendationsDocument7 pagesTwentieth Sunday in Ordinary Time - Year C: Music RecommendationsMcDaryl MateoNo ratings yet
- 2 PBDocument14 pages2 PBJennifer WatsonNo ratings yet
- Avery Smith Resume 2020-2021Document1 pageAvery Smith Resume 2020-2021api-547784527No ratings yet