Scope and Methods of Economics: I Learning Objectives
Uploaded by
Mics leonScope and Methods of Economics: I Learning Objectives
Uploaded by
Mics leon1
SCOPE AND METHODS OF ECONOMICS
I Learning Objectives:
At the end of this module, learners must be able to:
1. Identify the origin and standard definition of economics;
2. Explain the history of economics;
3. Outline the economic methods in proper sequence;
4. Summarize the limitations of economic models;
5. Explain the various approaches to economic thinking; and
6. Differentiate microeconomics from macroeconomics.
II Key Terms
Economics Normative economics
Scarcity Positive economics
Economic analysis Microeconomics
Economic theory Macroeconomics
III Core Contents
INTRODUCTION
This module introduces economics by discussing its basic background, history and
classifications and approaches that are useful for both business and non-business
students. Economics is about the very survival of humanity that is why it is central to
every other branch of social science. This science deals with the human behavior and
his decision making in managing limited resources to satisfy his unlimited needs and
wants- hence the science of scarcity and allocation.
IV In-Text Activity
Why should you learn economics?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CE5eJbaHL8s
Module I. SCOPE AND METHODS OF ECONOMICS Principles of Economics with LRT
ACTayson (2020)
2
A. Definition and History of Economics
The word economics was derived from the Greek words oikos (household) and
nomos (management). Ancient economics therefore was equivalent to management of
households (oikonomous). The etymology of its equivalent in Sanskrit, arthashashtra ,
arth meant purpose and shashtra meant science. In simple definition, economics if the
study of human behavior to seek benefits.
Economics is considered as a social science as it was introduced by Adam
Smith, the father of Economics. In his book “Wealth of the Nations”, he referred to the
term as the study of the nature and causes of wealth of nations. It is a social science
because it basically leans on the human behavior in addressing their respective needs.
As a standard definition, economics is a social science that deals with the
efficient allocation of scarce resources to satisfy the unlimited human wants and needs.
In the 19th century economics was the hobby of gentlemen of leisure and the
vocation of a few academics; economists wrote about economic policy but were rarely
consulted by legislators before decisions were made. Today there is hardly a
government, international agency, or large commercial bank that does not have its own
staff of economists. Many of the world’s economists devote their time to teaching
economics in colleges and universities around the world, but most work in various
research or advisory capacities, either for themselves (in economics consulting firms), in
industry, or in government (Blaug, 1999, revised by Enriquez, 2020).
B. Economic Methods
Economic analysis is the process of directing economic relationships by examining
economic behavior and events and determining the causal relationships among the data
and activities observed.
A student in economics who attempts to analyze relationships among economic
variables must learn to draw conclusions from the particular to general through
deductive reasoning which necessitates the use of the first tool in Economics which is
logic.
On the other hand, the economic analyst uses statistics to quantitatively describe an
economic behaviour and therefore serves as a basis in hypothesis testing.
The third tool of economics is mathematics which enables the analyst to
conceptualize and quantify a hypothesis for empirical validation.
Purposes of Economic Analysis
1. Economic analysis is an aid in understanding how economy operates because it
explains how economic variables are related to one another.
2. It permits the prediction of results of changes in the economic variables.
Module I. SCOPE AND METHODS OF ECONOMICS Principles of Economics with LRT
ACTayson (2020)
3
3. It serves as the basis of policy formulation.
Economic Policy
Economic policy consists of intervention of courses of action taken by the
government or other private institutions to manipulate the results of economic activity.
The economic policies adopted by the government may be monetary, fiscal or trade for
the purpose of achieving economic welfare.
Construction of Economic Theory
Just like any other field of science, formulating theories in economics requires a
thorough methodology specified below.
1. Specification and definition of postulates.- Postulates are given conditions upon
which a theory will be erected. For example we may postulate about the
consumer behaviour in a supermarket, specifically, the relationship of their
income to the degree of their satisfaction.
2. Observation of facts.- In the situation, the activity in question is the exchange f
groceries between the supermarkets and the consumers, the activity should be
observed thoroughly. As facts emerge, we can identify significant observation.
The hair color of the consumers or the color of the grocery personnel’s uniform is
not likely to matter but the weekly budget of consumers and the quantity of
available groceries will be important.
3. Application of the rules of logic to the observed facts.- Deductive chains of logic
may believe that certain effects follow certain causes in regular manner. We may
reason that because consumers with larger incomes are willing to pay higher
prices for specific goods, an increase in consumer income may likely lead to
higher prices. This tentative conclusion is called hypotheses.
4. Test the formulated hypotheses and generalize a principle.- The tools of statistics
and econometrics will equip us to test the quantified observed data. From the
results, we can now come up to our theory or principle in economics.
C. The Functions of Economic Theory
The principal functions of economics fall into two categories: (1) to explain the nature
of economic activity and (2) to predict what will happen to the economy as facts change.
Positive economics is supposed to be completely objective, limited to the cause-
and-effect relationships of economic activity; it is therefore concerned with the way
economic relationships are. It is factual and is used to describe occurrence of a
phenomenon.
Normative economics however, is concerned with what ought to be or what should
be. This is more subjective and more judgmental. In contrast, normative economics is
more predictive than descriptive in usage.
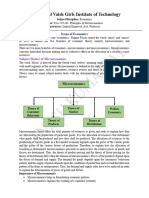
D. Major Divisions of Economics
Module I. SCOPE AND METHODS OF ECONOMICS Principles of Economics with LRT
ACTayson (2020)
4
Price theory (microeconomic theory) and the theory of the economy (macroeconomic
theory) constitute the basic analytical tool kit of the discipline of economics.
Microeconomics is concerned primarily with the market activities on individual
economic units such as consumers, resource owners, and business firms. It is
concerned with the flow of goods and services from business firms to consumers, the
composition of the flow and the process for establishing relative prices of the
component parts of the flow. It is concerned too with the flow of resources (or its
services) from resource owners to business firms, with their evaluation, and with their
allocation among alternative uses.
Macroeconomics is concerned to the economic system as a whole rather than
individual economic unit of which it is composed. The particular goods and services
making up the flow from business firms to consumers are not integral parts of the
analysis, nor are the individual resources or service moving from resource owners to
business firms. The value of the overall flow of goods (net national product) and the
overall flow of resources (national income) receive the focus of attention.
Macroeconomics concentrates on the causes of change in aggregate movement of
goods and services, and the general employment level resources. Macroeconomics has
much to say about the nature of economic growth and the conditions necessary for the
expansion of productive capacity and national income time.
Moreover, the distinction is to be understood as relative in nature. The problems of a
city municipal corporation and macro in nature as compared to those of individual
citizens, but a city unit is micro as compared to a state, and the state unit is micro as
compared to the nation and the national unit is micro as compared to a global unit.
All economic problems and activities, whether micro or macro, are ultimately connected
with making a choice and optimization. They emerge out of and are concerned with
human behavior.
V Session Summary
Economics is a social science that deals with the efficient allocation of scarce
resources to satisfy the unlimited human wants and needs. It came from the Greek root
word oikomos which means household management. Logic, statistics and mathematics
are key methods in making economic analysis
Just like any other science, the construction of economic theory includes
processes such as: (1)Specification and definition of postulates , (2) Observation of
facts, (3)application of the rules of logic to the observed facts and (4)test the formulated
hypotheses to generalize a principle.
In analyzing economic theories, students taking up economics may follow the
economic approached-positive and normative economics. These two approaches utilizes
facts and predictions for decision making. Macroeconomics and microeconomics are the
Module I. SCOPE AND METHODS OF ECONOMICS Principles of Economics with LRT
ACTayson (2020)
5
two major divisions of economics. Macroeconomics tackles the broader and aggregate
level while Microeconomics is concern with individual economic decisions.
V SELF-ASSESSMENT
Economics is a course included in your program not just because it has to be
included as mandated, but because it focuses on issues that affects everyone
-everywhere-everyday. You are now task to create a one-page essay about the
economics of yourself-the decisions that you do as a scarce resource-because, Yes, you
are! As a college student, cite and discuss examples of your personal decisions (could
range from small matters to big life-changing decisions) in which you think you have
applied some economic way of thinking.
VI REFERENCES
Please refer to the references indicated in the syllabus.
Module I. SCOPE AND METHODS OF ECONOMICS Principles of Economics with LRT
ACTayson (2020)
You might also like
- A Critical Analysis of The Merchant of Venice100% (1)A Critical Analysis of The Merchant of Venice8 pages
- Objectives:: Chapter 1: Introduction To The Study of EconomicsNo ratings yetObjectives:: Chapter 1: Introduction To The Study of Economics8 pages
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Economic TheoryNo ratings yetChapter 1 - Introduction To Economic Theory12 pages
- Micro-Economics اقتصاد جزئي باللغة الإنكليزية جامعة هنديةNo ratings yetMicro-Economics اقتصاد جزئي باللغة الإنكليزية جامعة هندية114 pages
- Applied Economics: Module No. 1: Week 1: First QuarterNo ratings yetApplied Economics: Module No. 1: Week 1: First Quarter7 pages
- Summary On Economics and Scope and Methodology of Economics Student: Tran Van Quyet ID: 5101 - 3744 1-Definition of EconomicsNo ratings yetSummary On Economics and Scope and Methodology of Economics Student: Tran Van Quyet ID: 5101 - 3744 1-Definition of Economics4 pages
- ECN 202: Introductory Macroeconomics: Module 1: Introduction To MacroeconomicsNo ratings yetECN 202: Introductory Macroeconomics: Module 1: Introduction To Macroeconomics18 pages
- Syllabus Class: - BBA I Year Subject: - Micro EconomicsNo ratings yetSyllabus Class: - BBA I Year Subject: - Micro Economics64 pages
- Basic Microeconomics Chapter 2: Economic Theory Theory: Pangasinan State UniversityNo ratings yetBasic Microeconomics Chapter 2: Economic Theory Theory: Pangasinan State University4 pages
- Applied Business Economics Coursepack FinalNo ratings yetApplied Business Economics Coursepack Final82 pages
- Wedefit Macro Economics Short Note For SJS G12No ratings yetWedefit Macro Economics Short Note For SJS G1219 pages
- Managerial Economics Final 2 Hons I Year PDFNo ratings yetManagerial Economics Final 2 Hons I Year PDF23 pages
- Economics: While Discussing The Nature of Economics, One Has To Consider (1) The Subject MatterNo ratings yetEconomics: While Discussing The Nature of Economics, One Has To Consider (1) The Subject Matter23 pages
- Chapter I - Fundamentals of MacroeconomicsNo ratings yetChapter I - Fundamentals of Macroeconomics19 pages
- TOPIC1 PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMIC THEORYNo ratings yetTOPIC1 PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMIC THEORY3 pages
- T S M E L 1 - C - 0: HE Cope and Ethod of Conomics Ecture HNo ratings yetT S M E L 1 - C - 0: HE Cope and Ethod of Conomics Ecture H11 pages
- Introduction To Macroeconomics StructureNo ratings yetIntroduction To Macroeconomics Structure173 pages
- Delegation: The Basics and More of Being A Great LeaderNo ratings yetDelegation: The Basics and More of Being A Great Leader15 pages
- Highways and Byways of Literary Criticism in Sanskrit - BookNo ratings yetHighways and Byways of Literary Criticism in Sanskrit - Book105 pages
- Ingeniero, Angela Mae M. Bachelor of Arts in Political Science 2-ANo ratings yetIngeniero, Angela Mae M. Bachelor of Arts in Political Science 2-A2 pages
- Engineering Ethics (HSS-424) : Dr. Imtiaz Alam Bahria University, IslambadNo ratings yetEngineering Ethics (HSS-424) : Dr. Imtiaz Alam Bahria University, Islambad42 pages
- (Celtech College) : Central Luzon College of Science and Technology, IncNo ratings yet(Celtech College) : Central Luzon College of Science and Technology, Inc3 pages
- 01 ING B1 Comprension Textos Orales 22 23No ratings yet01 ING B1 Comprension Textos Orales 22 234 pages
- A Study of Abhidhamma_ DhammahadayavibhaṅgaNo ratings yetA Study of Abhidhamma_ Dhammahadayavibhaṅga7 pages
- Leadership and Governance: Daughters of Charity - St. Louise de Marillac Educational System Sorsogon Cluster100% (1)Leadership and Governance: Daughters of Charity - St. Louise de Marillac Educational System Sorsogon Cluster9 pages
- Literature (English) : Paper 0486/01 Paper 1 (Open Books)No ratings yetLiterature (English) : Paper 0486/01 Paper 1 (Open Books)20 pages
- Objectives:: Chapter 1: Introduction To The Study of EconomicsObjectives:: Chapter 1: Introduction To The Study of Economics
- Micro-Economics اقتصاد جزئي باللغة الإنكليزية جامعة هنديةMicro-Economics اقتصاد جزئي باللغة الإنكليزية جامعة هندية
- Applied Economics: Module No. 1: Week 1: First QuarterApplied Economics: Module No. 1: Week 1: First Quarter
- Summary On Economics and Scope and Methodology of Economics Student: Tran Van Quyet ID: 5101 - 3744 1-Definition of EconomicsSummary On Economics and Scope and Methodology of Economics Student: Tran Van Quyet ID: 5101 - 3744 1-Definition of Economics
- ECN 202: Introductory Macroeconomics: Module 1: Introduction To MacroeconomicsECN 202: Introductory Macroeconomics: Module 1: Introduction To Macroeconomics
- Syllabus Class: - BBA I Year Subject: - Micro EconomicsSyllabus Class: - BBA I Year Subject: - Micro Economics
- Basic Microeconomics Chapter 2: Economic Theory Theory: Pangasinan State UniversityBasic Microeconomics Chapter 2: Economic Theory Theory: Pangasinan State University
- Economics: While Discussing The Nature of Economics, One Has To Consider (1) The Subject MatterEconomics: While Discussing The Nature of Economics, One Has To Consider (1) The Subject Matter
- T S M E L 1 - C - 0: HE Cope and Ethod of Conomics Ecture HT S M E L 1 - C - 0: HE Cope and Ethod of Conomics Ecture H
- Delegation: The Basics and More of Being A Great LeaderDelegation: The Basics and More of Being A Great Leader
- Highways and Byways of Literary Criticism in Sanskrit - BookHighways and Byways of Literary Criticism in Sanskrit - Book
- Ingeniero, Angela Mae M. Bachelor of Arts in Political Science 2-AIngeniero, Angela Mae M. Bachelor of Arts in Political Science 2-A
- Engineering Ethics (HSS-424) : Dr. Imtiaz Alam Bahria University, IslambadEngineering Ethics (HSS-424) : Dr. Imtiaz Alam Bahria University, Islambad
- (Celtech College) : Central Luzon College of Science and Technology, Inc(Celtech College) : Central Luzon College of Science and Technology, Inc
- Leadership and Governance: Daughters of Charity - St. Louise de Marillac Educational System Sorsogon ClusterLeadership and Governance: Daughters of Charity - St. Louise de Marillac Educational System Sorsogon Cluster
- Literature (English) : Paper 0486/01 Paper 1 (Open Books)Literature (English) : Paper 0486/01 Paper 1 (Open Books)