Lab Manual I Sem Basic Electrical
Uploaded by
Goutami T SunthankarLab Manual I Sem Basic Electrical
Uploaded by
Goutami T SunthankarBASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY
Course Code 21ELE17/27 CIE Marks 50
Teaching Hours/Week (L:T:P) 0:0:2 SEE Marks 50
Credits 01 Exam Hours 03
Course objectives:
After studying this course, students should be able to
(i)To explain how to verify KCL and KVL for DC circuit and maximum power transfer theorem.
(ii) To explain power and power factor measurement of different types of lamps.
(iii) To explain measurement of impedance for R-L circuits.
(iv) To explain measurement of power consumed in a 3-phase load.
(v)To explain methods of controlling a lamp from different places.
(vi)To explain the effect of Open and Short circuit in simple circuits and measurement of earth resistance.
Sl.NO Experiments
1 Verification of KCL and KVL for DC circuits
2 Verification of maximum power theorem.
3 Measurement of Current, Power and Power Factor of Incandescent Lamp, Fluorescent Lamp and LED Lamp.
4 Measurement of Resistance and Inductance of a Choke coil using three voltmeter method.
5 Determination of Phase and Line quantities in three phase star and delta connected loads.
6 Measurement of 3- phase Power using Two Wattmeter Method.
7 Determination of efficiency of a single phase transformer by direct load test.
8 Two Way and Three Way Control of Lamp and Formation of Truth Table.
9 Measurement of Earth Resistance
10 Study of effect of Open and Short circuit in simple circuits.
Course outcomes
At the end of the course the student will be able to:
CO1: Conduct experiment to verify KCL and KVL and maximum power transfer theorem for DC circuits.
CO2: Conduct experiments to compare power factor of different types of lamps.
CO3: Conduct experiments to measure impedance of an electrical circuit and power consumed by a 3-phase load
CO4: Understand two-way and three-way control of lamps and measurement of earth resistance.
CO5: Explain the effects of open and short circuits in simple circuits.
Continuous Internal Evaluation (CIE): The CIE marks awarded in case of Practical shall be based on the weekly
evaluation of laboratory journals/ reports/laboratory record after the conduction of every experiment and one practical test. The
maximum marks prescribed for the former and the latter shall be 35 and 15. The total CIE marks shall be the sum of marks secured by
students in the above events.
Semester End Evaluation (SEE): The practical examinations to be conducted as per the time table of University with a
batch wise strength of not more than 10-15 students per batch
.(i) All laboratory experiments are to be included for practical examination.
(ii) Breakup of marks and the instructions printed on the cover page of answer script to be strictly adhered by the examiners.
(iii)Students can pick one experiment from the questions lot prepared by the examiners.
(iv) Change of experiment is allowed only once and 15% Marks allotted to the procedure part to be made zero
VDIT Haliyal ENE
1
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-1
Verification of KVL and KCL for DC circuits.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
2
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
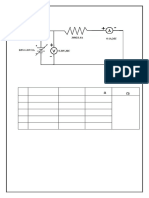
Fig no 1. circuit diagram Kirchhoff’s Voltage Laws
Fig no 2. circuit diagram Kirchhoff’s Current Laws
VDIT Haliyal ENE
3
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-1: Date; __ / __ / 202_
Aim: To verify KVL and KCL for DC circuits.
1. Kirchhoff’s Voltage Laws ∑ Voltage = 0
2. Kirchhoff’s current low ∑ Current = 0
System under consideration:
1-D.C. supply of rating; a) Voltage : _____Volts ,Current : ________Amps
2- Resistance R1= ________ Ohms R2 = ________ Ohms R3= ______Ohms
Apparatus required: The apparatus required to conduct the experiment are given in Table 1.
TABLE 1 Apparatus required
SL No. Apparatus/Instruments Range Type Qty
1. D.C. power supply 12V/2A 1
2. Voltmeter 0-300V M.C 5
3. Ammeter 0-5 A M.C 5
4. Three Resistance Box 1
Theory
Procedure:
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Laws
1. Make the connections as per circuit diagram shown in Fig.1.
2. Switch on the supply
3. Take the readings of voltmeters
4. Switch off the supply.
Kirchhoff’s current low
1. Make the connection as per circuit diagram shown in Fig. 2.
2. Switch on supply
3. Take the readings of ammeter ,
4. Switch off the supply.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
4
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
SPECIMEN CALCULATIONS
R1= ________ Ohms R2 = ________ Ohms And R3= ______Ohms
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Laws
Supply voltage Vs = _______ Volts DC
Equivalent resistance Req = R1 + R2 + R3 = ________ Ohms
𝑉
Current I = = ________ Amps
𝑅𝑒𝑞
Voltage across Resistance (R1 ) V1 = R1 * I = ______ Volta
Voltage across Resistance ( R2 ) V2 = R2 * I = _______Volts
Voltage across Resistance ( R3 ) V3 = R3* I = _______Volts
Voltage across Resistance ( Req ) Vt = V1+ V2 + V3 = __________Volts
Tabular Column:
Theoretically Value ( calculated) Practical Value ( Mater reading)
Voltmeter Voltmeter Voltmeter Voltmeter Voltmeter Voltmeter Voltmeter Voltmeter
Vt V1 V2 V3 VS VL1 VL2 VL3
Results:
Conclusions:
VDIT Haliyal ENE
5
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
SPECIMEN CALCULATIONS
Kirchhoff’s current low:
Supply voltage Vs = 12 Volts DC
1 1 1 1
Equivalent resistance Req = + +
𝑅𝑒𝑞 𝑅1 𝑅2 𝑅𝑒
𝑉
Current flow in Resistance (R1) I1 = = ________ Amps
𝑅1
𝑉
Current flow in Resistance (R2) I2 = = ________ Amps
𝑅2
𝑉
Current flow in Resistance (R3) I3 = = ________ Amps
𝑅3
Total Current flow in circuit It = I1 + I2 + I3 = ________ Amps
Tabular Column:
Theoretically Value ( calculated) Practical Value ( Mater reading)
Ammeter Ammeter Ammeter Ammeter Ammeter Ammeter Ammeter Ammeter
It I1 I2 I3 IS IL1 IL2 IL3
Results:
Conclusions:
VDIT Haliyal ENE
6
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
VDIT Haliyal ENE
7
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-2
Verification of maximum power theorem.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
8
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Verification of Maximum power transfer theorem.
Fig No1. Circuit diagram of the Maximum power transfer theorem
Fig No2. Circuit diagram of the determine the open circuit voltage
Fig No3. Determine resistance
VDIT Haliyal ENE
9
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-2: Date; __ / __ / 202_
Aim: To verify Maximum power transfer theorem for DC circuits.
System under consideration:
1-D.C. supply of rating; Voltage: _____Volts, Current: ________Amp
2-Resistance box 100 ohms to 2 K.ohms
Apparatus required: The apparatus required to conduct the experiment are given in Table 1.
TABLE 1 Apparatus required
SL No. Apparatus/Instruments Range Qty
1. Power supply 0-30Volts 1
2. Voltmeter 0.30 volts 2
3. Ammeter 0.2 Amps 2
4. Resistor 1K 4
5 DRB 0-1000ohms 1
Theory
rocedure:
1 Make the connections as per circuit diagram shown in Fig.1.
2 Switch on the supply
3 Increase the load (resistance) step by step.
4 Take the readings of voltmeter and Ammeter
5 Switch off the supply.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
10
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Tabular Column:
Resistance Voltage Current power
Sl.No RL VL I P = VL X I
SPECIMEN CALCULATIONS:
Power for each value of Load. P = VL X I
VDIT Haliyal ENE
11
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
VTH = _____- Volts [Remove the load, (Show in fig No2) and
determine the open circuit voltage using multimeter (VTH)]
RTH = _____ Ohms [Remove the load and short circuit the
voltage source ( Show In fig No3 ) Find the looking back resistance (RTH) using
multimeter.]
𝑉𝐿
IL =
𝑅𝑇𝐻 +𝑅𝐿
Calculate the power delivered to the load P max = 𝐼𝐿2 𝑋 𝑅𝐿
Verify maximum transfer theorem.
Practical Value Theoretical Value
Maximum power transfer theorem P max
Resistance transfer theorem RTH
VDIT Haliyal ENE
12
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-3
Measurement of current, power and power factor of incandescent
lamp and LED lamp.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
13
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Fig no1. Circuit diagram Measurement of current, power and power factor of lamps
VDIT Haliyal ENE
14
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-3: Date; __ / __ / 202_
Aim: Measurement of current, power and power factor of incandescent lamp, fluorescent lamp,
and LED lamp.
System under consideration:
• Florescent Lamp; Watts _______, Voltage _________ Power Factor _______
• Incandescent Lamp; Watts _______, Voltage _________
• Led Lamp; Watts _______, Voltage _________ Power Factor _______
Apparatus required: The apparatus required to conduct the experiment are given in Table 1.
TABLE 1 Apparatus required
SL No. Apparatus/Instruments Range Type Qty
1. Voltmeter 0-300 Volts M.I 1
2. Ammeter 0.150Mili Amps M.I 1
3. Wattmeter 300volts/250mili Amps UPF/LPF 1
4. Tube light 40 Watts 1
5. LED Lamp 9 Watts 1
6. Incandescent
I lamp 60 watts 1
Theory
Procedure:
1. Make the connections as per circuit diagram shown in Fig.1.
2. Connect the incandescent bulb in the bulb holder
3. Switch on the supply
4. Take the readings of voltmeter, Ammeter and Wattmeter
5. Connect the tube light in the lamp holder with help of holder adapter
6. Take the readings of voltmeter, Ammeter and Wattmeter
7. Connect the LED lamp in the holder
8. Take the reading of the voltmeter, Ammeter and Wattmeter
9. Switch off the supply.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
15
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Tabular Column:
Type of load Voltmeter Ammeter Wattmeter
Incandescent Lamp
Florescent Lamp
Led Lamp
SPECIMEN CALCULATIONS
Calculation
Watt meter constant = V * I * Cos∅/ Full scale reading
𝑾
Power factor Cos ∅ =
𝑽∗ 𝑰
TYPE OF LOAD Power factor
Incandescent Lamp
Florescent Lamp
Led Lamp
Results:
Conclusions:
VDIT Haliyal ENE
16
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-4
Measurement of resistance and inductance of a choke coil using 3
voltmeter methods.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
17
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Fig no1. circuit diagram inductance coli
VDIT Haliyal ENE
18
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-4: Date; __ / __ / 202_
Aim: Measurement of resistance and inductance of a choke coil using 3 voltmeter method..
System under consideration:
• Choke coil ; 40 Watts, 230 Voltage
• Resistance : ______ ohms
Apparatus required: The apparatus required to conduct the experiment are given in Table 1.
TABLE 1 Apparatus required
SL No. Apparatus/Instruments Range Type Qty
1. Voltmeter 0-300 Volts M.I 3
2. Ammeter 0.150Mili Amps M.I 1
3. choke coil 1
4. Resistance load 1
Theory
Procedure:
1) Make the connections as per circuit diagram shown in Fig.1.
2) Switch on the supply
3) Take the readings of voltmeters and Ammeter
4) Switch off the supply.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
19
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Tabular Column: R-L circuit
Voltmeter Voltmeter Voltmeter
Ammeter
Total resistance inductance
V VR VL I
SPECIMEN CALCULATIONS
𝑽𝟐 − 𝑽𝟐𝑹 − 𝑽𝟐𝑳
Resistance of the coil Vr = = _________ Volts
𝟐𝑽𝑹
𝑽𝒓
Power factor of the induction coil 𝐜𝐨𝐬 ∅ = = __________
𝑽𝑳
𝑽𝑳
Impedance of the inductance coil Z = = __________ ohms
𝑰
Resistance of the choke coil Rc = Z cos∅ = ________Ohms
Reactance of the choke coil XL = √𝒁𝟐 − 𝑹𝒄𝟐 = _____________Ohms
𝑿𝑳
Induction of the choke coil L= =___________m. H
𝟐𝝅𝒇
Resistance of the Inductance of the
choke coil choke coil
Results:
Conclusions:
VDIT Haliyal ENE
20
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-5:
Voltage and Current relationships of three phase star/delta circuits.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
21
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Fig no1. Connection diagram three phase star circuits
Fig no 2. Connection diagram three phase delta circuits
VDIT Haliyal ENE
22
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-5: Date; __ / __ / 202_
Aim:. Verification of Voltage and Current relationships of three phase star/delta loads
System under consideration:
• Transformer : ______KVA , _______Volts, ___________Amps
Apparatus required: The apparatus required to conduct the experiment are given in Table 1.
TABLE 1 Apparatus required
SL No. Apparatus/Instruments Range Type Qty
1. Voltmeter 0-600/300 Volts M.I 2
2. Ammeter 0.10Mili Amps M.I 2
3. Resistance load Three phase load 1
Theory
Procedure: Star
1) Make the connections as per circuit diagram shown in Fig.1.
2) Switch on the supply
3) Increase the load step by step.
4) Take the readings of voltmeter, Ammeter and Wattmeter
5) Switch off the supply.
Procedure: Delta
1) Make the connections as per circuit diagram shown in Fig.1.
2) Switch on the supply
3) Increase the load step by step.
4) Take the readings of voltmeter, Ammeter and Wattmeter
5) Switch off the supply.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
23
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Tabular Column: Star
Line Line Phase Phase
Voltmeter Ammeter Voltmeter Ammeter
Tabular Column: Delta
Line Line Phase Phase
Voltmeter Ammeter Voltmeter Ammeter
SPECIMEN CALCULATIONS:
Calculation Star
Line voltage 𝑉𝐿 = √3 𝑉𝑃 ( Phase Voltage)
Line Current 𝐼𝐿 = 𝐼𝑃 ( Phase Current)
Calculation : Delta
Line voltage 𝑉𝐿 = 𝑉𝑃 ( Phase Voltage)
Line Current 𝐼𝐿 = √3 𝐼𝑃 ( Phase Current)
Results:
Conclusions:
VDIT Haliyal ENE
24
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-6
Measurement of three phase’s power using two wattmeter methods.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
25
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Fig no 1. Circuit diagram Measurement of three phase power using two wattmeter method
VDIT Haliyal ENE
26
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-6: Date; __ / __ / 202_
Aim:. Measurement of three phase power using two wattmeter method.
System under consideration:
• Three phase Load : ________KVA , _______Volts, ___________Amps
Apparatus required: The apparatus required to conduct the experiment are given in Table 1.
TABLE 1 Apparatus required
SL No. Apparatus/Instruments Range Type Qty
1. Voltmeter 0-600/300 Volts M.I 1
2. Ammeter 0.10Mili Amps M.I 1
3. Wattmeter 600volt 10 Amps Upf 2
4. Resistance load Three phase load 1
Theory
Procedure: Resistive load
1. Make the connections as per circuit diagram shown in Fig.1.
2. Switch on the supply
3. Increase the load step by step.
4. Take the readings of voltmeter, Ammeter and Wattmeter
5. Switch off the supply.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
27
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Tabular Column:
Star Connected Load Delta Connected load
Voltmeter Ammeter Wattmeter Wattmeter Voltmeter Ammeter Wattmeter Wattmeter
SPECIMEN CALCULATIONS:
Calculation Resistive load W1 + W2 = √3 𝑉 𝐼
Load = Wt = W1 + W2 watts
Load = √3 𝑉 𝐼 watts
Star Connected Load Delta Connected load
W1 + W2 √3 𝑉 𝐼 W1 + W2 √3 𝑉 𝐼
VDIT Haliyal ENE
28
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-7
Determination of efficiency of a single phase transformer by direct
load test.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
29
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Fig no1. circuit diagram load test transformer
VDIT Haliyal ENE
30
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-7: Date; __ / __ / 202_
Aim:. Load test on a single phase transformer.
System under consideration:
• Transformer : ______KVA , _______Volts, ___________Amps
Apparatus required: The apparatus required to conduct the experiment are given in Table 1.
TABLE 1 Apparatus required
SL No. Apparatus/Instruments Range Type Qty
1) Voltmeter 0-300 Volts M.I 2
2) Ammeter 0.150Mili Amps M.I 2
3) Wattmeter 300volts/250mili Amps UPF/LPF 2
4) Resistance load 1
Theory
Procedure:
1. Make the connections as per circuit diagram shown in Fig.1.
2. Switch on the supply
3. Increase the load step by step.
4. Take the readings of voltmeter, Ammeter and Wattmeter
5. Switch off the supply.
Tabular Column:
No load Voltage Vo = ___________
Voltmeter Ammeter Voltmeter Ammeter
VDIT Haliyal ENE
31
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
SPECIMEN CALCULATIONS
Calculation
Input power 𝑷𝒊𝒏 = 𝑽𝒔 𝑿 𝑰𝒔
Output power 𝑷𝒐𝒖𝒕 = 𝑽𝑳 𝑿 𝑰𝑳
𝑷𝒐𝒖𝒕 𝑽𝑳 𝑿 𝑰𝑳
Efficiency = X100 = X 100
𝑷𝒊𝒏 𝑽𝒔 𝑿 𝑰𝒔
𝑽𝒐 −𝑽𝒔
Regulation = X 100
𝑽𝒐
Efficiency Regulation
VDIT Haliyal ENE
32
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-8
Two ways and three way Control of lamp and formation of truth table.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
33
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Fig No1: Wiring diagram, two way control of a lamp
Fig No2: Wiring diagram, three way control a lamp
VDIT Haliyal ENE
34
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-8: Date; __ / __ / 202_
Aim:. Two way and three way Control of lamp and formation of truth table.
Two way control of a lamp
Three way control of a lamp
System under consideration:
Two way Switch
Apparatus required: The apparatus required to conduct the experiment are given in Table 1.
TABLE 1 Apparatus required
SL No. Apparatus/Instruments Range Qty
1. Wiring board -- 1
2. Holder - 1
3. Two way Switch 6 Amps 2
4. Intermediate switch 6 amps 1
5 Lamp 100 Watts 1
6 Supply board -- 1
Pipes , wires ,junction boxes
7
and switch box
Theory
VDIT Haliyal ENE
35
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Procedure: Two way control of a lamp
1. Study the given wiring diagram, Fig no1
2. Make the location point, Switchboard, and lamp holder.
3. Place the wires along with in the pipe.
4. Fix the bulb holder, switches on the box.
5. Give a supply to the wires circuit.
6. Test the working of light
7. Truth table
Switch 1 Switch 2 Lamp
S-A C-L
S-A D-L
S-B C-L
S-B D-L
8. Switch off the supply.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
36
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Procedure: Three way control of a lamp
1. Study the given wiring diagram, fig no2.
2. Make the location point, Switchboard, and lamp holder.
3. Place the wires along with in the pipe.
4. Fix the bulb holder, switches on the box.
5. Give a supply to the wires circuit.
6. Test the working of light
7. Truth table
Switch 1 Switch 3 Switch 2 Lamp
S-A M-O N-P C-L
S-A M-O N-P D-L
S-A M-P N-O C-L
S-A M-P N-O D-L
S-B M-O N-P C-L
S-B M-O N-P D-L
S-B M-P N-O C-L
S-B M-P N-O D-L
7.Switch off the supply.
Results: Conclusions:
VDIT Haliyal ENE
37
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
VDIT Haliyal ENE
38
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiments 9:
Measurement of earth resistance.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
39
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
VDIT Haliyal ENE
40
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-9: Date; __ / __ / 202_
Aim:. Measurement of Earth resistance
.
System under consideration:
Apparatus required: The apparatus required to conduct the experiment are given in Table 1.
TABLE 1 Apparatus required
SL No. Apparatus/Instruments Range Qty
1. Earth tester 1
2. Pipe earth point 1
3. Spike rod 2
4. 2.5 mm sq Wire 10 mtrs
5. Measurement Tape 1
Theory
Procedure:
1. Connect C1 and P1 terminals on the test set to the earth electrode (Fig No 1.).
2. Drive a probe into the earth 16 meters from the centre of the electrode and connect to
terminal C2.This probe should be driven to a depth of 6 – 12 inches.
3. Drive another probe into the earth midway between the electrodes and probe C2 and
connect to terminal P2. This probe should be driven to a depth 6 – 12 inches.
4. Record the resistance measurement.
5. Move the potential probe 2 meters farther away from the electrode and make a second
measurement.
6. Move the potential probe 2 meters closer to the electrode and make a third measurement.
7. If the three measurements agree with each other within a few present of their average, then
the average of the three measurements may be used as the electrode resistance.
8. If the three measurements disagree by more than a few present from their average, then
additional measurement procedures are required.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
41
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Tabular Column:
Sl.No Distance Voltage Current Resistance
Feet Volts Amps Ohms
Resistance = voltage/ current
Results:
Conclusions:
VDIT Haliyal ENE
42
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiments 10
Study the effect of the open and short circuit in simple circuit.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
43
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Fig No 1 Closed circuit
Fig 2. Open circuit Fig 3. Open circuit
Fig 4. Open circuit Fig 5. Short circuit
Fig 6. Short circuit Fig 7. Short circuit
VDIT Haliyal ENE
44
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Experiment-10: Date; __ / __ / 202_
Aim:. study the effect of the open and short circuit in simple circuit
.
System under consideration:
Apparatus required: The apparatus required to conduct the experiment are given in Table 1.
TABLE 1 Apparatus required
SL No. Apparatus/Instruments Range Qty
1. OC and SC testing kit 230 V 1
2. LED s 3 watts 3
3.
4.
5
6
Theory
Procedure:
1 Make the connections as per circuit diagram shown in Fig.1.
2 Switch on the supply
3 Make the closed circuit of Fig 1. Note down LEDs are ON or OFF
4 Make the open circuit of Fig 2. Note down LED are which ON and Off
5 Make the open circuit of Fig 3. Note down LED are which ON and Off
6 Make the open circuit of Fig 4. Note down LED are which ON and Off
7 Make the short circuit of Fig 5. Note down LED are which ON and Off
8 Make the open circuit of Fig 6. Note down LED are which ON and Off
9 Make the open circuit of Fig 7. Note down LED are which ON and Off
10 Switch off the supply.
VDIT Haliyal ENE
45
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
Tabular Column:
LED 1 LED 2 LED3
Fig No1 Closed circuit
Fig No2 Open circuit
Fig No3 Open circuit
Fig No4 Open circuit
Fig No5 Short circuit
Fig No6 Short circuit
Fig No7 Short circuit
Results:
Conclusions:
VDIT Haliyal ENE
46
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
VDIT Haliyal ENE
47
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I/II Sem
VDIT Haliyal ENE
48
You might also like
- Hourglass Workout Program by Luisagiuliet 276% (21)Hourglass Workout Program by Luisagiuliet 251 pages
- The Hold Me Tight Workbook - Dr. Sue Johnson100% (16)The Hold Me Tight Workbook - Dr. Sue Johnson187 pages
- Read People Like A Book by Patrick King-Edited62% (65)Read People Like A Book by Patrick King-Edited12 pages
- Livingood, Blake - Livingood Daily Your 21-Day Guide To Experience Real Health77% (13)Livingood, Blake - Livingood Daily Your 21-Day Guide To Experience Real Health260 pages
- COSMIC CONSCIOUSNESS OF HUMANITY - PROBLEMS OF NEW COSMOGONY (V.P.Kaznacheev,. Л. V. Trofimov.)94% (212)COSMIC CONSCIOUSNESS OF HUMANITY - PROBLEMS OF NEW COSMOGONY (V.P.Kaznacheev,. Л. V. Trofimov.)212 pages
- Donald Trump & Jeffrey Epstein Rape Lawsuit and Affidavits83% (1016)Donald Trump & Jeffrey Epstein Rape Lawsuit and Affidavits13 pages
- The 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York Times94% (34)The 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York Times3 pages
- The 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York Times95% (21)The 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York Times3 pages
- Jeffrey Epstein39s Little Black Book Unredacted PDF75% (12)Jeffrey Epstein39s Little Black Book Unredacted PDF95 pages
- The 4 Hour Workweek, Expanded and Updated by Timothy Ferriss - Excerpt23% (954)The 4 Hour Workweek, Expanded and Updated by Timothy Ferriss - Excerpt38 pages
- A Project Report On Survey On Customer Satisfaction of Philips Lightings50% (6)A Project Report On Survey On Customer Satisfaction of Philips Lightings47 pages
- Podar International School, Ambegaon STD: Vii Subject: Science100% (2)Podar International School, Ambegaon STD: Vii Subject: Science6 pages
- IEC Exp 2 Verification of Kirchoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and Kirchoff's Current Law (KCL)No ratings yetIEC Exp 2 Verification of Kirchoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and Kirchoff's Current Law (KCL)4 pages
- 1basic Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21No ratings yet1basic Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-2182 pages
- Network Analysis and Simulation LaboratoryNo ratings yetNetwork Analysis and Simulation Laboratory33 pages
- Experiment 1-Current Voltage MeasurementNo ratings yetExperiment 1-Current Voltage Measurement8 pages
- M.M. Engineering College - Mullana: Laboratory Manual Practical Experiment Instruction SheetNo ratings yetM.M. Engineering College - Mullana: Laboratory Manual Practical Experiment Instruction Sheet3 pages
- DC Lab - Exp - 2 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)No ratings yetDC Lab - Exp - 2 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)5 pages
- World University of Bangladesh Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering (EEE)No ratings yetWorld University of Bangladesh Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering (EEE)5 pages
- Electrical Technology Lab: Lab Manual I, Ii SemesterNo ratings yetElectrical Technology Lab: Lab Manual I, Ii Semester34 pages
- BEEE Lab Observation (Print Both Sides)No ratings yetBEEE Lab Observation (Print Both Sides)46 pages
- Electrical Workshop Practice: Laboratory ManualNo ratings yetElectrical Workshop Practice: Laboratory Manual30 pages
- DC Lab Exp 2 Student Manual (Fall 22-23)No ratings yetDC Lab Exp 2 Student Manual (Fall 22-23)6 pages
- Lab 2 - Kirchoff's current and voltage laws(1)100% (1)Lab 2 - Kirchoff's current and voltage laws(1)8 pages
- EE-104 (Electrical Circuit Lab 1 To 30 Pegs)No ratings yetEE-104 (Electrical Circuit Lab 1 To 30 Pegs)30 pages
- Experiment 3: To Verify Kirchhoff's Voltage and Current Laws ExperimentallyNo ratings yetExperiment 3: To Verify Kirchhoff's Voltage and Current Laws Experimentally3 pages
- Design of Electrical Circuits using Engineering Software ToolsFrom EverandDesign of Electrical Circuits using Engineering Software ToolsNo ratings yet
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Leaving Certificate ExaminationNo ratings yetCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Leaving Certificate Examination12 pages
- A Survey of Light Emitting Diode (LED) Display Board: Gowrishankar Kasilingam, Mritha Ramalingam and Chandra SekarNo ratings yetA Survey of Light Emitting Diode (LED) Display Board: Gowrishankar Kasilingam, Mritha Ramalingam and Chandra Sekar4 pages
- The Night Light Robbery - How The LED Bulb Industry Is Ensuring Customers Keep Coming Back - India TodayNo ratings yetThe Night Light Robbery - How The LED Bulb Industry Is Ensuring Customers Keep Coming Back - India Today17 pages
- Design Characteristics and Development of A Nozzle For Coaxial Laser CladdingNo ratings yetDesign Characteristics and Development of A Nozzle For Coaxial Laser Cladding10 pages
- Image Processing: Research Opportunities and Challenges: December 2010No ratings yetImage Processing: Research Opportunities and Challenges: December 20106 pages
- Part 8 (Final A) of Ghana Building CODE (2012)No ratings yetPart 8 (Final A) of Ghana Building CODE (2012)32 pages
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University: Natural Resources and Energy LawNo ratings yetDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University: Natural Resources and Energy Law29 pages
- Ed Grade 9 Unit Practice Test Science Electrical Principles TechnologiesNo ratings yetEd Grade 9 Unit Practice Test Science Electrical Principles Technologies14 pages
- Kim Lighting B30 Series Bollard Brochure 1983No ratings yetKim Lighting B30 Series Bollard Brochure 198320 pages
- Bescom-Demand Side Management: Department of Electrical& Electronics EngineeringNo ratings yetBescom-Demand Side Management: Department of Electrical& Electronics Engineering38 pages
- Admin - Contentimages - Op - Light Brochure PDFNo ratings yetAdmin - Contentimages - Op - Light Brochure PDF7 pages
- Livingood, Blake - Livingood Daily Your 21-Day Guide To Experience Real HealthLivingood, Blake - Livingood Daily Your 21-Day Guide To Experience Real Health
- COSMIC CONSCIOUSNESS OF HUMANITY - PROBLEMS OF NEW COSMOGONY (V.P.Kaznacheev,. Л. V. Trofimov.)COSMIC CONSCIOUSNESS OF HUMANITY - PROBLEMS OF NEW COSMOGONY (V.P.Kaznacheev,. Л. V. Trofimov.)
- Donald Trump & Jeffrey Epstein Rape Lawsuit and AffidavitsDonald Trump & Jeffrey Epstein Rape Lawsuit and Affidavits
- The 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York TimesThe 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York Times
- The 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York TimesThe 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York Times
- Jeffrey Epstein39s Little Black Book Unredacted PDFJeffrey Epstein39s Little Black Book Unredacted PDF
- The 4 Hour Workweek, Expanded and Updated by Timothy Ferriss - ExcerptThe 4 Hour Workweek, Expanded and Updated by Timothy Ferriss - Excerpt
- A Project Report On Survey On Customer Satisfaction of Philips LightingsA Project Report On Survey On Customer Satisfaction of Philips Lightings
- Podar International School, Ambegaon STD: Vii Subject: SciencePodar International School, Ambegaon STD: Vii Subject: Science
- IEC Exp 2 Verification of Kirchoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and Kirchoff's Current Law (KCL)IEC Exp 2 Verification of Kirchoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and Kirchoff's Current Law (KCL)
- M.M. Engineering College - Mullana: Laboratory Manual Practical Experiment Instruction SheetM.M. Engineering College - Mullana: Laboratory Manual Practical Experiment Instruction Sheet
- DC Lab - Exp - 2 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)DC Lab - Exp - 2 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)
- World University of Bangladesh Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering (EEE)World University of Bangladesh Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering (EEE)
- Electrical Technology Lab: Lab Manual I, Ii SemesterElectrical Technology Lab: Lab Manual I, Ii Semester
- Experiment 3: To Verify Kirchhoff's Voltage and Current Laws ExperimentallyExperiment 3: To Verify Kirchhoff's Voltage and Current Laws Experimentally
- Design of Electrical Circuits using Engineering Software ToolsFrom EverandDesign of Electrical Circuits using Engineering Software Tools
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with Projects
- Employability Skills: Brush up Your ElectronicsFrom EverandEmployability Skills: Brush up Your Electronics
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Leaving Certificate ExaminationCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Leaving Certificate Examination
- A Survey of Light Emitting Diode (LED) Display Board: Gowrishankar Kasilingam, Mritha Ramalingam and Chandra SekarA Survey of Light Emitting Diode (LED) Display Board: Gowrishankar Kasilingam, Mritha Ramalingam and Chandra Sekar
- The Night Light Robbery - How The LED Bulb Industry Is Ensuring Customers Keep Coming Back - India TodayThe Night Light Robbery - How The LED Bulb Industry Is Ensuring Customers Keep Coming Back - India Today
- Design Characteristics and Development of A Nozzle For Coaxial Laser CladdingDesign Characteristics and Development of A Nozzle For Coaxial Laser Cladding
- Image Processing: Research Opportunities and Challenges: December 2010Image Processing: Research Opportunities and Challenges: December 2010
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University: Natural Resources and Energy LawDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University: Natural Resources and Energy Law
- Ed Grade 9 Unit Practice Test Science Electrical Principles TechnologiesEd Grade 9 Unit Practice Test Science Electrical Principles Technologies
- Bescom-Demand Side Management: Department of Electrical& Electronics EngineeringBescom-Demand Side Management: Department of Electrical& Electronics Engineering