Kippap AnswerKey Steel1
Kippap AnswerKey Steel1
Uploaded by
Rene TeCopyright:
Available Formats
Kippap AnswerKey Steel1
Kippap AnswerKey Steel1
Uploaded by
Rene TeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Kippap AnswerKey Steel1
Kippap AnswerKey Steel1
Uploaded by
Rene TeCopyright:
Available Formats
KIPPAP EDUCATION
Shear and Bending Stress in Beams
ANSWER KEY
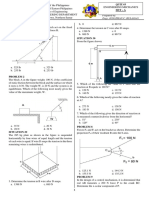
Situation 1
A simple beam has a span of 8 m and supports a total uniformly
distributed load of 20 kN/m.
Properties of W 480 x 86:
A = 10800 mm2 Ix = 383.13 x 106 mm4
bf = 180 mm tw = 12 mm
tf = 15 mm
d = 480 mm
1. Calculate the maximum moment in the beam in kN-m.
A. 260 kN-m C. 130 kN-m
B. 230 kN-m D. 160 kN-m
𝑊𝐿2 (20)(8)2
MMAX = = = 160 kN-m
8 8
2. Calculate the maximum bending stress in the beam in MPa.
A. 200.227 MPa C. 227.100 MPa
B. 100.227 MPa D. 107.221 MPa
𝑀𝑐 (160𝑥106 )(480/2)
fb = = = 100.227 MPa
𝐼 383.13𝑥106
3. Calculate the maximum shear in the beam in kN.
A. 60 kN C. 80 kN
B. 70 kN D. 90 kN
𝑊𝐿 (20)(8)
VMAX = = = 80 kN
2 2
4. Calculate the average shear stress in the beam in MPa.
A. 14.9 MPa C. 18.4 MPa
B. 13.9 MPa D. 19.4 MPa
𝑉 80,000
fv = = = 13.889
𝑑𝑡𝑤 (480)(12)
5. Calculate the maximum shear stress in the beam in MPa.
A. 21.16 MPa C. 12.61 MPa
B. 11.62 MPa D. 16.21 MPa
𝑉𝑄
fv = Q = (225x12)(225/2)+(180x15)(232.5) = 931500
𝐼𝐵
(80,000)(931500)
fv = = 16.209 MPa
(383.13𝑥106 )(12)
Kippap Education
0905 664 2628 kippapeducation@gmail.com CE Board Exam Review
KIPPAP EDUCATION
Shear and Bending Stress in Beams
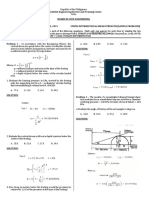
Situation 2
A wide flange section has the following properties:
bf = 150 mm Ix = 108 x 106 mm4
tf = 12 mm Fv = 0.40Fy
tw = 9 mm Q @ N.A. = 380 x 103 mm3
d = 300 mm Fy = 250 MPa
6. Determine the shear capacity of the section.
A. 270 kN C. 250 kN
B. 260 kN D. 240 kN
Fv = 0.4(250) = 100
𝑉 𝑉
fv = 100 = V = 270,000 N = 270 kN
𝑑𝑡𝑤 (300)(9)
7. Determine the safe uniform load that the section could carry if length of
the beam is 10 m.
A. 56 kN/m C. 45 kN/m
B. 65 kN/m D. 54 kN/m
𝑊𝐿 (𝑊)(10)
VMAX = 270 = W = 54 kN/m
2 2
8. Determine the shear flow of the portion of the flange 15 mm from the edge.
A. 64.8 N/mm C. 29502 N/mm
B. 25920 N/mm D. 86.4 N/mm
𝑉𝑄
q = Q = (15x12)(144) = 25920
𝐼
(270,000)(25920)
q = = 64.8 N/mm
(108𝑥106 )
9. Determine the shear flow at the neutral axis.
A. 590 N/mm C. 290 N/mm
B. 950 N/mm D. 850 N/mm
(270,000)(380𝑥103 )
q = = 950 N/mm
(108𝑥106 )
10. Determine the shear flow 44 mm from the N.A.
A. 580.4 N/mm C. 840.5 N/mm
B. 540.8 N/mm D. 850.4 N/mm
𝑉𝑄
q = Q = (150x12)(144)+(9x94)(44+94/2) = 336186
𝐼
(270,000)(336186)
q = = 840.465 N/mm
(108𝑥106 )
Kippap Education
0905 664 2628 kippapeducation@gmail.com CE Board Exam Review
KIPPAP EDUCATION
Shear and Bending Stress in Beams
Situation 3
A simple beam has a span of 10 m and supports a superimposed uniformly
distributed load of 12 kN/m.
Properties of W 450 x 70:
A = 8700 mm2 Ix = 274.7 x 106 mm4
bf = 150 mm tw = 10 mm
tf = 15 mm Wb = 70 kg/m
d = 450 mm
11. What is the average shearing stress in the beam?
A. 14.9 MPa C. 14.1 MPa
B. 11.4 MPa D. 11.9 MPa
𝑉 𝑊𝐿
fv = V = W = 12 + 70(9.81/1000) = 12.6867
𝑑𝑡𝑤 2
(12.6867)(10)
V = = 63.4335 kN
2
(63433.5)
fv = = 14.096 MPa
(450)(10)
12. Determine the maximum shearing stress in the beam.
A. 16.4 MPa C. 41.6 MPa
B. 14.6 MPa D. 46.4 MPa
𝑉𝑄
fv = Q = (150x15)(217.5)+(10x210)(210/2) = 709875
𝐼𝐵
(63433.5)(709875)
fv = = 16.392 MPa
(274.7𝑥106 )(10)
13. Calculate the maximum bending stress in the beam.
A. 129.9 MPa C. 179.9 MPa
B. 199.2 MPa D. 157.2 MPa
𝑀𝑐
fb = 𝐼
𝑊𝐿2 (12.6867)(10)2
MMAX = = = 158.584 kN-m
8 8
(158.584𝑥106 )(450/2)
fb = = 129.892 MPa
274.7𝑥106
Kippap Education
0905 664 2628 kippapeducation@gmail.com CE Board Exam Review
You might also like
- Ansi MH16.1 2012 (R2019) PDFDocument144 pagesAnsi MH16.1 2012 (R2019) PDFJoseNo ratings yet
- Mastery Exam 1 KEY 2 1Document3 pagesMastery Exam 1 KEY 2 1Jirpp EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- HGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Document3 pagesHGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Kim Ryan PomarNo ratings yet
- Water Surface Profiles: Correction FactorDocument6 pagesWater Surface Profiles: Correction FactorGerald OrtizNo ratings yet
- Long Span Beams - SalahuddinDocument16 pagesLong Span Beams - SalahuddinSalahuddin Shaikh0% (1)
- BDM Example 6 - 20180101Document23 pagesBDM Example 6 - 20180101mustafurade1No ratings yet
- Discussion - Design of W-Shapes For Combined Bending and TorsionDocument2 pagesDiscussion - Design of W-Shapes For Combined Bending and TorsionnaimNo ratings yet
- Design of A Notched Section at The End of A BeamDocument5 pagesDesign of A Notched Section at The End of A BeamBobaru MariusNo ratings yet
- Plate 4Document33 pagesPlate 4sammy lopez100% (1)
- Set BDocument12 pagesSet BDan Casurao100% (1)
- Coaching N2023 FNCDocument77 pagesCoaching N2023 FNCGon MirNo ratings yet
- 2019 Hyd MayDocument13 pages2019 Hyd MayChantal Faye GacusanNo ratings yet
- Mastery Test MT1 and MT2 Solution: None of TheseDocument6 pagesMastery Test MT1 and MT2 Solution: None of TheseU-line Anne Roque VillafloresNo ratings yet
- Hydrau 4Document3 pagesHydrau 4Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- Possible Board Problem November 2021Document4 pagesPossible Board Problem November 2021Gleb De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Eval 1 Review May 2021Document4 pagesEval 1 Review May 2021Kiesha SantosNo ratings yet
- Module 1 EarthworksDocument1 pageModule 1 EarthworksMohammad Hussein Masiu BacaramanNo ratings yet
- Geotech Examinee - SDocument6 pagesGeotech Examinee - SRodelNo ratings yet
- Quiz #3 - Eng'g MechanicsDocument4 pagesQuiz #3 - Eng'g MechanicsAnthony Jay PoraqueNo ratings yet
- Q P A Q 1600 4 (4) Q 100 Kpa: SolutionDocument8 pagesQ P A Q 1600 4 (4) Q 100 Kpa: SolutionFrancis John Buac100% (1)
- Refresher Module 04 - M6 - Intermodal Transportation SystemDocument1 pageRefresher Module 04 - M6 - Intermodal Transportation SystemKiki Do youNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4 Experts - Soil Mech PartDocument4 pagesQuiz 4 Experts - Soil Mech PartBenjamin Benicarlo Juanillo IIINo ratings yet
- Hge Refresher Exam 9 SolutionDocument12 pagesHge Refresher Exam 9 SolutionaceeeceeeNo ratings yet
- Structural Soln Nov 2018 PDFDocument19 pagesStructural Soln Nov 2018 PDFrey martiNo ratings yet
- 2022 Nov Final Preboard MathDocument8 pages2022 Nov Final Preboard MathJOHN CARLO DE GUZMAN AMBAY (JCDGA)No ratings yet
- MODULAR QUIZ - 44 - Geotechnical Engineering 4Document8 pagesMODULAR QUIZ - 44 - Geotechnical Engineering 4Cornelio J. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Preboard - With AnswersDocument4 pagesPreboard - With AnswersPrince HernandezNo ratings yet
- Maximum Stresses On A Pole Subjected To Combined LoadingsDocument2 pagesMaximum Stresses On A Pole Subjected To Combined LoadingsShiela GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Hge Pre-Board QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesHge Pre-Board QuestionnairegregNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1Document3 pagesAssignment - 1chritNo ratings yet
- Coach HGE (Oct 9, 2021)Document7 pagesCoach HGE (Oct 9, 2021)Glaiza MarieNo ratings yet
- Calculus Problem SetDocument1 pageCalculus Problem SetJoyce DueroNo ratings yet
- MIT Math Correl 4th Term AY 2013 2014 Retake B PDFDocument9 pagesMIT Math Correl 4th Term AY 2013 2014 Retake B PDFNadine PascualNo ratings yet
- V0L2 PDFDocument4 pagesV0L2 PDFJohannie Nina ClaridadNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Plane and Solid Geometry - Set 3Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 - Plane and Solid Geometry - Set 3Mark Lester Lualhati100% (1)
- Fliuids MechanicsDocument8 pagesFliuids MechanicsCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam: Soil CDocument3 pagesMidterm Exam: Soil CKathlyn Mae BeberinoNo ratings yet
- Sedc RefresherDocument56 pagesSedc RefresherHarold GarciaNo ratings yet
- Eval 1 Review Nov 2020Document5 pagesEval 1 Review Nov 2020Shiela GonzalesNo ratings yet
- MEGAREVIEW HGE Terms RefresherDocument2 pagesMEGAREVIEW HGE Terms RefresherDarlene Delos Santos100% (1)
- Mste Nov 2022 Questions Part 1Document23 pagesMste Nov 2022 Questions Part 1Mark Anthony Mores FalogmeNo ratings yet
- Steel Design 9 Nov 2020 PDFDocument1 pageSteel Design 9 Nov 2020 PDFJustine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Preboard 3 Math Surveying With Answers Nov 2017 Set A 1Document3 pagesPreboard 3 Math Surveying With Answers Nov 2017 Set A 1Engr. Jobert S. De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Level 4 Practice ModuleDocument8 pagesLevel 4 Practice ModuleJulianFlorenzFalconeNo ratings yet
- PSAD 4 May 5 2023Document19 pagesPSAD 4 May 5 2023Renne Jude Rollorata100% (1)
- April 2024 - PSAD 19Document2 pagesApril 2024 - PSAD 19Ram Canicula100% (1)
- Policarpio 5 - Refresher SECDocument2 pagesPolicarpio 5 - Refresher SECMigaea100% (1)
- Correl Mock Hydraulics Set ADocument15 pagesCorrel Mock Hydraulics Set AMariah Kathleen LacsinaNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 StructuralDocument20 pagesExam 2 StructuralMs. Engr100% (2)
- Nov23 Coaching Engr. Besavilla 01 06 Nov. 2023Document14 pagesNov23 Coaching Engr. Besavilla 01 06 Nov. 2023Rhowelle Tibay100% (1)
- AlgebraDocument2 pagesAlgebramenma chanNo ratings yet
- Geotech 8Document18 pagesGeotech 8Bemzar Samson100% (1)
- F2F Handouts (Stress Distribution & Shear Strength of Soil) - SOLUTIONS & ANSWERSDocument5 pagesF2F Handouts (Stress Distribution & Shear Strength of Soil) - SOLUTIONS & ANSWERSSelling AqwNo ratings yet
- Kippap-Handout-SEC (40 RCD - Footings)Document10 pagesKippap-Handout-SEC (40 RCD - Footings)top1echolocoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam 17: Kippap EducationDocument8 pagesEvaluation Exam 17: Kippap EducationMichael MercadoNo ratings yet
- Two Open TanksDocument10 pagesTwo Open TanksMaverick TimbolNo ratings yet
- Ce 602 Compre 2023 2024Document7 pagesCe 602 Compre 2023 2024b.macahig.475608No ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document1 pageQuiz 2senior highNo ratings yet
- Tsu m22 Practice Problems Steel DesignDocument3 pagesTsu m22 Practice Problems Steel DesignMark Lester Valdoz100% (1)
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 12Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 12Justine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- (02-01) Geotechnical Engineering - Set 4Document2 pages(02-01) Geotechnical Engineering - Set 4Ram CaniculaNo ratings yet
- CE EVALUATION EXAM No. 6 - Channels, Weir, Hydrodynamics, Soil Prop (Answer Key)Document7 pagesCE EVALUATION EXAM No. 6 - Channels, Weir, Hydrodynamics, Soil Prop (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la Cruz100% (1)
- Project 44 PDF FreeDocument3 pagesProject 44 PDF FreeMJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Steel 3Document3 pagesSteel 3Mayya Bona100% (1)
- Design: Rigid Solutions - Final CoachingDocument11 pagesDesign: Rigid Solutions - Final CoachingEugene Ralph TimoteoNo ratings yet
- What Is Management?Document7 pagesWhat Is Management?Rene TeNo ratings yet
- Refresher 2 Answer KeyDocument3 pagesRefresher 2 Answer KeyRene TeNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Studies of Piezoelectric As A Source For Street LightingDocument6 pagesFeasibility Studies of Piezoelectric As A Source For Street LightingRene TeNo ratings yet
- Fixed End MomentsDocument134 pagesFixed End MomentsRene TeNo ratings yet
- D R MDocument4 pagesD R Mstarry08No ratings yet
- Hydrology: A Teaching Demonstration byDocument15 pagesHydrology: A Teaching Demonstration byRene TeNo ratings yet
- Module 3.1 - Flexure in BeamsDocument8 pagesModule 3.1 - Flexure in BeamsJUDY ANN MALANANo ratings yet
- An Improved Quadrilateral Flat Element With Drilling Degrees of Freedom For Shell Structural AnalysisDocument35 pagesAn Improved Quadrilateral Flat Element With Drilling Degrees of Freedom For Shell Structural AnalysisDaniele Di LucaNo ratings yet
- Varun DankeDocument5 pagesVarun DankeTuanHungNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design Guide For Masonry Buildings: Donald Anderson Svetlana BrzevDocument113 pagesSeismic Design Guide For Masonry Buildings: Donald Anderson Svetlana BrzevVladimir Sánchez CalderónNo ratings yet
- Prasenjit Short CircuitDocument17 pagesPrasenjit Short CircuitDhrubajyoti Bhattacharjee100% (2)
- Shear Wall Design Presentation1Document11 pagesShear Wall Design Presentation1Parag KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Reinforced Concrete Design: CIVL 4136/6136Document6 pagesIntermediate Reinforced Concrete Design: CIVL 4136/6136Ahmed AjelNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete Structures - AssignmentDocument14 pagesPrestressed Concrete Structures - AssignmentGanesh MistercoolNo ratings yet
- 3.032 Problem Set 2 Solutions: Due: Start of Lecture, 09.21.07Document16 pages3.032 Problem Set 2 Solutions: Due: Start of Lecture, 09.21.07Pkay TandohNo ratings yet
- El47500-Psb DDocument26 pagesEl47500-Psb DWahyu WidartoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Inclined Shear Reinforcement in Reinforced Concrete BeamDocument12 pagesEffects of Inclined Shear Reinforcement in Reinforced Concrete BeamvivekNo ratings yet
- 01 Prajwal JiwtodeDocument20 pages01 Prajwal Jiwtode01 - Prajwal JiwtodeNo ratings yet
- MosDocument12 pagesMosAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- RC Skeleton in Residential BuildingsDocument12 pagesRC Skeleton in Residential BuildingsMoHamed M. Scorpi100% (1)
- Design and Const2Document101 pagesDesign and Const2Sigue Ramel HinayasNo ratings yet
- Rc2 Flat Theory PartDocument17 pagesRc2 Flat Theory PartascendancyyfirisaNo ratings yet
- Design Model For Bolted Moment End Plate ConnectioDocument54 pagesDesign Model For Bolted Moment End Plate Connectioสุทธิพงษ์ สีกองเสนNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 11 CompositeDCB Delamination V5 1Document16 pagesTutorial 11 CompositeDCB Delamination V5 1UdhamNo ratings yet
- Finite Elements: Modelling Methods, Implicit and Explicit AnalysisDocument32 pagesFinite Elements: Modelling Methods, Implicit and Explicit Analysisadeelyj100% (1)
- Lec 3.1Document10 pagesLec 3.1Samawat AhsanNo ratings yet
- 99 253 Testing Machines and Testing Systems For Metals E enDocument48 pages99 253 Testing Machines and Testing Systems For Metals E enWinter NaiNo ratings yet
- Shear Force & Bending Moment Diagram LectureDocument27 pagesShear Force & Bending Moment Diagram Lectureilocam313100% (4)
- Tree FormsDocument59 pagesTree FormsSAGAR KUTENo ratings yet