0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
214 viewsImpaired Gas Exchange NCP
Impaired Gas Exchange NCP
Uploaded by
Romel BaliliThe nursing care plan is for a 26-year-old female patient admitted with dyspnea, generalized edema, and left lower chest pain. The nursing diagnosis is impaired gas exchange related to accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. Goals are to improve oxygen saturation, reduce respiratory rate and dyspnea, and increase comfort. Interventions include positioning, breathing exercises, oxygen therapy, diuretic medication, and education. Evaluation after 8 hours found improved oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, and decreased symptoms, meeting the goals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Impaired Gas Exchange NCP
Impaired Gas Exchange NCP
Uploaded by
Romel Balili0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
214 views3 pagesThe nursing care plan is for a 26-year-old female patient admitted with dyspnea, generalized edema, and left lower chest pain. The nursing diagnosis is impaired gas exchange related to accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. Goals are to improve oxygen saturation, reduce respiratory rate and dyspnea, and increase comfort. Interventions include positioning, breathing exercises, oxygen therapy, diuretic medication, and education. Evaluation after 8 hours found improved oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, and decreased symptoms, meeting the goals.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The nursing care plan is for a 26-year-old female patient admitted with dyspnea, generalized edema, and left lower chest pain. The nursing diagnosis is impaired gas exchange related to accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. Goals are to improve oxygen saturation, reduce respiratory rate and dyspnea, and increase comfort. Interventions include positioning, breathing exercises, oxygen therapy, diuretic medication, and education. Evaluation after 8 hours found improved oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, and decreased symptoms, meeting the goals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
214 views3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCP
Impaired Gas Exchange NCP
Uploaded by
Romel BaliliThe nursing care plan is for a 26-year-old female patient admitted with dyspnea, generalized edema, and left lower chest pain. The nursing diagnosis is impaired gas exchange related to accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. Goals are to improve oxygen saturation, reduce respiratory rate and dyspnea, and increase comfort. Interventions include positioning, breathing exercises, oxygen therapy, diuretic medication, and education. Evaluation after 8 hours found improved oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, and decreased symptoms, meeting the goals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
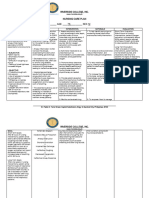
Davao Doctors College, Inc.
College of Allied Health Sciences N.C.P
Nursing Program Nursing Care Plan
Name of Patient: Patient M. Date of Admission: 10/6/2022 Age: 26 Sex: Female Civil Status: N/A
Chief Complaint: 48-Hour history of progressive dyspnea, Generalized edema, and Left lower chest pain with non-productive cough
Attending Physician: Dr. Magallona
Date / Cues Nursing Goals & Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Time Diagnosis Objectives
October 6, Subjective/s: Impaired Gas Within 8 hours if INDEPENDENT: INDEPENDENT: GOAL MET
2022 - The patient exchange r/t nursing intervention, A. Assist the patient in A. To facilitate lung
@3:00 pm verbalized, accumulation of the patient will be finding a comfortable expansion and reduce After 8 hours of
fluid in pleural able to: position (e.g., semi- the work of breathing. nursing intervention
“I experienced space aeb Fowler's) that the patient able to:
fluid retention dyspnea, - Demonstrate optimizes lung
that went way elevated RR, improved gas expansion and - The patient's
beyond the o2sat of 92%, exchange as encourages deeper oxygen saturation
usual hormone and presence of evidenced by an breathing. has increased to
fluctuations or pleural effusion. increase in oxygen 95%
indulgence in saturation to ≥ 95%.
overly salty Scientific basis: B. Respiratory - The patient's
B. Encourage the exercises help in lung
food.” The nursing - The patient's respiratory rate has
patient to perform expansion, prevent
diagnosis of respiratory rate will decreased and
“I presented to "Impaired Gas decrease to within deep-breathing atelectasis (lung remained within the
the emergency Exchange" is the normal range exercises, coughing, collapse), and normal range (18
department supported by (e.g., 12-20 breaths and spirometry as promote the cpm)
with a 48-hour the scientific per minute) appropriate. clearance of
history of basis that - Reported
respiratory secretions.
progressive pleural effusion, - Report a reduction decreased in
dyspnea, characterized by in dyspnea and symptoms such as
generalized the increased comfort C. Educate the patient
and caregivers on the C. Educating the shortness of breath
edema and left accumulation of during breathing, and improved
lower chest fluid in the indicating improved importance of proper patient and caregivers comfort.
pain with a pleural space, gas exchange and positioning and offer on proper positioning
non-productive restricts lung lung function. guidance on activities and respiratory
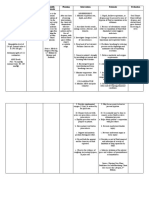
Davao Doctors College, Inc.
College of Allied Health Sciences N.C.P
Nursing Program Nursing Care Plan
cough.” expansion and that may improve gas techniques like
alters the exchange such as diaphragmatic and
Objectives: mechanics of diaphragmatic pursed-lip breathing
- RR: 34 cpm respiration. This breathing and pursed- helps optimize lung
- HR: 144 bpm leads to lip breathing can be
mechanics, increase
- O2sat: 92% impaired particularly helpful.
oxygenation, and
ventilation and
ABG Result: gas exchange in reduce the work of
- Metabolic the alveoli, breathing, leading to
acidosis: causing reduced improved gas
pH: 7.134 oxygen uptake exchange and overall
HCO3: 6 and carbon respiratory function.
dioxide removal.
- (+) Pleural The
effusion compromised
lung function,
often associated DEPENDENT: DEPENDENT:
with conditions A. Administer oxygen A. Helps raise the
such as heart @3L per minute via patient's blood oxygen
failure or nasal canulla saturation levels (SpO2)
inflammatory to a normal range
diseases like (typically 95% or higher)
Systemic Lupus to ensure that cells
Erythematosus receive an adequate
(SLE), further supply of oxygen for
exacerbates the metabolism and organ
impairment, function.
ultimately
resulting in
decreased
arterial B. Administer B. To treat the fluid
oxygenation Furosemide as per accumulation in the
levels pleural space of the
Davao Doctors College, Inc.
College of Allied Health Sciences N.C.P
Nursing Program Nursing Care Plan
(hypoxemia) physician’s order. patient.
and an elevated COLLABORATIVE: COLLABORATIVE:
partial pressure A. Collaborate with a A. This procedure can
of carbon physician or help drain excess fluid
dioxide from the pleural
respiratory therapist
(hypercapnia).
to perform space, relieving
Consequently,
thoracentesis or pressure on the lungs
addressing the
effusion and chest tube insertion and improving gas
optimizing lung as appropriate for exchange.
function are the patient's
essential to condition.
alleviate
impaired gas
exchange in
affected
individuals.
https://
onlinelibrary.wil
ey.com/doi/
abs/
10.1002/978111
8702864.ch7
You might also like
- Subjective Cues:: Nursing Care ProcessDocument8 pagesSubjective Cues:: Nursing Care ProcessBianca Marithè RejanoNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Nursing Care Plan FormDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Nursing Care Plan FormissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- NCP KoDocument1 pageNCP Kojiellianemae100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMiggy SikatNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKim Gabrielle Exene LeeNo ratings yet
- NCP 2 CabalunaDocument7 pagesNCP 2 CabalunaIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Document4 pagesAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAndrea Francesca SantosNo ratings yet
- NCP For AsthmaDocument2 pagesNCP For AsthmawaadNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Client: N. D. Age: 39 Gender: Male Medical Diagnosis: Community Acquired Pneumonia, Moderate Risk, PTBDocument24 pagesNursing Care Plan Client: N. D. Age: 39 Gender: Male Medical Diagnosis: Community Acquired Pneumonia, Moderate Risk, PTBGertrude Araneta JavierNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion - NCPDocument7 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion - NCPVianah Eve EscobidoNo ratings yet
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Document6 pagesRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Ariane NCP 1Document2 pagesAriane NCP 1Kristian Ray EraulaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionDiane ReyNo ratings yet
- NCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioDocument5 pagesNCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioRio BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Case 3 Care of Client With GI, PUD, Cancer, Liver FailureDocument33 pagesCase 3 Care of Client With GI, PUD, Cancer, Liver FailureNyeam NyeamNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument3 pagesLiver CirrhosisJonica CamposNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University Nursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageFar Eastern University Nursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationSarah CarreteroNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesFluid Volume DeficitRuby AnneNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDocument2 pagesScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPneumoniaPia MedinaNo ratings yet
- Risk For Injury DengueDocument3 pagesRisk For Injury DengueLouise BandalaNo ratings yet
- Fistula NCPDocument1 pageFistula NCPHasna LisnaNo ratings yet
- NCP-Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument9 pagesNCP-Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionKarel LuNo ratings yet
- NCP FormatDocument4 pagesNCP FormatCoreen Kaye TanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: STGDocument11 pagesAssessment Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: STGGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalGiselle RomeroNo ratings yet
- Risk For InfectionDocument5 pagesRisk For InfectionVianah Eve EscobidoNo ratings yet
- Macular Degeneration NCPDocument3 pagesMacular Degeneration NCPReann LeeNo ratings yet
- Concept Map PsoriasisDocument1 pageConcept Map PsoriasisEran Mark RojasNo ratings yet
- Short TermDocument2 pagesShort TermJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis - InfographicDocument1 pageAppendicitis - Infographicapi-518183280No ratings yet
- NCP Gastric CancerDocument6 pagesNCP Gastric Cancerhayascent hilarioNo ratings yet
- NCP For Activity in ToleranceDocument5 pagesNCP For Activity in Tolerancekaycee_periaNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument3 pagesNCP Risk For Electrolyte ImbalanceLouie ParillaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective "Masakit Yung Opera Sa Akin" Short Term ObjectiveDocument12 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective "Masakit Yung Opera Sa Akin" Short Term ObjectiveRaphael FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Concept MapDocument1 pagePneumonia Concept MapsekwetNo ratings yet
- NCP InfectionDocument3 pagesNCP InfectionPrince AhmirNo ratings yet
- NCP - Hygiene and ComfortDocument3 pagesNCP - Hygiene and ComfortJaella EpeNo ratings yet
- NCP Skin IntegityDocument3 pagesNCP Skin Integityclydell joyce masiarNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- FDARDocument4 pagesFDARshiNo ratings yet
- Subjective Cues: Independent: On The: "Nahihirapa N Ako Huminga" AsDocument5 pagesSubjective Cues: Independent: On The: "Nahihirapa N Ako Huminga" AsYessaminNo ratings yet
- NCP - Multiple BruisesDocument3 pagesNCP - Multiple BruisesLeogalvez BedanoNo ratings yet
- CiticolineDocument2 pagesCiticolineKerima Danica Lising GayoNo ratings yet
- Problem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Document10 pagesProblem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Raidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- NCP HemothoraxDocument3 pagesNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- NCP FinalDocument16 pagesNCP FinalEuleen Tria PadrigoNo ratings yet
- Jeacey Paraluman, Daisyree Dano Z: InterventionsDocument2 pagesJeacey Paraluman, Daisyree Dano Z: Interventions2090320No ratings yet
- NCP - Sta. 6Document2 pagesNCP - Sta. 6vmasalarda2019No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationclydell joyce masiarNo ratings yet
- Biology 1 Post-Test: DIRECTIONS: Select The Best Answer To Each of TheDocument3 pagesBiology 1 Post-Test: DIRECTIONS: Select The Best Answer To Each of TheGette AcupanNo ratings yet
- Park Tools 2008 CatalogDocument52 pagesPark Tools 2008 CatalogmladenpitesaNo ratings yet
- Toodledo Startup Guide: A. Help TabDocument13 pagesToodledo Startup Guide: A. Help TabAlbert Iturbe RecasensNo ratings yet
- What Is StrategyDocument6 pagesWhat Is StrategySamridh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- CL Aerospace ERJ 135 145 Legacy Support ProgramDocument14 pagesCL Aerospace ERJ 135 145 Legacy Support Programyann.lepeuNo ratings yet
- Refers To The Manner of Delegating Assignment, Orders and Instructions To The NursingDocument6 pagesRefers To The Manner of Delegating Assignment, Orders and Instructions To The NursingJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Kursus Kejurulatihan Tahap Satu MHC 2022Document2 pagesKursus Kejurulatihan Tahap Satu MHC 2022Aishah ZulkefliNo ratings yet
- @hawkeyefootball Game Notes Game #6 vs. Michigan StateDocument46 pages@hawkeyefootball Game Notes Game #6 vs. Michigan StateMarc MorehouseNo ratings yet
- Lab Exp 1Document6 pagesLab Exp 1Funny Americans VideosNo ratings yet
- Online Trading - Insta Plus DemoDocument25 pagesOnline Trading - Insta Plus DemogoveryNo ratings yet
- CSE 131 Midterm (Fa16) : Ranjit Jhala October 28th, 2016Document7 pagesCSE 131 Midterm (Fa16) : Ranjit Jhala October 28th, 2016Alex Z. YangNo ratings yet
- I C S (Pocso) S J, S C.C. 2019: (Prosecution)Document34 pagesI C S (Pocso) S J, S C.C. 2019: (Prosecution)Pratyush RaiNo ratings yet
- Let ReviewerDocument13 pagesLet ReviewerGwyndyl CajillaNo ratings yet
- Guide English Science 2023Document2 pagesGuide English Science 2023nabilaahsan16No ratings yet
- AminesDocument12 pagesAminesMadhu SomavarapuNo ratings yet
- Management Training Courses PDFDocument8 pagesManagement Training Courses PDFogwang emmanuelNo ratings yet
- List of Architecture Thesis Topic 2020Document6 pagesList of Architecture Thesis Topic 2020vaishnavi karvekarNo ratings yet
- 400 MtrsDocument79 pages400 MtrsCarl Malone TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Comparatives and Superlatives Practice: Activity TypeDocument6 pagesComparatives and Superlatives Practice: Activity TypecarlosNo ratings yet
- CS 202, Spring 2007 Epp, Chapter 5 Aaron BloomfieldDocument82 pagesCS 202, Spring 2007 Epp, Chapter 5 Aaron BloomfieldJuwudy LeeNo ratings yet
- designerspry-kg.13-05-24Document15 pagesdesignerspry-kg.13-05-24mehurunisahNo ratings yet
- Turbocharger TCR22 - Refitting The Silencer: Application ReasonDocument2 pagesTurbocharger TCR22 - Refitting The Silencer: Application ReasonmariodalNo ratings yet
- Delen Christine Joy Pontines 18-53346 11-01-1999 22 Brgy. Conde Itaas, Batangas City Filipino 09165982354Document3 pagesDelen Christine Joy Pontines 18-53346 11-01-1999 22 Brgy. Conde Itaas, Batangas City Filipino 09165982354Christine Joy DelenNo ratings yet
- Лиши LishiDocument18 pagesЛиши LishiRahymjanNo ratings yet
- Konversi SKS Ke ECTS Kampus UNESADocument15 pagesKonversi SKS Ke ECTS Kampus UNESALiana Putri SusantiNo ratings yet
- 1 Proyect - Extreme SportsDocument8 pages1 Proyect - Extreme SportsJustin ErazoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 0Document8 pagesAssignment 0Sheeba SNo ratings yet
- 5 Levels of Leadership EditedDocument12 pages5 Levels of Leadership EditedTrang ToNo ratings yet
- Henry Fayols: 14 Principles in ManagementDocument7 pagesHenry Fayols: 14 Principles in ManagementLee PhungNo ratings yet
- Definition of Foreign Folk DanceDocument2 pagesDefinition of Foreign Folk DanceJimel TolentinoNo ratings yet