0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 viewsNCP Group Task
NCP Group Task
Uploaded by
HILARY MAE MARIN1. The patient, a 41 week pregnant woman, presented with severe pain and discomfort during labor. On examination, her cervix was 3cm dilated but progressing slowly.
2. The nursing diagnosis was risk for disturbed maternal-fetal dyad related to shoulder dystocia from gestational diabetes. The plan was for the patient to maintain fluid balance, prevent complications, and improve the labor pattern within 2 hours.
3. Interventions included monitoring signs of infection, evaluating fatigue and labor progress, managing any distress, and preparing for amniotomy or alternative delivery if needed. The goal was for the patient to have a safe delivery and recovery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
NCP Group Task
NCP Group Task
Uploaded by
HILARY MAE MARIN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views2 pages1. The patient, a 41 week pregnant woman, presented with severe pain and discomfort during labor. On examination, her cervix was 3cm dilated but progressing slowly.
2. The nursing diagnosis was risk for disturbed maternal-fetal dyad related to shoulder dystocia from gestational diabetes. The plan was for the patient to maintain fluid balance, prevent complications, and improve the labor pattern within 2 hours.
3. Interventions included monitoring signs of infection, evaluating fatigue and labor progress, managing any distress, and preparing for amniotomy or alternative delivery if needed. The goal was for the patient to have a safe delivery and recovery.
Original Title
NCP Group Task (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
1. The patient, a 41 week pregnant woman, presented with severe pain and discomfort during labor. On examination, her cervix was 3cm dilated but progressing slowly.
2. The nursing diagnosis was risk for disturbed maternal-fetal dyad related to shoulder dystocia from gestational diabetes. The plan was for the patient to maintain fluid balance, prevent complications, and improve the labor pattern within 2 hours.
3. Interventions included monitoring signs of infection, evaluating fatigue and labor progress, managing any distress, and preparing for amniotomy or alternative delivery if needed. The goal was for the patient to have a safe delivery and recovery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views2 pagesNCP Group Task
NCP Group Task
Uploaded by
HILARY MAE MARIN1. The patient, a 41 week pregnant woman, presented with severe pain and discomfort during labor. On examination, her cervix was 3cm dilated but progressing slowly.
2. The nursing diagnosis was risk for disturbed maternal-fetal dyad related to shoulder dystocia from gestational diabetes. The plan was for the patient to maintain fluid balance, prevent complications, and improve the labor pattern within 2 hours.
3. Interventions included monitoring signs of infection, evaluating fatigue and labor progress, managing any distress, and preparing for amniotomy or alternative delivery if needed. The goal was for the patient to have a safe delivery and recovery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Group Members: NCMA219 RLE
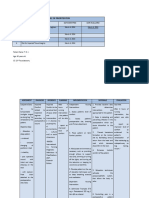
ASSESSMENT NURSING DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
- Castro, Myca LABORATORY COURSE TASKJonalyn
- Salvador, 3
- Marin, Hilary BSN 2-YB-16
- Tanael, Ma. Crisheil Jem
Hypothetical Subjective Risk for disturbed Within 1 to 2 hours
- Reformina, Shannel Maeof 1. Review history of 1. To identify possible After rendering all t
Data: maternal-fetal dyad rendering nursing labor, onset, and duration. causes, needed diagnostic necessary nursing
- “Sobrang sakit na po, related to shoulder intervention, the patient studies, and appropriate interventions, the pa
Doc hindi ko na po dystocia as manifested will be able to: interventions. was able to:
kaya hindi na rin po by gestational diabetes
1. Manifest and maintain 2. Monitor for signs of 2. Development of amnionitis 1. Maintain a fluid bal
ako komportable” as at 28 weeks age of
fluid balance, as will be amnionitis. Note the is related to length of labor, so as evidenced by moist
verbalized by the gestation and
evidenced by moist mucous cervix condition, elevated that delivery should occur mucous membranes an
patient. spontaneous rupture of
membranes, and appropriate temperature or odor, and within 24 hr after rupture of appropriate urine outp
membrane at 3cm.
Objective Data: urine output. color of vaginal membranes. A rigid cervix
- AOG: 41 weeks discharge. will not dilate, impending
- Cervix: 3cm dilated 2. Prevent from suffering fetal descent/labor progress. 2. Prevent further
to further possible complications.
upon internal 3. Evaluate the current
examination, 7cm complications. 3. Excess maternal exhaustion
level of fatigue, as well as
after 4 hours, 10cm contributes to secondary
3. Improve labor pattern activity and rest prior to 3. Improve labor patte
after internal dysfunction, or may be the
and reduce identified risk onset of labor. and reduced the identi
examination result of prolonged labor/false
factors. risk factors.
- Fundic Height: labor.
40cm 4. Note for effacement, 4. Handle and manage
4. Handle and manage any 4. These indicators of labor
- The head had fetal station, and fetal distress.
indicators of fetal distress. progress may identify a
crowned in a presentation.
contributing cause of 5. Have normal FHR l
occipito-anterior 5. Display FHR within prolonged labor
position normal limits, with good 5. Review bowel habits good variability, and n
- Notices that the variability, and no late and regularity of deceleration noted.
5. Bowel fullness may hinder
head did not extend deceleration. evacuation. uterine activity and interfere
normally on the with the fetal descent. 6. Prevent severe vagi
perineum 6. Prevent severity chances 6. Assess for bladder
tears and bladder injur
- The chin appeared of vaginal tears and bladder fullness over symphysis 6. A full bladder may inhibit
to be fixed in the injury. pubis. uterine activity and interfere
perineum with the fetal descent. 7. Feel less fatigue.
- Patient attempted 7. Lessen current level of 7. Place client in lateral
to deliver the fatigue. recumbent position. 7. Relaxation may correct a
shoulders after 3 hypertonic pattern. 8. Be freed from suffe
8. Be free from possible Ambulation may assist
contractions but not
further sufferings. gravitational forces in Goal met.
achieved.
- Normal Pelvic stimulating normal labor
Ultrasound 8. Note sign of fetal pattern and cervical dilation.
- Fetal movement is distress, cessation of
8. To monitor indication of
actively normal. contractions, presence of
developing uterine tear or
vaginal bleeding. acute rupture necessitating
emergency surgery.
9. Prepare client for
amniotomy assist with the 9. Active management of
procedure when cervix is labor protocols may support
3-4 cm dilated. amniotomy once presenting
part is engaged to accelerate
labor/help prevent dystocia.
10. Assess for
malpositioning using 10. To help assess the fetus’
Leopold’s maneuvers and current position and
findings on internal determine fetal distress.
examination (location of
fontanelles and cranial
sutures).
11. Note for the color and
11. To assess the stage of the
amount of amniotic fluid
membrane rupture.
when bag of water
rupture.
12. Assess FHR manually 12. To identify if there’s a
or electronically. Note possible fetal distress.
variability, periodic
changes, and baseline
rate.
13. Prepare for delivery in 13. This is an alternative
posterior position. delivery technique for
Alternatively, apply dystocia.
vacuum extractor as
indicated.
14. This is an alternative way
14. Prepare for cesarean to deliver the fetus to avoid
delivery if fetus fails to further maternal-fetal
descend. complications.
You might also like
- Covid Vaccines from a Spiritual Perspective: Consequences for the Soul and Spirit and for Life after DeathFrom EverandCovid Vaccines from a Spiritual Perspective: Consequences for the Soul and Spirit and for Life after DeathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlanDickson,Emilia Jade100% (3)
- Conduction of DeliveryDocument31 pagesConduction of Deliverysagi mu100% (3)
- NURSING CARE PLAN: Risk For Fetal Injury Related To Shoulder DystociaDocument5 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN: Risk For Fetal Injury Related To Shoulder DystociaJa Lo67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan: Submitted To: Submitted By: Ms Kamini Manisha Joshi Asst. Prof. Acn Msc. Nursing 1 SemesterDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan: Submitted To: Submitted By: Ms Kamini Manisha Joshi Asst. Prof. Acn Msc. Nursing 1 SemesterDIMPYNo ratings yet
- Duran, Fatima Medriza B. - DR Written OutputsDocument9 pagesDuran, Fatima Medriza B. - DR Written OutputsFatima Medriza DuranNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMark FernandezNo ratings yet
- Ramos-2bn NCP Delivery RoomDocument2 pagesRamos-2bn NCP Delivery RoomLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Defining Characteristic S Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Plan of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale Subjective: Short Term: IndependentDocument1 pageDefining Characteristic S Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Plan of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale Subjective: Short Term: Independentboomer SeargeNo ratings yet
- Forceps Delivery ActivityDocument3 pagesForceps Delivery ActivityReyniel BulaklakNo ratings yet
- NCP Alterations in Normal LaborDocument9 pagesNCP Alterations in Normal LaborCameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum Problems, CAD, Angina Pectoris, Cardiomyopathy, HF, DVT, PEDocument17 pagesIntrapartum Problems, CAD, Angina Pectoris, Cardiomyopathy, HF, DVT, PEPaulineNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument5 pagesNCP PainChloe Crystal DorojaNo ratings yet
- Problems With The PassagewayDocument2 pagesProblems With The PassagewayPrilay Pring AlcopraNo ratings yet
- INTRAPARTUMDocument16 pagesINTRAPARTUMKurt GuanteroNo ratings yet
- NCP Aleeyah 2nDocument2 pagesNCP Aleeyah 2nLiza MinonaNo ratings yet
- Case Discussion: Mayan, Mercurio, Murillo BSN 2-ADocument11 pagesCase Discussion: Mayan, Mercurio, Murillo BSN 2-ADhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Face PresentationDocument29 pagesFace PresentationMadhu Bala100% (1)
- Final Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesFinal Nursing Care PlanDickson,Emilia Jade100% (1)
- MCN PartographDocument2 pagesMCN PartographAlec Anon100% (1)
- Now, Try Some Big Leap.: Keep GoingDocument10 pagesNow, Try Some Big Leap.: Keep GoingCameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Syphilis Nursing NotesDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Syphilis Nursing Notesblaire100% (1)
- Head To Toe Assessment of Pregnant WomanDocument8 pagesHead To Toe Assessment of Pregnant Womanacademic purposesNo ratings yet
- NCPPPDocument2 pagesNCPPPKyuSheenNo ratings yet
- Fernandez Fetal Malposition 3Document2 pagesFernandez Fetal Malposition 3Mark FernandezNo ratings yet
- Periodical Examination #3 Postpartal Period/Puerperium EngrossmentDocument10 pagesPeriodical Examination #3 Postpartal Period/Puerperium EngrossmentprestienhannahvNo ratings yet
- PPDS Prep - Normal LabourDocument37 pagesPPDS Prep - Normal LabourArum HastutiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledMON RUSSEL FRIASNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Dystocia NCPDocument6 pagesShoulder Dystocia NCPNicole Genevie MallariNo ratings yet
- Post-Term Labor - NCPDocument7 pagesPost-Term Labor - NCPCameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- RECAP - ColoredDocument8 pagesRECAP - Coloredreminder to be happyNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTweenie DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Labor DystociaDocument8 pagesDysfunctional Labor Dystociamardsz100% (2)
- NCP Severe Labor PainDocument3 pagesNCP Severe Labor PainPaolo EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum 111: 1. Examine The Woman For Emergency SignsDocument7 pagesIntrapartum 111: 1. Examine The Woman For Emergency SignsJane MartinNo ratings yet
- Impaired Comfort NCPDocument2 pagesImpaired Comfort NCPMegan PagapongNo ratings yet
- NCP Hydatidiform Mole PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Hydatidiform Mole PDFKimNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern - PBL4Document4 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern - PBL4Vian RiveraNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledIvan VillapandoNo ratings yet
- Intra Sample ExamDocument26 pagesIntra Sample ExamFraiza BirowaNo ratings yet
- PDF NCP For Intranatal MotherDocument12 pagesPDF NCP For Intranatal MotherDaily DoseNo ratings yet
- NCP Term 2Document3 pagesNCP Term 2Cassandra Grace Muerong Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Ob2 Sas 6Document7 pagesOb2 Sas 6fwmwr7wr64No ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta NCPDocument2 pagesAbruptio Placenta NCPjohncarlo ramos100% (1)
- Lyceum-Northwestern UniversityDocument9 pagesLyceum-Northwestern UniversityGwyneth PastorNo ratings yet
- OSCE Sp1 Feto Breech PresentationDocument7 pagesOSCE Sp1 Feto Breech PresentationobbyNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument35 pagesEctopic Pregnancyhoney requermeNo ratings yet
- Psychological Changes of PregnancyDocument2 pagesPsychological Changes of PregnancyMicah NayraNo ratings yet
- Labor Delivery NewbornDocument4 pagesLabor Delivery NewbornMello D. ConsulNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJanina Kirsten DevezaNo ratings yet
- 2s2022 Ncm109 Rle Learn Mat 1Document18 pages2s2022 Ncm109 Rle Learn Mat 1Guia SalandananNo ratings yet
- 1 Labor and Delivery ProcessDocument13 pages1 Labor and Delivery ProcessBardiaga JmayNo ratings yet
- NCM 107maternal FinalsDocument84 pagesNCM 107maternal FinalsFranz goNo ratings yet
- (Maternal) FINALSDocument86 pages(Maternal) FINALSRM DemetilloNo ratings yet
- NOTES - Module 2 - Admitting A Woman in Active LaborDocument2 pagesNOTES - Module 2 - Admitting A Woman in Active LaborLorraine PanchoNo ratings yet
- MCN Lect Module 2.5 Complications of Labor and Birth 4Document6 pagesMCN Lect Module 2.5 Complications of Labor and Birth 4AmethystNo ratings yet
- The Labor Progress Handbook: Early Interventions to Prevent and Treat DystociaFrom EverandThe Labor Progress Handbook: Early Interventions to Prevent and Treat DystociaNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle Related Disorders: Volume 7: Frontiers in Gynecological EndocrinologyFrom EverandMenstrual Cycle Related Disorders: Volume 7: Frontiers in Gynecological EndocrinologySarah L. BergaNo ratings yet
- Your Developing Baby, Conception to Birth: Witnessing the Miraculous 9-Month JourneyFrom EverandYour Developing Baby, Conception to Birth: Witnessing the Miraculous 9-Month JourneyNo ratings yet
- Matary Surgical Instruments 2012Document100 pagesMatary Surgical Instruments 2012Raouf Ra'fat Soliman100% (6)
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Document10 pagesSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Cervical InsufficiencyDocument23 pagesCervical InsufficiencyyogitharajNo ratings yet
- Kode Diagnosis Bedah Saraf Icd 9Document6 pagesKode Diagnosis Bedah Saraf Icd 9Hendrique NeloNo ratings yet
- Epstein 1985Document7 pagesEpstein 1985AnaNo ratings yet
- Endotracheal Tube SuctioningDocument5 pagesEndotracheal Tube SuctioningArlene DalisayNo ratings yet
- Sanchit Singla 100905089 Eic 3 (Attending Tute With Eic 2)Document29 pagesSanchit Singla 100905089 Eic 3 (Attending Tute With Eic 2)sanchit2418No ratings yet
- Pinhole Surgical Technique For Treatment of Marginal Tissue Recession: A Case SeriesDocument6 pagesPinhole Surgical Technique For Treatment of Marginal Tissue Recession: A Case SeriesEliza DraganNo ratings yet
- Modified AcceptedDocument28 pagesModified Acceptedaarushi singhNo ratings yet
- OrifDocument5 pagesOrifHugh JacobsNo ratings yet
- ViOL Sylfirm XDocument12 pagesViOL Sylfirm Xmichellelyt1993No ratings yet
- Pitch Deck - Stroke2Prevent - AView and BronchusDocument23 pagesPitch Deck - Stroke2Prevent - AView and Bronchusvastfas1No ratings yet
- PIPER Neonatal - Management of Subgaleal Haemorrhage in Neonatal TransportDocument6 pagesPIPER Neonatal - Management of Subgaleal Haemorrhage in Neonatal TransportAkarsh chaturvediNo ratings yet
- MCN Exam 2 - INTRAPARTUMDocument5 pagesMCN Exam 2 - INTRAPARTUMMarites PasionNo ratings yet
- Transes MidtermDocument16 pagesTranses MidtermDexter NicolasNo ratings yet
- DR Roshan - Imaging in ImplantsDocument230 pagesDR Roshan - Imaging in ImplantsSupriya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of ThoraxDocument68 pagesAnatomy of Thoraxangela marie abadillaNo ratings yet
- GROUP-44 RadiographerDocument2 pagesGROUP-44 Radiographeryadav dNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument9 pagesEctopic Pregnancy - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfKatherine DavilaNo ratings yet
- BLOOD - FinalDocument8 pagesBLOOD - FinalanuNo ratings yet
- Unit 12Document14 pagesUnit 12KumareshNo ratings yet
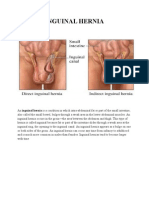
- Inguinal HerniaDocument4 pagesInguinal HerniaRegine SitchonNo ratings yet
- Surgical Mesh ManufacturersDocument5 pagesSurgical Mesh ManufacturersVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- History of Perioperative Nursing 2023Document10 pagesHistory of Perioperative Nursing 2023Boniface MogakaNo ratings yet
- TAP Paper PublishedDocument8 pagesTAP Paper PublishedMotaz AbusabaaNo ratings yet
- 17corneal DystrophiesDocument15 pages17corneal Dystrophies2begeniusNo ratings yet
- Membaca Ekg Untuk PemulaDocument15 pagesMembaca Ekg Untuk PemulaChristopher NjotokusgitoNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument21 pagesBiology ProjectsivaNo ratings yet
- Continuing Education 1: Horizontal Alveolar Ridge Augmentation: The Importance of Space MaintenanceDocument11 pagesContinuing Education 1: Horizontal Alveolar Ridge Augmentation: The Importance of Space MaintenanceJuan Jose Sosa BerganzaNo ratings yet
- Tri Soft Shell Technique.12Document8 pagesTri Soft Shell Technique.12Apps OmNo ratings yet