0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 viewsUnit 5: Social Issues and Environmental Education
Unit 5: Social Issues and Environmental Education
Uploaded by
1611 Dmello Myron MosesThe document contains multiple choice questions about environmental issues and policies in India. Some key points covered include:
- The UN conference on the human environment was held in Stockholm in 1972.
- Several important Acts related to environmental protection and pollution control in India came into force in the 1970s-1980s, including the Environment Protection Act, Water Prevention and Control Act, and Wildlife Protection Act.
- Family welfare programs aiming to control population growth in India began in the 1950s-1960s by promoting a two-child norm per family.
- Key agencies involved in environmental regulation in India include the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs).
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Unit 5: Social Issues and Environmental Education
Unit 5: Social Issues and Environmental Education
Uploaded by
1611 Dmello Myron Moses0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 views6 pagesThe document contains multiple choice questions about environmental issues and policies in India. Some key points covered include:
- The UN conference on the human environment was held in Stockholm in 1972.
- Several important Acts related to environmental protection and pollution control in India came into force in the 1970s-1980s, including the Environment Protection Act, Water Prevention and Control Act, and Wildlife Protection Act.
- Family welfare programs aiming to control population growth in India began in the 1950s-1960s by promoting a two-child norm per family.
- Key agencies involved in environmental regulation in India include the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs).
Original Description:
6dhzjznz js snxnxjxnx nsmajs
Smsksms8sks
Original Title
Mskd.dmdkdkbshshzbhzjsnz
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document contains multiple choice questions about environmental issues and policies in India. Some key points covered include:
- The UN conference on the human environment was held in Stockholm in 1972.
- Several important Acts related to environmental protection and pollution control in India came into force in the 1970s-1980s, including the Environment Protection Act, Water Prevention and Control Act, and Wildlife Protection Act.
- Family welfare programs aiming to control population growth in India began in the 1950s-1960s by promoting a two-child norm per family.
- Key agencies involved in environmental regulation in India include the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs).
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 views6 pagesUnit 5: Social Issues and Environmental Education
Unit 5: Social Issues and Environmental Education
Uploaded by
1611 Dmello Myron MosesThe document contains multiple choice questions about environmental issues and policies in India. Some key points covered include:
- The UN conference on the human environment was held in Stockholm in 1972.
- Several important Acts related to environmental protection and pollution control in India came into force in the 1970s-1980s, including the Environment Protection Act, Water Prevention and Control Act, and Wildlife Protection Act.
- Family welfare programs aiming to control population growth in India began in the 1950s-1960s by promoting a two-child norm per family.
- Key agencies involved in environmental regulation in India include the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs).
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Unit 5: Social Issues and Environmental Education
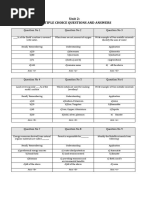
1. The UN conference on the human environment held in:
(a) Stockholm (b) Paris (c) London (d) Japan
2. The UN conference on the human environment held in:
(a) 1972 (b) 1985 (c) 1986 (d) 1981
3. The Environment Protection Act (EPA) came into force from:
(a) 1972 (b) 1985 (c) 1986 (d) 1981
4. The Air Prevention and control Act came into force from:
(a) 1972 (b) 1985 (c) 1986 (d) 1981
5. The pollution level in atmosphere is measured in:
(a) Parts per million (b) milligram
(c) Microgram per cubic meter (d) All of the above
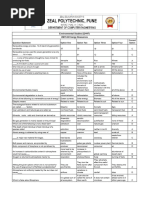
6. The motor vehicle act was passed in:
(a) 1972 (b) 1948 (c) 1939 (d) 1981
7. The Water Prevention and control Act came into force from:
(a) 1974 (b) 1964 (c) 1984 (d) 1994
8. The Wildlife Protection Act came into force from:
(a) 1972 (b) 1982 (c) 1952 (d) 1981
9. The Amendment to the Wildlife Protection Act came into:
(a) 2000 (b) 2002 (c) 2001 (d) 2003
10. The Amendment to the Wildlife Protection Act prevents the use of resources:
(a) Naturally (b) Artificially (c) Commercially (d) All of the above
11. The Wildlife Protection Act is adopted by all except:
(a) Jammu (b) Kashmir(c) Nagaland (d) All the above
12. The Forest Prevention and control Act came into force from:
(a) 1960 (b) 1948 (c) 1980 (d) 1990
13. Family welfare program (FWP) came in:
(a) 1961 (b) 1981 (c) 1951 (d) 1990
14. According to FWP, one family should not have children more than:
(a) One (b) Two (c) Three (d) Four
15. Today’s need suggest having:
(a) Only one child (b) Many children (c) Two children (d) Four children
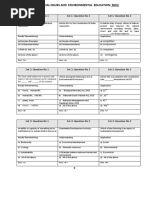
16. A group of individuals of a particular area at a specific time is referred as:
(a)Population (b) Pollution (c) Community (d) Society
17. The level of birth defined as an index is called
(a) Migration (b) Emigration (c) Natality (d) Mortality
18. The level of death defined as an index is called
(a) Migration (b) Emigration (c) Natality (d) Mortality
19. The movement of inhabitants from one place to another is called
(a) Migration (b) Emigration (c) Transmigration (d) Remigration
20. The movement of inhabitants back to their home country is called
(a) Migration (b) Emigration (c) Transmigration (d) Remigration
21. The movement of inhabitant’s entry a new country to settle permanently is:
(a) Migration (b) Emigration (c) Transmigration (d) Immigration
22. The movement of inhabitant’s leaving a country to settle in another country:
(a) Migration (b) Emigration (c) Transmigration (d) Immigration
23. The movement of inhabitants from densely populated area into an area with
lesser population is called
(a) Migration (b) Emigration (c) Transmigration (d) Immigration
24. The movement of inhabitants from villages to cities is called
(a) Migration (b) Emigration (c) Transmigration (d) Immigration
25. The Indian tradition believes in __________ of nature.
(a) Destruction (b) Extraction (c) Pollution (d) Preservation
26. In India several Acts were passed from:
(a) 1970-1980 (b) 1969-1989 (c) 1972-1986 (d) None of the above
27. Environmental laboratories are established by:
(a) State Government (b) Central Government
(c) Municipal Corporation (d) None of the above
28. EIA stand for:
(a) Environmental Impact Assessment (b) Economical Investment Assessment
(c) Evaluation Important Assessment (d) None of the above
29. CPCB stand for:
(a) Control of pollution by Central Bureau
(b) Central pollution control board
(c) Central Population Control Bank (d) None of the above
30. SPCB stand for
(a) State of pollution by Central Bureau
(b) State pollution control board
(c) State Population Control Bank (d) None of the above
31. The chairman of CPCB is nominated by:
(a) Central Government (b) State Government
(c ) Prime Minister of India (d) Chief Justice of supreme court
32. The chairman of SPCB is nominated by:
(a) Central Government (b) State Government
(c ) Prime Minister of India (d) Chief Justice of supreme court
33. The chairman of Wildlife Advisory board is nominated by:
(a) Central Government (b) State Government
(c ) Prime Minister of India (d) Chief Justice of supreme court
34. National Human Rights commission in India is headed by:
(a) Central Government (b) State Government
(c ) Prime Minister of India (d) Chief Justice of supreme court
35.As per EPA 1986, environment does not include:
(a) Air (b) Space (c) Water (d) Land
36. Carbon credit is meant for ________
(a) Deforestation (b) Protection of environment
(c) Rural infrastructure (d) Diamond trading
37. Which state has made it compulsory to harvest rain water
for all buildings?
(a) Rajasthan (b) West Bengal (c) Tamilnadu (d) Maharashtra
38. In Mumbai what is the minimum plot area for which rain water
harvesting is mandatory?
(a) 2000 Sq.m (b) 500 Sq.m (c) 1000 Sq.m (d) 1500 Sq.m
39. Noise pollution has been inserted in the Air Prevention and
Control Act in:
(a) 1987 (b) 1977 (c) 1967 (d) 1957
40. WWF international is located in _______
(a) India (b) America (c) Canada (d) Switzerland
41. Runoff water from surface is conserved by:
(a) Rain water Conservation (b) Rain water harvesting
(c) Water storage (d) none of the above
43. Shortage of water faced can be solved by:
(a)Well digging (b) Rain water harvesting
(c) Water storage (d) none of the above
44. The main advantage of water shed approach is _____
(a) High cost (b) Time consuming
(c) Environmental friendly (d) none
45. The prime objective of watershed management is focus on water:
(a) Utilization (b) Conservation (c) Analysis (d) None of the above
46. _________of rivers help to redistribute water logging:
(a) Interlinking (b) Dam (c) Diverting water (d) none of the above
47. Article _______of India Constitution deals with fundamental duties:
(a) 48-A (b) 5-A (g) (c) 21 (d) 19
48. ________technology is highly useful for Environment and health
(a) Digital (b) Chemical (c) Information (d) Computational
49. An organization that works outside government ____
(a) NGO (b) Nature lovers (c) Activists (d) Antisocial
50. NGO has freedom to take issues in _____
(a) Society (b) Parliament (c) Municipality (d) None of the above
You might also like
- EVS Unit 3 MCQDocument5 pagesEVS Unit 3 MCQTanishka PatilNo ratings yet
- Museum: The BasicsDocument4 pagesMuseum: The Basicszenzen10% (1)
- EST MCQ CH 5Document23 pagesEST MCQ CH 51213- sanjana chavanNo ratings yet
- Est MCQ ImpDocument37 pagesEst MCQ ImpRambo GamingNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain - Environmental Science Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocument3 pagesAcid Rain - Environmental Science Questions and Answers - SanfoundrySangNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Environmental Pollution MCQDocument10 pagesUnit IV Environmental Pollution MCQPranav GawandeNo ratings yet
- Est Chapter 1 MCQDocument10 pagesEst Chapter 1 MCQPavan MaliNo ratings yet
- EVS - Unit 2 MCQDocument15 pagesEVS - Unit 2 MCQTanishka Patil100% (2)
- Module-5 - Environmental Acts Objective Questions & AnswerDocument5 pagesModule-5 - Environmental Acts Objective Questions & Answervamshi krishnaNo ratings yet
- EVSMCQ's On Unit 4Document21 pagesEVSMCQ's On Unit 459himanshu yadavNo ratings yet
- Est MCQ Mega PDF 1Document650 pagesEst MCQ Mega PDF 1Omkar Gore100% (1)
- Est - MCQ 560 827Document268 pagesEst - MCQ 560 827yopyyt120No ratings yet
- MCQs 22447Document45 pagesMCQs 22447Yash PawarNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Sample Questions For EVS (22447) I SchemeDocument8 pagesTopic 1: Sample Questions For EVS (22447) I SchemeShrikant ManeNo ratings yet
- Est Msbte Imp McqsDocument7 pagesEst Msbte Imp McqsHARSH PATLENo ratings yet
- 22447-mcq-EVS MCQ With AnswersDocument20 pages22447-mcq-EVS MCQ With Answerskomal ghodkeNo ratings yet
- Est 22447 QB 051019Document43 pagesEst 22447 QB 051019Priya YadavNo ratings yet
- Est U-2 MCQDocument9 pagesEst U-2 MCQVinod MarneNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Environmental Studies EST 22447 Unit Test 1Document12 pagesMechanical Environmental Studies EST 22447 Unit Test 1Arvind YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Environmental Pollution Notes, MCQ & QuestionsDocument11 pagesUnit-4 Environmental Pollution Notes, MCQ & QuestionsMohana NNo ratings yet
- CO1 - MCQsDocument13 pagesCO1 - MCQsMARUF SHAIKHNo ratings yet
- EST MCQ 1 ST UNITDocument23 pagesEST MCQ 1 ST UNITDhanesh Uday PujareNo ratings yet
- Advance Java MCQDocument107 pagesAdvance Java MCQSabesta Andresta BilluNo ratings yet
- MAN Mcqs 22509 Management MCQs MSBTE Exam MCQs - MSBTE All Clear Msbte Solution All Diploma Study MaterialDocument16 pagesMAN Mcqs 22509 Management MCQs MSBTE Exam MCQs - MSBTE All Clear Msbte Solution All Diploma Study Materialdonnoorain69No ratings yet
- Et Ut2 Question BankDocument13 pagesEt Ut2 Question BankDrupad DhamdhereNo ratings yet
- Django Lab1 ComponentDocument5 pagesDjango Lab1 Componentsunil.iseNo ratings yet
- Msbtes E-Content: Program - Civil Engineering Program Code - Ce Course-Environmental Studies Course Code - 22447Document21 pagesMsbtes E-Content: Program - Civil Engineering Program Code - Ce Course-Environmental Studies Course Code - 22447Aditya Mhaisale100% (1)
- Sample PaperDocument4 pagesSample PaperHarsh MouryNo ratings yet
- AJP (22517) Unit Test 2 CMIF5I 2022-23Document4 pagesAJP (22517) Unit Test 2 CMIF5I 2022-23Dhaval SarodeNo ratings yet
- Basics of Forensics QuestionsDocument12 pagesBasics of Forensics QuestionsOmckar BadekaarNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Winter 2022Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Winter 2022harshy0816No ratings yet
- Nis 22620 QB 050320Document9 pagesNis 22620 QB 050320OMENo ratings yet
- EST MCQ 2 ST UNITDocument18 pagesEST MCQ 2 ST UNITDhanesh Uday PujareNo ratings yet
- Est MCQ 3rd UnitDocument21 pagesEst MCQ 3rd UnitDhanesh Uday PujareNo ratings yet
- 12 Barrage Projects and Dams On Godavari RiverDocument9 pages12 Barrage Projects and Dams On Godavari RiverPisini RajaNo ratings yet
- WMN CH 2 NotesDocument14 pagesWMN CH 2 Notessonavanepranitee100% (1)
- Course-Environmental Studies Course Code - 22447 5. Social Issues and Environmental Education Unit Outcome - UO 5a, 5b and 5cDocument14 pagesCourse-Environmental Studies Course Code - 22447 5. Social Issues and Environmental Education Unit Outcome - UO 5a, 5b and 5cPathanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank ETIDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank ETIVaibhavNo ratings yet
- CO3 - MCQsDocument12 pagesCO3 - MCQsPranav MhatreNo ratings yet
- Evs Module 5 MCQDocument19 pagesEvs Module 5 MCQHisham AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Unit V Social Issue and Environmental Education MCQDocument4 pagesUnit V Social Issue and Environmental Education MCQPranav Gawande100% (1)
- Unit1 BASICS OF PCS and GSMDocument39 pagesUnit1 BASICS OF PCS and GSMRashmika MandannaNo ratings yet
- MCOs On 1stDocument16 pagesMCOs On 1stmy pcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (NP)Document13 pagesChapter 3 (NP)Prachiti PatilNo ratings yet
- Weekly Diary MegaprojectDocument13 pagesWeekly Diary Megaprojectdhanashrisubhedar1112No ratings yet
- Ar6015 - Spa-Mcq BankDocument17 pagesAr6015 - Spa-Mcq BankSrilakshmi PriyaNo ratings yet
- AWT Q & ADocument22 pagesAWT Q & AMasoom RezaNo ratings yet
- Department of Collegiate and Technical EducationDocument7 pagesDepartment of Collegiate and Technical EducationHarsha Samagara50% (2)
- 2022 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document3 pages2022 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Shubham ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- ETI U-II Notes - CDocument48 pagesETI U-II Notes - Cshraddha_mundadada100% (1)
- Exercise 1. Write A Program To Change The Background Colour of Applet When User Performs Events Using MauseDocument2 pagesExercise 1. Write A Program To Change The Background Colour of Applet When User Performs Events Using MauseGanesh EkambeNo ratings yet
- AJPDocument10 pagesAJPRupesh Bavge100% (1)
- Iot Based Air Quality - 1Document17 pagesIot Based Air Quality - 1ALNATRON GROUPSNo ratings yet
- EST ReportDocument20 pagesEST Reportkrishna kumavatNo ratings yet
- MSWM UNIT V Objective Type Question Bank WebsiteDocument7 pagesMSWM UNIT V Objective Type Question Bank Websitedhanashri musaleNo ratings yet
- MTH174 Unit 2 3 Set 2mcqsDocument6 pagesMTH174 Unit 2 3 Set 2mcqsgareebiopNo ratings yet
- 2016 Summer Model Answer PaperDocument29 pages2016 Summer Model Answer Papersurajmore2368No ratings yet
- Evironmental Studies Vtu Question Bank Unit 1Document15 pagesEvironmental Studies Vtu Question Bank Unit 1rachitha sNo ratings yet
- Management MCQ'S: By:-Vishal ChavareDocument28 pagesManagement MCQ'S: By:-Vishal Chavare666-Sameer YeleNo ratings yet
- Evs QB 2Document7 pagesEvs QB 2adithidhatri1219No ratings yet
- Module 5 MCQDocument5 pagesModule 5 MCQBriarNo ratings yet
- Biological Characteristics of Plant Species in Tehsil Takht-e-Nasrati, PakistanDocument6 pagesBiological Characteristics of Plant Species in Tehsil Takht-e-Nasrati, PakistanOpenaccess Research paperNo ratings yet
- W 13Document12 pagesW 13matsiasNo ratings yet
- Birding 2024 JunDocument72 pagesBirding 2024 Junjahaziel22No ratings yet
- Handbook Oil PalmDocument87 pagesHandbook Oil PalmMohd Farid Mohd Nor80% (5)
- Scientific EnglishDocument50 pagesScientific EnglishatikindNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W9Document7 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W9Patricia Ann MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Basics of High-Performance Building Design - Sam Hui PDFDocument60 pagesBasics of High-Performance Building Design - Sam Hui PDF185412No ratings yet
- Full Download Official Guide to Texas State Parks and Historic Sites Revised Edition Laurence Parent PDF DOCXDocument50 pagesFull Download Official Guide to Texas State Parks and Historic Sites Revised Edition Laurence Parent PDF DOCXchantpareed100% (6)
- 1 Senegal Report Country WiseDocument86 pages1 Senegal Report Country WiseMisgatesNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Bahasa Inggris (Coral Reef and Coral Community Fish)Document7 pagesJurnal Bahasa Inggris (Coral Reef and Coral Community Fish)TomyPetrusNo ratings yet
- Rau IAS Prelims Campass 2019Document164 pagesRau IAS Prelims Campass 2019Peera MohidinNo ratings yet
- Blue WhaleDocument2 pagesBlue Whale23. Muhammad Ammar NashwanNo ratings yet
- Draft National Water Policy 2012Document3 pagesDraft National Water Policy 2012Gargi NanjanathNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS - Natural Resources & Environmental Law: Atty. Donna Z. GasgoniaDocument5 pagesSYLLABUS - Natural Resources & Environmental Law: Atty. Donna Z. GasgoniaMikki ManiegoNo ratings yet
- Conf. 9.24: (Rev. Cop17) Criteria For Amendment of Appendices I and IiDocument18 pagesConf. 9.24: (Rev. Cop17) Criteria For Amendment of Appendices I and Iileonita soebagioNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Chapter 10 - The Urban WorldDocument27 pagesLecture - Chapter 10 - The Urban WorldErgita KokaveshiNo ratings yet
- 1234Document6 pages1234Kuldeepsinh J. DodiyaNo ratings yet
- Brief Notes On The Meaning and Importance of Food Chain and Food WebDocument2 pagesBrief Notes On The Meaning and Importance of Food Chain and Food WebSumitNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan CookingDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan CookingRia Lopez100% (5)
- Watershed WebquestDocument4 pagesWatershed Webquestapi-264874516No ratings yet
- Stewards Winter 2009Document28 pagesStewards Winter 2009snrecommNo ratings yet
- High and Low BiodiversityDocument60 pagesHigh and Low BiodiversityJohn Lyndel AlolonNo ratings yet
- Bennachie Trails Map PDFDocument1 pageBennachie Trails Map PDFMaisie JaneNo ratings yet
- Society For The Conserv Ation of Philippine Wetlands. IncDocument23 pagesSociety For The Conserv Ation of Philippine Wetlands. IncKris OliquinoNo ratings yet
- CIP Annual Report 2000Document66 pagesCIP Annual Report 2000cip-libraryNo ratings yet
- IELTS Latest EssaysDocument7 pagesIELTS Latest Essayssanand11No ratings yet
- Ecology Lesson Plan 1Document4 pagesEcology Lesson Plan 1Michael Van EttenNo ratings yet
- The Fox Is A Hound: Patriotic Jim PeaseDocument20 pagesThe Fox Is A Hound: Patriotic Jim PeasenewspubincNo ratings yet
- Green HRM: An Innovative Approach To Environmental SustainabilityDocument6 pagesGreen HRM: An Innovative Approach To Environmental SustainabilityAnis ShaikhNo ratings yet