Lab 02 Amplitude Demodulation: ELE3203 Communication Systems
Lab 02 Amplitude Demodulation: ELE3203 Communication Systems
Uploaded by
FAseeh MalikCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 02 Amplitude Demodulation: ELE3203 Communication Systems
Lab 02 Amplitude Demodulation: ELE3203 Communication Systems
Uploaded by
FAseeh MalikOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Lab 02 Amplitude Demodulation: ELE3203 Communication Systems
Lab 02 Amplitude Demodulation: ELE3203 Communication Systems
Uploaded by
FAseeh MalikCopyright:
Available Formats
ELE3203 Communication Systems
Lab 02
Amplitude Demodulation
Student name: _____________________________
Student ID: ________________________________
Date:=
Objective
To study the function of Amplitude Demodulation. Also to vary the modulation index and see how it
affects the output signal.
Prepared By: Rajalakshmi S Menon, ADW
Apparatus Required
a) Hardware Tools: Computer system
b) Software Tool: MATLAB 7.0 and above version.
Introduction
Demodulation is a process in the reception of any Amplitude Modulated (A.M) signals whether used
for broadcast or two-way radio communication systems. Demodulation is the process by which the
original information bearing signal, i.e. the modulation is extracted from the incoming overall
received signal.
The demodulator is the circuit, or for a software defined radio, the software that is used to recover the
information content from the overall incoming modulated signal.AM demodulators are found in many
items of radio equipment: broadcast receivers etc.
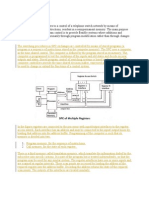
Fig 1: Demodulator Signal
Methods of AM Demodulation
1. Envelope detector is a very simple method of the demodulation that does not require any
coherent demodulator.
2. Product detector multiplies the incoming signal by the signal of a local oscillator with the
same frequency and phase as the carrier of the incoming signal. After filtering, the original
audio signal will result.
Procedure
The following blocks are required to draw the block diagram as shown in the Figure 1.
Prepared By: Rajalakshmi S Menon, ADW
1. Carrier Signal Source
2. Message Signal Source
3. Blocks for viewing the signals – Scope
4. Product Block
We can find these blocks in the following locations of Simulink Library.
Carrier, Message, Constant blocks
Simulink –> Sources –> Sine wave
Simulink –> Sources –> Constant
View Block
Simulink –> Sink –> Scope
Product and Summer Block
Simulink –> Math Operations–> Product
Simulink –> Math Operations–> Summer
Analog Filter Design
Simulink–> DSP System Toolbox–> Filtering–> Filter Implementations–> Analog Filter Design
Figure 2: Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation Block Diagram
Block parameters can be changed by selecting the block and parameter to be used are given below:
Carrier Signal frequency = 2*pi*25 and sampling time=1/5000
Message Signal frequency = 2*pi and sampling time=1/5000
Amplitudes of Message Signal is 1 and Carrier Signal is 3
Analog Filter Design Filter Order= 4
Calculations
Prepared By: Rajalakshmi S Menon, ADW
The amplitude modulated signal can be expressed as:
Where u is modulation index, which may vary:
Demodulation by Squaring
The high frequency component will be removed after the filtering:
Synchronous Demodulator
After the multiplication,
The low pass filter will remove high frequency components, so that we may recover m (t).
Diagram and Explanation
Prepared By: Rajalakshmi S Menon, ADW
Fig 3: Amplitude Modulation and Demodulated Signal Block Diagram
In Fig 3, we can see the Amplitude Modulated Signal being implemented on Simulink whereas the
various blocks of this diagram are described underneath with their implementation.
Message Signal:
The message signal in this Simulink diagram is implemented through Sine Wave which can be
extracted from Simulink –> Sources –> Sine wave whereas sine wave amplitude and frequency can
be altered as per requirements resulting into “Message Signal”.
Attributes of Message Signal
Message Signal frequency = 2*pi
Sampling Time= 1/5000
Message Signal = Vm sin(2πfmt) # fm must be smaller than fc
Message Signal Amplitude = Vm = 1
Carrier Signal:
Prepared By: Rajalakshmi S Menon, ADW
The carrier signal in this Simulink diagram is implemented through Sine Wave which can be extracted
from Simulink –> Sources –> Sine wave whereas sine wave amplitude and frequency can be put to
generate the “Carrier Signal”.
Attributes of Carrier Signal
Carrier Signal frequency = 2*pi*25
Sampling time= 1/5000
Carrier Signal = Vc sin(2πfct)
Carrier Signal Amplitude = Vc = 3
Modulation Index:
In this experiment of AM, the
constant block is also very useful which has been used two times where we may assign any constant
value, and we may extract them from Simulink –> Sources –> Constant.
When carrier amplitude is altered with respect to message signal,
Modulated Signal = (Vc+ Vmsin(2 πfmt))*sin(2 πfct)
In terms of modulation index (m=Am/Ac) the equation becomes
Modulated signal = Vc (1+ msin(2 πfmt))*sin(2 πfct)
Where,
Vc = Carrier signal amplitude
Vm = Message signal amplitude
fc= Carrier frequency
fm =Message frequency
Product:
This block is used to multiply the two signals “Message Signal” and the “Carrier
Signal” which results into the “Amplitude Modulated Signal” as can be extracted
from Simulink –> Math Operations–> Product.
Adder:
Prepared By: Rajalakshmi S Menon, ADW
This block is used to add the two signals or constant values in this construction and can be extracted
from the Simulink –> Math Operations–> Summer.
Scope:
This block in Simulink is used to display the signals output in virtual environment, and can
be extracted Simulink –> Sink –> Scope.
Butterworth Filter:
This Simulink block is being used to filter high frequency components as the
“Low Pass Filter”, and can be extracted from Simulink–> DSP System Toolbox–>
Filtering–> Filter Implementations–> Analog Filter Design
Results and Discussions
Prepared By: Rajalakshmi S Menon, ADW
1. Comment on your results.
Fig 4: Amplitude Modulation and Demodulated Signal Block Diagram
As it can be seen from Fig 4, that message signal has been recovered from the Amplitude modulated
signal having modulation index of 0.5 from the implementation of Butterworth filter.
2. Upload your Simulink file.
Yes, the Simulink file has been attached with this Lab report.
3. Explain your result. (Identify each block function)
Prepared By: Rajalakshmi S Menon, ADW
The detailed explanation has been provided in “Diagram and Explanation” section stated above
which clearly signifies the importance of “Butterworth filter” that how through its implementation the
“high frequency components” have been removed, and we have gotten the “AM Demodulated
Signal” which is the key requirement in this lab.
4. What will happen to the waveform when the modulation index m=1. Attach the scope results
and Comment on your result.
Fig 5: Amplitude Modulation and Demodulated Signal Block Diagram with m= 1.0
Prepared By: Rajalakshmi S Menon, ADW
Fig 6: Amplitude Modulation and Demodulated Signal Block Diagram with m= 1.0
The numeric value of efficiency when m = 1.0 is about 33 %. AM has a maximum practical efficiency
of about 33 % due to the limitations placed on modulation index.
Prepared By: Rajalakshmi S Menon, ADW
5. What will happen to the waveform when the modulation index m<1. Attach the scope results
and Comment on your result.
Fig 7: Amplitude Modulation and Demodulated Signal Block Diagram with m= 0.8
Fig 8: Amplitude Modulation and Demodulated Signal Block Diagram with m= 0.8
The efficiency of AM transmission is limited by the restraint to keep m < 1.0 in order to have a valid
results while for maximum efficiency, the modulation index should be equal to 1.0.
Prepared By: Rajalakshmi S Menon, ADW
6. What will happen to the waveform when the modulation index m>1. Attach the scope results
and Comment on your result.
Fig 9: Amplitude Modulation and Demodulated Signal Block Diagram with m= 1.2
Fig 10: Amplitude Modulation and Demodulated Signal Block Diagram with m= 1.2
The conclusion is that efficiency may be increased by increasing the value of the modulation index,
m, but if you use a value > 1.0 there will be distortion introduced in the receiver.
Prepared By: Rajalakshmi S Menon, ADW
Conclusion and Observation
In this lab, we have learnt about the implementation of Amplitude Demodulation in Simulink using
the “Butterworth filter” which is one of the important filters in the DSP signal block, and learnt
about that how the variations in modulation index will vary the “Demodulated Signal” and it physical
interpretation.
Note: please upload your Simulink file with the lab report (as prove of
your work), without it your report will be considered as a copy.
Include a Lab Report with
1) Introduction
2) Procedure
3) Calculations
4) Diagram and explanation
Note: the Lab Report has to be typed and not handwritten
Prepared By: Rajalakshmi S Menon, ADW
You might also like
- MSA15 Tuning GuideDocument32 pagesMSA15 Tuning GuidePero Peric100% (13)
- Multi Stage Space-Division Switching Solved Problems PDFDocument4 pagesMulti Stage Space-Division Switching Solved Problems PDFmohammed draey75% (4)
- Libshitz, S. P., Vanderkooy, J. - Pulse Code Modulation An OverviewDocument16 pagesLibshitz, S. P., Vanderkooy, J. - Pulse Code Modulation An OverviewMartinAggroweNo ratings yet
- Problem For Chapter 2Document3 pagesProblem For Chapter 2Thành VỹNo ratings yet
- Commsys Lab EXPERIMENT 8 Full ReportDocument8 pagesCommsys Lab EXPERIMENT 8 Full ReportShaarveen RajNo ratings yet
- Snowpro Core Certification GuideDocument5 pagesSnowpro Core Certification GuideharinithinNo ratings yet
- ELE 3203 Communication Systems: Student Name ID NumberDocument16 pagesELE 3203 Communication Systems: Student Name ID NumberKhawla AlameriNo ratings yet
- ELE 3203 Communication Systems: Student Name ID NumberDocument12 pagesELE 3203 Communication Systems: Student Name ID NumberKhawla AlameriNo ratings yet
- DSB SC Final ProjectDocument14 pagesDSB SC Final ProjectOscar Mauricio Sarmiento UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Frequency Modulation Analysis: Experiment # 6Document5 pagesFrequency Modulation Analysis: Experiment # 6Ghaznooq Ahmad100% (1)
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsFrom EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Double Sideband Full CarrierDocument20 pagesDouble Sideband Full CarrierIzzat Rodzman0% (2)
- Communication Lab1 2018Document55 pagesCommunication Lab1 2018Faez FawwazNo ratings yet
- DC Lab VivaDocument5 pagesDC Lab VivaAbir HoqueNo ratings yet
- Sound Pressure Meter (08-4c4)Document10 pagesSound Pressure Meter (08-4c4)Sri Krishna RakeshNo ratings yet
- Frequency Modulation and Demodulation TechniquesDocument80 pagesFrequency Modulation and Demodulation Techniquessatpals56100% (1)
- FlexPreDem FRP Final CCNDocument69 pagesFlexPreDem FRP Final CCNDr. Vaibhav Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- 15EC306J Cycle 2 ExptsDocument28 pages15EC306J Cycle 2 ExptsSanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- MANUAL COMMUNICATION LAB-II, KEC-651,2020-21, Even SemDocument18 pagesMANUAL COMMUNICATION LAB-II, KEC-651,2020-21, Even SemPiyushNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Experiments ECE-P-672Document9 pagesPower Electronics Experiments ECE-P-672Sai SomayajulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: 1.1. Wireless Communication SystemsDocument28 pagesChapter-1: 1.1. Wireless Communication Systemskarthick_mariner92No ratings yet
- Lab 3-CDocument6 pagesLab 3-CMUHAMMAD AMMAR100% (1)
- Communication SystemDocument63 pagesCommunication SystemAthar BaigNo ratings yet
- 3ECE-AC Lab ManualDocument62 pages3ECE-AC Lab ManualShannon DunnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 - Signal Space Approach and Gram Schmidt ProcedureDocument20 pagesLecture 04 - Signal Space Approach and Gram Schmidt ProcedureKhoa PhamNo ratings yet
- Advanced Communication Lab Manual PDFDocument61 pagesAdvanced Communication Lab Manual PDFRachel BartonNo ratings yet
- Path Loss Propagation ModelsDocument5 pagesPath Loss Propagation ModelsFarEast Ramdzan100% (1)
- DC CheatsheetDocument2 pagesDC CheatsheetRashi SinghNo ratings yet
- Adc Lab Manual STUDENTDocument59 pagesAdc Lab Manual STUDENTramNo ratings yet
- Ec51 Digital CommunicationDocument18 pagesEc51 Digital CommunicationvijayprasathmeNo ratings yet
- Sirisha Kurakula G00831237 ProjectDocument12 pagesSirisha Kurakula G00831237 ProjectSirisha Kurakula0% (1)
- Question Bank Communication SystemsDocument47 pagesQuestion Bank Communication SystemsGajanan ArhaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Spread Spectrum CommunicationsDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Spread Spectrum CommunicationsSriramNo ratings yet
- Bit-Error-Rate (BER) Simulation Using MATLABDocument6 pagesBit-Error-Rate (BER) Simulation Using MATLABstarman222No ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Angle Modulation and DemodulationDocument48 pagesChapter 4-Angle Modulation and DemodulationElias HedamoNo ratings yet
- Keyboard I 8051Document3 pagesKeyboard I 8051sachinshym100% (1)
- 007 - Bit Error RateDocument21 pages007 - Bit Error RateKos GayoNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Ece 304 Assignment-1Document9 pagesDigital Communication Ece 304 Assignment-1ramjee26No ratings yet
- Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK)Document11 pagesAmplitude Shift Keying (ASK)Hang ShengNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Amplitude Shift KeyingDocument51 pagesExperiment 1 Amplitude Shift KeyingMuthu Vijay DeepakNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Mannual: Simulation, Modeling & AnalysisDocument37 pagesLaboratory Mannual: Simulation, Modeling & AnalysisshubhamNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Mobile Radio Channel Modelling & Mitigations: 3.2 Mitigation Techniques For Fading Wireless ChannelsDocument34 pagesChapter Three Mobile Radio Channel Modelling & Mitigations: 3.2 Mitigation Techniques For Fading Wireless ChannelsChimd-AR DibaNo ratings yet
- OFDM Modulation and DemodulationDocument25 pagesOFDM Modulation and DemodulationAparna MishraNo ratings yet
- Stored Program ControlDocument2 pagesStored Program ControlJanuvasanth VJNo ratings yet
- Department of E.C.E.: Digital Communications Lab ManualDocument29 pagesDepartment of E.C.E.: Digital Communications Lab Manualమొక్కపాటి మాధవిNo ratings yet
- QB 2Document10 pagesQB 2Abhishek RaoNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer Networks: Transmission ImpairmentDocument30 pagesData Communication and Computer Networks: Transmission Impairmentwarke abayNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication VTU Unit 1Document56 pagesDigital Communication VTU Unit 1raghudathesh50% (2)
- Vi Sem Ece Simulation Practical Lab Manual (Diploma "L" Scheme Lab Manual) S.No Name of The Experiment Page NoDocument24 pagesVi Sem Ece Simulation Practical Lab Manual (Diploma "L" Scheme Lab Manual) S.No Name of The Experiment Page Nobiswajit7sarkarNo ratings yet
- A Conceptual Study of OFDM-based Multiple Access SchemesDocument7 pagesA Conceptual Study of OFDM-based Multiple Access SchemeswoodksdNo ratings yet
- Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK)Document41 pagesQuadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK)Luis Fernando Grueso-TenorioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - HandoffDocument25 pagesLecture 5 - HandoffSANJIDA AKTERNo ratings yet
- How Delta-Sigma Adcs Work, Part 1: by Bonnie BakerDocument6 pagesHow Delta-Sigma Adcs Work, Part 1: by Bonnie BakervishvinnyNo ratings yet
- QPSK Mod&Demodwith NoiseDocument32 pagesQPSK Mod&Demodwith Noisemanaswini thogaruNo ratings yet
- C Programming for the PIC Microcontroller: Demystify Coding with Embedded ProgrammingFrom EverandC Programming for the PIC Microcontroller: Demystify Coding with Embedded ProgrammingNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Digital Communication Systems Using SIMULINKFrom EverandModeling of Digital Communication Systems Using SIMULINKNo ratings yet
- Optical and Microwave Technologies for Telecommunication NetworksFrom EverandOptical and Microwave Technologies for Telecommunication NetworksNo ratings yet
- LAB01 - Amplitude Modulation - Sep 2020Document11 pagesLAB01 - Amplitude Modulation - Sep 2020FAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Communication SystemDocument12 pagesLab 4 Communication SystemKhawla AlameriNo ratings yet
- AM DemodulationDocument4 pagesAM DemodulationAzharul IslamNo ratings yet
- 386 1Document9 pages386 1FAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- 460 Unit 1Document40 pages460 Unit 1FAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microsoft Azure FundamentalsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Microsoft Azure FundamentalsFAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- Udemy Bonus Lecture Perpetual v10Document4 pagesUdemy Bonus Lecture Perpetual v10FAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- DIY Stair Climbing Robot: RationaleDocument9 pagesDIY Stair Climbing Robot: RationaleFAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- Date / / Time: Total Mark:: Issue 18/08/2011 Revision Date 25/06/2018 Ref No. ECT-ACAF-ACAFO-FRM.027Document4 pagesDate / / Time: Total Mark:: Issue 18/08/2011 Revision Date 25/06/2018 Ref No. ECT-ACAF-ACAFO-FRM.027FAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2 - Micro - CompleteDocument9 pagesAssignment - 2 - Micro - CompleteFAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- DC & Ac TSTBDocument21 pagesDC & Ac TSTBFAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 BTDocument13 pagesExperiment 7 BTFAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- ConclusionDocument2 pagesConclusionFAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Breadboarding: ECE 380: Lab 02Document16 pagesIntroduction To Breadboarding: ECE 380: Lab 02FAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- STA200 - O2 - Summer20 - Online 2 - Tonguc Cagin - Final AssessmentDocument7 pagesSTA200 - O2 - Summer20 - Online 2 - Tonguc Cagin - Final AssessmentFAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- Academic Year: Semester: Course InformationDocument2 pagesAcademic Year: Semester: Course InformationFAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- Logic Diagram by VHDL Code (RTL Viewer)Document3 pagesLogic Diagram by VHDL Code (RTL Viewer)FAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- LAb 2 Multiplexer and DecoderDocument11 pagesLAb 2 Multiplexer and DecoderFAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Diode R & RDocument15 pagesLab 1 Diode R & RFAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- 7 Segment Display Lab 4Document9 pages7 Segment Display Lab 4FAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- Toyota & GM - Group 1Document12 pagesToyota & GM - Group 1Aditi MurarkaNo ratings yet
- Valcor Scientific Industrial SV75Document2 pagesValcor Scientific Industrial SV75Carlitos RuizNo ratings yet
- Non Monetary Awards 2022 To CEZVspDocument2 pagesNon Monetary Awards 2022 To CEZVspDEE MRT VZMNo ratings yet
- EZC100B3030 - Circuit Breaker Easypact EZC100B - TMD - 30 A - 3 Poles 3d - Schneider ElectricDocument4 pagesEZC100B3030 - Circuit Breaker Easypact EZC100B - TMD - 30 A - 3 Poles 3d - Schneider ElectricPaul Ramos CarcaustoNo ratings yet
- A055R763 RevA - S0L1-L1Document9 pagesA055R763 RevA - S0L1-L1Arief supriyatnoNo ratings yet
- Large - PROFINET IO RT Networks For Factory Automation A Case StudyDocument4 pagesLarge - PROFINET IO RT Networks For Factory Automation A Case StudyPedro GodoiNo ratings yet
- Faq Opc XML Da Datenaustausch v10 enDocument33 pagesFaq Opc XML Da Datenaustausch v10 enseamohNo ratings yet
- 2nd LAC SessionDocument3 pages2nd LAC SessionSamSamEstoqueNo ratings yet
- Vacon NX, Non-Regenerative Front End FI9 UD01217B PDFDocument48 pagesVacon NX, Non-Regenerative Front End FI9 UD01217B PDFSilvian IonescuNo ratings yet
- EE436 HW1 Spring2014Document2 pagesEE436 HW1 Spring2014techaddicttNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Penetration TestingDocument56 pagesA Guide To Penetration TestingSplycho GoranNo ratings yet
- Free 98 361 Exam Questions PDF MicrosoftDocument6 pagesFree 98 361 Exam Questions PDF Microsoftcienciax33% (3)
- Dispatching: in PPCDocument14 pagesDispatching: in PPCmohd hameedNo ratings yet
- Cetol PDFDocument34 pagesCetol PDFpalani100% (1)
- Intel Ethernet Controller E810-CAM2-CAM1-XXVAM2 Product BriefDocument4 pagesIntel Ethernet Controller E810-CAM2-CAM1-XXVAM2 Product BriefslideinatorNo ratings yet
- Datasheet ArcadiaDocument4 pagesDatasheet ArcadiaAnonymous 1P2S4tbMNo ratings yet
- DO Automating SALT PDFDocument96 pagesDO Automating SALT PDFkela_hss86No ratings yet
- ARG DidYouKnow Chemical Infographic PrintDocument1 pageARG DidYouKnow Chemical Infographic PrintALBEIRO MOLINANo ratings yet
- CSC339 - Computer Communication and Networks: By: Dr. Abdul WahidDocument27 pagesCSC339 - Computer Communication and Networks: By: Dr. Abdul WahidDanish UttraNo ratings yet
- JD - AmsDocument3 pagesJD - AmsSenthaNo ratings yet
- BR 6000 Hach HRDocument3 pagesBR 6000 Hach HRshdphNo ratings yet
- Ericsson 3G Chapter 1 (General) - WCDMA RAN OptDocument47 pagesEricsson 3G Chapter 1 (General) - WCDMA RAN OptMehmet Can KahramanNo ratings yet
- H.Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) (PDFDrive)Document261 pagesH.Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) (PDFDrive)Hananto100% (1)
- Data PDFDocument48 pagesData PDFjohnNo ratings yet
- PDF 5Document19 pagesPDF 54073Himanshu PatleNo ratings yet
- Dell Technologies Proven Professional Exam UpdatesDocument9 pagesDell Technologies Proven Professional Exam UpdatesMỹ Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Cloud Security PHD ThesisDocument4 pagesCloud Security PHD Thesisafknyfene100% (2)