VCM
VCM
Uploaded by
Learners DotcomCopyright:
Available Formats
VCM
VCM
Uploaded by
Learners DotcomCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
VCM
VCM
Uploaded by
Learners DotcomCopyright:
Available Formats
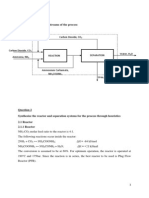
VINYL CHLORIDE MONOMER (VCM) PRODUCTION UNIT
(VCM production technology reported in a book by Seider et al. (1998))
Pure ethylene, stored as a gas at 70 °F and 1000 psia, with a flow rate of 20 tons/hr, and pure chlorine,
stored as a liquid at 70 °F and 150 psia, with a flow rate of 50 tons/hr enter the mixer operated at 2 atm. The
mixer outlet then goes to the reactor operating at 363 K and 1 atm. In this stoichiometric reactor, the
following chlorination reaction occurs with 98% conversion of ethylene to 1, 2-dichloroethane:
C2H4 + Cl2 = C2H4Cl2
ethylene chlorine dichloroethane
In the next, mixer operated at 1.4 atm allows the mixing of the recycled stream from splitter with the reactor
product. The outlet stream of this mixer is then condensed fully to liquid phase in a condenser at 298 K
before being pumped to an evaporator. The pump has discharged the liquid at 26 atm. The evaporator
performs the phase change operation and then the vapor temperature is increased in the same unit to 515 K.
In the subsequent step, outlet stream of evaporator is introduced in the second reactor (RStoic) in which the
following pyrolysis reaction occurs:
C2H4Cl2 = C2H3Cl + HCI
dichloroethane VCM hydrogen chloride
The dichloroethane is converted to VCM and it takes place spontaneously at 773 K and 25 atm with 65%
conversion. To reduce carbon deposition in the heat exchanger, the hot vapor stream leaving the reactor is
quenched in a quencher yielding a saturated vapor stream at 443 K. Quencher effluent stream is condensed
to liquid phase in a heat exchanger at 279 K and then fed to a DSTWU column. In the next, bottom stream
of 1st column is introduced in another DSTWU column. The first column mainly separates HCl from other
components, while the second column purifies VCM from the rests. Both the distillation columns have 10
theoretical stages (including condenser and reboiler) and a total condenser along with the specifications,
shown in the following Table.
% Recovery of LK/HK in distillate Pressure (atm)
Block Light key (LK) Heavy key (HK) Condenser Reboiler
1st column 99.9% of HCI 0.1% of VCM 20 22
2nd column 99.9% of VCM 0.1% of dichloroethane 7.5 8
Finally, a Splitter splits bottom stream of second column to ensure the recycling of 99.999% of bottom as
recycle stream to second mixer. A purge stream is introduced to prevent accumulation of unreacted
components. Using the POLYSRK property method, simulate the complete plant to compute the
composition of all streams.
You might also like
- 01 Refinery BasicsDocument94 pages01 Refinery Basicsjtichemical100% (1)
- Plant Design ProjectDocument8 pagesPlant Design ProjectAbhishek SagarNo ratings yet
- Assignment Aspen PlusDocument8 pagesAssignment Aspen PlusVinayak PathakNo ratings yet
- Distillation Aspen HysysDocument66 pagesDistillation Aspen HysysCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Full Report Assignment 2Document34 pagesFull Report Assignment 2Miss Kycha YssabelNo ratings yet
- Urea SynthesisDocument11 pagesUrea SynthesisSean Suraj JeremiahNo ratings yet
- MEK - Methods 2520of 2520productionDocument4 pagesMEK - Methods 2520of 2520productionJob MateusNo ratings yet
- FCC Facilities KFUPMDocument8 pagesFCC Facilities KFUPMAMANo ratings yet
- Problems Associated in Tablet ManufacturingDocument12 pagesProblems Associated in Tablet ManufacturingRajib Chowdhury100% (1)
- Plant DesignDocument39 pagesPlant DesignHaiqal Aziz100% (2)
- Flowsheeting Sheet (1) 21/2/2015: Ag-CatalystDocument5 pagesFlowsheeting Sheet (1) 21/2/2015: Ag-CatalystAhmed Hamdy Khattab100% (1)
- Chapter 2 (Blueprint)Document4 pagesChapter 2 (Blueprint)John Patrick Sanay NunezNo ratings yet
- Design (Ch.1 Problems)Document5 pagesDesign (Ch.1 Problems)John UnkNo ratings yet
- Dehydrogenation Process Description المشروعDocument5 pagesDehydrogenation Process Description المشروعsaeed909909No ratings yet
- 1) Introduction To VCM Process: 1.1vinyl Chloride From AcetyleneDocument12 pages1) Introduction To VCM Process: 1.1vinyl Chloride From AcetyleneSaleamlak ZerihunNo ratings yet
- Simulation 8Document2 pagesSimulation 8moulitechNo ratings yet
- Tame Process BasicsDocument10 pagesTame Process BasicsD'Bayour Toke Osuolale100% (1)
- Lecture PIKDocument20 pagesLecture PIKKaldera MarchelinaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1: Chem 2002 - Process Systems Analysis - 2016-2017Document20 pagesTutorial Sheet 1: Chem 2002 - Process Systems Analysis - 2016-2017ajali1957No ratings yet
- Direct ChlorinationDocument2 pagesDirect ChlorinationAshley Hartzenberg100% (1)
- Anidrido OftalicoDocument3 pagesAnidrido OftalicoLuisAntonioDavilaZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Urea Plant TrainingDocument34 pagesUrea Plant TrainingUtkarsh Sharma100% (1)
- 2 NDDocument5 pages2 NDfarkhan_kergon3137No ratings yet
- B59EI Mechanical Engineering Science 9 - Thermodynamics Tutorial - Regeneration #1Document1 pageB59EI Mechanical Engineering Science 9 - Thermodynamics Tutorial - Regeneration #1hamza2595No ratings yet
- Che F244 1183 C 2015 2Document4 pagesChe F244 1183 C 2015 2shubhamNo ratings yet
- Indian Coal To Chemicals New Rev8Document167 pagesIndian Coal To Chemicals New Rev8Swarnim RajNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Production of Cyclohexane-Oxime Via Cyclohexanone AmmoximationDocument9 pagesCatalytic Production of Cyclohexane-Oxime Via Cyclohexanone AmmoximationKevin ThomasNo ratings yet
- 2-Eha PRCS1Document45 pages2-Eha PRCS1MARISSE LYN DORADONo ratings yet
- Process Descp. Start-Up OperationDocument24 pagesProcess Descp. Start-Up OperationManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Simulation Lab Problem-1: Chem 2002 - Process Systems Analysis - 2016-2017Document5 pagesSimulation Lab Problem-1: Chem 2002 - Process Systems Analysis - 2016-2017ajali1957No ratings yet
- Manufacture of UreaDocument36 pagesManufacture of UreaNandadulal GhoshNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines: 363 P. Casal ST., Quiapo, ManilaDocument10 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines: 363 P. Casal ST., Quiapo, ManilaJohannah Jane Abuel0% (1)
- Procsses and Numerical ProblemsDocument80 pagesProcsses and Numerical Problemslipit83749No ratings yet
- Taller IV - Primera Ley Sistemas Abiertos Primera ParteDocument2 pagesTaller IV - Primera Ley Sistemas Abiertos Primera ParteSteven Gonzalez CardonaNo ratings yet
- CL405 2021 End Term ExaminationDocument4 pagesCL405 2021 End Term ExaminationArpit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Urea ProjectDocument17 pagesUrea ProjectAbdo Shaaban100% (2)
- VC ManufactureDocument20 pagesVC ManufactureCiara AlarcónNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument44 pagesIntroductionJudebarb94No ratings yet
- Process SelectionDocument8 pagesProcess SelectionSwathi SNo ratings yet
- Shantanu DasDocument10 pagesShantanu DasarunkdevassyNo ratings yet
- 2020 CHEE2001 Week 8 Tutorial SheetDocument6 pages2020 CHEE2001 Week 8 Tutorial SheetMuntaha ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Production of Ethylene GlycolDocument15 pagesProduction of Ethylene Glycoldrami9475% (4)
- Removal of Benzene From GasolineDocument24 pagesRemoval of Benzene From GasolineNicholas Cecil Munsami100% (1)
- Exam 25/06/2018: Exercise 1 (10 Points)Document1 pageExam 25/06/2018: Exercise 1 (10 Points)KuloNo ratings yet
- 2017CHE008 DetailedProcessDescription1Document17 pages2017CHE008 DetailedProcessDescription1Xi Liinett AqkoNo ratings yet
- Power PlantDocument63 pagesPower PlantSatheesh Sekar100% (4)
- Review For CL 306Document2 pagesReview For CL 306malakaramiitNo ratings yet
- CBE 202 HW 2 (Revised)Document2 pagesCBE 202 HW 2 (Revised)김민성No ratings yet
- U3-1 Recycling Purge BypassDocument11 pagesU3-1 Recycling Purge BypassValeria De la BorbollaNo ratings yet
- DWSIM Abstract PDFDocument3 pagesDWSIM Abstract PDFredagalihNo ratings yet
- 3 - Process Flow Diagram Part II Vinyle Chloride ManufactureDocument19 pages3 - Process Flow Diagram Part II Vinyle Chloride ManufactureOmar Al-abadi100% (1)
- National Fertilizers Limited Nan Gal PunjabDocument3 pagesNational Fertilizers Limited Nan Gal PunjabNirmanyu JamwalNo ratings yet
- ME 401 Applied Thermodynamics-Problems PDFDocument5 pagesME 401 Applied Thermodynamics-Problems PDFVikasKumarSharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 PDFDocument1 pageAssignment 1 PDFRoydia SimanNo ratings yet
- DMCDocument12 pagesDMCShariq AliNo ratings yet
- Taller Iv - Primera Ley Sistemas Abiertos Primera ParteDocument2 pagesTaller Iv - Primera Ley Sistemas Abiertos Primera ParteJorge Gomez0% (1)
- Process Description of Ammonia PlantDocument12 pagesProcess Description of Ammonia PlantSridharNo ratings yet
- Assignments 4SY2015 2016Document6 pagesAssignments 4SY2015 2016Carlito H. Monasque Jr.No ratings yet
- ChE328 HW5 2024Document2 pagesChE328 HW5 2024Ayla LâlNo ratings yet
- PDDocument2 pagesPDnur_ika_1No ratings yet
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersFrom EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Energy Conversion for Electricity and Coproducts: Principles, Technologies, and EquipmentFrom EverandSustainable Energy Conversion for Electricity and Coproducts: Principles, Technologies, and EquipmentNo ratings yet
- C - Fluid Mechanics - PP - AnsDocument4 pagesC - Fluid Mechanics - PP - Anszyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Coulson & Richardson's Chemical Engineering. Vol. 6, Chemical Engineering Design, 4th Ed-219-223 (1) - 3Document1 pageCoulson & Richardson's Chemical Engineering. Vol. 6, Chemical Engineering Design, 4th Ed-219-223 (1) - 3yeri abatamanNo ratings yet
- 2013 Fouling 1Document9 pages2013 Fouling 1mitsuboshi702No ratings yet
- Sample Problem #9Document9 pagesSample Problem #9Dozdi100% (8)
- Wärtsilä MSF Marine LowResDocument7 pagesWärtsilä MSF Marine LowResBarbara VasconcelosNo ratings yet
- SRU Unit Waste Heat BoilerDocument6 pagesSRU Unit Waste Heat BoilerMaheesha Gunathunga100% (1)
- CE 3107-Hydraulics and Hydraulic StructuresDocument2 pagesCE 3107-Hydraulics and Hydraulic StructuresPranto KhanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Heat TransferDocument12 pagesReviewer in Heat TransferKristian Allen B. DomingoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4: Material Balance BasisDocument11 pagesChapter - 4: Material Balance BasisFahad KhokharNo ratings yet
- BioreactorDocument3 pagesBioreactorSTAFF JINNAH COLLEGENo ratings yet
- Operational Flexibility of A CDocument27 pagesOperational Flexibility of A CKim Howard CastilloNo ratings yet
- VST TBV Non-Contact CATALOG 2021-HDDocument7 pagesVST TBV Non-Contact CATALOG 2021-HDJaydeep PanchalNo ratings yet
- P5Document1 pageP5geneveve colasitoNo ratings yet
- S2021 Midterm SolutionsDocument9 pagesS2021 Midterm SolutionsNaseri ShaunNo ratings yet
- Process Engineer Kuala Lumpur MY1906Document1 pageProcess Engineer Kuala Lumpur MY1906Nguyen SangNo ratings yet
- Of Vortex Generators"": Final ReportDocument7 pagesOf Vortex Generators"": Final Reportramazan akyolNo ratings yet
- Mahler AGS Broschuere 0920 A4 ViewDocument20 pagesMahler AGS Broschuere 0920 A4 Viewchen19111005 KFUEITNo ratings yet
- Assignment4 CastingDocument2 pagesAssignment4 CastingAkashkumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Data KP Fix Terbaru (AutoRecovered)Document21 pagesData KP Fix Terbaru (AutoRecovered)amelia mardhotillahNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORT PHENOMENA - Unit 4 - NotesDocument47 pagesTRANSPORT PHENOMENA - Unit 4 - NotesRathi ManiNo ratings yet
- Offshore Pipelines Design, Installation, and Maint... - (1 Introduction)Document2 pagesOffshore Pipelines Design, Installation, and Maint... - (1 Introduction)Sujan KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Sulfur and Sulfuric AcidDocument20 pagesSulfur and Sulfuric AcidZakia LuthfianaNo ratings yet
- Term and ProblemDocument23 pagesTerm and ProblemJohn Errol MarinoNo ratings yet
- Cen29305 ch00-fmDocument24 pagesCen29305 ch00-fmhadjer14No ratings yet
- 1.0 Reaction KineticsDocument142 pages1.0 Reaction KineticsKhairul Aswari Ab RahmanNo ratings yet
- ARE Module 3 NotesDocument47 pagesARE Module 3 NotesSamyak DhutaleNo ratings yet
- Tinta SprayDocument9 pagesTinta SprayManuel F O MouraNo ratings yet