Lab 3
Uploaded by
DƯƠNG NGUYỄN THÁI BÌNHCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 3
Uploaded by
DƯƠNG NGUYỄN THÁI BÌNHCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Lab 3
Uploaded by
DƯƠNG NGUYỄN THÁI BÌNHCopyright:
Available Formats
Electronic Circuit Labs Differential Amplifiers
Lab 3 – Differential Amplifiers
Aims:
[1] To understand BJT differential amplifier configurations: CS, CG, CD and their
characteristic parameters: Ad, Acm and CMRR (Common-Mode Rejection Ratio).
[2] To understand how to increase the CMRR value.
[3] To measure characteristic parameters (Ad, Acm, CMRR) of BJT differential amplifier
circuits and to draw the conclusion about the effects of emitter resistor on CMRR.
1. Background
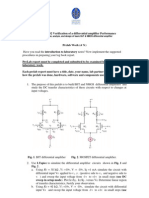
- Consider the circuit on figure H1.1, write the formulas for vid, vicm, Ad, Acm, CMRR in
two modes: difference-mode and common-mode (output voltage is the voltage at C-
terminal of one BJT). Then write the formulas for vo1 (voltage at C-terminal of Q1) and vo2
(voltage at C-terminal of Q2) with respect to v1, v2, Ad and Acm.
- Redo previous steps for the circuit in figure H1.2.
- Based on above formulas, compare two amplifier circuits shown in figure H1.1 and
H1.2.
2. Experiment preparation
- Review the BJT Differential Pair theories: Microelectronic Circuits 6th Edition,
Sedra/Smith, pages 612-628.
- Read the Experiment procedure carefully.
- Download the datasheet of BJT 2SD468, read it carefully.
- Write the experiment preparation, including:
Principle schemes of all experiment circuits.
Formulas and calculated results (if available).
Method for measuring circuit parameters.
Photo all the tables in lab manual (in order to record or draw the results
immediately while doing the experiments).
3. Materials
- Main kit: ELECTRONIC LAB ANA-MAIN
- Module: BJT differential AMP
- Oscilloscope: GRS-6052A
Nguyen Phuoc Bao Duy – Bach Khoa University 1
Electronic Circuit Labs Differential Amplifiers
- Multimeter: Fluke 45
- Connectors
4. Experiment procedure
4.1 Determine quiescent point and β
- Construct the circuit on figure H3.1a using module BJT differential AMP as shown
on figure H3.1b.
- Measure the parameters and fill in Table 4.1.
Table 4.1 - Biasing parameters
VC1 VC2 VB1 VB2 VE IB1 IB2 IC1 IC2 1 2
[V] [V] [mV] [mV] [V] [A] [A] [mA] [mA]
4.2 Differential Amplifier with emitter resistor RE
a. Construct the circuit on figure H3.2a (difference-mode) using module BJT differential
AMP as shown on figure H3.2b.
b. The frequency of function generator is set to 1kHz, adjust the amplitude to achieve
v1pp = v2pp = 50mV. Use the oscilloscope to watch the waveform then fill in Table 4.2a.
Nguyen Phuoc Bao Duy – Bach Khoa University 2
Electronic Circuit Labs Differential Amplifiers
Table 4.2a - Differential Amplifier with emitter resistor - Difference-Mode
v1p-p
[mV]
v2p-p
[mV] AC
Phase
v1 vs v2
[degree] AC
vidp-p
[mV]
Nguyen Phuoc Bao Duy – Bach Khoa University 3
Electronic Circuit Labs Differential Amplifiers
Table 4.2a - Differential Amplifier with emitter resistor - Difference-Mode
vicmp-p
[mV]
vo1p-p
[V] AC
Phase
v1 vs vo1
[degree] AC
vo2p-p
[V]
Phase
vo1 vs vo2
[degree]
Ad AC
[V/V]
AC
c. Construct the circuit on figure H3.2c (common-mode) using module BJT differential
AMP as shown on figure H3.2d.
d. The frequency of function generator is set to 1kHz, adjust the amplitude to achieve
v1pp = v2pp = 1V. Use the oscilloscope to watch the waveform then fill in Table 4.2b.
e. From the measured results, calculate CMRR (dB).
Nguyen Phuoc Bao Duy – Bach Khoa University 4
Electronic Circuit Labs Differential Amplifiers
Table 4.2b - Differential Amplifier with emitter resistor - Common-Mode
v1p-p
[V]
v2p-p
[V] AC
Phase
v1 vs v2
[degree] AC
vidp-p
[mV]
vicmp-p
[mV]
vo1p-p
AC
[V]
Phase
v1 vs vo1
[degree] AC
Nguyen Phuoc Bao Duy – Bach Khoa University 5
Electronic Circuit Labs Differential Amplifiers
Table 4.2b - Differential Amplifier with emitter resistor - Common-Mode
vo2p-p
[V]
Phase
vo1 vs vo2 AC
[degree]
Acm
[V/V] AC
4.3 Differential Amplifier with Constant Current Source
a. Construct the circuit on figure H3.3a using module BJT differential AMP as shown on
figure H3.3b.
b. Adjust VR1 so that the voltages at C-terminals of Q1 and Q2 are equal to those
measured in Table 4.1 (in order to keep the quiescent point unchanged). Keep the value
of VR unchanged during the rest of this experiment.
Nguyen Phuoc Bao Duy – Bach Khoa University 6
Electronic Circuit Labs Differential Amplifiers
c. Construct the circuit on figure H3.3c (difference-mode) using module BJT differential
AMP as shown on figure H3.3d.
d. The frequency of function generator is set to 1kHz, adjust the amplitude to achieve
v1pp = v2pp = 50mV. Use the oscilloscope to watch the waveform then fill in Table 4.3a.
Table 4.3a - Differential Amplifier with Constant Current Source - Difference-Mode
v1p-p
[mV]
v2p-p
[mV] AC
Phase
v1 vs v2
[degree] AC
vidp-p
[mV]
Nguyen Phuoc Bao Duy – Bach Khoa University 7
Electronic Circuit Labs Differential Amplifiers
Table 4.3a - Differential Amplifier with Constant Current Source - Difference-Mode
vicmp-p
[mV]
vo1p-p
[V] AC
Phase
v1 vs vo1
[degree] AC
vo2p-p
[V]
Phase
vo1 vs vo2
[degree]
Ad AC
[V/V]
AC
e. Construct the circuit on figure H3.3e (common-mode) using module BJT differential
AMP as shown on figure H3.3f.
f. The frequency of function generator is set to 1kHz, adjust the amplitude to achieve v1pp
= v2pp = 1V. Use the oscilloscope to watch the waveform then fill in Table 4.3b.
g. From the measured results, calculate CMRR (dB).
Nguyen Phuoc Bao Duy – Bach Khoa University 8
Electronic Circuit Labs Differential Amplifiers
Table 4.3b - Differential Amplifier with Constant Current Source - Common-Mode
v1p-p
[V]
v2p-p
[V] AC
Phase
v1 vs v2
[degree] AC
vidp-p
[mV]
vicmp-p
[mV]
vo1p-p
AC
[V]
Phase
v1 vs vo1
[degree] AC
Nguyen Phuoc Bao Duy – Bach Khoa University 9
Electronic Circuit Labs Differential Amplifiers
Table 4.3b - Differential Amplifier with emitter resistor - Common-Mode
vo2p-p
[V]
Phase
vo1 vs vo2 AC
[degree]
Acm
[V/V] AC
5. Further questions for the experiment report
- Analysis and compare experiment results with calculated results.
- Compare two types of bias circuits: with emitter resistor and with constant
current source.
Nguyen Phuoc Bao Duy – Bach Khoa University 10
You might also like
- Eee334 Lab#1 Ltspice and Lab Orientation - Instruments and Measurements0% (1)Eee334 Lab#1 Ltspice and Lab Orientation - Instruments and Measurements9 pages
- Arcam Alpha10 10p Power Amplifier Service ManualNo ratings yetArcam Alpha10 10p Power Amplifier Service Manual19 pages
- Al-Blaqa Applied University Faculty of Engineering TechnologyNo ratings yetAl-Blaqa Applied University Faculty of Engineering Technology9 pages
- OPERATION AMPLIFIER - Voltage Follower Configuration Learning OutcomeNo ratings yetOPERATION AMPLIFIER - Voltage Follower Configuration Learning Outcome3 pages
- (ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 2 Final ReportNo ratings yet(ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 2 Final Report11 pages
- RC Coupled Amplifier - DC Operation - EXERCISE 7No ratings yetRC Coupled Amplifier - DC Operation - EXERCISE 715 pages
- Ecgr3156 Experiment 1 BJT Differential Pair With BJT Current MirrorNo ratings yetEcgr3156 Experiment 1 BJT Differential Pair With BJT Current Mirror8 pages
- PH 411 Physics Laboratory I (Electronics) : Instruction Manual IndexNo ratings yetPH 411 Physics Laboratory I (Electronics) : Instruction Manual Index28 pages
- EXPT. No. 4 Study of Common-Emitter AmplifierNo ratings yetEXPT. No. 4 Study of Common-Emitter Amplifier2 pages
- CO#1 Describe, Analyze, and Design of Basic BJT & NMOS Differential AmplifierNo ratings yetCO#1 Describe, Analyze, and Design of Basic BJT & NMOS Differential Amplifier6 pages
- Electronics and Communication Circuits Lab. Experiment #4 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Bridge RectifierNo ratings yetElectronics and Communication Circuits Lab. Experiment #4 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier8 pages
- فيزياء الالكترونية (3) -1-150-صور-88-92,94-98,100-105No ratings yetفيزياء الالكترونية (3) -1-150-صور-88-92,94-98,100-10516 pages
- Experiment No. 5: Half-Wave Rectifier Ece00L-Basic Electronics LaboratoryNo ratings yetExperiment No. 5: Half-Wave Rectifier Ece00L-Basic Electronics Laboratory5 pages
- LAB 2 Transistor Djm20042 Sesi1 2022.2023No ratings yetLAB 2 Transistor Djm20042 Sesi1 2022.202311 pages
- Design of Electrical Circuits using Engineering Software ToolsFrom EverandDesign of Electrical Circuits using Engineering Software ToolsNo ratings yet
- IM1019 L5 Consumer Markets and Buyer BehaviorNo ratings yetIM1019 L5 Consumer Markets and Buyer Behavior51 pages
- Types of Sources: Name: M. Sravya Sri Roll No.: 22R21A04A1 Branch& Sec: ECE-BNo ratings yetTypes of Sources: Name: M. Sravya Sri Roll No.: 22R21A04A1 Branch& Sec: ECE-B9 pages
- ESC201 Lab Updated Schedule - 2024-25 Sem-INo ratings yetESC201 Lab Updated Schedule - 2024-25 Sem-I1 page
- Verification of Thevenin's & Norton's TheoremNo ratings yetVerification of Thevenin's & Norton's Theorem16 pages
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: December 2015 Semester End Main ExaminationsNo ratings yetBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: December 2015 Semester End Main Examinations3 pages
- Slidesgo Understanding Emitter Followers Principles and Applications in Electronics 20241121084346V0lFNo ratings yetSlidesgo Understanding Emitter Followers Principles and Applications in Electronics 20241121084346V0lF10 pages
- Costruzioni Elettroniche: Mod. KLV 1000 Linear Amplifier100% (2)Costruzioni Elettroniche: Mod. KLV 1000 Linear Amplifier4 pages
- LAb - 02 - Voltage and Current Divider RuleNo ratings yetLAb - 02 - Voltage and Current Divider Rule6 pages
- Eee334 Lab#1 Ltspice and Lab Orientation - Instruments and MeasurementsEee334 Lab#1 Ltspice and Lab Orientation - Instruments and Measurements
- Al-Blaqa Applied University Faculty of Engineering TechnologyAl-Blaqa Applied University Faculty of Engineering Technology
- OPERATION AMPLIFIER - Voltage Follower Configuration Learning OutcomeOPERATION AMPLIFIER - Voltage Follower Configuration Learning Outcome
- Ecgr3156 Experiment 1 BJT Differential Pair With BJT Current MirrorEcgr3156 Experiment 1 BJT Differential Pair With BJT Current Mirror
- PH 411 Physics Laboratory I (Electronics) : Instruction Manual IndexPH 411 Physics Laboratory I (Electronics) : Instruction Manual Index
- CO#1 Describe, Analyze, and Design of Basic BJT & NMOS Differential AmplifierCO#1 Describe, Analyze, and Design of Basic BJT & NMOS Differential Amplifier
- Electronics and Communication Circuits Lab. Experiment #4 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Bridge RectifierElectronics and Communication Circuits Lab. Experiment #4 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier
- فيزياء الالكترونية (3) -1-150-صور-88-92,94-98,100-105فيزياء الالكترونية (3) -1-150-صور-88-92,94-98,100-105
- Experiment No. 5: Half-Wave Rectifier Ece00L-Basic Electronics LaboratoryExperiment No. 5: Half-Wave Rectifier Ece00L-Basic Electronics Laboratory
- Design of Electrical Circuits using Engineering Software ToolsFrom EverandDesign of Electrical Circuits using Engineering Software Tools
- Types of Sources: Name: M. Sravya Sri Roll No.: 22R21A04A1 Branch& Sec: ECE-BTypes of Sources: Name: M. Sravya Sri Roll No.: 22R21A04A1 Branch& Sec: ECE-B
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: December 2015 Semester End Main ExaminationsBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: December 2015 Semester End Main Examinations
- Slidesgo Understanding Emitter Followers Principles and Applications in Electronics 20241121084346V0lFSlidesgo Understanding Emitter Followers Principles and Applications in Electronics 20241121084346V0lF
- Costruzioni Elettroniche: Mod. KLV 1000 Linear AmplifierCostruzioni Elettroniche: Mod. KLV 1000 Linear Amplifier