Particles
Particles
Uploaded by
donquijote2010Copyright:
Available Formats
Particles
Particles
Uploaded by
donquijote2010Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Particles
Particles
Uploaded by
donquijote2010Copyright:
Available Formats
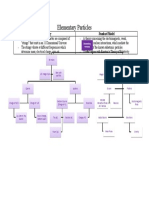
What is the Particles
All particles are either fermions or bosons.
ATOM
nucleus
electron
universe made of? proton u u u d
Bosons uud quarks d d
It is made of particles. Fermions
Atoms are made of particles, Spin 1⁄2, 3⁄2, 5⁄2, ... Spin 0, 1, 2, ... neutron d u u d
light is made of particles, udd quarks d u
Matter is made of fermions. Forces are carried by bosons.
and even gravity is Fermions obey the exclusion Bosons do not obey the
made of particles. principle: they cannot be in the exclusion principle: they can
same place at the same time. pass right through each other.
Fundamental Particles
This shows all the known fundamental particles in the standard model of particle physics
and some hypothetical particles that many physicists expect will be discovered.
u c t Boson Fermion
Fundamental Fermions d s b super- Fundamental Bosons super-
e μ τ partners partners
νe νμ ντ [predicted] [predicted]
particle
particle
partner
partner
electric
electric
symbol
symbol
charge
field or force
charge
super-
super-
family
mass
mass
anti-
anti-
carried
spin
spin
spin
spin
name name by boson
1.5–3.5 ~ electro- ~
u up quark 1⁄ +2⁄3 ¯
u u 0
2 MeV γ photon magnetism 1 0 0 self γ 1⁄
2
1 ~ (light)
1⁄ 3.5–6.0 ¯
d down quark 2 −1⁄ 3 d d 0 ~
MeV
W− W boson weak force −1 80 GeV W+ W 1⁄
~ 1 ~ 2
1.1–1.4 Z boson (radioactivity)
Quarks
c charm quark 1⁄ +2⁄3 ¯
c c 0 Z 0 91 GeV self Z
2 GeV
2 ~ ~
70–130 ¯ strong force
s strange quark 1⁄2 −1⁄3 s s 0 g gluon 1 0 0 self g 1⁄
2
MeV (binds quarks)
170–180 ~
t top quark 1⁄ +2⁄3 ¯
t t 0
2 GeV graviton ~
G gravity 2 0 0 self G 3⁄
3 [predicted] 2
4.1–4.4 ~
b bottom quark 1⁄2 −1⁄3 ¯
b b 0
GeV
higgs field ~
H higgs 0 114–185 self 1⁄
Quarks have three color charges: red, green, & blue. (creates mass) 0 H 2
H− [predicted] −1 GeV H+
[predicted]
511 ~
e− electron 1⁄
2 −1 e+ e 0
keV Antiparticles. Each particle has an antiparticle with the same mass and
1 ~ spin, but opposite charge. A particle with no charge may be its own antipar-
electron <2.2
νe 1⁄
2 0 ν¯e νe 0 ticle. Anti-electrons are called positrons.
neutrino eV
Chirality. Particles may have left-handed or right-handed spins.
~
Leptons
106 Supersymmetry theory proposes a partner boson for each fermion and a
μ− muon 1⁄
2 −1 μ+ μ 0
MeV partner fermion for each boson. The superpartner has the same charge as
2 ~ the standard particle but its spin differs by ½ and its mass is greater. Names
muon <170
νμ 1⁄
2 0 ν¯μ νμ 0 of superpartners: Add “s” for bosons, ex., sfermion, squark, slepton,
neutrino keV
selectron, sneutrino. Add “ino” for fermions, ex., bosino, photino, wino, zino,
1.8 ~ gluino, gravitino, higgsino.
τ− tau 1⁄
2 −1 τ+ τ 0 Superpositions. Some particles are linear superpositions (mixtures) of
GeV
3 other particles. For example, the predicted neutralino is a mixture of the
tau <16 ~
ντ 1⁄
2 0 ν¯τ ντ 0 neutral photino, zino, and higgsino.
neutrino MeV String theory proposes that all fundamental particles are actually tiny
vibrating strings.
Other fundmental particles may yet be discovered.
Composite Particles — Hadrons
Composite particles are composed of other particles, sometimes in complicated ways involving superpositions (mixtures) of particles.
This shows some of the hundreds of known composite particles.
Baryons Mesons
Baryons are fermions composed of three quarks. Mesons are bosons composed of a quark and antiquark.
This shows only the baryons made of u, d, & s quarks. This shows only the mesons made of u, d, & s quarks.
The nucleons are the proton and neutron. Pi mesons carry the nuclear force between nucleons.
sym name quarks charge mass
p proton K0 ds̄ K+ us̄ kaon
p+ uud n0 udd uud +1 938
n neutron udd 0 940
π0/η0 uū/dd̄
spin 1⁄2 Σ+ uus Σ0/Λ0 uds Σ− dds sigma & lambda MeV spin 0 π− dū π+ ud̄ pion & eta
η′0 ss̄
Ξ0 uss Ξ− dss xi K− sū K̄ 0 sd̄ kaon
Δ++ uuu Δ+ uud Δ0 udd Δ− ddd delta
K*0 ds̄ K*+ us̄ kaon
Σ*+ uus Σ*0 uds Σ*− dds sigma ρ0/ω0 uū/dd̄
spin 3⁄2 spin 1 ρ− dū ρ+ ud̄ rho, omega, & phi
Ξ*0 uss Ξ*− dss xi φ0 ss̄
omega-minus K*− sū K̄ *0 sd̄ kaon
Ω− sss
© 2005-2009 Keith Enevoldsen elements.wlonk.com
You might also like
- Matlab Codes: 1 Inertial RegimeDocument4 pagesMatlab Codes: 1 Inertial Regimedebdip1993No ratings yet
- Interpretation of SpectrogramDocument48 pagesInterpretation of SpectrogramPrakash Chavali100% (6)
- Chemistry Paper 1 Notes BundleDocument37 pagesChemistry Paper 1 Notes Bundleemilysacre123No ratings yet
- Phychem Quantum Mechanics 3Document1 pagePhychem Quantum Mechanics 39gt5vx9fg7No ratings yet
- 2.3 ChemistryDocument11 pages2.3 ChemistryAvighna Reddy DargulaNo ratings yet
- O Level Nuclear Physics and RadioactivityDocument16 pagesO Level Nuclear Physics and RadioactivityMd Safwat100% (1)
- Atomic Models Summary DiagramDocument1 pageAtomic Models Summary DiagramSmartToiletNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Positioning - BasicsDocument73 pagesElectricity and Magnetism: Positioning - BasicsVLADIMIR YOLVIS CHOQUEHUANCA GALINDONo ratings yet
- Molecular Chemical Bonding NotesDocument2 pagesMolecular Chemical Bonding NotesMeera KumarNo ratings yet
- Ap One Pagers Combined PDFDocument10 pagesAp One Pagers Combined PDFJack KirbyNo ratings yet
- 2 12Document22 pages2 12Kira BezkorovainaNo ratings yet
- Consists of Experiencing DevelopmentDocument2 pagesConsists of Experiencing DevelopmentFahri SaputraNo ratings yet
- Elementary ParticlesDocument1 pageElementary ParticlesClarisse ParonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Doodle NotesDocument2 pagesChemical Bonding Doodle Notesemyatthu55No ratings yet
- Structure of Atom Chemistry Mind MapDocument2 pagesStructure of Atom Chemistry Mind MapPratibha GadheNo ratings yet
- AQA Knowledge Mat Atomic Structure V3pptxDocument4 pagesAQA Knowledge Mat Atomic Structure V3pptxsuryn001.304No ratings yet
- Light and SoundDocument19 pagesLight and SoundroysougatashankarNo ratings yet
- 01 Matter and RadiationDocument146 pages01 Matter and RadiationAnish KarnaNo ratings yet
- Padhle 11th - Structure of AtomDocument32 pagesPadhle 11th - Structure of AtomShashank shekharNo ratings yet
- Pudding Negatively: ChargeDocument9 pagesPudding Negatively: ChargeAdeel MohdNo ratings yet
- Colorful Pastel Decimals Math Maze WorksheetDocument2 pagesColorful Pastel Decimals Math Maze WorksheetJessa FerrerNo ratings yet
- Science PosterDocument1 pageScience PosterBasel H.No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure NotesDocument8 pagesAtomic Structure Notesapi-364565466No ratings yet
- Mass Spectrometry - FactRecallDocument2 pagesMass Spectrometry - FactRecallFarhan TanveerNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Nuclei - 1Document24 pagesAtoms and Nuclei - 1bhaveshmalhotra9911No ratings yet
- Band Theory, Semiconductors PDFDocument6 pagesBand Theory, Semiconductors PDFpervyguy738No ratings yet
- Atomic structureDocument19 pagesAtomic structurehamnahf24No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Coursebook 5e - Pagenumber - PDF - Google DriveDocument1 pageCambridge IGCSE Chemistry Coursebook 5e - Pagenumber - PDF - Google Drivezx8g4mbzmrNo ratings yet
- Phychem Quantum Mechanics 1Document1 pagePhychem Quantum Mechanics 19gt5vx9fg7No ratings yet
- Review - 11 - Atomic, Nuclear, and Particle PhysicsDocument4 pagesReview - 11 - Atomic, Nuclear, and Particle Physicsnadeemubaid21No ratings yet
- 2 - Orbitals PDFDocument13 pages2 - Orbitals PDFRyle AquinoNo ratings yet
- EE5508 Lecture 5Document51 pagesEE5508 Lecture 5violetal1323No ratings yet
- Particles in PhysicsDocument1 pageParticles in PhysicsSamNo ratings yet
- Dual NatureDocument1 pageDual NaturerewakarshiNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument20 pagesElectricityJürgen GeermanNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A2 Book 1-2-1-26Document30 pagesEdexcel A2 Book 1-2-1-26Tahiyat AhsanNo ratings yet
- 4 Unit-IV (Schpc11)Document23 pages4 Unit-IV (Schpc11)valar1982valarNo ratings yet
- Elementary Particles: Fermions FermionsDocument1 pageElementary Particles: Fermions FermionshastalosovariosNo ratings yet
- Zirconia Graphite RefractoryDocument6 pagesZirconia Graphite RefractoryBagas Prasetyawan Adi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- STOICHIOMETRYDocument1 pageSTOICHIOMETRYRafsanNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Preumont Chapter 4Document36 pagesMechatronics Preumont Chapter 4ibrahim el hajjNo ratings yet
- Water Retention of Hydraulic Cement-Based Mortars and PlastersDocument4 pagesWater Retention of Hydraulic Cement-Based Mortars and PlastersDiego ZV100% (1)
- Unit 4 Atomic StructureDocument4 pagesUnit 4 Atomic StructurejaneandersonwongNo ratings yet
- Padhle 11th - Structure of AtomDocument29 pagesPadhle 11th - Structure of AtomKomal MeenaNo ratings yet
- Extrinsic SemiconductorsDocument4 pagesExtrinsic SemiconductorsPratheek UNo ratings yet
- C1 - Tranferencia de Energia Fotones - MACocaDocument17 pagesC1 - Tranferencia de Energia Fotones - MACocaAquiles MedinaNo ratings yet
- F321-01Jun16 124511.inddDocument8 pagesF321-01Jun16 124511.inddvanessabrauneisNo ratings yet
- (Gs Material Science) : Structure of Atom and Interatomic BondingDocument23 pages(Gs Material Science) : Structure of Atom and Interatomic BondingramlakhanNo ratings yet
- Im 1482154379 PDFDocument23 pagesIm 1482154379 PDFramlakhanNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectroscopy NotesDocument16 pagesMass Spectroscopy NotesMirthu sujeeNo ratings yet
- Chem NotesDocument98 pagesChem NotesFedeNo ratings yet
- Eicbornhabercycleposter 733782Document1 pageEicbornhabercycleposter 733782Joko SusiloNo ratings yet
- Magnetron - RadartutorialDocument1 pageMagnetron - RadartutorialSabine HmNo ratings yet
- downloadChemistryGCSENotesAQA1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableMind Maps1.1Document1 pagedownloadChemistryGCSENotesAQA1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableMind Maps1.1isabellechapman741No ratings yet
- 01 Atomic TheoryDocument33 pages01 Atomic TheorybsjaramillaNo ratings yet
- Electro-Electrical 2 Curriculum Guide 2012Document11 pagesElectro-Electrical 2 Curriculum Guide 2012Edwin SorianoNo ratings yet
- Atomic structureDocument1 pageAtomic structureZaid AliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AS Notes 5Document1 pageChemistry AS Notes 5cassandra.on134No ratings yet
- 005 - Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption IonizationDocument5 pages005 - Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption IonizationSriraam subburajNo ratings yet
- Ap 5Document4 pagesAp 5MARTÍN SOLANO MARTÍNEZNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines-I: Belts & Ropes DriveDocument43 pagesMechanics of Machines-I: Belts & Ropes DriveAnonymous kbPP3CCcNo ratings yet
- MSCPH 504Document198 pagesMSCPH 504Mahak YadavNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Compression Testing of WoodDocument5 pagesLab 6 - Compression Testing of WoodManikandan Selvam0% (1)
- StrengthDocument74 pagesStrengthAdrianKarlBonaNo ratings yet
- Definite IntegralDocument12 pagesDefinite IntegralJeremiahLimNo ratings yet
- Electus Distribution Reference Data Sheet: POLYMOVS PDFDocument2 pagesElectus Distribution Reference Data Sheet: POLYMOVS PDFFarshad yazdi100% (2)
- Littelfuse Surge Protection For Photovoltaic SystemsDocument12 pagesLittelfuse Surge Protection For Photovoltaic SystemsMiguel GarzaNo ratings yet
- (Synthese Library 406) Alberto Cordero - Philosophers Look at Quantum Mechanics (2019, Springer International Publishing) PDFDocument316 pages(Synthese Library 406) Alberto Cordero - Philosophers Look at Quantum Mechanics (2019, Springer International Publishing) PDFSunkulp Goel100% (2)
- Comments On The Elovich Equation: T To, T, T, To TDocument3 pagesComments On The Elovich Equation: T To, T, T, To TMiguelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document29 pagesLecture 3Chamath JayawardanaNo ratings yet
- Pde in DIPDocument20 pagesPde in DIPAhlad KumarNo ratings yet
- Solve Schrödinger Equation For Hydrogen Atom - + ExampleDocument10 pagesSolve Schrödinger Equation For Hydrogen Atom - + ExampleperedexNo ratings yet
- All Tables Class XiiDocument23 pagesAll Tables Class XiiSakshi KantNo ratings yet
- Physics PaperDocument7 pagesPhysics PaperEhtisham KhattakNo ratings yet
- Millikans Oil Drop Experiment: SES Instruments Pvt. LTDDocument2 pagesMillikans Oil Drop Experiment: SES Instruments Pvt. LTDAmit JangirNo ratings yet
- Complementary Relativity - Beyond The Lorentz Transformations - Eng+ItaDocument40 pagesComplementary Relativity - Beyond The Lorentz Transformations - Eng+ItaLeonardo RubinoNo ratings yet
- Nernst EquationDocument7 pagesNernst Equationantony2288No ratings yet
- MODULE IN GEN. CHEMISTRY 2 MODULE 1 Q3 Week 1Document19 pagesMODULE IN GEN. CHEMISTRY 2 MODULE 1 Q3 Week 1dioquinojoshua949No ratings yet
- 1.1 Sample Problems PDFDocument10 pages1.1 Sample Problems PDFLance Adrian BengalanNo ratings yet
- Computation of Transmission Lines Parameters-Ex1Document10 pagesComputation of Transmission Lines Parameters-Ex1Anonymous gAVMpR0aNo ratings yet
- Quaternions: (Com S 477/577 Notes)Document21 pagesQuaternions: (Com S 477/577 Notes)Manuel CebolloNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Moving Coil GalvanometerDocument18 pagesPhysics Project Moving Coil GalvanometerShàùryà Priyanshu100% (1)
- Angle and Angle MeasuresDocument20 pagesAngle and Angle MeasuresKenneth ArlandoNo ratings yet
- Singly Reinforced Beam DesignDocument7 pagesSingly Reinforced Beam Designravi1214No ratings yet
- Workbook - EquilibriumDocument57 pagesWorkbook - EquilibriumBruce Walker100% (1)
- AtomsFirst2e Day6 Sec3.7-3.8 CHMY171 Fall 2015Document17 pagesAtomsFirst2e Day6 Sec3.7-3.8 CHMY171 Fall 2015Claudius MorpheusNo ratings yet
- Ana ChemDocument14 pagesAna ChemSamuel MagannonNo ratings yet
- PP For CH 30Document40 pagesPP For CH 30allah rakha swabiNo ratings yet