0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 viewsChecklist For Cva
Checklist For Cva
Uploaded by
Camille Neypes Carrera1. The document provides a checklist for performing a neurological assessment of a patient who may have experienced a cerebrovascular accident (CVA).
2. The assessment involves testing the 12 cranial nerves, motor function, reflexes, and mental status. Sensation, strength, coordination, and speech are evaluated.
3. Vital signs will be monitored, diagnostic tests may be ordered, medications like anticoagulants will be given, and complications of the CVA will be watched for in developing a nursing care plan and anticipating the patient's outcome.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Checklist For Cva
Checklist For Cva
Uploaded by
Camille Neypes Carrera0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views2 pages1. The document provides a checklist for performing a neurological assessment of a patient who may have experienced a cerebrovascular accident (CVA).
2. The assessment involves testing the 12 cranial nerves, motor function, reflexes, and mental status. Sensation, strength, coordination, and speech are evaluated.
3. Vital signs will be monitored, diagnostic tests may be ordered, medications like anticoagulants will be given, and complications of the CVA will be watched for in developing a nursing care plan and anticipating the patient's outcome.
Original Title
Checklist for Cva
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
1. The document provides a checklist for performing a neurological assessment of a patient who may have experienced a cerebrovascular accident (CVA).
2. The assessment involves testing the 12 cranial nerves, motor function, reflexes, and mental status. Sensation, strength, coordination, and speech are evaluated.
3. Vital signs will be monitored, diagnostic tests may be ordered, medications like anticoagulants will be given, and complications of the CVA will be watched for in developing a nursing care plan and anticipating the patient's outcome.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views2 pagesChecklist For Cva
Checklist For Cva
Uploaded by
Camille Neypes Carrera1. The document provides a checklist for performing a neurological assessment of a patient who may have experienced a cerebrovascular accident (CVA).
2. The assessment involves testing the 12 cranial nerves, motor function, reflexes, and mental status. Sensation, strength, coordination, and speech are evaluated.
3. Vital signs will be monitored, diagnostic tests may be ordered, medications like anticoagulants will be given, and complications of the CVA will be watched for in developing a nursing care plan and anticipating the patient's outcome.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
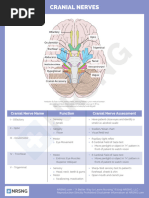
PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST FOR • Cranial Nerve III-Oculomotor and Cranial
CEREBROVASCULAR ACCIDENT NerveIV-Trochlear
Assess six ocular movements and pupil
1. Introduce yourself, and verify the client’s identity. reactions. (Light Reflex) (Six directions)
2. Perform hand hygiene • Cranial Nerve V- Trigeminal
3. Provide client privacy o While the client looks upward, lightly touch
4. We will identify the patient’s priority needs by: the lateral sclera of the eye to elicit the blink
• Determining the client’s history such as reflex.
Presence of pain in the head, back, or o To test light sensation, have the client
extremities close their eyes, and wipe a wisp of cotton
• Any history of loss of consciousness, over the client’s forehead and paranasal
fainting, paralysis, uncontrolled muscle sinuses.
movements, and loss of memory o To test deep sensation, use alternating
blunt and sharp ends of a safety pin over
• Problems with smell, vision, taste, touch, or
the same area.
hearing
• Cranial Nerve VI- Abducens
• Disorientation to time, place, or person (Ask
o Assess directions of gaze. (Pen towards
the client the city and state of residence, time
px)
of day, date, and names of family members.)
• Cranial Nerve VII-Facial
(Where are you now?) (What date is it
o Ask the client to smile, raise the eyebrows,
today?)
frown, puff out cheeks, and close eyes
• Speech disorders (Ask the client to read
tightly.
some words, and to respond to simple verbal • Cranial Nerve VIII-Auditory
and written commands like “point to your o Assess the client’s ability to hear the
toes, “or “Raise your left arm”.) spoken word and the vibrations of a tuning
5. After we identify the priority needs, we will now fork.
assess the client in the emergency room and we • Cranial Nerve IX-Glossopharyngeal
will check for the; o Apply tastes on the posterior tongue for
• chief complaint identification. Ask the client to move their
• vital signs tongue from side to side and up and down.
• for orders to be carried out initially • Cranial Nerve X-Vagus
• and for patient safety and positioning o Assessed with CN IX; assess the client’s
6. Next, we will now demonstrates / performs correct speech for hoarseness
neurologic assessment • Cranial Nerve XI-Accessory
First is the MSE (Mental status exam) o Ask the client to shrug their shoulders
To assess immediate recall: against resistance from your hands and to
o Ask the client to repeat a series of three turn their head to the side against
digits-e.g, 7-4-3-spoken slowly. resistance from your hand. Repeat for the
other side.
To assess recent memory: • Cranial Nerve XII-Hypoglossal
o Ask the client to recall the recent events of o Ask the client to protrude tongue at midline,
the day, such as how he got to the clinic. then move it from side to side.
o Ask the client to recall information given Level of Consciousness
early in the interview-like the name of a • Apply the Glasgow Coma Scale:
doctor or nurse. o Eye response, motor response, and verbal
To assess remote memory: response
Hello sir, Are you okay?
o Ask the client to describe a previous illness Can you show me your tongue?
or surgery. Can you do this? (Thumb)
To test the ability to concentrate or attention span, Assessment of reflexes
have the client to recite the alphabet. Test reflexes using a percussion hammer, comparing
one side of the body with the other to evaluate the
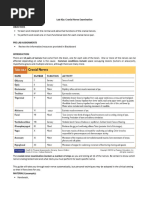
CRANIAL NERVE EXAMINATION symmetry of response
• Cranial Nerve I-Olfactory • Biceps Reflex
o Ask the client to close their eyes and The biceps reflex tests the spinal cord levels
identify different mild aromas such as C-5, C-6. (Inner Elbow)
coffee and vanilla. • Triceps Reflex
• Cranial nerve II-Optic The triceps reflex tests the spinal cord levels
o Ask the client to read Snellen’s chart; C-7, C-8. (Outer elbow)
check visual fields by confrontation, and • Brachioradialis Reflex
conduct an ophthalmoscopic examination. The brachioradialis reflex tests the spinal
(Cover 1 eye and read vv, 40m away) cord levels C-3, C-6. (Side of the wrist)
(Cover r eye patient and left eye nurse. Say • Achilles Reflex
stop when the px see the N finger) The Achilles reflex tests the spinal cord
levels S-1, S-2. (Ankle)
• Plantar (Babinski’s) Reflex 7. Next, Anticipates diagnostic tests and possible
The plantar or Babinski’s reflex is superficial. outcome. (CT scan, MRI, PET scan, lumbar
It might be absent in adults without pathology puncture, ECG and Skull x-ray)
or overridden by voluntary control. (Hill down 8. We will be monitoring for complications in the ICU.
to fingers) (Change in level of consciousness and
responsiveness. Maintenance of BP)
Motor Function 9. Anticipate drugs to be given and their mechanisms
Gross Motor and Balance Tests of action. (Warfarin- Anticoagulant for long term
• Walking Gait case. Depletes functional vit k reserves and
o Ask the client to walk across the room and reduces the synthesis of active clotting factors.)
back, and assess the client’s gait. 10. We will also Identify possible complications of
• Romberg’s Test CVA (Tissue Ischemia and Cardiac dysrhythmic),
o Ask the client to stand with feet together 11. And lastly, we will formulate nursing care plan for
and arms resting at the sides, first with client with CVA and anticipate expected outcome
eyes open, then closed. of the client in the scenario.
• Standing On One Foot with Eyes Closed
o Ask the client to close their eyes and stand
on one foot, then the other. Stand close to
the client during this test.
• Heel-Toe Walking
o Ask the client to walk a straight line, placing
the heel of one foot directly in front of the
toes of the other foot.
• Toe or Heel Walking
o Ask the client to walk several steps on the
toes and then on the heels
Fine Motor Test for the Upper Extremities
• Finger-to-Nose Test
o Ask the client to abduct and extend arms at
shoulder height and rapidly touch the nose
alternately with one index finger and then
the other. Have the client repeat the test
with eyes closed if the test is performed
easily.
• Alternating Supination and Pronation of
Hands-on Knees
o Ask the client to pat both knees with the
palms of both hands and then with the
backs of hands, alternately, at an ever-
increasing rate.
• Finger to Nose and Nurse’s Finger
o Ask the client to touch your nose and then
your index finger
• Fingers to Fingers
o Ask the client to spread arms broadly at
shoulder height and then bring fingers
together at the midline, first with eyes open
and then closed, first slowly and then
rapidly
• Fingers to Thumb (Same Hand)
o Ask the client to touch each finger of one
hand to the thumb of the same hand as
rapidly as possible.
• Fine Motor tests for the Lower Extremities
o Ask the client to lie supine and to perform
these tests;
• Heel Down Opposite Shin
o Ask the client to place the heel of one foot
just below the opposite knee and run the
heel down the shin to the foot. Repeat with
the other foot. The client may also use a
sitting position for this test.
• Toe or Ball of Foot to the Nurse’s Finger
o Ask the client to touch your finger with the
large toe of each foot.
You might also like
- Cranial Nerve AssessmentDocument42 pagesCranial Nerve AssessmentValeryn Quiman100% (11)
- CARSURIN Company Profile (2020)Document25 pagesCARSURIN Company Profile (2020)Imron Rosyadi100% (1)
- DRUG FREE Workplace Policy ProgramDocument6 pagesDRUG FREE Workplace Policy ProgramRupert VillaricoNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument11 pagesAssessmentFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Cranial NervesDocument30 pagesAssessment of Cranial NervesAmery MaligayaNo ratings yet
- Neuro NotesDocument17 pagesNeuro NotesAngelica Marie MacaslingNo ratings yet
- Cs Neuro 016 Cranial - NervesDocument2 pagesCs Neuro 016 Cranial - NervesnwxwgvqkscNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve Test Cranial Nerve I: OlfactoryDocument2 pagesCranial Nerve Test Cranial Nerve I: OlfactoryjisooNo ratings yet
- Neuro Vital Signs AssessmentDocument2 pagesNeuro Vital Signs AssessmentDanniella AbriaNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Neurological System: Preparation Mastered CommentsDocument9 pagesAssessing The Neurological System: Preparation Mastered CommentsJo PigarNo ratings yet
- HA Lec ReportDocument29 pagesHA Lec ReportRhelina MinNo ratings yet
- Neurologic SystemDocument74 pagesNeurologic SystemHylla TanNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve-1Document35 pagesPeripheral Nerve-1Manirarora EtienneNo ratings yet
- NeuroDocument8 pagesNeurokrezeltayaNo ratings yet
- S14-CN Exam - REVIEW For FINAL-F20-BB-1202Document73 pagesS14-CN Exam - REVIEW For FINAL-F20-BB-1202Michael MerlinNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Neurological System PDFDocument7 pagesAssessing The Neurological System PDFYousuf Azhar AlamiaNo ratings yet
- CNS ExaminationDocument59 pagesCNS ExaminationSania ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Inbound 2795149120147640433Document52 pagesInbound 2795149120147640433elainemNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve AssessmentDocument42 pagesCranial Nerve Assessmentmalik003100% (1)
- Cranialnerveassessmentfinal 140501113414 Phpapp01 PDFDocument42 pagesCranialnerveassessmentfinal 140501113414 Phpapp01 PDFAlma Baterina100% (1)
- Cranial Nerve Assessment SheetDocument1 pageCranial Nerve Assessment SheetirmakrsekNo ratings yet
- neurological examinationDocument39 pagesneurological examinationvaishrai.98No ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve ExaminationDocument46 pagesCranial Nerve Examination966342No ratings yet
- Neurological System RetdemDocument2 pagesNeurological System RetdemBabyJane GRomeroNo ratings yet
- 2 Neurological Assessment ActivityDocument13 pages2 Neurological Assessment Activityapi-688305379No ratings yet
- Perception and Coordination 2Document58 pagesPerception and Coordination 2Jhensczy Hazel Maye AlbaNo ratings yet
- 2 Approach To The Neuro Exam Feb 2011Document35 pages2 Approach To The Neuro Exam Feb 2011suaqaziNo ratings yet
- Activity 2a Cranial NervesDocument11 pagesActivity 2a Cranial Nervesxochilred6No ratings yet
- Neurological AssessmentDocument25 pagesNeurological Assessmentleih jsNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve Assessment: Nerve Name Function Test IDocument9 pagesCranial Nerve Assessment: Nerve Name Function Test IBecky Mariñas ReducaNo ratings yet
- Cranial-Nerve-Examination Copy Copy-1Document27 pagesCranial-Nerve-Examination Copy Copy-1cvmqx7yppdNo ratings yet
- Test CN I (Olfactory)Document3 pagesTest CN I (Olfactory)frechel kimNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve4ACerebellar Testing PDFDocument76 pagesCranial Nerve4ACerebellar Testing PDFSam VeraNo ratings yet
- 2_5370591123129506119 copyDocument32 pages2_5370591123129506119 copyq7yggdfznsNo ratings yet
- Use The Following Criteria in Evaluating The Skill PerformanceDocument4 pagesUse The Following Criteria in Evaluating The Skill Performancekookie100% (1)
- Canas, Patricia Gan, Razel Ruelo, Vanessa Aquino, Camile Guillano, Christabelle BSN IiiDocument73 pagesCanas, Patricia Gan, Razel Ruelo, Vanessa Aquino, Camile Guillano, Christabelle BSN IiiGan BangNo ratings yet
- Checklist Assessing The Neurological System: S.No Steps YES NODocument9 pagesChecklist Assessing The Neurological System: S.No Steps YES NOpramod kumawat100% (1)
- Neurological ExaminationDocument240 pagesNeurological Examinationramadan0% (1)
- Neurological AssessmentDocument76 pagesNeurological Assessmentjcabatit3No ratings yet
- Cranial NerveDocument3 pagesCranial NerveMatty JolbitadoNo ratings yet
- Cranial NerveDocument3 pagesCranial NerveMatty JolbitadoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of NeuroDocument38 pagesAssessment of NeuroumairdammarNo ratings yet
- 1st Yr SpottersDocument230 pages1st Yr Spotterskidsamir3.0No ratings yet
- CranialNrvDocument20 pagesCranialNrvS ArtNo ratings yet
- Neurological System: (Health Assessment)Document33 pagesNeurological System: (Health Assessment)Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesCranial Nerves Cranial NervesAngela CudiaNo ratings yet
- Neuro ExamDocument58 pagesNeuro ExamChristina TuchsenNo ratings yet
- Assessing Cranial Nerve FunctionDocument1 pageAssessing Cranial Nerve FunctionSITTIE JOBAISAH TOMINAMAN ALINo ratings yet
- 12 Cranial Nerve Assessment Sensory and Motor FunctionDocument10 pages12 Cranial Nerve Assessment Sensory and Motor FunctionVignesh VigneshNo ratings yet
- CNS AhnDocument190 pagesCNS Ahni am sigmaNo ratings yet
- NeurologicalDocument11 pagesNeurologicalHiba V.ANo ratings yet
- Neurological ExaminationDocument71 pagesNeurological ExaminationAmbreen SabaNo ratings yet
- Neuro Exam FlattenedDocument66 pagesNeuro Exam Flattenedwaleed734445No ratings yet
- Central Nervous System AssessmentDocument37 pagesCentral Nervous System AssessmentVIDYANo ratings yet
- CN TestingDocument2 pagesCN TestingSandeepNo ratings yet
- Assessing Neurologic SystemDocument6 pagesAssessing Neurologic SystemKathlyn LopeñaNo ratings yet
- Assessing NeuroDocument7 pagesAssessing NeuroRoldan BalangyaoNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesCranial Nervesmp_329100% (1)
- OCULOPATHY - Disproves the orthodox and theoretical bases upon which glasses are so freely prescribed, and puts forward natural remedial methods of treatment for what are sometimes termed incurable visual defectsFrom EverandOCULOPATHY - Disproves the orthodox and theoretical bases upon which glasses are so freely prescribed, and puts forward natural remedial methods of treatment for what are sometimes termed incurable visual defectsNo ratings yet
- Power Sleep: The Revolutionary Program That Prepares Your Mind for Peak PerformanceFrom EverandPower Sleep: The Revolutionary Program That Prepares Your Mind for Peak PerformanceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (11)
- ISO 11731 LegionellaDocument43 pagesISO 11731 Legionellaozgegundogdu18No ratings yet
- 11:00 IG1 3-Apr-2024 14-Jun-2024 1203-Speed Way Safety Training Centre LLC IG IG2 3-Apr-2024 14-Jun-2024 1203-Speed Way Safety Training Centre LLC IGDocument1 page11:00 IG1 3-Apr-2024 14-Jun-2024 1203-Speed Way Safety Training Centre LLC IG IG2 3-Apr-2024 14-Jun-2024 1203-Speed Way Safety Training Centre LLC IGAli MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Sop Od DermatophytosisDocument10 pagesSop Od DermatophytosisAnanyaNo ratings yet
- Technical Activity D.S and P.ADocument5 pagesTechnical Activity D.S and P.AMONTYMER HERNANDO MORENONo ratings yet
- Stress Test: By: Honey Shah 20MBA084 Submitted To: DR - Reshma SableDocument8 pagesStress Test: By: Honey Shah 20MBA084 Submitted To: DR - Reshma Sablehoney shahNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Appendicitis Score For Identifying Acute Appendicitis in Children Presenting With Acute Abdominal Pain To The Emergency DepartmentDocument5 pagesPediatric Appendicitis Score For Identifying Acute Appendicitis in Children Presenting With Acute Abdominal Pain To The Emergency DepartmentShikya AbnasNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety Testing and Maintenance Log BookDocument27 pagesFire Safety Testing and Maintenance Log BookSaber HussainiNo ratings yet
- BS en 00140-1999Document22 pagesBS en 00140-1999myenas87No ratings yet
- 3i HIRURGIJA - ŽELUCA I CRIJEVA Nejra Kikanović, Naida Kikanović I Indir Kulanić1275776300763Document20 pages3i HIRURGIJA - ŽELUCA I CRIJEVA Nejra Kikanović, Naida Kikanović I Indir Kulanić1275776300763Basketball is my loveNo ratings yet
- Measurement Uncertainty in Water Microbiology May Not Estimate The Laboratorys PrecisionDocument4 pagesMeasurement Uncertainty in Water Microbiology May Not Estimate The Laboratorys Precisionkhoi moleNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 05 - Employee - Selection - References - and - TestingDocument10 pagesChapter - 05 - Employee - Selection - References - and - TestingPanda QuinnNo ratings yet
- Iso 15883 5 2021Document15 pagesIso 15883 5 2021vadesh2000No ratings yet
- Site Master FileDocument68 pagesSite Master Filearohikenna522No ratings yet
- Get My Sgot Is 157 and My SGPT Is 76.what DoineeddotoforfreeDocument2 pagesGet My Sgot Is 157 and My SGPT Is 76.what DoineeddotoforfreePiyush BhartiNo ratings yet
- Statistics & Probability: Tests of HypothesisDocument7 pagesStatistics & Probability: Tests of HypothesisJeffrey R. AbadNo ratings yet
- 02B Evidences-Proof of Current CompetenciesDocument3 pages02B Evidences-Proof of Current CompetenciesKay Ann Torre100% (1)
- TEMD - Diabetus Mellitus-2022Document324 pagesTEMD - Diabetus Mellitus-2022ali sağdıçNo ratings yet
- Psa - Prostate - JuscheckDocument1 pagePsa - Prostate - JuscheckVivian Gabriela Rojas EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Ranjit Kumar-Research Methodology A Step-by-Step G-15-16Document2 pagesRanjit Kumar-Research Methodology A Step-by-Step G-15-16Trendy NewsNo ratings yet
- Med PTMDocument133 pagesMed PTMHarvinder SahotaNo ratings yet
- DR - Ajith Joy: Current DesignationsDocument2 pagesDR - Ajith Joy: Current Designationsinaam488No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MethodologyDocument9 pagesChapter 2 MethodologyPrincess Lynn Aquino PaduaNo ratings yet
- University of Makati College of Allied Health Studies Center of NursingDocument32 pagesUniversity of Makati College of Allied Health Studies Center of NursingE.J. PelayoNo ratings yet
- 113 Job 1 CWEDocument5 pages113 Job 1 CWEkieranmstevensNo ratings yet
- Statistics Question BankDocument52 pagesStatistics Question BankDyllan MatandaneNo ratings yet
- 24 Hour Urine CollectionDocument3 pages24 Hour Urine CollectionFatima Neshreen SarahadilNo ratings yet
- Energized Electrical Work PermitDocument2 pagesEnergized Electrical Work Permitabdulwadood_engineerNo ratings yet
- Counselling Schedule For 2nd Round of Counselling For MBBS BDS Courses 133Document1 pageCounselling Schedule For 2nd Round of Counselling For MBBS BDS Courses 133Dog CatNo ratings yet