0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
295 views Biochem SuperTable
Biochem SuperTable
Uploaded by
Princess MarielleThis document provides a summary of key biochemical pathways including:
1. Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, Krebs cycle, glycogenesis/glycogenolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, fatty acid/triglyceride synthesis, beta-oxidation, ketogenesis, cholesterol synthesis, urea cycle, heme metabolism, and amino acid disorders.
2. For each pathway, it lists the key regulating steps, substrates, end products, and relevant clinical correlates from deficiencies.
3. It also provides a mnemonic device to help remember each pathway's location, rate-limiting step, and substrate/end products.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Biochem SuperTable
Biochem SuperTable
Uploaded by
Princess Marielle0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
295 views2 pagesThis document provides a summary of key biochemical pathways including:
1. Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, Krebs cycle, glycogenesis/glycogenolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, fatty acid/triglyceride synthesis, beta-oxidation, ketogenesis, cholesterol synthesis, urea cycle, heme metabolism, and amino acid disorders.
2. For each pathway, it lists the key regulating steps, substrates, end products, and relevant clinical correlates from deficiencies.
3. It also provides a mnemonic device to help remember each pathway's location, rate-limiting step, and substrate/end products.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document provides a summary of key biochemical pathways including:
1. Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, Krebs cycle, glycogenesis/glycogenolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, fatty acid/triglyceride synthesis, beta-oxidation, ketogenesis, cholesterol synthesis, urea cycle, heme metabolism, and amino acid disorders.
2. For each pathway, it lists the key regulating steps, substrates, end products, and relevant clinical correlates from deficiencies.
3. It also provides a mnemonic device to help remember each pathway's location, rate-limiting step, and substrate/end products.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
295 views2 pages Biochem SuperTable
Biochem SuperTable
Uploaded by
Princess MarielleThis document provides a summary of key biochemical pathways including:
1. Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, Krebs cycle, glycogenesis/glycogenolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, fatty acid/triglyceride synthesis, beta-oxidation, ketogenesis, cholesterol synthesis, urea cycle, heme metabolism, and amino acid disorders.
2. For each pathway, it lists the key regulating steps, substrates, end products, and relevant clinical correlates from deficiencies.
3. It also provides a mnemonic device to help remember each pathway's location, rate-limiting step, and substrate/end products.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
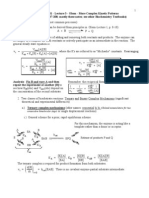
BIOCHEM SUPERTABLE
PATHWAY LOCATION RATE-LIMITING SUBSTRATE & END-PRODUCT CLINICAL CORRELATES MNEMONIC
STEP
Glycolysis Cytoplasm Phosphofructokinase-1 Substrate: Glucose Deficiency Process: Gross Annoying Guys Favor Ass Fuck But
(Inhibited by: Citrate, ATP, ↓ End-product: Pyruvate/lactate Dreamy Gorgeous Nerdy Boys Always Prefer Pretty
insulin?)
(inhibited by glucagon) Pyruvate kinase Hemolytic anemia Peppy Awesome Princesses
Yield: 2 ATP, 2 NADH 5/7 PFK (muscle) Low exercise capacity Enzymes: Hot Pretty Pussy Always Takes Great Pussy
ATP Pyruvate DH Congenital lactic acidosis preparation for Eventual Penetration
G3P shuttle: 1 NADH = 1.5 ATP
Malate asparate: 1 NADH = 2.5 ATP
Arsenic poison Inhibits pyruvate DH
Anerobic: 2 ATP
Gluconeogenesi Both (liver, Fructose 1,6- Substrate: Intermediates of
s kidney) bisphosphatase glycolysis and TCA
End-product: Glucose
Krebs Cycle Mitochondria Isocitrate Substrate: Acetyl-CoA Process: Citrate Is Kreb’s Starting Substrate For Making
Dehydrogenase Yield: 2CO2, 1GTP, 3NADH, 2 Oxaloacetate
FADH2 10 ATP
Glycolysis + TCA 30/32 ATP
1 NADH = 2.5 ATP, 1 FADH2 = 1.5 ATP
Glycogenesis Cytosol (liver, Glycogen synthase Substrate: a-D-glucose *Clinical correlates: read glycogen storage diseases
muscle) (Elongation of glycogen End-product: Glycogen
chains)
Glycogenolysis Cytosol (liver, Glycogen phosphorylase Substrate: Glycogen
muscle) (Shortening of glycogen chain) End-product: Glucose – liver,
G6P – muscle
Galactose Cytosol (liver) UDP-hexose-4-epimerase Substrate: Galactose
UDP galactose to UDP glucose
Galactokinase deficiency Galactosemia, galactosuria
GALT deficiency (Classic Galactosemia, galactosuria
galactosemia)
Fructose Cytosol? (liver) NA Substrate: Fructose
Fructokinase deficiency Essential fructosuria: benign, asymptomatic
Aldolase B deficiency Hereditary fructose intolerance: profound hypoglycemia
<,
Pentose Cytosol (RBC, Glucose-6-phosphate Substrate: Glucose-6-phosphate
Phosphate liver, adipose DH End-product: NADPH, Ribose-
etc) G6PD deficiency ↓NADPH ↓glutathione reductase free radicals, peroxide accumulation
Pathway G6P to 6-phosphogluconate 5-phosphate
(HMP) NADPH oxidase Chronic granulomatous disease (neutrophils unable to convert O2 to superoxide,
deficiency hence unable to kill bacteria)
Fatty Acid / TG Cytosol Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Substrate: Acetyl-CoA
Synthesis Acetyl CoA to Malonyl CoA End-product: Palmitoyl-CoA
Citrate shuttle Yield (Palmitate): 106 ATP
Beta oxidation Mitochondria Carnitine-palmitoyl End-product: Acetyl-CoA,
transferase NADH, FADH2
Carnitine shuttle
Ketogenesis Mitochondria HMG CoA Synthase Substrate: Acetyl-CoA
Acetoacetyl CoA + Acetyl CoA End-product: Acetoacetate, B-
HMG CoA Diabetic Very high glucagon, very low insulin
hydroxybutyrate, acetone
ketoacidosis
Cholesterol Cytoplasm HMG CoA Reductase Substrate: Acetyl-CoA
Synthesis (SER) HMG CoA Mevalonate End-product: Cholesterol
Requirement: 2NADPH
Amino Acid See TN
Urea Cycle Both (liver) Carbamoyl phosphate Substrate: NH3, aspartate, CO2 Process: Old Colorful Cars Are Always Fond of Awesome
synthase I End-product: Urea Umbrellas
NH3 + CO2 Carbamoyl Requirement: 3 ATP
PO4
Heme Both (1 and
st
ALA synthase Substrate: Succinyl + Glycine See TN Process: Some Good Doctors Palpate Heart Under Cover
Metabolism last 3 steps in Glycine + Succinyl CoA End-product: Heme Producing Heme
mitochondria) aminolevulinic acid
Ethanol
Polyol Pathway Conversion of glucose to sorbitol Glucose Sorbitol (Aldose reductase) Diabetes No sorbitol dehydrogenase Accumulation
Sorbitol Fructose (Sorbitol dehydrogenase) of sorbitol in retina, lens, kidney, schwann cells
retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy
AMINO ACID DISORDERS
Phenylketonuria ↓ phenylalanine ↑ tyrosine Severe mental retardation, failure to walk/talk,
seizure
Alkaptonuria ↑ homogentisic acid Urine turns black on standing
Connective tissue is dark
Albinism Defective melanin synthesis from tyrosine Absence of pigment
Tyrosinemia ↑ fumarylacetoacetate Liver and kidney failure, CNS, cabbage-like odor
Homocystinuria Defect in methionine degradation Ectopia lentis, osteoporosis, mental retardation,
↓ cysteine ↑ homocysteine stroke risk
Cystinuria COLA Defects: Cystine, Ornithine, Lysine, Kidney stones
Arginine
Methylmalonic Methylmalonyl CoA mutase deficiency Seizure, encephalopathy, stroke
Acidemia
Maple Syrup Urine Blocked degradation of Leucine, Isoleucine, Maple-smell of urine
Disease Valine (LIV)
Deficiency in a-ketoacid DH complex
Histidinemia Defective histidase Benign
You might also like
- BIOCHEMISTRY - Summary of PathwaysDocument8 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY - Summary of PathwaysWendy Mae100% (12)
- Biochemistry MnemonicsDocument20 pagesBiochemistry MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- 2 Long Exam Feedback: BiochemistryDocument7 pages2 Long Exam Feedback: BiochemistryManila MedNo ratings yet
- CP4490 Practice Questions Exam 1 S20 PDFDocument4 pagesCP4490 Practice Questions Exam 1 S20 PDFAvia YossefiNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument113 pagesBiochemistryMohammed Faizuddin siddiqui100% (1)
- Rate Limiting Step PDFDocument1 pageRate Limiting Step PDFCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Biochem SuperTable PDFDocument2 pagesBiochem SuperTable PDFPrincess MarielleNo ratings yet
- Penn Biochem Pathways: End. Retic. Galactose 1-PhosphateDocument1 pagePenn Biochem Pathways: End. Retic. Galactose 1-Phosphaterjlewis7No ratings yet
- Summary of PathwaysDocument1 pageSummary of Pathwaysayan100% (1)
- Biochem CompreDocument72 pagesBiochem CompreStd DlshsiNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument2 pagesParasitologygnb2104No ratings yet
- Biochemistry One Liner PDFDocument13 pagesBiochemistry One Liner PDFMinaz PatelNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Notes ProteinsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Notes ProteinsRegine Chua100% (1)
- Systemic PathologyDocument326 pagesSystemic PathologyRory Nannery100% (1)
- Topnotch Microbiology Supertable by DR - Cocoy Calderon Jaffar Pineda Troy Soberano UPDATED NOVEMBER 2017Document16 pagesTopnotch Microbiology Supertable by DR - Cocoy Calderon Jaffar Pineda Troy Soberano UPDATED NOVEMBER 2017Jaybee Sarmiento100% (1)
- Investigation PDFDocument26 pagesInvestigation PDFsonia87100% (1)
- Biochemistry One LinersDocument11 pagesBiochemistry One Linerssandeep MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Metab DisordersDocument36 pagesMetab DisordersDaena TimtimanNo ratings yet
- Goljan Lecture OrderDocument2 pagesGoljan Lecture OrderKweku Grant-Acquah100% (1)
- Step 1 Study Schedule TemplateDocument12 pagesStep 1 Study Schedule Templatelaxge54No ratings yet
- Glycogen MetabolismDocument2 pagesGlycogen MetabolismKaran SinghNo ratings yet
- AKTUBiochemistry BP203 TNotesDocument64 pagesAKTUBiochemistry BP203 TNotesMonica Nguyen100% (1)
- Peptic UlcerDocument53 pagesPeptic UlcerBassant Ahmed Mahmoud Ragab Abdallah AyaadNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Handout For BiochemistryDocument33 pagesComprehensive Handout For BiochemistryRichter Asturia100% (2)
- MID Bacteria Charts JkuoDocument17 pagesMID Bacteria Charts Jkuotsukino143100% (2)
- Bacteria ChartsDocument11 pagesBacteria ChartsFlowerNo ratings yet
- Step1 AdviceDocument9 pagesStep1 AdvicetsaokwNo ratings yet
- Davinci Medical AcademyDocument19 pagesDavinci Medical Academysk100% (1)
- Metabolic Disorders 01Document41 pagesMetabolic Disorders 01Brent LagartoNo ratings yet
- Notes 02 Clinical Chemistry 2Document6 pagesNotes 02 Clinical Chemistry 2Brent LagartoNo ratings yet
- Medical Mnemonics For MicroorgDocument4 pagesMedical Mnemonics For Microorgkenz18096No ratings yet
- Urea Cycle LehningerDocument34 pagesUrea Cycle LehningerMohamadJamaludinNo ratings yet
- Micro Tables Part 2Document10 pagesMicro Tables Part 2hectorNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Pathways Poster PDFDocument1 pageMetabolic Pathways Poster PDFAlex DatsiukNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7.1 Inborn Errors of MetabolismDocument119 pagesLesson 7.1 Inborn Errors of Metabolismmisaki06100% (2)
- Clinical PathologyDocument13 pagesClinical Pathologyapi-19710563100% (1)
- ImmunologyDocument69 pagesImmunologyburhaninho100% (5)
- Intracellular Signal TransductionDocument42 pagesIntracellular Signal TransductionYunita FatmalaNo ratings yet
- PhisioDocument15 pagesPhisiojohnNo ratings yet
- Balamand Faculty of MedicineDocument32 pagesBalamand Faculty of MedicineAnonymous 5FtD4bONo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument229 pagesEnzymesJimwell AxalanNo ratings yet
- ReviewersDocument1 pageReviewersRalph Renon CasamayorNo ratings yet
- Ch.1 Baby Robbins OutlineDocument11 pagesCh.1 Baby Robbins OutlinePA2014100% (4)
- Biochemistry QsDocument48 pagesBiochemistry QsFaisal AshiqNo ratings yet
- Kaplan Biochemistry: Study Online atDocument2 pagesKaplan Biochemistry: Study Online atShaz Chindhy100% (1)
- 06.disorder of Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument47 pages06.disorder of Carbohydrate MetabolismRizka NizarNo ratings yet
- Glucose Quiz 1 @ukrok1Document4 pagesGlucose Quiz 1 @ukrok1Omran BashirNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument18 pagesBiochemistryVivian Tamara Suárez100% (1)
- Cocci Rod 4 Main Classifications: Gram Staph, Strep Bacillus Clostridium Neisseria Pleiomorphic Enterobact-EriceaeDocument2 pagesCocci Rod 4 Main Classifications: Gram Staph, Strep Bacillus Clostridium Neisseria Pleiomorphic Enterobact-EriceaeKimberly KanemitsuNo ratings yet
- Important Terms - Tropical InfectionDocument8 pagesImportant Terms - Tropical InfectionTimothy JordanNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Antigenic StructureDocument36 pagesBacterial Antigenic Structuredearsaran0% (1)
- Board Review Blood SupplyDocument6 pagesBoard Review Blood Supplynewguy927No ratings yet
- Embryology: Lung DevelopmentDocument91 pagesEmbryology: Lung DevelopmentPrarthanaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Patho PDFDocument623 pagesPulmonary Patho PDFNabeel Shahzad100% (1)
- Biochem 2.0 BTRDocument35 pagesBiochem 2.0 BTR7y67kccdbgNo ratings yet
- 5.8 Gluconeogensis by TGDocument115 pages5.8 Gluconeogensis by TGoumerNo ratings yet
- 5. Carbohydrate metabolism -3 PBBScDocument54 pages5. Carbohydrate metabolism -3 PBBScvishweshnagarajNo ratings yet
- A 59-Year-Old Man With A History of Diabetes and Alcohol Abuse Is Brought To The Emergency Room in A Semiconscious and Minimally Responsive StateDocument43 pagesA 59-Year-Old Man With A History of Diabetes and Alcohol Abuse Is Brought To The Emergency Room in A Semiconscious and Minimally Responsive StateAnonymous eDD0YqzPMNo ratings yet
- Substrates&EnzymesDocument15 pagesSubstrates&EnzymesTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- GluconeogenesisDocument21 pagesGluconeogenesisNoor Al Huda MohammedNo ratings yet
- 1.01 - HEENT Summary TablesDocument6 pages1.01 - HEENT Summary TablesPrincess MarielleNo ratings yet
- 2.02 - Nutritional Status AssessmentDocument3 pages2.02 - Nutritional Status AssessmentPrincess MarielleNo ratings yet
- 2.01 - Vibrio, Campylobacter, HelicobacterDocument2 pages2.01 - Vibrio, Campylobacter, HelicobacterPrincess MarielleNo ratings yet
- MasterlistDocument31 pagesMasterlistPrincess MarielleNo ratings yet
- Innovasion Vol 5 Issue 2-6-13Document8 pagesInnovasion Vol 5 Issue 2-6-13Princess MarielleNo ratings yet
- De Leon - Antepartum Fetal SurveillanceDocument2 pagesDe Leon - Antepartum Fetal SurveillancePrincess MarielleNo ratings yet
- (Leaflet) Hong Kong Guideline For Physical ActivityDocument18 pages(Leaflet) Hong Kong Guideline For Physical ActivityPrincess MarielleNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Enzyme ActionDocument2 pagesMechanism of Enzyme ActionBlazy InhumangNo ratings yet
- Enzyme FermentationDocument17 pagesEnzyme FermentationAli AhsanNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Structure, Classification and Mechanism of ActionDocument35 pagesEnzyme Structure, Classification and Mechanism of ActionAdeenNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis + Evaluations 4/23/2003Document30 pagesGluconeogenesis + Evaluations 4/23/2003Ajay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- 3 EnzymesDocument3 pages3 EnzymesTala AlkhawajaNo ratings yet
- Soal BIOKIM Nomor 3Document4 pagesSoal BIOKIM Nomor 3Siti RositahNo ratings yet
- Degradation of Glycogen (Glycogenolysis)Document27 pagesDegradation of Glycogen (Glycogenolysis)Hassan HarunaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme WorksheetDocument3 pagesEnzyme WorksheetMR_Hughes0% (1)
- EnzymesDocument25 pagesEnzymesAbdirazak AliNo ratings yet
- MKBS313 CT1 MemoDocument3 pagesMKBS313 CT1 MemoLeane MinnaarNo ratings yet
- Bi-Bi RXNDocument12 pagesBi-Bi RXNbelabelawNo ratings yet
- DnlodDocument43 pagesDnlod312887No ratings yet
- LRR FMGE BiochemistryDocument226 pagesLRR FMGE BiochemistryVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- Enzyme InhibitionDocument7 pagesEnzyme InhibitionJane Docdoc100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration GlycolysisDocument1 pageCellular Respiration GlycolysisReigne CuevasNo ratings yet
- Gluco Neo GenesisDocument36 pagesGluco Neo GenesisAmalia DarwisNo ratings yet
- Activity - Enzyme WorksheetDocument1 pageActivity - Enzyme WorksheetImay ParaderoNo ratings yet
- 1969 - The Redox State of Free Nicotinamide-Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate in The Cytoplasm of Rat LiverDocument11 pages1969 - The Redox State of Free Nicotinamide-Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate in The Cytoplasm of Rat LiverRaymond LaBoyNo ratings yet
- Oksidasi PiruvatDocument14 pagesOksidasi Piruvatadelia salsabilaNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument16 pagesEnzymesArooj AbidNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis: The 3 Stages of GlycolysisDocument11 pagesGlycolysis: The 3 Stages of Glycolysismaiang23No ratings yet
- ENZYMESDocument2 pagesENZYMESKathleene AulidaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19-The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle: Multiple ChoiceDocument10 pagesChapter 19-The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle: Multiple ChoiceLa SavesNo ratings yet
- Pyrimidine & Biosynthesis of DeoxyribonucleotidesDocument46 pagesPyrimidine & Biosynthesis of DeoxyribonucleotidesRabia ButoolNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Regulation (Article) - Khan AcademyDocument19 pagesEnzyme Regulation (Article) - Khan Academyteam TSOTARENo ratings yet
- Assignment CH62Document3 pagesAssignment CH62Swathi SNo ratings yet
- Enzymology SyllabusDocument1 pageEnzymology SyllabusKamlesh SahuNo ratings yet
- QueryDocument8 pagesQuerysubhash221103No ratings yet
- Toothpickase LabDocument2 pagesToothpickase Labjoannekimm150% (1)
- Quiz On Enzyme KineticsDocument3 pagesQuiz On Enzyme KineticsHens Christian FuentesNo ratings yet