Composition and Construction of ECD-V3 Pump System
Composition and Construction of ECD-V3 Pump System
Uploaded by
Вячеслав ГлушакCopyright:
Available Formats
Composition and Construction of ECD-V3 Pump System
Composition and Construction of ECD-V3 Pump System
Uploaded by
Вячеслав ГлушакCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Composition and Construction of ECD-V3 Pump System
Composition and Construction of ECD-V3 Pump System
Uploaded by
Вячеслав ГлушакCopyright:
Available Formats
This session describes the construction and operation of the ECD-V3 pump with respect to the pumping and
injection of fuel.
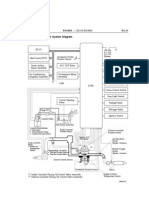
1 Composition and Construction of ECD-V3 Pump System
Overflow Sensor Position
Valve
Fuel Temperature
Sensor Solenoid Spill
Feed
Pump NE Sensor Valve
Fuel Filter
Intake
Temperature
Sensor Crankshaft
Position
Sensor
Throttle
Nozzle Accelerator
Pressure Chamber Coolant Position
Temperature Sensor
Delivery Valve Sensor
Plunger Timing Control Valve
Intake
Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor
Sensor Signal Sensor Signal
(NE Signal)
Engine Crankshaft
ECU
Position Sensor
Solenoid Spill Valve Actuation Signal
• Solenoid Spill Valve (SPV) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - This actuator, which performs the function of the spill ring of the
previous distributor type pump, controls the injection quantity.
• NE Sensor (NE) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - This sensor, which detects the camshaft position of the pump,
also inputs the number of revolutions of the pump (one-half the
number of revolutions of the engine) to the engine ECU.
• Fuel Temperature Sensor (THF) - - - - - - - - - - This sensor detects the temperature of the fuel.
• Correction Resistor or ROM - - - - - - - - - - - - - This part makes corrections to the injection quantity and injection timing.
• Timing Control Valve (TCV)- - - - - - - - - - - - - - This actuator, which performs the function of the timer of the
previous distributor type pump, controls the injection timing.
Fuel Temperature Sensor (THF) Solenoid Spill Valve (SPV)
NE Sensor (NE)
Timing Control Valve
Pressure Chamber Timer Piston (TCV)
Regulating Valve
Cam Plate Delivery Pump
Plunger
9 SERVICE TECH Vol.465 03-4
2 Operation of ECD-V3 Pump
2-1 Fuel Suction and Injection
The mechanism for the suction and pumping/distribution of the fuel is basically the same as for the previous
distributor type pump. However, it differs in the aspect that it controls the fuel injection quantity by opening and
closing a solenoid spill valve by way of electric signals. The solenoid spill valve is provided in the passage that
links the pump chamber with the pressure chamber.
Suction Stroke
As the plunger descends, it draws fuel from the suction port into the pressure chamber. At this time, the solenoid
spill valve is energized and closed.
Pump Chamber Solenoid Spill Valve
Speed Sensor Cam Plate (closed)
Roller Ring
Suction Port (open)
Suction Port : open Pulsar
Distribution Port : closed
Solenoid Spill Valve: closed Pressure Chamber
to Nozzle
Drive Shaft Plunger Distribution Port (closed)
Pumping Stroke (Injection)
The plunger ascends while rotating, in order to pressurize and pump the fuel in the pressure chamber.
Solenoid Spill Valve
(closed)
Suction Port (closed)
Suction Port : closed
Distribution Port : open
Solenoid Spill Valve: closed
Distribution Port (open)
End of Injection
When the solenoid spill valve is no longer energized, the spill valve opens. Then, the high-pressure fuel in the
pressure chamber spills into the pump chamber, thus reducing its pressure and ending the injection of fuel.
Solenoid Spill Valve
(open)
Suction Port (closed)
Suction Port : closed
Distribution Port : open
Solenoid Spill Valve: open
Distribution Port (open)
SERVICE TECH Vol.465 03-4
10
3 Solenoid Spill Valve (SPV)
The solenoid spill valve, which is located in the passage that links the pump chamber of the injection pump with the
pressure chamber, is a type of solenoid valve that turns ON/OFF (opens and closes) in accordance with the signals
from the engine ECU.
When the coil of the solenoid spill valve is energized, the spill valve closes, thus closing the passage that links the
pressure chamber with the pump chamber. As a result, the plunger pressurizes the fuel in the pressure chamber and
pumps it into the nozzles through which the fuel is injected.
When the solenoid spill valve is no longer energized, the spill valve opens, thus opening the passage between the
pressure chamber and pump chamber. The pressurized fuel spills into the pump chamber, thus decreasing the
pressure in the pressure chamber and ending the pumping of fuel.
Solenoid Spill Valve
Coil
Pump Chamber
Coil energized ........ valve closed
Valve (during suction or injection)
Coil non-energized . valve open
Pressure
(end of injection)
Chamber
to Nozzle
Plunger
3-1 Types of Solenoid Spill Valves
The solenoid spill valve is directly related to the control of the fuel injection volume. Therefore, it must provide high
levels of precision, quick response, and pressure resistance, as well as a large spill volume.
There are two types of solenoid spill valves: the pilot valve type, and the direct-acting solenoid valve type. The
direct-acting solenoid valve type is widely used today.
The pumps are classified into the ECD-V3, ECD-V3 (ROM), and ECD-V3 direct-acting valve types, depending on
the type of solenoid spill valve and the injection volume correction method that are being used.
Correction
Type Characteristic Solenoid Spill Valve (SPV)
Method
Correction
An externally mounted correction Resistor
ECD-V3 resistor is able to correct the final
injection quantity.
The data of an externally mounted
ROM
ROM is used to correct the final injection Pilot Valve Type
ECD-V3
quantity. It realizes a higher precision
(ROM)
level of correction than the previous type
(correction resistor).
ROM
ECD-V3 A direct-acting SPV is used to achieve
Direct-Acting Valve high levels of response and spill
Types performance.
Direct-Acting Type
11 SERVICE TECH Vol.465 03-4
Pilot Valve Type
This type consists of a main valve, pilot valve, and a solenoid coil. When the solenoid coil is energized, it pulls on
the pilot valve (downward in the diagram), thus closing the pilot spill port.
At this time, the high-pressure fuel, which flowed in from the pressure chamber via the restriction, fills the main
valve. The resulting hydraulic pressure firmly closes the main valve.
When the solenoid coil is no longer energized, the pilot valve opens, allowing the fuel in the main valve to spill
through the pilot spill port. Thus, the pressure in the main valve decreases suddenly. This pressure difference
causes the main valve to open considerably, effectively ending the injection of fuel.
Pilot Valve Type
Solenoid Spill Valve
Control Spring
Coil
Pilot Spring
Main Spring
Pilot Valve
Main Valve
Plunger
Pressure Chamber
Direct-Acting Solenoid Valve Type
This solenoid spill valve provides a quick response at a higher level of precision. It consists of a spool valve and
a solenoid coil. The spool valve, which acts directly in accordance with electric signals, opens and closes the
passage that links the pressure chamber and the pump chamber.
Cross Section View Enlargement View
Spool Valve Valve Body Core Coil
Valve Body Spring Coil Spool Valve Spring Armature
SERVICE TECH Vol.465 03-4
12
You might also like
- Ford Ranger Mazda BT-50 Oil Pump PrimingDocument1 pageFord Ranger Mazda BT-50 Oil Pump PrimingMaster Xeoto100% (1)
- EC 4JH1-T EL (Ver1) PDFDocument79 pagesEC 4JH1-T EL (Ver1) PDFchakkaphong NgamdeeNo ratings yet
- E ECD0106Document3 pagesE ECD0106Miguel Chacon100% (5)
- 5L E Ve Pump Denso Repair ManualDocument32 pages5L E Ve Pump Denso Repair ManualEfrain Di Matias100% (15)
- EDocument23 pagesEUliAlejandroRodriguezCorianga100% (2)
- Service Manual RSV GovernorDocument33 pagesService Manual RSV GovernorВячеслав Глушак100% (1)
- EECD0001Document36 pagesEECD0001Sergey Gusev100% (3)
- HINO J08C J05C Type Engine PDFDocument29 pagesHINO J08C J05C Type Engine PDFDiego Cadena100% (3)
- 2ZR-FE Engine Control-System DiDocument1 page2ZR-FE Engine Control-System DiEddie Tai100% (1)
- 4m41 Pump160061130 Bomba VE VRZ EE14E 11162 VRZ Service ManualDocument117 pages4m41 Pump160061130 Bomba VE VRZ EE14E 11162 VRZ Service Manualesyjam86% (7)
- DTC 14 Timing Control System Malfunction: Circuit DescriptionDocument3 pagesDTC 14 Timing Control System Malfunction: Circuit DescriptionFerry Darmawan100% (1)
- DENSO X2 InstructionDocument13 pagesDENSO X2 InstructionAnonymous 5tkF5bFwO100% (5)
- Pump Denso hp0Document63 pagesPump Denso hp0DenisEcheverri100% (5)
- Ajuste de Bomba VRZDocument37 pagesAjuste de Bomba VRZJose David Huanca Taype100% (1)
- The Factory Boost Jets NAVARA D40Document7 pagesThe Factory Boost Jets NAVARA D40Icram Ibrahimo100% (1)
- HP0 Supply Pump PCV Unit Disassembly and Assembly PDFDocument4 pagesHP0 Supply Pump PCV Unit Disassembly and Assembly PDFDenisEcheverri100% (5)
- Denso Original CatalogueDocument16 pagesDenso Original Catalogueегор100% (1)
- Anatomy VivaDocument5 pagesAnatomy VivaAhmedNo ratings yet
- Tractor Parts CatalogDocument335 pagesTractor Parts Catalogmario100% (2)
- ECD-V4 OutlineDocument4 pagesECD-V4 OutlineВячеслав Глушак100% (2)
- Denso - Ecd IIDocument26 pagesDenso - Ecd IIMohamed Yousif Hamad100% (4)
- CRS (ECD-U2P) For Land CruiserDocument45 pagesCRS (ECD-U2P) For Land CruiserВячеслав Глушак100% (2)
- Denso - Ecd IIDocument26 pagesDenso - Ecd IIVASEK100% (7)
- Spill Control Valve InspectionDocument1 pageSpill Control Valve InspectionArdi AgusmanNo ratings yet
- Control Elec Ecd-V3Document21 pagesControl Elec Ecd-V3Fabian Henao Calle100% (1)
- Denso CR - HP3 NissanDocument14 pagesDenso CR - HP3 NissanHerbert Sanchez86% (7)
- Denso PartsDocument10 pagesDenso PartsMilisav MisicNo ratings yet
- Back Leak TestDocument13 pagesBack Leak Testcartronix201050% (2)
- Bk2q-9k546-Ag 20190701 115501Document2 pagesBk2q-9k546-Ag 20190701 115501คุณชายธวัชชัย เจริญสุขNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Common Rail DelphiDocument68 pagesHyundai Common Rail DelphiJATC75% (4)
- Toyota 5l Valve ClearanceDocument5 pagesToyota 5l Valve ClearancedennoNo ratings yet
- Service Bulletin: Fuel Injection PumpDocument6 pagesService Bulletin: Fuel Injection PumpAnonymous wpUyixsj100% (2)
- Injection Pump Test SpecificationsDocument2 pagesInjection Pump Test SpecificationsEdinson Ariel Chavarro QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Denso CR HP3 Nissan-Pathfinder YD2k2Document11 pagesDenso CR HP3 Nissan-Pathfinder YD2k2james santiago100% (3)
- HP3 Repair PDFDocument18 pagesHP3 Repair PDFTeoh Yew Heng100% (4)
- DENSO X2 Instruction PDFDocument13 pagesDENSO X2 Instruction PDFQuy MingNo ratings yet
- Service Bulletin: Fuel Injection PumpDocument14 pagesService Bulletin: Fuel Injection PumpKrunoslav100% (1)
- Ve Pump Denso Repair Manual PDFDocument32 pagesVe Pump Denso Repair Manual PDFNikola Mitev100% (2)
- EbDocument62 pagesEbUliAlejandroRodriguezCorianga100% (2)
- Adjustment of Valve Clearance: No. 1 No. 3 EX EXDocument11 pagesAdjustment of Valve Clearance: No. 1 No. 3 EX EXDavid QuispeNo ratings yet
- 1 Hdfte Servise Manual Denso TestplanDocument37 pages1 Hdfte Servise Manual Denso Testplanbattulgap_1No ratings yet
- Injection Pump Test S Pecifications 196000-417#Document4 pagesInjection Pump Test S Pecifications 196000-417#Juan Gabriel Ochoa100% (1)
- DTC P0045/34 Turbo/Super Charger Boost Control Solenoid Circuit / OpenDocument4 pagesDTC P0045/34 Turbo/Super Charger Boost Control Solenoid Circuit / OpenYani Yani67% (3)
- Denso Control Valve & Rod 2016Document4 pagesDenso Control Valve & Rod 2016Екатерина Калашникова100% (2)
- Hyundai Mighty W Engine CrsDocument38 pagesHyundai Mighty W Engine CrsVictor Alfonso Russi Aldana100% (1)
- 1KD EduDocument5 pages1KD EduMakokha Mumelo100% (2)
- Denso CR - Hp2 NissanDocument31 pagesDenso CR - Hp2 NissanMarcelo Diesel88% (8)
- Service Manual: Common Rail System For NISSAN YD1-K2 Type EngineDocument40 pagesService Manual: Common Rail System For NISSAN YD1-K2 Type EngineBryan Edu Curay ZavalaNo ratings yet
- Injection Pump Calibration Data: 1. Test ConditionsDocument3 pagesInjection Pump Calibration Data: 1. Test ConditionsElson DorigonNo ratings yet
- 1458718041Document24 pages1458718041Jose Camacho Hernandez100% (1)
- 1HD-T 2Document37 pages1HD-T 2HERMAWAN100% (2)
- Valve Clearance (1Hz, 1Hd T) : InspectionDocument4 pagesValve Clearance (1Hz, 1Hd T) : InspectionArief Soeharto100% (2)
- Iniettori Delphi e DensoDocument1 pageIniettori Delphi e DensoAmadeus De La CruzNo ratings yet
- VDO Diesel IAM Roadmap Q3 2018 ENDocument13 pagesVDO Diesel IAM Roadmap Q3 2018 ENLuis Miranda100% (2)
- SI433 ADocument21 pagesSI433 ASubhojit Samonta100% (7)
- DENSO - Epair Manual Pump EDC V3-V5Document118 pagesDENSO - Epair Manual Pump EDC V3-V5Bui Nam100% (1)
- Sec 1I (4HL1)Document12 pagesSec 1I (4HL1)Susilo purwanggi100% (3)
- (Oto-Hui - Com) Edc Hino s05Document2 pages(Oto-Hui - Com) Edc Hino s05ahmed_eng_1500No ratings yet
- Bomba de Alta Presion Denso HP2 PDFDocument4 pagesBomba de Alta Presion Denso HP2 PDFDiegoD'AmbrosioNo ratings yet
- Denso HP4Document87 pagesDenso HP4Abraham Janco Janco100% (4)
- Common Rail D. - Engine - 2 PDFDocument38 pagesCommon Rail D. - Engine - 2 PDFEdi Susianto100% (1)
- Engine Control System Diagram: Ls430 - New Features 8Document1 pageEngine Control System Diagram: Ls430 - New Features 8bob loblawNo ratings yet
- Engine Control System Diagram: Engine - 3Uz-Fe Engine 70Document21 pagesEngine Control System Diagram: Engine - 3Uz-Fe Engine 70bob loblaw83% (6)
- Service Manual R721 TYPE GOVERNORDocument48 pagesService Manual R721 TYPE GOVERNORВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic SensorDocument1 pageUltrasonic SensorВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Speed SensorDocument4 pagesSpeed SensorВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Types of Systems in ECD-V SeriesDocument4 pagesTypes of Systems in ECD-V SeriesВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Product Introduction Product Introduction: LEXUS LS600h/LS600hL Hybrid System Power Control Unit (PCU)Document4 pagesProduct Introduction Product Introduction: LEXUS LS600h/LS600hL Hybrid System Power Control Unit (PCU)Вячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Starter ManualDocument161 pagesStarter ManualВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- 8th Session Injector Construction and OperationDocument4 pages8th Session Injector Construction and OperationВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- DNSDD LicenseDocument1 pageDNSDD LicenseВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Statement of Axis Account No:917010040330266 For The Period (From: 09-06-2021 To: 08-09-2021)Document13 pagesStatement of Axis Account No:917010040330266 For The Period (From: 09-06-2021 To: 08-09-2021)Saurabh DandriyalNo ratings yet
- ch 7Document441 pagesch 7captainshivamsparrow16No ratings yet
- List of Pre-Owned Vehicles For Sale - 09.30.22Document22 pagesList of Pre-Owned Vehicles For Sale - 09.30.22adFWSVNo ratings yet
- Do You Do Any Sport ?Document3 pagesDo You Do Any Sport ?Minh ThưNo ratings yet
- 4nhbx Zgy5g PDFDocument442 pages4nhbx Zgy5g PDFSyed Haris IftikharNo ratings yet
- Documentation On The Re-Creation of A Pair of Medieval Hide ShoesDocument5 pagesDocumentation On The Re-Creation of A Pair of Medieval Hide ShoesFarid ElkhshabNo ratings yet
- Camshaft Timing M62 VanosDocument10 pagesCamshaft Timing M62 Vanosmjassbong100% (1)
- Connect 4 Workbook Answer Key (WWW - Languagecentre.ir)Document37 pagesConnect 4 Workbook Answer Key (WWW - Languagecentre.ir)nnnalireza104No ratings yet
- Contoh Portofolio EsportDocument24 pagesContoh Portofolio EsportAndrew Christian SalindehoNo ratings yet
- Cbe Educational Tour 2018: Master ListDocument49 pagesCbe Educational Tour 2018: Master ListCharity Lumactod AlangcasNo ratings yet
- Genesis Games PDFDocument15 pagesGenesis Games PDFRed RedNo ratings yet
- (0 - 1) HalloweenDocument69 pages(0 - 1) HalloweenCandiceNo ratings yet
- Excel Project Management TemplateDocument17 pagesExcel Project Management TemplateHydel & Thermal PP S&MNo ratings yet
- Worksheet # 1Document1 pageWorksheet # 1Jhayne LlagasNo ratings yet
- Shooting DrillsDocument2 pagesShooting DrillsnemetrixNo ratings yet
- New Holland B95TC Loader Backhoe Parts Manual PDFDocument1,094 pagesNew Holland B95TC Loader Backhoe Parts Manual PDFsamuel benavides100% (1)
- The FITT Principle G12 ModuleDocument6 pagesThe FITT Principle G12 ModulejuanNo ratings yet
- Libro 1 DiegoDocument23 pagesLibro 1 DiegoMalu Bahamondes Lisboa0% (1)
- Inter CableDocument1 pageInter Cablealberto porcelliNo ratings yet
- FiatCoupe16VT KJ - XDFDocument14 pagesFiatCoupe16VT KJ - XDFFrancDarkNo ratings yet
- Favorite Sports PersonalityDocument4 pagesFavorite Sports PersonalityBoobalan R100% (3)
- RM B2P Video Worksheets U3Document2 pagesRM B2P Video Worksheets U3ВечнаяNo ratings yet
- Improv Intermediate Course Lesson 1Document3 pagesImprov Intermediate Course Lesson 1StevenMorganNo ratings yet
- Hazard Assessment For PPEDocument5 pagesHazard Assessment For PPEYoga Pramuditya SoemodilogoNo ratings yet
- Ballroom DancesDocument25 pagesBallroom DancesMariel MaquinianaNo ratings yet
- Colberg Et Al., (2016) Physical Activity Exercise and DiabetesDocument15 pagesColberg Et Al., (2016) Physical Activity Exercise and DiabetesAna Flávia SordiNo ratings yet
- The Top songs in the worldDocument4 pagesThe Top songs in the worldОльга МихайленкоNo ratings yet
- Participles. Multiple PracticesDocument9 pagesParticiples. Multiple PracticesShMendez2013No ratings yet