0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
305 viewsAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluations
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluations
Uploaded by
Ajay SupanThe patient is experiencing anxiety related to their hyperthyroidism. The nursing diagnosis is anxiety related to physiological factors such as increased thyroid hormones. The plan is to provide interventions over 5 hours to help the patient relax and identify healthy ways to manage feelings of anxiety. Interventions include observing for signs of anxiety, staying calm with the patient, explaining procedures, and reducing external stimuli. The goal is for the patient to feel less anxious and have their anxiety reduced to a manageable level. Evaluations will be done after 5 hours to assess if the patient appears relaxed with reduced anxiety.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluations
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluations
Uploaded by
Ajay Supan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
305 views4 pagesThe patient is experiencing anxiety related to their hyperthyroidism. The nursing diagnosis is anxiety related to physiological factors such as increased thyroid hormones. The plan is to provide interventions over 5 hours to help the patient relax and identify healthy ways to manage feelings of anxiety. Interventions include observing for signs of anxiety, staying calm with the patient, explaining procedures, and reducing external stimuli. The goal is for the patient to feel less anxious and have their anxiety reduced to a manageable level. Evaluations will be done after 5 hours to assess if the patient appears relaxed with reduced anxiety.
Original Title
NCP 1 HYPERTHYROID
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The patient is experiencing anxiety related to their hyperthyroidism. The nursing diagnosis is anxiety related to physiological factors such as increased thyroid hormones. The plan is to provide interventions over 5 hours to help the patient relax and identify healthy ways to manage feelings of anxiety. Interventions include observing for signs of anxiety, staying calm with the patient, explaining procedures, and reducing external stimuli. The goal is for the patient to feel less anxious and have their anxiety reduced to a manageable level. Evaluations will be done after 5 hours to assess if the patient appears relaxed with reduced anxiety.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
305 views4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluations
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluations
Uploaded by
Ajay SupanThe patient is experiencing anxiety related to their hyperthyroidism. The nursing diagnosis is anxiety related to physiological factors such as increased thyroid hormones. The plan is to provide interventions over 5 hours to help the patient relax and identify healthy ways to manage feelings of anxiety. Interventions include observing for signs of anxiety, staying calm with the patient, explaining procedures, and reducing external stimuli. The goal is for the patient to feel less anxious and have their anxiety reduced to a manageable level. Evaluations will be done after 5 hours to assess if the patient appears relaxed with reduced anxiety.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluations
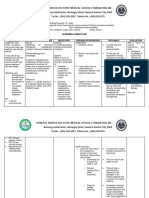
SUBJECTIVE: Observe behavior After 5 hours of nursing
Anxiety related to After 5 hours of nursing indicative of the level of intervention patient appear
“Nagaalala ako, masama physiological factor: intervention patient will anxiety. relaxed, reported reduced
ang pakiramdan ko, hindi pseudo catecholamine appear relax, will report - Mild anxiety may be anxiety to a manageable
ko alam ang gagawin” as effect of thyroid hormones reduced anxiety to a displayed by irritability and level and identified healthy
verbalized by the patient as evidenced by extraneous manageable level and will insomnia. Severe anxiety ways to deal with feelings.
movement, restlessness and identify healthy ways to progressing to the panic
tremors. deal with feelings. state may produce feelings
OBJECTIVE: of impending doom, terror,
inability to speak or move,
Palpitation shouting or swearing.
Restlessness
Irritability Monitor physical
Enlargement of the responses, noting
thyroid gland palpitations, repetitive
Tremors movements,
Weight loss hyperventilation, insomnia.
Rapid heartbeat - Increased number of
Frequent bowel [beta]-adrenergic receptor
movements sites, coupled with effects
Hyperactivity of excess thyroid
Difficulty sleeping hormones, produce clinical
manifestations of
Intolerance to heat
catecholamine excess even
when normal levels of
norepinephrine
or epinephrine exist.
Vital Sign:
TEMP: 38.33C Stay with the patient,
PR: 110 bspm maintaining a calm
RR: 21 cpm manner.
BP: 132/84 mmHg Acknowledge fear and
allow the patient’s
behavior to belong to the
patient.
- Affirms to patient or SO
that although patient feels
out of control, environment
is safe. Avoiding personal
responses to inappropriate
remarks or actions prevents
conflicts or overreaction to
a stressful situation.
Describe and explain
procedures, surrounding
environment, or sounds
that may be heard by the
patient.
- Provides accurate
information, which reduces
distortions
and confusion that can
contribute to anxiety and/or
fear reactions.
Speak in brief statements.
Use simple words.
- Attention span may be
shortened, concentration
reduced, limiting the
ability to assimilate
information.
Reduce external stimuli:
Place in a quiet room;
provide soft, soothing
music; reduce bright lights;
reduce the number of
persons having contact
with the patient.
- Creates a therapeutic
environment; shows
recognition that unit
activity or personnel may
increase patient’s anxiety.
Discuss with patient and/or
someone reasons for
emotional lability and/or
psychotic reaction.
- Understanding that
behavior is physically
based enhances acceptance
of the situation and
encourages different
responses and approaches.
Reinforce the expectation
that emotional control
should return as drug
therapy progresses.
- Provides information and
reassures patient that the
situation is temporary and
will improve with
treatment.
Administer antianxiety
agents or sedatives and
monitor effects.
- May be used in
conjunction with a medical
regimen to reduce effects
of hyperthyroid secretion.
Refer to support systems as
needed: counseling, social
services, pastoral care.
- Ongoing therapy support
may be desired or required
by patient/SO if crisis
precipitates lifestyle
alterations
You might also like
- Trataka Intelligence Memory Super BainDocument14 pagesTrataka Intelligence Memory Super BainSreeraj Guruvayoor S67% (3)
- Nursing Care Process (NCP) Risk-Prone Health Behavior PrepartumDocument2 pagesNursing Care Process (NCP) Risk-Prone Health Behavior PrepartumFrederene JavelonaNo ratings yet
- NCP 3rd YearDocument6 pagesNCP 3rd YearTotoro AblogNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Care Plan New BornDocument10 pagesPostpartum Care Plan New BornUche Edwards-ShahidNo ratings yet
- Hypertension, Anxiety, Airway NCPDocument6 pagesHypertension, Anxiety, Airway NCPHana Sanchez AlobaidanNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism (Drug Study)Document2 pagesHypothyroidism (Drug Study)Krisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Opiate Withdrawal Survival GuideDocument61 pagesOpiate Withdrawal Survival GuideTito Devico100% (1)
- Mirror WritingDocument5 pagesMirror Writingtaniamatos100% (1)
- Case Study Icu Sem 6Document30 pagesCase Study Icu Sem 6BM2-0619 Mohd Khairul Naaim Bin PenchariNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Brokenshire CollegeDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Brokenshire CollegeJai GoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Mebeverine Hydrochloride Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name: Mebeverine Hydrochloride Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Assessment & Drug EffectsNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- NCP VacuumDocument5 pagesNCP VacuumCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Potassium CHLORIDEDocument20 pagesPotassium CHLORIDEAnto PaulNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Marife: 45 Years Old Assessment Diagnosis Background Study/ Planning Implementation Rationale Expected Outcome/ EvaluationDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan Marife: 45 Years Old Assessment Diagnosis Background Study/ Planning Implementation Rationale Expected Outcome/ EvaluationAngelica Malacay RevilNo ratings yet
- Rationale: This Will Assess Pain LevelDocument7 pagesRationale: This Will Assess Pain LevelCoreyNo ratings yet
- L&D Careplan 1 KarenDocument4 pagesL&D Careplan 1 KarenSimran SandhuNo ratings yet
- NCP Notes Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument3 pagesNCP Notes Acute GlomerulonephritisMargareth DandanNo ratings yet
- NCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thDocument2 pagesNCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For PalliaDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan For Palliakarl_poorNo ratings yet
- NCP PPHDocument2 pagesNCP PPHMark Joseph Christian100% (1)
- NCP For Insomnia PDFDocument2 pagesNCP For Insomnia PDFEca0% (1)
- To Know The Diagnostic ExamDocument23 pagesTo Know The Diagnostic ExamKaren Ai KonnoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan2Document13 pagesNursing Care Plan2Nna ANn CastleNo ratings yet
- BSN 2F - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesBSN 2F - Drug Study22 - Fernandez, Lyza Mae D.No ratings yet
- 2 HyperthyroidismDocument3 pages2 HyperthyroidismAisha MarieNo ratings yet
- Aaa Gastrectomy NCP FinalDocument13 pagesAaa Gastrectomy NCP Finallexzaf100% (1)
- MetronidazoleDocument4 pagesMetronidazoleapi-3797941100% (4)
- 4 Flow Chart PretermDocument4 pages4 Flow Chart PretermYeni PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaNo ratings yet
- Depot-Ped: 3 Months: 11.25 MG or 30 MG Q12weeks. (SQ) Lupron: Children: Initially, 50Document3 pagesDepot-Ped: 3 Months: 11.25 MG or 30 MG Q12weeks. (SQ) Lupron: Children: Initially, 50thuey epeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Group-5 - NCP - Ges HypDocument2 pagesGroup-5 - NCP - Ges HypWallen Jey Velasco100% (1)
- NCP Readiness UTI 1Document5 pagesNCP Readiness UTI 1Mary Grace AgataNo ratings yet
- PeritonitisDocument6 pagesPeritonitisDiane ArgoteNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument29 pagesCase Study On Peptic Ulcer DiseaseREYJAN APOLONIONo ratings yet
- Deficient Knowledge - NCPDocument2 pagesDeficient Knowledge - NCPEmmeline Dycangchon-GarmaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Problem Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objective of Care Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Problem Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objective of Care Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationplug06100% (1)
- Guaifenesin Drug CardDocument1 pageGuaifenesin Drug CardJessie JenningsNo ratings yet
- MG Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMG Drug StudySandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPJo Chiko FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Artillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument5 pagesArtillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanCrystelle MonaresNo ratings yet
- NCP GeriaDocument2 pagesNCP GeriaEitan LopezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plankreny1050% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan - HYPERTENSIONDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - HYPERTENSIONJas Slk0% (1)
- Care of The Client With Pulmonary Tuberculosis Utilizing Orem's TheoryDocument13 pagesCare of The Client With Pulmonary Tuberculosis Utilizing Orem's TheoryRazel Kinette AzotesNo ratings yet
- NCP Imbalanced NutritionDocument3 pagesNCP Imbalanced NutritionAav Canlas100% (1)
- Case Study Main OtDocument56 pagesCase Study Main Otamier_s100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Breast Cancer NCP PDFDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Breast Cancer NCP PDFMaina BarmanNo ratings yet
- Generic Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMary Shine GonidaNo ratings yet
- Fluorosis: Fluoride Toxicity: Patient Management & MonitoringDocument24 pagesFluorosis: Fluoride Toxicity: Patient Management & MonitoringdrjriNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRanusha AnushaNo ratings yet
- NCP CholeraDocument2 pagesNCP CholeraMichael Angelo Garcia RafananNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFINAL Drug StudycasedraftNo ratings yet
- Food HygieneDocument31 pagesFood Hygienehemihema100% (1)
- Drug-Study NCPDocument5 pagesDrug-Study NCPMURILLO, FRANK JOMARI C.No ratings yet
- TonsillitisDocument44 pagesTonsillitisBheru Lal100% (1)
- TRAMADOLDocument4 pagesTRAMADOLRudie Lee PascualNo ratings yet
- DS OfloxacinDocument2 pagesDS OfloxacinjessicamaysNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Table - Docx - StudentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Table - Docx - StudentLuigi LauNo ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument2 pagesNifedipineapi-3797941100% (3)
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- HALOPERIDOLDocument1 pageHALOPERIDOLAlyxen Pelingen75% (4)
- ENALAPRIL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesENALAPRIL Drug StudyAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Carboprost Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCarboprost Drug StudyAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Fibrillation NCPDocument3 pagesVentricular Fibrillation NCPAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Planning Interventions Evaluations: Nursing Diagnosis SubjectiveDocument2 pagesAssessment Planning Interventions Evaluations: Nursing Diagnosis SubjectiveAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Supan-Clinical Case AnalysisDocument7 pagesSupan-Clinical Case AnalysisAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Bengin Prostatic HypertrophyDocument3 pagesCase Analysis Bengin Prostatic HypertrophyAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis OcdDocument3 pagesCase Analysis OcdAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument3 pagesPneumoniaAjay Supan100% (1)
- Sleep DeprivationDocument23 pagesSleep DeprivationMelody ManadongNo ratings yet
- Consciousness and SleepDocument5 pagesConsciousness and SleepMaria Tena TapayanNo ratings yet
- WK 8 Consciousness and SleepDocument11 pagesWK 8 Consciousness and SleepZenib ZiaNo ratings yet
- Session 1Document15 pagesSession 1Feona82No ratings yet
- Prevent RelapseDocument27 pagesPrevent RelapseRichard Guth100% (1)
- A Quasi Experimental Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Selected Calisthenics On Quality of Sleep Among Elderly in Selected Old Age Homes, PunjabDocument8 pagesA Quasi Experimental Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Selected Calisthenics On Quality of Sleep Among Elderly in Selected Old Age Homes, PunjabIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Using in Children and Adolescents: BenzodiazepinesDocument4 pagesUsing in Children and Adolescents: BenzodiazepinesEunike KaramoyNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgDeZ3FQkI84X1GQy8u5a0Nep5UKNESbHpzKyqBBtHk SWLnA4LqdE2PS1Yawhawr1mOLnvLmG2BbNhjmglb Zlow1zL6Bc94qwxJC7yzl-bsOCzFhRsza1piHY pmJJm-vpifzcNjsrsFdpDocument16 pagesACFrOgDeZ3FQkI84X1GQy8u5a0Nep5UKNESbHpzKyqBBtHk SWLnA4LqdE2PS1Yawhawr1mOLnvLmG2BbNhjmglb Zlow1zL6Bc94qwxJC7yzl-bsOCzFhRsza1piHY pmJJm-vpifzcNjsrsFdpKristel Kate Melchor TugadeNo ratings yet
- 12th Graders - YDT Practice ExamDocument29 pages12th Graders - YDT Practice Examzuleyhaelmas056No ratings yet
- Assessment of Nidra As Adharaniya Vega & Its Management With Bhramari PranayamDocument15 pagesAssessment of Nidra As Adharaniya Vega & Its Management With Bhramari PranayamDr Kirti BhatiNo ratings yet
- Skala TidurDocument2 pagesSkala TidurMaris JessicaNo ratings yet
- Pie Chart SampleDocument2 pagesPie Chart SampleNguyên Minh100% (1)
- Common Sleep Disorders in ChildrenDocument10 pagesCommon Sleep Disorders in ChildrenHajrin PajriNo ratings yet
- Measures of Fatigue: Geri B. NeubergerDocument9 pagesMeasures of Fatigue: Geri B. NeubergerSanda GainaNo ratings yet
- SPM Cefr Reading Paper Worksheet Part 1 and Part 2Document6 pagesSPM Cefr Reading Paper Worksheet Part 1 and Part 2Nur HafezaNo ratings yet
- DD DemensiaDocument25 pagesDD DemensiaPutri HarahapNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument11 pagesAssignmentUjjwal MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive PsychiatryDocument7 pagesComprehensive PsychiatryOrangee JuceeyNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 4 - Module 2Document14 pagesEnglish: Quarter 4 - Module 2Sofia SantosNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Sample Osce Exam eDocument4 pagesPsychiatry Sample Osce Exam ePNo ratings yet
- InsomniaDocument9 pagesInsomniaMuthu NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentally WrongDocument9 pagesFundamentally WrongAnandh .rNo ratings yet
- 11 Tips To Treat InsomniaDocument7 pages11 Tips To Treat Insomniashivaniikumarii7889No ratings yet
- 9-Çeldi̇ri̇ci̇ SorularDocument4 pages9-Çeldi̇ri̇ci̇ Sorularsafaaltug00No ratings yet
- Preparation and Practice Answer KeyDocument16 pagesPreparation and Practice Answer KeyHiệp Nguyễn TuấnNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of Combing Hair With Horn CombDocument19 pagesThe Benefits of Combing Hair With Horn CombsudipNo ratings yet
- Sleep and Depression - Results From Psychobiological Studies: An OverviewDocument37 pagesSleep and Depression - Results From Psychobiological Studies: An OverviewSalamaNo ratings yet