Python
Uploaded by
mepade9551Python
Uploaded by
mepade9551The Ultimate Python Cheat Sheet
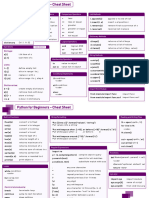
Keywords Basic Data Structures
Keyword Description Code Examples Type Description Code Examples
Boolean The Boolean data type is ## Evaluates to True:
False, Boolean data type False == (1 > 2)
either True or False. 1<2 and 0<=1 and 3>2 and 2>=2 and 1==1
True True == (2 > 1)
Boolean operators are and 1!=0
ordered by priority:
Logical operators ## Evaluates to False:
not → and → or
and, → Both are true True and True # True bool(None or 0 or 0.0 or '' or [] or
or, → Either is true True or False # True {} or set())
not → Flips Boolean not False # True
Rule: None, 0, 0.0, empty strings, or empty container
1, 2, 3 types evaluate to False
break Ends loop prematurely while True:
break # finite loop Integer, An integer is a positive or ## Arithmetic Operations
Float negative number without x, y = 3, 2
continue Finishes current loop iteration while True: decimal point such as 3. print(x + y) # = 5
continue print(x - y) # = 1
print("42") # dead code A float is a positive or print(x * y) # = 6
negative number with print(x / y) # = 1.5
class Defines new class class Coffee: floating point precision print(x // y) # = 1
# Define your class such as 3.1415926. print(x % y) # = 1
print(-x) # = -3
def Defines a new function or class def say_hi(): Integer division rounds print(abs(-x)) # = 3
method. print('hi') toward the smaller integer print(int(3.9)) # = 3
(example: 3//2==1). print(float(3)) # = 3.0
if, Conditional execution: x = int(input("ur val:")) print(x ** y) # = 9
elif, - “if” condition == True? if x > 3: print("Big")
else - "elif" condition == True? elif x == 3: print("3") String Python Strings are ## Indexing and Slicing
- Fallback: else branch else: print("Small") sequences of characters. s = "The youngest pope was 11 years"
s[0] # 'T'
String Creation Methods: s[1:3] # 'he' Slice [::2]
for, # For loop # While loop does same
while for i in [0,1,2]: j = 0 1. Single quotes s[-3:-1] # 'ar'
print(i) while j < 3: >>> 'Yes' s[-3:] # 'ars' 1 2 3 4
print(j); j = j + 1 2. Double quotes
>>> "Yes" x = s.split() 0 1 2 3
in Sequence membership 42 in [2, 39, 42] # True 3. Triple quotes (multi-line) x[-2] + " " + x[2] + "s" # '11 popes'
>>> """Yes
is Same object memory location y = x = 3 We Can""" ## String Methods
x is y # True 4. String method y = " Hello world\t\n "
[3] is [3] # False >>> str(5) == '5' y.strip() # Remove Whitespace
True "HI".lower() # Lowercase: 'hi'
None Empty value constant print() is None # True 5. Concatenation "hi".upper() # Uppercase: 'HI'
>>> "Ma" + "hatma" "hello".startswith("he") # True
lambda Anonymous function (lambda x: x+3)(3) # 6 'Mahatma' "hello".endswith("lo") # True
"hello".find("ll") # Match at 2
return Terminates function. Optional def increment(x): Whitespace chars: "cheat".replace("ch", "m") # 'meat'
return value defines function return x + 1 Newline \n, ''.join(["F", "B", "I"]) # 'FBI'
result. increment(4) # returns 5 Space \s, len("hello world") # Length: 15
Tab \t "ear" in "earth" # True
Complex Data Structures
Type Description Example Type Description Example
List Stores a sequence of l = [1, 2, 2] Dictionary Useful data structure for cal = {'apple' : 52, 'banana' : 89,
elements. Unlike strings, you print(len(l)) # 3 storing (key, value) pairs 'choco' : 546} # calories
can modify list objects (they're
Reading Read and write elements by print(cal['apple'] < cal['choco'])
mutable).
and specifying the key within the # True
Adding Add elements to a list with (i) [1, 2].append(4) # [1, 2, 4] writing brackets. Use the keys() cal['cappu'] = 74
elements append, (ii) insert, or (iii) list [1, 4].insert(1,9) # [1, 9, 4] elements and values() functions to print(cal['banana'] < cal['cappu'])
concatenation. [1, 2] + [4] # [1, 2, 4] access all keys and values of # False
the dictionary
print('apple' in cal.keys()) # True
Removal Slow for lists [1, 2, 2, 4].remove(1) # [2, 2, 4]
print(52 in cal.values()) # True
Reversing Reverses list order [1, 2, 3].reverse() # [3, 2, 1]
Dictionary You can access the (key, for k, v in cal.items():
Sorting Sorts list using fast Timsort [2, 4, 2].sort() # [2, 2, 4] Iteration value) pairs of a dictionary print(k) if v > 500 else ''
with the items() method. # 'choco'
Indexing Finds the first occurrence of [2, 2, 4].index(2)
an element & returns index. # index of item 2 is 0 Member- Check with the in keyword if basket = {'apple', 'eggs',
Slow worst case for whole list [2, 2, 4].index(2,1) ship set, list, or dictionary contains 'banana', 'orange'}
traversal. # index of item 2 after pos 1 is 1 operator an element. Set membership print('eggs' in basket) # True
is faster than list membership. print('mushroom' in basket) # False
Stack Use Python lists via the list stack = [3]
operations append() and pop() stack.append(42) # [3, 42] List & set List comprehension is the l = ['hi ' + x for x in ['Alice',
stack.pop() # 42 (stack: [3]) comprehe concise Python way to create 'Bob', 'Pete']]
stack.pop() # 3 (stack: []) nsion lists. Use brackets plus an # ['Hi Alice', 'Hi Bob', 'Hi Pete']
expression, followed by a for
Set An unordered collection of basket = {'apple', 'eggs', clause. Close with zero or l2 = [x * y for x in range(3) for y
unique elements (at-most- 'banana', 'orange'} more for or if clauses. in range(3) if x>y] # [0, 0, 2]
once) → fast membership O(1) same = set(['apple', 'eggs', Set comprehension works
squares = { x**2 for x in [0,2,4]
'banana', 'orange']) similar to list comprehension.
if x < 4 } # {0, 4}
Subscribe to the 11x FREE Python Cheat Sheet Course:
https://blog.finxter.com/python-cheat-sheets/
You might also like
- Basic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To FalseNo ratings yetBasic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To False7 pages
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Merged Programming PythonNo ratings yet1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Merged Programming Python9 pages
- Basic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To FalseNo ratings yetBasic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To False8 pages
- Unit 3 Built-In Functions, Data Types, and OperatorsNo ratings yetUnit 3 Built-In Functions, Data Types, and Operators20 pages
- Discrete Structures Lab 1 Python Basics: 1 Python Installation 2 Python TutorialNo ratings yetDiscrete Structures Lab 1 Python Basics: 1 Python Installation 2 Python Tutorial8 pages
- Introduction of Python in Machine LearningNo ratings yetIntroduction of Python in Machine Learning70 pages
- Tổng hợp từ vựng hay từ việc đọc sách: Zero to OneNo ratings yetTổng hợp từ vựng hay từ việc đọc sách: Zero to One4 pages
- Hus Et Al., 2014 - Module 4 Algorithm and Comparison ScoresNo ratings yetHus Et Al., 2014 - Module 4 Algorithm and Comparison Scores18 pages
- Unconventional Machining Processes - Introduction and ClassificationNo ratings yetUnconventional Machining Processes - Introduction and Classification3 pages
- toaz.info-pe-04025-reservoir-i-pr_6995059d96587abe7d7be16a488f4728No ratings yettoaz.info-pe-04025-reservoir-i-pr_6995059d96587abe7d7be16a488f47289 pages
- Riftvally University Colledge Hawassa: Factor Affecting The Performace Micro and Small Enterprise100% (1)Riftvally University Colledge Hawassa: Factor Affecting The Performace Micro and Small Enterprise50 pages
- Structure and Written Expression Tes Bahasa Inggris100% (1)Structure and Written Expression Tes Bahasa Inggris12 pages
- NRN KNITTING & GARMENTS LTD - 7TH FUiN Electrical OA - 30072019No ratings yetNRN KNITTING & GARMENTS LTD - 7TH FUiN Electrical OA - 3007201920 pages
- Damopolii 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1567 042025No ratings yetDamopolii 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1567 0420257 pages
- Journal of Specialized Nursing Care, Vol 8, No 1 (2016)No ratings yetJournal of Specialized Nursing Care, Vol 8, No 1 (2016)8 pages
- 6.+821+-+Vol+23+N+2+-+pp.227-265+[PUBLISHED+30-01-2025]No ratings yet6.+821+-+Vol+23+N+2+-+pp.227-265+[PUBLISHED+30-01-2025]39 pages
- Innovative Bracket Design Concepts For The Installation of Aircraft SystemsNo ratings yetInnovative Bracket Design Concepts For The Installation of Aircraft Systems7 pages