Enzymes 1
Enzymes 1
Uploaded by
zarszCopyright:
Available Formats
Enzymes 1
Enzymes 1
Uploaded by
zarszOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Enzymes 1
Enzymes 1
Uploaded by
zarszCopyright:
Available Formats
● Enzymes in the circulatory
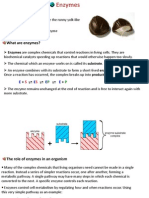
WHAT ARE ENZYMES? system regulate the clotting of
blood.
- Enzymes can be defined as biological
polymers that catalyze biochemical The Role of Enzymes in the Digestive
reactions. System
- The majority of enzymes are proteins Chemical digestion could not take place
with catalytic capabilities crucial to without the help of digestive enzymes.
perform different processes. Metabolic An enzyme is a protein that speeds up
processes and other chemical reactions chemical reactions in the body.
in the cell are carried out by a set of Digestive enzymes speed up chemical
enzymes that are necessary to sustain reactions that break down large food
life. molecules into small molecules.
- The initial stage of the metabolic Digestive enzymes are released, or
process depends upon the enzymes, secreted, by the organs of the digestive
which react with a molecule and is system.
called the substrate. Enzymes convert
the substrates into other distinct Amylase - produced in the mouth. It
molecules, which are known as helps break down large starch
products. molecules into smaller sugar molecules.
- The regulation of enzymes has been a Pepsin - produced in the stomach.
key element in clinical diagnosis. The Pepsin helps break down proteins into
macromolecular components of all amino acids.
enzymes consist of protein, except in
the class of RNA catalysts. Many Trypsin - produced in the pancreas.
ribozymes are molecules of ribonucleic Trypsin also breaks down proteins.
acid, which catalyze reactions in one of
Pancreatic lipase - produced in the
their own bonds.
pancreas. It is used to break apart fats.
● Enzymes are found in all tissues
and fluids of the body.
HOW DO ENZYMES WORK
● Catalysis of all reactions taking
place in metabolic pathways is
● Cells rely on enzymes to
carried out by intracellular
kick-start chemical reactions and
enzymes.
speed them up. Enzymes have a
● The enzymes in the plasma
unique way of kick-starting
membrane govern the catalysis in
reactions, they work by binding
the cells as a response to
one or more specific molecules
cellular signals.
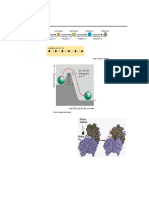
called reactants or substrates. The substrate fits a particular
Binding occurs at a special region active site like a key fits into a particular
on the enzyme called the active lock
site. Once the substrates bind to This theory of enzyme-substrate
the active site, they form what's interaction explains how enzymes
called an enzyme-substrate exhibit specificity for a particular
complex. substrate.
● As the enzymes in substrates
begin to react, some of the
chemical bonds in the substrates
begin to weaken. Causing them
to link together.
● The chemical reaction in the
active site leads to the formation
of a different molecule. This is
2. Induced Fit Model
called the products.
suggested by Daniel Koshland in
1958.
● Once the reaction has occurred,
The induced fit model shows that
the product is released on the
enzymes are rather flexible structures.
active site.
● The enzyme returns to its original According to the induced fit
state and It's free to react again model, the enzyme’s active site is not a
with another set of substrates. completely rigid fit for the substrate.
Instead, the active site will undergo a
conformational change when exposed
to a substrate to improve binding.
2 MODELS OF ENZYMES
1. Lock and Key Model
The lock and key model theory
first postulated by Emil Fischer in 1894
shows the high specificity of enzymes.
However, it does not explain the
stabilization of the transition state that
the enzymes achieve.
The lock and key model states One lactase enzyme can break down a
that the active site of an enzyme lot of lactose. This is why enzymes are
precisely fits a specific substrate. The also called catalyst because they can
induced fit model states that the active be used over and over again in the
site of an enzyme will undergo a reaction.
conformational change when binding a
substrate, to improve the fit. (Catalyst - a substance that increases
the rate of a chemical reaction without
Enzyme can either build up or break itself undergoing any permanent
down the substrates, calling it the chemical change.)
Products.
Enzymes can speed up reactions to FACTORS AFFECTING ENZYMES:
make processes effective for life.
Enzymes - enzymes activity can be
Enzymes often end in -ase, while affected by a variety of factors, enzymes
sugars ends with -ose work best within specific temperature
Ex: Enzymes = Lactase, Sugars = and Ph ranges.
Lactose
TEMPERATURE:
Lactose contains 2 sugar molecules Raising temperature generally
bound together or called disaccharides. speeds up a reaction, and lowering
Now, enzyme lactase has the ability to temperature slows down a reaction. The
break lactose into smaller parts that our suitable temperature for enzymes to
body can digest. With lactase Function properly is 37°C
enzymes, lactose can be broken
down quickly and digested. However, extreme high temperature can
cause enzymes to lose its shape,
However, there are people whose body denature, or take away the natural
doesn't produce enough lactase. And quality and stop working
there are people who are lactose
intolerant. Lactose intolerant people So ang pagtaas ng temperature more
cannot eat dairy products such as than 37°C ay nakakaapekto a chemical
products made with milk, such as bonds in the active site making them
cream, cheese, yogurt, ice cream and less suited to bind substrates.
butter. Products that contain lactose can
make them sick since their body lacks PH:
lactase enzymes. Each enzyme has an optimum
pH range. Changing from pH outside of
this rarge will slow enzyme activity.
Amino Acids present in the active site change in the reaction rate (part (a) of
are acidic or basic. Figure 18.7.1 ). At this point, so much
substrate is present that essentially all
- Fluctuation in PH can affect of the enzyme active sites have
amino acids. making it hard for substrate bound to them. In other words,
substrates to bind Extreme ph the enzyme molecules are saturated
value can denature enzymes. with substrate. The excess substrate
molecules cannot react until the
Enzymes LOSE FUNCTION when they substrate already bound to the enzymes
LOSE FORM or shape. has reacted and been released (or been
released without reacting).
The single most important
property of enzymes is the ability to Concentration of Enzyme
increase the rates of reactions occurring When the concentration of the
in living organisms, a property known as enzyme is significantly lower than the
catalytic activity. Because most concentration of the substrate (as when
enzymes are proteins, their activity is the number of taxis is far lower than the
affected by factors that disrupt number of waiting passengers), the rate
protein structure, as well as by factors of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is
that affect catalysts in general. directly dependent on the enzyme
concentration (part (b) of Figure 18.7.1
Factors that disrupt protein ). This is true for any catalyst; the
structure include temperature and pH; reaction rate increases as the
factors that affect catalysts in general concentration of the catalyst is
include reactant or substrate increased.
concentration and catalyst or enzyme
concentration. The activity of an Enzymes are required for most, if
enzyme can be measured by monitoring not all, processes required for life.
either the rate at which a substrate Enzymes catalyze a reaction by
disappears or the rate at which a reducing the activation energy needed
product forms. for the reaction to occur. However,
enzymes need to be tightly regulated to
Concentration of Substrate ensure that levels of the product do not
In the presence of a given rise to undesired levels. This is
amount of enzyme, the rate of an accomplished by enzyme inhibition.
enzymatic reaction increases as the
substrate concentration increases until a
limiting rate is reached, after which
further increase in the substrate
concentration produces no significant
Competitive Inhibitors ENZYME REGULATION ACTIVITY
Competitive inhibitors compete
with the substrate at the active site, and 2 Major Mechanism
therefore increase Km (the ● Regulation of Change in Activity
Michaelis-Menten constant). However, of Existing Enzyme
Vmax is unchanged because, with ● Regulation of Change in Enzyme
enough substrate concentration, the Concentration
reaction can still complete. The graph REGULATION OF CHANGE IN
plot of enzyme activity against substrate ACTIVITY OF EXISTING ENZYME
concentration would be shifted to the 1. Allosteric
right due to the increase of the Km, 2. Covalent Modification
whilst the Lineweaver-Burke plot would 3. Proteolysis
be steeper when compared with no 4. Compartmentalization
inhibitor. 5. Cascade Mechanism
6. Protein-Protein Interaction
Non-Competitive Inhibitors
Non-competitive inhibitors bind to REGULATION OF CHANGE IN
another location on the enzyme and as ENZYME CONCENTRATION
such decrease VMAX. However, KM is 1. Induction
unchanged. This is demonstrated by a 2. Repression
lower maximum on a graph plotting 3. Degradation
enzyme activity against substrate
concentration and a higher y-intercept ALLOSTERIC
on a Lineweaver-Burke plot when - allo (dot) + steric (phase)
compared with no inhibitor. - an enzyme having side other
than the active side
Positive Effector ( + modulator)
- if it increases enzyme activity
Negative Effector ( - modulator)
- if it decreases enzyme activity
● Relaxed State (Active Enzyme)
● Tensed State (Inactive Enzyme) :
no formation of enzyme substrate
(ES complex)
Three Important Enzymes CASCADE MECHANISM
1. Acetyl CoA Carboxylase - through Cascade of Reaction or
2. Aspartate transcarbamoylase amplification of signals, in which
3. Phosphofructokinase (PFK) small signals are converted into
greater response. (e.g., glycogen
metabolism regulation)
COVALENT MODIFICATION
- sharing of phosphate. PROTEIN-PROTEIN INTERACTION
- Protein kinase is the additional - in which 2 small protein
phosphate which is the product of regulation occurs.
phosphorylation. (e.g., calmodulin activated by calcium )
- Some enzymes are active and
inactive in phosphorylated states. --------------
Other Mechanism INDUCTION
● assertilation - is the increase in the enzyme
● diassertilation activity which occurs at the
● gamma carboxylation genetic level.
PROTEOLYSIS REPRESSION
- a.k.a limited proteolysis - decreases in the enzyme
- is a cleavage of peptides from synthase.
proteins
- some proteins get activated, DEGRADATION
some are produced in our body - a regulation in which enzyme
as an inactive zymogen degradation can be controlled.
- zymogen (proenzyme) is an
inactive precursor of an enzyme Two Mechanism
● Ubiquitin and ATP dependent
COMPARTMENTALIZATION proteolysis
- regulation of translocation of ● ATP independent proteolysis
enzyme occurs to the subcellular
compartment (e.g., Heme
synthesis occurs in mitochondria)
Heme synthesis
- A deficiency in an enzyme that
may lead to clinically significant
groups of disorders called
porphyrias.
You might also like
- 2 1 3 NotesDocument11 pages2 1 3 Notesapi-369706779No ratings yet
- Report Sheet: Color: Cyan Color: White Color: Colorless Color: ColorlessDocument6 pagesReport Sheet: Color: Cyan Color: White Color: Colorless Color: ColorlessMigs MlaNo ratings yet
- (Martin, John H.) Natural Gas ConversionDocument577 pages(Martin, John H.) Natural Gas Conversionfjguevara2No ratings yet
- 4-C1.1 Enzymes and MetabolismDocument42 pages4-C1.1 Enzymes and Metabolismmakaya02No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument3 pagesEnzymessashi bNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ChemistryDocument9 pagesEnzyme ChemistryVictor OmoloNo ratings yet
- VIII Biology HO 5Document6 pagesVIII Biology HO 5aditiroy201208No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesUsman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument41 pagesBiology ProjectGanesan Siva67% (12)
- Genes & Inheritance SeriesDocument58 pagesGenes & Inheritance SeriesKim HoangNo ratings yet
- Enzymes ...Document13 pagesEnzymes ...Glen MangaliNo ratings yet
- GCE AS Biology 3 ENZYME NoteDocument11 pagesGCE AS Biology 3 ENZYME Notengnicole090607No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument43 pagesEnzymesMaryam SabirNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Part 1Document23 pagesEnzymes Part 1judevolkovNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Principles of BiologyDocument18 pagesEnzymes: Principles of BiologyNaskar SouvikNo ratings yet
- Course Subject: Biochemistry Course Topic: EnzymesDocument5 pagesCourse Subject: Biochemistry Course Topic: EnzymesAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument11 pagesEnzymesMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio Chapter 6Document32 pagesCell Bio Chapter 6GuteNo ratings yet
- What Are Enzymes?: E E E EDocument15 pagesWhat Are Enzymes?: E E E EFarhana MuradNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Biology Lecture Prepared By: Waleed Zahoor Team Roshni Step-Up PakistanDocument11 pagesEnzymes: Biology Lecture Prepared By: Waleed Zahoor Team Roshni Step-Up PakistanRabia KhalilNo ratings yet
- Protein Denaturation: EnzymesDocument7 pagesProtein Denaturation: EnzymescharlesNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument6 pagesEnzymesSarah Farhah2000100% (1)
- Week 6 EnzymessDocument49 pagesWeek 6 EnzymessRechell Mae DaclesNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Form 3Document4 pagesEnzymes Form 3Ralph MuchingamiNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument16 pagesEnzymesalcedocedmerkNo ratings yet
- Enzymes New1Document19 pagesEnzymes New1AHMAD NAWAZNo ratings yet
- Lesson #8 - EnzymesDocument29 pagesLesson #8 - EnzymesMaya AwadNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Bio IgcseDocument7 pagesChap 5 Bio Igcseananya.arumugarajanNo ratings yet
- Module 11: EnzymesDocument3 pagesModule 11: EnzymesMariam EskandariNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument15 pagesEnzymeAljon Lara ArticuloNo ratings yet
- The Nature, Properties and Classifiication Ofi Enzymes and CofiactorsDocument24 pagesThe Nature, Properties and Classifiication Ofi Enzymes and CofiactorsuagboladeNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes CHPTR 5Document4 pagesBiology Notes CHPTR 5Wan HasliraNo ratings yet
- Enzymes (As Biology)Document42 pagesEnzymes (As Biology)Muhtasim FarhanNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument35 pagesGen Biomikechristian073No ratings yet
- Enzymes As CatalystsDocument6 pagesEnzymes As Catalystselena piovesanNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument3 pagesEnzymesArabela SimanganNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: A Protein With Catalytic Properties Due To Its Power of Specific ActivationDocument35 pagesEnzymes: A Protein With Catalytic Properties Due To Its Power of Specific ActivationAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument53 pagesEnzymesompurahardiNo ratings yet
- c1.1 EnzymesDocument36 pagesc1.1 Enzymeshwqhd asjdhuaNo ratings yet
- GEN BIOLOGY 1 Deptal 2nd Quarter Exam ReviewerDocument3 pagesGEN BIOLOGY 1 Deptal 2nd Quarter Exam ReviewerVanessa JimenezNo ratings yet
- Bio-Ch 5-EnzymesDocument6 pagesBio-Ch 5-EnzymesHassan RiazNo ratings yet
- EnzimasDocument19 pagesEnzimasLuis Alfonso Paez FuentesNo ratings yet
- Enzyme NotesDocument4 pagesEnzyme NotesPreethaNo ratings yet
- Final Study On EnzymeDocument9 pagesFinal Study On Enzymerosariopraveen007No ratings yet
- Enzymes: Enzymes Homeostasis Activation EnergyDocument6 pagesEnzymes: Enzymes Homeostasis Activation EnergyGowthami MarreddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 BioDocument23 pagesChapter 5 Biojoelmokwenxuan2No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument4 pagesEnzymesHeily NicoleNo ratings yet
- Lecture On EnzymesDocument26 pagesLecture On EnzymesDAVIE MATIASNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument3 pagesMetabolismFans TimeNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument5 pagesEnzymeseyosiyas tekleweyinNo ratings yet
- Enzyme CatalysisDocument35 pagesEnzyme CatalysisMihir IyerNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument34 pagesEnzymeDanica SantosNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 EnzymesDocument32 pagesUnit 3 EnzymessmilepathologyNo ratings yet
- AP BIO Febraury Break With AnswersDocument12 pagesAP BIO Febraury Break With AnswersMehak BectorNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 A EnzymesDocument3 pagesUnit 3 A EnzymesseecatpNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument12 pagesEnzymesAsima NaqviNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 3Document6 pagesEnzymes 3MituSamadderNo ratings yet
- icpUNIT 4Document8 pagesicpUNIT 4frankyupi22No ratings yet
- Enzyme UpdatedDocument42 pagesEnzyme UpdatedBukhari DiangkaNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument20 pagesEnzymesRICHARD NESTORNo ratings yet
- Jessica Lee Enzyme LabDocument15 pagesJessica Lee Enzyme LabAshalee JonesNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- 2 Hormone-FunctionDocument11 pages2 Hormone-FunctionzarszNo ratings yet
- 4 VitaminsDocument11 pages4 VitaminszarszNo ratings yet
- 3 Amino-Acids-And-PeptidesDocument17 pages3 Amino-Acids-And-PeptideszarszNo ratings yet
- Report FieldsDocument2 pagesReport FieldszarszNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Rate of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Designing A "Good" Nucleophilic SubstitutionDocument9 pagesFactors Affecting Rate of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Designing A "Good" Nucleophilic SubstitutionchuasioklengNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry Specialisation Syllabus of Iii & Iv SemestersDocument23 pagesM.Sc. Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry Specialisation Syllabus of Iii & Iv SemestersAnantha LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Acids and BasesDocument4 pagesLesson 5: Acids and BasesBellay KaleesiyNo ratings yet
- CV 20181212Document5 pagesCV 20181212Piyasan PraserthdamNo ratings yet
- Food Packaging: Closure, Sealing, Deterioration and Shelf-Life of FoodDocument56 pagesFood Packaging: Closure, Sealing, Deterioration and Shelf-Life of FoodDavid ElricoNo ratings yet
- Teo2004 PDFDocument9 pagesTeo2004 PDFFabian Loor CadenaNo ratings yet
- Cc3 Thermodynamics TheoryDocument20 pagesCc3 Thermodynamics TheorySubhradeep GhoshNo ratings yet
- 9701_s24_qp_23Document16 pages9701_s24_qp_23rantaolameNo ratings yet
- CHM143 Answer For Tutorial 6Document5 pagesCHM143 Answer For Tutorial 62023502121No ratings yet
- Syl BSC - Sem V VI 2015 PDFDocument77 pagesSyl BSC - Sem V VI 2015 PDFTrupti GaikwadNo ratings yet
- DSE Chemistry - Paper 2 by Dr. Samuel ChongDocument11 pagesDSE Chemistry - Paper 2 by Dr. Samuel Chonglht001023No ratings yet
- (Advances in Inorganic Chemistry and Radiochemistry 21) H.J. Emeléus and A.G. Sharpe (Eds.) - Elsevier, Academic Press (1978)Document315 pages(Advances in Inorganic Chemistry and Radiochemistry 21) H.J. Emeléus and A.G. Sharpe (Eds.) - Elsevier, Academic Press (1978)Thảo HàNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Mechanisms of Cementation of Cadmium Ions by Zinc PowderDocument10 pagesKinetic Mechanisms of Cementation of Cadmium Ions by Zinc Powdermangalord345No ratings yet
- Medical BiochemistryDocument264 pagesMedical BiochemistryKarren Taquiqui Plete100% (1)
- FTS JEE (Main & Advanced) 2019 - XII Studying - FinalDocument2 pagesFTS JEE (Main & Advanced) 2019 - XII Studying - FinalB.K.Sivaraj rajNo ratings yet
- Bath and Deposit Monitoring System For Electroless Nickel Plating ProcessDocument7 pagesBath and Deposit Monitoring System For Electroless Nickel Plating Processlaboratorio berritzenNo ratings yet
- Pearson Ch2 Answers-1Document12 pagesPearson Ch2 Answers-1Person GainableNo ratings yet
- Propylene HydrationDocument9 pagesPropylene HydrationDerya Akkanat Fırat100% (1)
- CRE Chapter 1 Overview of Chemical Reaction EngineeringDocument34 pagesCRE Chapter 1 Overview of Chemical Reaction EngineeringThịnh VănNo ratings yet
- Praxair's Oxygen Addition Technologies For Chemical Oxidation ReactionsDocument14 pagesPraxair's Oxygen Addition Technologies For Chemical Oxidation ReactionsCristian TorrezNo ratings yet
- Thermal Heat Pad: Chemistry Research ProjectDocument24 pagesThermal Heat Pad: Chemistry Research ProjectSiva NeshNo ratings yet
- Trial 1 Chemistry, Paper 2 (Soalan)Document11 pagesTrial 1 Chemistry, Paper 2 (Soalan)huda186No ratings yet
- Magnesium and Acid Worksheet - Answer KeyDocument3 pagesMagnesium and Acid Worksheet - Answer KeyVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Pre Board Examination in Majorship Specialization ScienceDocument11 pagesPre Board Examination in Majorship Specialization Science48pgcw62kkNo ratings yet
- Angew Chem Int Ed - 2023 - Guo - One Carbon Ring Expansion of Indoles and Pyrroles A Straightforward Access ToDocument9 pagesAngew Chem Int Ed - 2023 - Guo - One Carbon Ring Expansion of Indoles and Pyrroles A Straightforward Access ToAlages WaranNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Learning Activity SheetDocument9 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Learning Activity SheetMaria Sophia AlviolaNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Chemistry - J. Hepworth, Et Al., (RSC, 2002) BBS PDFDocument180 pagesAromatic Chemistry - J. Hepworth, Et Al., (RSC, 2002) BBS PDFKevin Wang50% (2)