0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
175 viewsIntroduction To Digital Image Processing
Digital image processing refers to using computers to modify digital images. It involves extracting useful data from images or changing images in some way, such as enhancing, editing, or compressing them. The core concept is taking an image as input and returning an image as output. Some applications of image processing include medicine, security, astronomy, and more. The main stages of digital image processing are image acquisition, enhancement, restoration, segmentation, description and representation, and object recognition.
Uploaded by
Abdataa waaqaaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
175 viewsIntroduction To Digital Image Processing
Digital image processing refers to using computers to modify digital images. It involves extracting useful data from images or changing images in some way, such as enhancing, editing, or compressing them. The core concept is taking an image as input and returning an image as output. Some applications of image processing include medicine, security, astronomy, and more. The main stages of digital image processing are image acquisition, enhancement, restoration, segmentation, description and representation, and object recognition.
Uploaded by
Abdataa waaqaaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 3
Introduction to Digital Image Processing
Digital Image processing refers to processing digital images by mean of a digital computer. It is
a branch of machine learning and AI that goes into the process of extracting useful data from
images or modifying images in a certain way. Image processing aims at improving images for
better human interpretation of their content in many ways. Examples of this are printing,
enhancement, editing, and compression.
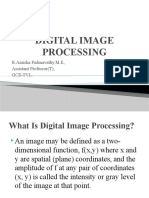
What is an Image?
An Image is a Visual Representation in the Form of a Function.
Images are generally defined over rectangular areas, and is a matrix.
Images can be matrices of intensity of Grey or color values.
This function is a 2D function f(x,y), where x and y are spatial coordinates. The origin is
the Top Left corner of the image.
The amplitude of f at any pair(x,y) is called the intensity or the Grey level of the image at
that point(the blackness or whiteness of that point).
Each pair (x,y) in the matrix is called a pixel.
o The higher the pixel count, the better the quality of the image, but the larger it is
in size and the harder it is to process.
o Digitizing an image causes an image to become an approximation of the real
scene. Digitization is done using its own algorithm, and there is some loss of
features and values when digitizing a real image.
Levels of Image Processing
Image Processing(Low) : inputs and outputs are images(enhancement, compression,
feature detection, restoration, noise removal, etc).
Image Analysis(Mid) : outputs are attributes extracted from images(matching,
segmentation, registration, etc).
Computer Vision(High) : an ensemble of objects extracted from images(Object detection,
object recognition, shape analysis, object tracking, etc).
The Work Flow of Image Processing
The core concept of image processing is taking an image and returning an image ie,
Input-> Image, Output -> Image
Going into depth, the process has 5 parts :
Image Acquisition and Preprocessing : The First step of the process, this is about
selecting our images.
Image Segmentation and Analysis : Extracting certain regions of an image and analyzing
the objects in them, the semantics of the image, and its description.
Feature Extraction : Extracting some characteristics from an image for a certain purpose.
Application of Image Processing : Things such as Image Classification, Face Detection,
Face Recognition, Optical Character Recognition, License Plate Recognition, etc.
Post processing : Modifying images in a certain way such as contrast adjustment .
What Do we need to Know to Get Started with Image
Processing?
Maths! It's very important to know linear algebra, since all images are technically
matrices, any process we do on an image is a linear algebra operation.
MATLAB(or another similar software). It's what we are going to be mostly use for
experimenting.
Some Applications of Image Processing
There are many real world applications in image processing in many fields such as:
Medicine : Such as Histogram Stretching, Noise Cleanup, Tumor Detection, etc, on
Medical Images(X-ray, MRI, etc).
Biology : Such as Organism Recognition, Clarifying Microscopic Images, etc.
Security and Biometrics : Face Recognition, Fingerprint Recognition, Iris Recognition,
etc.
Astronomy : Identifying Galaxies.
GIS(Geographic Information Systems) : Hurricane Recognition in Meteorology.
Law Enforcement : Speed Cameras, Plate Recognition, Face Recognition, Fingerprint
Recognition, Gesture Recognition, Suspect Tracking, etc.
Industrial Inspection : Automatic Inspection of Parts such as semiconductors for defects
or Sorting Produce. Image recognition can be more reliable than the human eye when
there is a huge amount of variables.
Human Computer Interaction : Gesture Recognition and Face Recognition to make
interaction more intuitive.
Why Do We Need Image Processing?
Image Acquisition :
o Correcting aperture, color balance, lightening, etc.
o Image Reconstruction.
o Creating 3d objects from images.
Prepare images for displaying/printing :
o Size Adjustment.
o Color-Mapping, gamma correction.
Facilitate picture storage and transformation.
o Efficient image storage/compression.
Enhance and Restore Images :
o Enhance personal images/libraries(enhancement meaning here enhancing the
experience of using digital images eg by adding information and tags to them).
o Color enhancement for security screening.
Information Extraction From Images :
o Reading Barcodes.
o Character Recognition.
Image Retrieval :
Text Based Image Retrieval : Searches for and fetches images by text(tags, names, etc).
Content Based Image Retrieval : Searches for and fetches images by using another image
by comparing content.
Sketch based Image Retrieval : Searches for and fetches images by comparing to a
sketch.
Semantic/Concept Based Image Retrieval : Searches for and fetches images by their
properties and objects.
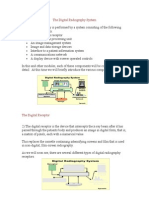
Stages in Digital Image Processing
Image Acquisition : The First stage. It is acquiring and digitizing images so processing
can be performed afterwards.
Image Enhancement : The Process of adjusting images so that the results are suitable for
display.
Image Restoration : Taking a corrupt or noisy image and restoring the clean/original
image.
Morphological Processing : Processing images based on shapes. It is applying a structural
element to an input image to create an output image of the same size.
Segmentation : Divide images into regions/constituent parts.
Description and Representation : Image regions transformed into suitable representation
for further processing. This is important for machine learning. An example of this is the
RGB Histogram and its use to approximate what an image is. Another Example is Pattern
Recognition.
Object Recognition : The Process of finding and labeling different objects in
images(Using the Description an Representation of the image).
You might also like
- Mastering Digital Images - Capture - Process - Display - Sell - Al Judge100% (1)Mastering Digital Images - Capture - Process - Display - Sell - Al Judge92 pages
- Image Processing Mainly Include The Following Steps:: IPPR Unit-1No ratings yetImage Processing Mainly Include The Following Steps:: IPPR Unit-18 pages
- Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB®No ratings yetPractical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB®27 pages
- Difference Between Computer Vision, Image Processing and Computer GraphicsNo ratings yetDifference Between Computer Vision, Image Processing and Computer Graphics3 pages
- 21 AD6703 UNIT I DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS[1]No ratings yet21 AD6703 UNIT I DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS[1]24 pages
- CSE-IT-312 DIP -2 Definition Steps and ApplicationNo ratings yetCSE-IT-312 DIP -2 Definition Steps and Application84 pages
- Digital Image Processing 1 (Virtual Exchange)No ratings yetDigital Image Processing 1 (Virtual Exchange)20 pages
- 1: Introduction To Digital Image ProcessingNo ratings yet1: Introduction To Digital Image Processing14 pages
- What Is Image Processing? Explain Fundamental Steps in Digital Image ProcessingNo ratings yetWhat Is Image Processing? Explain Fundamental Steps in Digital Image Processing15 pages
- Digital Image Processing: Submitted by Riya ShajiNo ratings yetDigital Image Processing: Submitted by Riya Shaji30 pages
- Image Processing in Artificial IntelligeNo ratings yetImage Processing in Artificial Intellige6 pages
- Port City International University: Mid Assignment100% (1)Port City International University: Mid Assignment16 pages
- Digital Image Processing and Its Implementation Using Mat LabNo ratings yetDigital Image Processing and Its Implementation Using Mat Lab8 pages
- Computer Imaging: Computer Vision Image ProcessingNo ratings yetComputer Imaging: Computer Vision Image Processing6 pages
- Question: What Is Image Processing? Explain Fundamental Steps in Digital Image ProcessingNo ratings yetQuestion: What Is Image Processing? Explain Fundamental Steps in Digital Image Processing5 pages
- Chapter Five Augmented Reality (AR) : Emerging Technologies100% (1)Chapter Five Augmented Reality (AR) : Emerging Technologies10 pages
- Chapter Four Internet of Things (Iot) : Iot Services+ Data+ Networks + SensorsNo ratings yetChapter Four Internet of Things (Iot) : Iot Services+ Data+ Networks + Sensors14 pages
- Perform Complex Test To Measure Engineering Properties of MaterialsNo ratings yetPerform Complex Test To Measure Engineering Properties of Materials82 pages
- Linux, KDE and Much Fun... : 1, Back Ground HistoryNo ratings yetLinux, KDE and Much Fun... : 1, Back Ground History12 pages
- Modern Linux Installation: A Mandrake Linux InstallNo ratings yetModern Linux Installation: A Mandrake Linux Install35 pages
- 5 - Lesson (Frequency Domain Image Processing)No ratings yet5 - Lesson (Frequency Domain Image Processing)58 pages
- Instruction I: Choose The Best Answer (2.5 Point Each)No ratings yetInstruction I: Choose The Best Answer (2.5 Point Each)5 pages
- Project Detecto!: A Real-Time Object Detection ModelNo ratings yetProject Detecto!: A Real-Time Object Detection Model3 pages
- DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING Lecture Series 1-Spring 2023No ratings yetDIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING Lecture Series 1-Spring 202341 pages
- BCA VI Sem Computer Graphics & MultimediaNo ratings yetBCA VI Sem Computer Graphics & Multimedia36 pages
- Enhancing Security Using Digital Image ProcessingNo ratings yetEnhancing Security Using Digital Image Processing9 pages
- Dept. of EEE, KUET EE 4235 Digital Image ProcessingNo ratings yetDept. of EEE, KUET EE 4235 Digital Image Processing49 pages
- Gis Modelling For Land Suitability Analysis For Urban Development ObjectivesNo ratings yetGis Modelling For Land Suitability Analysis For Urban Development Objectives14 pages
- Report On Image Processing 1 by Manan RawatNo ratings yetReport On Image Processing 1 by Manan Rawat2 pages
- Lecture 5 - Introduction To Didgital Image ProcessingNo ratings yetLecture 5 - Introduction To Didgital Image Processing25 pages
- ACUSON Sequoia 512 Ultrasound Platform: Advancing The Science of UltrasoundNo ratings yetACUSON Sequoia 512 Ultrasound Platform: Advancing The Science of Ultrasound10 pages
- A Database For Handwritten Text Recognition ResearchNo ratings yetA Database For Handwritten Text Recognition Research5 pages
- DIP Lecture 1 - Introduction To Digital Image ProcessingNo ratings yetDIP Lecture 1 - Introduction To Digital Image Processing4 pages
- Project Report Early Lung Cancer Detection Using Machine Learning and Image ProcessingNo ratings yetProject Report Early Lung Cancer Detection Using Machine Learning and Image Processing52 pages
- NIST Online Class: Pel7J003 Digital Image Processing Lecture-01No ratings yetNIST Online Class: Pel7J003 Digital Image Processing Lecture-0143 pages